How To Fix A Car Belt: A Comprehensive Guide

Fixing a car belt involves understanding its function, identifying problems, and knowing the correct replacement procedure. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide the tools and knowledge needed to confidently perform this essential maintenance task. Addressing issues promptly saves money and ensures vehicle reliability, promoting safer driving experiences. Drive belt replacement, serpentine belt maintenance and automotive belt inspection will be discussed in detail.
1. Understanding Car Belts and Their Importance
Car belts, often underestimated, are vital components that ensure the smooth operation of your vehicle. These belts drive various engine accessories, allowing them to function correctly. Understanding their purpose and types is crucial for maintenance and timely replacements.
1.1. The Role of Car Belts in Vehicle Operation
Car belts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine’s crankshaft to various peripheral devices. These include:
- Alternator: Charges the battery and powers the electrical system.
- Power Steering Pump: Assists in steering the vehicle.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Provides cool air inside the cabin.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature.
Without functional belts, these systems would fail, leading to potential engine damage and compromised driving conditions.
1.2. Types of Car Belts: V-Belts vs. Serpentine Belts
There are primarily two types of car belts:
- V-Belts: These belts are trapezoidal and fit into V-shaped grooves on pulleys. They are typically used in older vehicles or for driving specific accessories.
- Serpentine Belts: These are single, longer belts with multiple grooves that drive all engine accessories. They are more efficient and commonly found in modern vehicles.
| Belt Type | Shape | Application | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-Belt | Trapezoidal | Older vehicles, specific accessories | Lower |
| Serpentine | Flat with grooves | Modern vehicles, drives all accessories | Higher |
1.3. Common Materials Used in Car Belts
Car belts are typically made from durable materials like:
- Rubber: Provides flexibility and grip.
- Reinforcing Fibers (e.g., Polyester, Aramid): Add strength and prevent stretching.
- Fabric Coverings: Protect the belt from wear and environmental factors.
These materials ensure that belts can withstand high temperatures, constant flexing, and exposure to chemicals and debris.
2. Identifying Signs of a Failing Car Belt
Recognizing the signs of a failing car belt is essential to prevent breakdowns and costly repairs. Early detection allows for timely replacement and ensures vehicle reliability.
2.1. Squealing or Chirping Noises
One of the most common indicators of a worn or loose belt is a squealing or chirping noise, especially when the engine is first started or under heavy load. This noise is caused by the belt slipping on the pulleys due to reduced tension or a worn surface.
2.2. Visible Cracks and Wear
Regularly inspect your car belts for visible signs of wear, such as:
- Cracks: Small cracks on the belt’s surface indicate aging and reduced flexibility.
- Fraying: Frayed edges suggest that the belt is wearing down and may soon fail.
- Missing Chunks: Pieces of the belt missing mean that it is severely damaged and needs immediate replacement.
 Cracked serpentine belt indicating wear and potential failure
Cracked serpentine belt indicating wear and potential failure
2.3. Power Steering and Air Conditioning Problems
If you experience difficulties with power steering or reduced air conditioning performance, it could be due to a slipping or broken belt. These accessories rely on the belt to function correctly, and a failing belt can lead to their malfunction.
2.4. Overheating Engine
A broken or slipping belt can also cause the water pump to malfunction, leading to engine overheating. If you notice your engine temperature rising rapidly, check the belt’s condition and tension.
2.5. Battery Warning Light
If the alternator belt is failing, the alternator may not be charging the battery properly, causing the battery warning light to illuminate on the dashboard. This indicates a potential issue with the belt system.
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Urgency |
|---|---|---|
| Squealing or Chirping Noise | Loose or worn belt | Medium |
| Visible Cracks and Wear | Aging and deterioration of the belt material | High |
| Power Steering Problems | Slipping belt affecting power steering pump | Medium |
| Air Conditioning Problems | Slipping belt affecting AC compressor | Medium |
| Overheating Engine | Broken belt affecting water pump | High |
| Battery Warning Light | Failing belt affecting alternator charging | High |
3. Essential Tools and Materials for Car Belt Replacement
Replacing a car belt requires specific tools and materials to ensure the job is done safely and effectively. Having the right equipment on hand can save time and prevent complications.
3.1. Socket Set and Wrenches
A comprehensive socket set and a set of wrenches are essential for loosening and tightening bolts and fasteners. Different sizes may be required depending on the vehicle model.
