ESP Button Mercedes: Understanding and Troubleshooting Guide
The ESP button Mercedes is your gateway to enhanced vehicle stability. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by CARDIAGTECH.NET, will delve into the intricacies of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, exploring its function, troubleshooting common issues, and offering solutions to keep your ride safe and secure. Proper diagnostics and auto repair services can solve any issues.
1. What is the ESP Button on a Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is a crucial safety system in your Mercedes-Benz. Think of it as a virtual co-pilot, constantly monitoring your driving and intervening when it detects a potential loss of control. The ESP button allows you to temporarily deactivate or adjust the system’s sensitivity. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP uses sensors to detect skidding or loss of control and selectively brakes individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course. This is a very advanced system that requires specialized tools for diagnostics.
1.1 Understanding the ESP System
ESP works by comparing the driver’s intended direction (based on steering wheel angle) with the vehicle’s actual movement. If a discrepancy arises, indicating a skid or loss of traction, ESP kicks in. It selectively applies braking force to individual wheels and may also adjust engine power to help the driver regain control. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has found that ESP systems can significantly reduce single-vehicle crashes, particularly on slippery surfaces.
1.2 The Role of the ESP Button
The ESP button provides a degree of control over the system. Pressing it typically offers two modes:
-
ESP On (Default): The system operates at full capacity, providing maximum stability assistance.
-
ESP Off or Reduced Sensitivity: In some situations, like driving in deep snow or sand, a slight wheel spin can be beneficial. Deactivating or reducing ESP sensitivity allows for this controlled slippage, preventing the system from cutting power and potentially hindering forward progress.
1.3 ESP Symbol on the Dashboard
The ESP symbol, usually a car skidding, illuminates on the dashboard when the system is actively intervening. If the light stays on continuously, it indicates a malfunction within the ESP system. Addressing any dashboard warning lights as soon as possible is crucial for vehicle safety and performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools to help you identify and resolve ESP-related issues.
2. Identifying ESP Problems in Your Mercedes
Recognizing the signs of a malfunctioning ESP system is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety. Here are some common indicators:
2.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunction
-
Illuminated ESP Warning Light: This is the most obvious sign of a problem. The light may stay on constantly or flicker intermittently.
-
Reduced Engine Power: ESP can limit engine power to prevent wheelspin. If the system is malfunctioning, it might restrict power unnecessarily, even under normal driving conditions.
-
Unusual Braking Behavior: The system might apply brakes erratically or unevenly, especially during turns or on slippery surfaces.
-
Difficulty Maintaining Control: You might experience increased difficulty controlling the vehicle, especially in challenging driving conditions. The vehicle may feel unstable or prone to skidding.
2.2 Diagnosing ESP Issues with Diagnostic Tools
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic control units (ECUs) and sensors. Diagnostic tools can access the vehicle’s computer system, read error codes, and provide valuable insights into the nature of the problem. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of professional-grade diagnostic tools compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
-
Reading Error Codes: Diagnostic tools retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the ESP control unit. These codes pinpoint specific faults within the system. For example, a code might indicate a faulty wheel speed sensor or a problem with the yaw rate sensor.
-
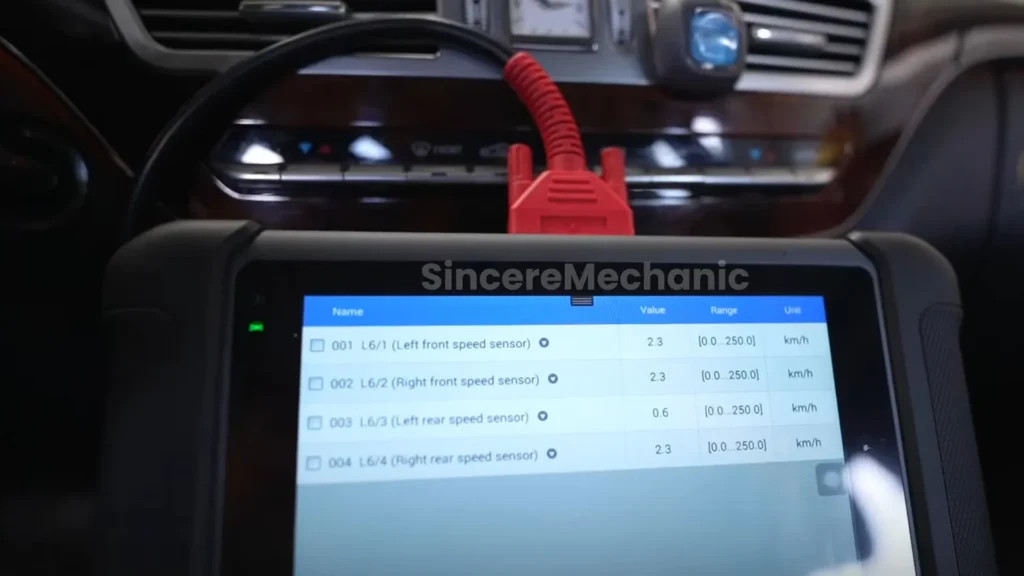
Live Data Monitoring: Many diagnostic tools can monitor live data from various sensors within the ESP system. This allows you to observe how the sensors are behaving in real-time and identify any anomalies. For example, you can monitor wheel speed sensor readings, steering angle sensor data, and yaw rate sensor output.