3.2. Belt Tensioner Tool
A belt tensioner tool is designed to release tension on the belt, allowing for easy removal and installation. This tool is particularly useful for serpentine belts with automatic tensioners.
3.3. Pry Bar
A pry bar can be used to gently lever components and adjust the belt’s position during installation. Exercise caution to avoid damaging any parts.
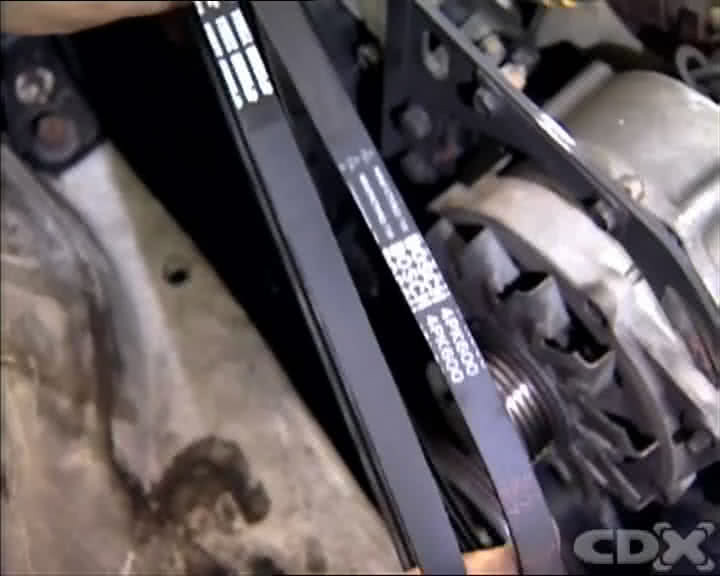
3.4. New Replacement Belt
Ensure you have the correct replacement belt for your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Refer to your vehicle’s manual or a parts catalog to find the appropriate belt size and type.
 Selection of car belts for various makes and models
Selection of car belts for various makes and models
3.5. Gloves and Safety Glasses
Protect your hands and eyes by wearing gloves and safety glasses during the replacement process. This will prevent injuries from sharp edges, debris, and chemicals.
3.6. Vehicle Repair Manual
A vehicle-specific repair manual provides detailed instructions and diagrams for belt replacement. This resource can be invaluable for ensuring you follow the correct procedures.
| Tool/Material | Purpose | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Socket Set and Wrenches | Loosening and tightening bolts | Essential |
| Belt Tensioner Tool | Releasing tension on the belt | Essential |
| Pry Bar | Adjusting belt position during installation | Helpful |
| New Replacement Belt | Replacing the old, worn belt | Essential |
| Gloves and Safety Glasses | Protecting hands and eyes | Essential |
| Vehicle Repair Manual | Providing detailed instructions and diagrams | Helpful |
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Car Belt
Replacing a car belt can be a straightforward process if you follow these steps carefully. Ensure you have the necessary tools and materials before starting.
4.1. Safety Precautions
- Turn off the engine: Ensure the engine is turned off and the keys are removed from the ignition.
- Allow the engine to cool: Wait for the engine to cool down to prevent burns.
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
4.2. Locating the Belt and Tensioner
- Identify the belt: Locate the belt you need to replace. This could be a V-belt or a serpentine belt.
- Find the tensioner: Identify the belt tensioner, which is usually spring-loaded or adjustable with a bolt.
4.3. Releasing Belt Tension
- Use a tensioner tool: Insert the belt tensioner tool into the tensioner and apply pressure to release the belt’s tension.
- Loosen the tensioner bolt: If the tensioner is adjustable, loosen the bolt to release the tension.
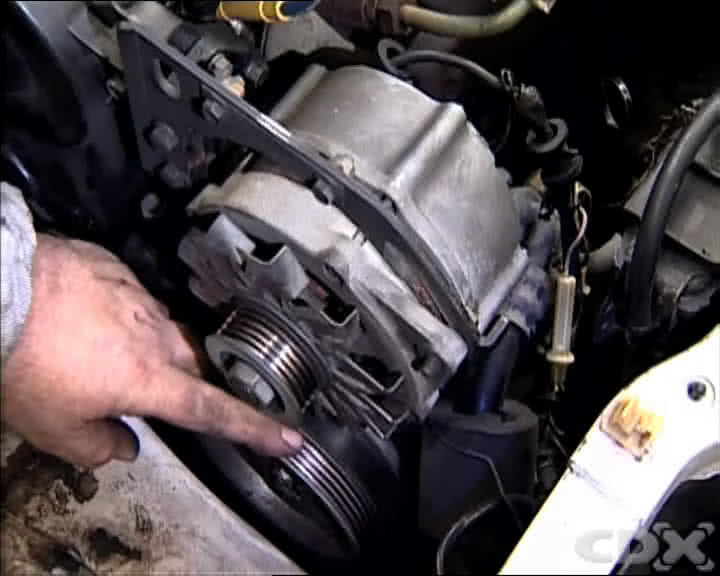
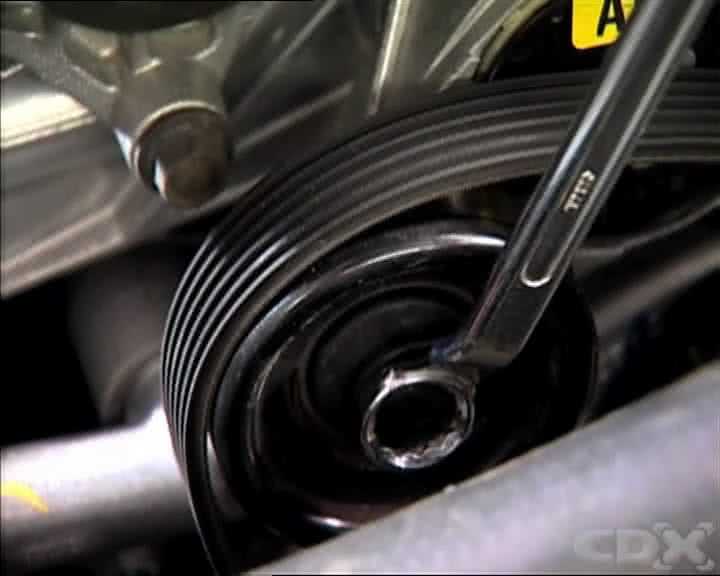 Using a wrench to adjust the belt tensioner for removal
Using a wrench to adjust the belt tensioner for removal
4.4. Removing the Old Belt
- Slip the belt off the pulleys: With the tension released, slip the old belt off each of the pulleys.
- Note the belt routing: Before removing the belt completely, take a photo or make a diagram of the belt’s routing to ensure you install the new belt correctly.
4.5. Inspecting Pulleys and Components
- Check for damage: Inspect the pulleys for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or excessive wear.
- Ensure free rotation: Make sure the pulleys rotate freely without any wobbling or unusual noises.
4.6. Installing the New Belt
- Follow the belt routing: Refer to your diagram or photo to ensure you route the new belt correctly around all the pulleys.
- Seat the belt properly: Make sure the belt is properly seated in the grooves of each pulley.
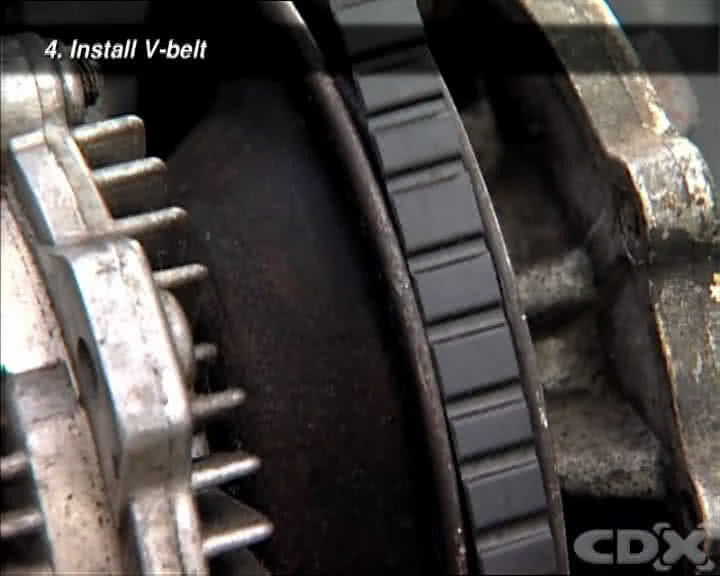 Installing the serpentine belt onto the pulleys in the correct sequence
Installing the serpentine belt onto the pulleys in the correct sequence
4.7. Tensioning the New Belt
- Apply tension: Use the tensioner tool or adjust the tensioner bolt to apply the correct tension to the new belt.