-
Actuator Testing: Some diagnostic tools offer actuator testing capabilities. This allows you to activate individual components within the ESP system, such as the ABS pump or individual wheel cylinders, to verify their functionality.
2.3 When to Seek Professional Help
While some ESP issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting, it’s important to seek professional help when:
- You lack the necessary diagnostic tools or expertise.
- The problem persists after attempting basic troubleshooting steps.
- The vehicle exhibits significant handling problems or safety concerns.
A qualified mechanic can perform a thorough inspection of the ESP system, accurately diagnose the problem, and recommend appropriate repairs. CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with experienced technicians in your area.
3. Common Causes of ESP Problems
Several factors can contribute to ESP malfunctions in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Understanding these common causes can help you narrow down the potential source of the problem.
3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Wheel speed sensors are critical components of the ESP system. They measure the rotational speed of each wheel and transmit this data to the ESP control unit. This information is used to detect wheel slippage and initiate corrective actions.
-
Causes of Failure:
- Physical Damage: Road debris, impacts, or corrosion can damage the sensor itself.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the signal from the sensor to the control unit.
- Sensor Contamination: Dirt, grease, or other contaminants can interfere with the sensor’s ability to accurately measure wheel speed.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Sensor Testing: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s resistance and output voltage. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring harness for any breaks, shorts, or corrosion.
- Cleaning: Clean the sensor and surrounding area to remove any contaminants.
-
Replacement: If the sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new, high-quality sensor. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of replacement wheel speed sensors for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides this data to the ESP control unit. This information is used to determine the driver’s intended direction.
-
Causes of Failure:
- Misalignment: Improper wheel alignment can affect the sensor’s accuracy.
- Sensor Damage: Impacts or wear and tear can damage the sensor itself.
- Electrical Issues: Problems with the sensor’s wiring or power supply can cause malfunctions.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Calibration: Recalibrate the steering angle sensor using a diagnostic tool.
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor and wiring for any signs of damage.
- Sensor Testing: Use a diagnostic tool to monitor the sensor’s output and verify its accuracy.
-
Replacement: If the sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced and then calibrated with a diagnostic tool.
3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunctions
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. This information is used to detect skidding or loss of control.
-
Causes of Failure:
- Sensor Damage: Impacts or vibrations can damage the sensor.
- Electrical Issues: Problems with the sensor’s wiring or power supply can cause malfunctions.
- Mounting Problems: Loose or damaged mounting hardware can affect the sensor’s accuracy.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor and wiring for any signs of damage.
- Sensor Testing: Use a diagnostic tool to monitor the sensor’s output and verify its accuracy.
- Mounting Check: Ensure the sensor is securely mounted and properly aligned.
-
Replacement: If the sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced.
3.4 ABS Pump Issues
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) pump is an integral part of the ESP system. It provides the hydraulic pressure needed to apply brakes to individual wheels.
-
Causes of Failure:
- Pump Motor Failure: The pump motor can wear out over time or fail due to electrical issues.
- Valve Problems: Valves within the pump can become clogged or malfunction, affecting brake pressure.
- Hydraulic Leaks: Leaks in the pump or brake lines can reduce hydraulic pressure.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the pump and brake lines for any leaks or damage.
- Pump Motor Test: Use a diagnostic tool to activate the pump motor and verify its functionality.
- Valve Testing: Use a diagnostic tool to test the operation of individual valves within the pump.
-
Repair or Replacement: Depending on the nature of the problem, the ABS pump may need to be repaired or replaced.
3.5 Low Battery Voltage
A weak or failing battery can cause a variety of electrical problems in modern vehicles, including ESP malfunctions. Low voltage can interfere with the operation of sensors and control units.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Battery Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Load Test: Perform a load test to assess the battery’s ability to deliver current under load.
- Charging System Check: Verify that the charging system is functioning properly and charging the battery.
-
Battery Replacement: If the battery is found to be weak or failing, it should be replaced.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting the ESP System
Sometimes, the ESP system may trigger unnecessarily due to a temporary glitch or sensor error. Resetting the system can resolve these issues.