- Check tension specifications: Refer to your vehicle’s manual for the recommended belt tension specifications.
4.8. Final Checks and Adjustments
- Ensure proper alignment: Double-check that the belt is properly aligned on all pulleys.
- Start the engine: Reconnect the battery, start the engine, and observe the belt to ensure it runs smoothly without any slipping or unusual noises.
- Recheck tension: After running the engine for a few minutes, turn it off and recheck the belt tension.
| Step | Description | Important Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Safety Precautions | Turn off engine, cool down, disconnect battery | Prevents injuries and electrical shorts |
| 2. Locate Belt and Tensioner | Identify the belt and tensioner location | Ensures correct component identification |
| 3. Release Belt Tension | Use tensioner tool or loosen tensioner bolt | Allows for easy belt removal |
| 4. Remove the Old Belt | Slip the belt off pulleys, note the belt routing | Ensures correct installation of the new belt |
| 5. Inspect Pulleys | Check for damage and ensure free rotation | Prevents premature wear on the new belt |
| 6. Install the New Belt | Follow the belt routing, seat the belt properly | Ensures correct belt path and function |
| 7. Tensioning the New Belt | Apply correct tension using tool or adjust bolt | Prevents slipping and ensures proper accessory function |
| 8. Final Checks and Adjustments | Ensure alignment, start engine, recheck tension | Verifies correct installation and operation |
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Replacing a Car Belt
Replacing a car belt can be a simple task, but avoiding these common mistakes can save you time and prevent potential problems.
5.1. Not Using the Correct Belt
Using the wrong size or type of belt can lead to improper tension, slippage, and premature wear. Always refer to your vehicle’s manual or a parts catalog to ensure you have the correct replacement belt.
5.2. Incorrect Belt Routing
Routing the belt incorrectly can cause it to rub against other components, leading to damage and failure. Always double-check the belt routing diagram before installing the new belt.
5.3. Over- or Under-Tensioning the Belt
Improper belt tension can lead to slippage, noise, and premature wear on the belt and pulleys. Use a tension gauge to ensure the belt is tensioned to the manufacturer’s specifications.
5.4. Neglecting Pulley Inspection
Failing to inspect the pulleys for damage can result in the new belt wearing out quickly or even breaking. Always check the pulleys for cracks, chips, and free rotation before installing the new belt.
5.5. Forgetting Safety Precautions
Ignoring safety precautions, such as disconnecting the battery and allowing the engine to cool, can lead to injuries and electrical shorts. Always prioritize safety when working on your vehicle.
| Mistake | Consequence | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Belt | Improper tension, slippage, premature wear | Use the correct belt size and type |
| Incorrect Belt Routing | Belt rubbing, damage, failure | Double-check routing diagram |
| Over/Under-Tensioning | Slippage, noise, premature wear | Use a tension gauge to set correct tension |
| Neglecting Pulley Inspection | Premature belt wear, belt breakage | Inspect pulleys for damage and free rotation |
| Forgetting Safety | Injuries, electrical shorts | Disconnect battery, allow engine to cool |
6. Maintaining Your Car Belt for Longevity
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your car belts and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Regular inspections and timely replacements are essential for ensuring optimal performance.
6.1. Regular Visual Inspections
Inspect your car belts regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, and missing chunks. Early detection of these issues can prevent more significant problems.
6.2. Checking Belt Tension
Periodically check the belt tension to ensure it is within the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose belts can slip, while overly tight belts can put excessive strain on the pulleys and bearings.
6.3. Cleaning the Belts and Pulleys
Keep the belts and pulleys clean by removing dirt, debris, and oil. Use a clean cloth and a mild degreaser to wipe down the surfaces.
6.4. Avoiding Oil and Chemical Contamination
Prevent oil and chemical contamination of the belts, as these substances can degrade the rubber and reduce their lifespan. Repair any leaks promptly.
6.5. Following Recommended Replacement Intervals
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended replacement intervals for car belts. Even if the belts appear to be in good condition, they can weaken over time and fail unexpectedly.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspections | Monthly | Early detection of wear and damage |
| Checking Belt Tension | Every 6 Months | Prevents slippage and excessive strain |
| Cleaning Belts and Pulleys | Annually | Removes dirt and debris, prolongs belt life |
| Avoiding Contamination | As Needed | Prevents degradation of belt material |
| Replacement Intervals | Per Manual | Ensures timely replacement, prevents unexpected breakdowns |
7. Troubleshooting Common Car Belt Problems
Even with proper maintenance, car belts can sometimes experience problems. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them.
7.1. Belt Squealing
- Cause: Loose belt, worn belt, contaminated belt, or misaligned pulleys.
- Troubleshooting: Check belt tension, inspect belt condition, clean belt and pulleys, and align pulleys.
7.2. Belt Slipping
- Cause: Loose belt, worn belt, or overloaded accessories.
- Troubleshooting: Check belt tension, inspect belt condition, and reduce load on accessories.
7.3. Belt Breaking
- Cause: Old belt, damaged belt, over-tensioned belt, or pulley problems.
- Troubleshooting: Replace the belt, inspect pulleys, and adjust belt tension.
7.4. Belt Walking Off Pulleys
- Cause: Misaligned pulleys, damaged pulleys, or incorrect belt routing.
- Troubleshooting: Align pulleys, replace damaged pulleys, and verify belt routing.
| Problem | Possible Cause(s) | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Squealing | Loose, worn, or contaminated belt, misaligned pulleys | Check tension, inspect condition, clean, and align pulleys |
| Belt Slipping | Loose or worn belt, overloaded accessories | Check tension, inspect condition, and reduce accessory load |
| Belt Breaking | Old or damaged belt, over-tensioning, pulley issues | Replace belt, inspect pulleys, and adjust tension |
| Walking Off Pulleys | Misaligned or damaged pulleys, incorrect routing | Align pulleys, replace damaged pulleys, and verify routing |
8. The Importance of Professional Car Belt Service
While many car belt issues can be addressed with DIY methods, certain situations require professional service to ensure safety and accuracy.
8.1. When to Seek Professional Help
- Complex Belt Systems: Modern vehicles with multiple serpentine belts and intricate routing may require specialized knowledge and tools.
- Lack of Experience: If you are uncomfortable working on your car or lack experience with belt replacement, it’s best to seek professional help.
- Unusual Symptoms: If you notice unusual symptoms, such as excessive noise, vibration, or overheating, consult a mechanic to diagnose the problem.
8.2. Benefits of Professional Service
- Expert Diagnosis: Professional mechanics can accurately diagnose belt-related issues and recommend the appropriate solutions.
- Proper Installation: Trained technicians can ensure that the new belt is installed correctly and tensioned to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Warranty Protection: Professional service may come with a warranty, providing peace of mind in case of future problems.
8.3. Finding a Reliable Mechanic
- Check Reviews and Ratings: Look for mechanics with positive reviews and high ratings from other customers.
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations on reliable mechanics in your area.
- Verify Certifications: Ensure the mechanic is certified by reputable organizations, such as the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
| Situation | Recommendation | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Belt Systems | Seek Professional Help | Ensures accurate and safe belt replacement |
| Lack of Experience | Seek Professional Help | Prevents damage to vehicle and potential injuries |
| Unusual Symptoms | Consult a Mechanic | Accurate diagnosis and appropriate solutions |
| Finding a Reliable Mechanic | Check Reviews, Ask for Recommendations, Verify Certifications | Ensures quality service and expertise |
9. Upgrading Car Belts for Enhanced Performance
For car enthusiasts looking to improve their vehicle’s performance, upgrading to high-performance car belts can provide several benefits.
9.1. Types of Performance Car Belts
- Kevlar Belts: These belts are made with Kevlar fibers, which offer superior strength and heat resistance compared to standard rubber belts.
- Polyurethane Belts: These belts provide excellent grip and durability, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
- Reinforced Rubber Belts: These belts feature additional reinforcing materials, such as aramid or fiberglass, for increased strength and longevity.
9.2. Benefits of Upgraded Belts
- Improved Power Transfer: Upgraded belts can handle higher loads and transmit power more efficiently, resulting in improved acceleration and performance.
- Increased Durability: High-performance belts are designed to withstand extreme conditions and last longer than standard belts, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Reduced Slippage: Upgraded belts offer better grip and reduced slippage, ensuring that all engine accessories function optimally.