4.1 When to Attempt an ESP Reset
Attempt an ESP reset when:
- The ESP warning light illuminates intermittently.
- You suspect a temporary sensor error.
- You have recently performed maintenance on the ESP system.
Note: If the ESP warning light remains on after a reset, it indicates a more serious problem that requires further diagnosis.
4.2 Methods for Resetting the ESP System
-
Method 1: Using a Diagnostic Tool
- Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Select the ESP control unit.
- Look for a “Reset” or “Clear Fault Codes” option.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reset the system.
-
Method 2: Steering Wheel Calibration
- Start the engine.
- Turn the steering wheel fully to the left.
- Turn the steering wheel fully to the right.
- Return the steering wheel to the center position.
- Turn off the engine.
- Restart the engine.
- Drive the vehicle in a straight line for a short distance.
-
Method 3: Battery Disconnect (Use with Caution)
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Wait for 15-30 minutes.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Warning: Disconnecting the battery can reset other electronic systems in the vehicle. Be sure to have your radio code and other important information readily available. This method is generally not recommended unless other methods have failed.
4.3 Precautions and Considerations
- Consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific instructions on resetting the ESP system.
- Always use a compatible diagnostic tool.
- Be careful when disconnecting the battery.
- If you are unsure about any step, seek professional help.
5. Tools and Equipment for ESP Repair
Having the right tools and equipment is essential for effectively diagnosing and repairing ESP problems. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of tools for automotive repair professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
5.1 Essential Diagnostic Tools
-
OBD-II Scanner: A basic OBD-II scanner can read and clear generic fault codes.
-
Professional Diagnostic Tool: A professional-grade diagnostic tool provides access to advanced features, such as live data monitoring, actuator testing, and module programming. Look for tools that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and support ESP diagnostics.
-
Multimeter: A multimeter is used to measure voltage, resistance, and current. It’s essential for testing sensors and wiring.
5.2 Specialized Tools for ESP System Repair
-
Wheel Speed Sensor Tester: This tool is specifically designed to test the functionality of wheel speed sensors.
-
Steering Angle Sensor Calibrator: This tool is used to calibrate the steering angle sensor after replacement or realignment.
-
Hydraulic Pressure Tester: This tool is used to measure the hydraulic pressure in the ABS pump and brake lines.
5.3 Safety Equipment
-
Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
-
Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
-
Jack Stands: Use jack stands to safely support the vehicle when working underneath.
-
Wheel Chocks: Use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system.
6.1 Regular Inspections and Maintenance
- Check Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the sensors regularly.
- Inspect Brake System: Check the brake pads, rotors, and brake lines for wear and tear. Replace worn components promptly.
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain proper tire pressure to ensure optimal traction and stability.
- Wheel Alignment: Ensure proper wheel alignment to prevent premature wear on tires and suspension components.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly inspect and maintain brake fluid levels.
6.2 Driving Habits That Can Affect ESP Performance
- Aggressive Driving: Avoid sudden acceleration, braking, and steering maneuvers, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Driving with Worn Tires: Replace worn tires promptly to maintain optimal traction.
- Overloading the Vehicle: Avoid overloading the vehicle, as this can affect its stability.
6.3 The Importance of OEM Parts
When replacing components in the ESP system, it’s always best to use original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. OEM parts are designed to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle and ensure optimal performance and reliability. While aftermarket parts may be less expensive, they may not meet the same quality standards and could potentially compromise the safety and performance of the ESP system.
7. Troubleshooting Specific ESP Error Codes
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) provide valuable information about the nature of an ESP problem. Here are some common ESP error codes and their potential causes:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Unit Fault | Faulty ESP control unit, wiring problems, low battery voltage |
| C1101 | Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right – Implausible Signal | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring problems, sensor contamination, damaged wheel bearing |
| C1200 | Steering Angle Sensor – Internal Fault | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring problems, sensor misalignment |
| C1300 | Yaw Rate Sensor – Signal Error | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring problems, sensor misalignment, damaged mounting hardware |
| C1400 | ABS Pump Motor – Electrical Fault | Faulty ABS pump motor, wiring problems, low battery voltage |
| C1500 | Brake Pressure Sensor – Signal Error | Faulty brake pressure sensor, wiring problems, hydraulic leaks |
| C1600 | CAN Communication Fault | Problems with the Controller Area Network (CAN) communication, faulty control units, wiring problems |
| C1700 | Undervoltage | Low battery voltage, faulty charging system, wiring problems |
| C1800 | Component N47-5 (ESP sensor cluster) : Faulty | Faulty ESP sensor cluster, wiring problems, sensor misalignment |
| C1900 | ESP Hydraulic Unit : Faulty | Faulty ESP hydraulic unit, wiring problems, internal component failure |
Note: This is not an exhaustive list of ESP error codes. Consult a repair manual or diagnostic database for a complete list of codes and their descriptions.
8. ESP Button Mercedes: Real-World Scenarios
Understanding how the ESP system functions in different driving scenarios is crucial for maximizing its benefits and avoiding potential problems.
8.1 ESP in Winter Driving Conditions
In winter driving conditions, such as snow, ice, or slush, the ESP system can be invaluable for maintaining control of the vehicle. The system can detect wheel slippage and apply brakes to individual wheels to help prevent skidding.
- When to Use ESP: Keep ESP enabled under most winter driving conditions.
- When to Disable ESP (Temporarily): In deep snow or slush, disabling ESP temporarily can allow for some wheel spin, which can help the vehicle gain traction and move forward. However, remember to re-enable ESP once you are out of the challenging situation.
8.2 ESP and Off-Road Driving
ESP is generally not designed for off-road driving. In off-road situations, wheel spin can be beneficial for navigating challenging terrain.
- When to Disable ESP: Disable ESP when driving off-road to allow for wheel spin and prevent the system from interfering with your progress.
- Considerations: Be aware that disabling ESP will reduce the vehicle’s stability and increase the risk of skidding. Drive with caution and adapt your driving style to the conditions.
8.3 ESP and Performance Driving
In performance driving situations, such as track days or autocross events, ESP can sometimes interfere with the driver’s ability to control the vehicle.
- When to Disable ESP: Experienced drivers may choose to disable ESP in performance driving situations to allow for more control over the vehicle’s handling.
- Considerations: Disabling ESP in performance driving situations requires a high level of skill and experience. Be aware of the risks involved and drive within your limits.
9. ESP Button Mercedes: Legal and Safety Considerations
The ESP system is a critical safety feature in your Mercedes-Benz. It’s important to understand the legal and safety considerations related to the system.
9.1 Legality of Disabling ESP
In most jurisdictions, it is legal to temporarily disable ESP. However, it is generally not legal to permanently disable or modify the ESP system in a way that compromises its functionality.
9.2 Potential Safety Risks of Disabling ESP
Disabling ESP can significantly reduce the vehicle’s stability and increase the risk of skidding or loss of control, especially in challenging driving conditions.
9.3 Insurance Implications
Modifying or disabling the ESP system could potentially void your vehicle’s insurance coverage in the event of an accident.
9.4 Always Consult a Professional
If you have any questions or concerns about the ESP system, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ESP Button Mercedes
-
What does the ESP button do in my Mercedes? The ESP button allows you to temporarily reduce the sensitivity of or deactivate the Electronic Stability Program (ESP).
-
When should I turn off ESP in my Mercedes? You might turn off ESP temporarily when driving in deep snow or sand to allow for wheel spin.
-
Is it safe to drive with the ESP light on? Driving with the ESP light on indicates a malfunction and reduces vehicle stability. It’s best to have it checked by a professional.
-
How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes? You can try resetting the system using a diagnostic tool, steering wheel calibration, or by disconnecting the battery (with caution).
-
What are the common causes of ESP problems in Mercedes vehicles? Common causes include wheel speed sensor issues, steering angle sensor problems, yaw rate sensor malfunctions, and ABS pump issues.
-
Can a low battery affect the ESP system? Yes, low battery voltage can cause ESP malfunctions.
-
Should I use OEM parts when repairing the ESP system? Yes, using OEM parts ensures optimal performance and reliability.
-
Where can I find a reliable Mercedes-Benz mechanic? CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with experienced technicians in your area.
-
What diagnostic tools are recommended for ESP repair? Professional diagnostic tools, multimeters, and specialized sensor testers are recommended.
-
Is it legal to permanently disable ESP? No, it is generally not legal to permanently disable or modify the ESP system in a way that compromises its functionality.
Conclusion: Ensuring Optimal ESP Functionality
The ESP system is a vital safety feature in your Mercedes-Benz, providing enhanced stability and control in challenging driving situations. By understanding how the system works, recognizing common problems, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure its optimal functionality and keep yourself and your passengers safe. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. From professional-grade diagnostic tools to high-quality replacement parts, we have everything you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. If you’re facing challenges with your ESP system, don’t hesitate to contact our experts at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our team can provide tailored advice and connect you with the right tools and resources to resolve any issues promptly. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools suitable for Mercedes-Benz vehicles that can read error codes, monitor live data, and perform actuator tests to pinpoint the source of your ESP problems. Contact us today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our full range of products and services. Let us help you maintain a safe and reliable driving experience.