9.3. Considerations When Upgrading
- Compatibility: Ensure that the upgraded belts are compatible with your vehicle’s pulleys and accessories.
- Cost: High-performance belts can be more expensive than standard belts, so consider your budget when making a decision.
- Installation: Upgraded belts may require professional installation to ensure proper fit and tension.
| Belt Type | Material | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kevlar Belts | Kevlar Fibers | Superior Strength, Heat Resistance | Compatibility, Cost |
| Polyurethane Belts | Polyurethane | Excellent Grip, Durability | Compatibility, Cost |
| Reinforced Rubber | Rubber with Aramid or Fiberglass Reinforcement | Increased Strength, Longevity | Compatibility, Cost |
10. Cost Considerations for Car Belt Replacement
Understanding the costs associated with car belt replacement can help you budget for this essential maintenance task.
10.1. Factors Affecting Replacement Cost
- Type of Belt: Serpentine belts tend to be more expensive than V-belts due to their complexity and multiple functions.
- Vehicle Model: The make and model of your vehicle can affect the cost of replacement belts, as some vehicles require specialized belts.
- Labor Costs: If you choose to have a professional mechanic replace the belt, labor costs can vary depending on the shop’s hourly rate and the complexity of the job.
10.2. DIY vs. Professional Replacement
- DIY: Replacing the belt yourself can save on labor costs, but requires the right tools, knowledge, and time.
- Professional: Professional replacement ensures the job is done correctly and may come with a warranty, but involves higher costs.
10.3. Average Replacement Costs
- V-Belt: $20 – $50 for the belt, plus labor if professionally installed.
- Serpentine Belt: $30 – $100 for the belt, plus labor if professionally installed.
- Total Cost (Professional): $80 – $200, depending on the vehicle and labor rates.
| Cost Factor | DIY Cost | Professional Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Cost | $20 – $100 (depending on type) | Included in Total Cost |
| Labor Cost | $0 | $50 – $100 (depending on complexity and rates) |
| Total Cost | $20 – $100 | $80 – $200 |
11. Environmental Considerations for Disposing of Old Car Belts
Proper disposal of old car belts is essential to minimize environmental impact. Understanding the correct methods ensures responsible waste management.
11.1. Recycling Car Belts
- Check with Local Recycling Centers: Some recycling centers accept car belts and other rubber products for recycling.
- Contact Automotive Parts Stores: Many automotive parts stores have recycling programs for used belts and other automotive components.
11.2. Proper Disposal Methods
- Avoid Incineration: Incinerating car belts can release harmful pollutants into the air.
- Landfill Disposal: If recycling is not an option, dispose of the belt in a designated landfill.
11.3. Environmental Impact of Improper Disposal
- Soil and Water Contamination: Improper disposal of car belts can lead to soil and water contamination due to the release of chemicals and rubber particles.
- Air Pollution: Burning car belts can release toxic fumes into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and health problems.
| Disposal Method | Environmental Impact | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling | Reduces waste, conserves resources | Check Local Recycling Centers, Contact Parts Stores |
| Landfill Disposal | Minimal impact if done properly | Use Designated Landfill |
| Incineration | Releases Harmful Pollutants | Avoid Incineration |
12. The Future of Car Belt Technology
Car belt technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Exploring these advancements provides insight into future trends and innovations.
12.1. Advancements in Belt Materials
- Improved Rubber Compounds: New rubber compounds are being developed to enhance belt durability, flexibility, and heat resistance.
- Advanced Reinforcing Fibers: Advanced reinforcing fibers, such as carbon fiber and graphene, are being incorporated into belts to increase strength and reduce stretching.
12.2. Smart Belt Technology
- Integrated Sensors: Smart belts with integrated sensors can monitor belt tension, wear, and temperature, providing real-time data to the vehicle’s computer system.
- Predictive Maintenance: This data can be used to predict belt failures and schedule maintenance proactively, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
12.3. Electric Vehicle Applications
- Optimized Belts for EVs: Electric vehicles require specialized belts for driving accessories such as air conditioning compressors and water pumps.
- Increased Efficiency: These belts are designed to operate efficiently and quietly, minimizing energy consumption and maximizing vehicle range.
| Advancement | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Materials | New Rubber Compounds, Advanced Reinforcing Fibers | Enhanced Durability, Flexibility, and Heat Resistance |
| Smart Belt Technology | Integrated Sensors, Predictive Maintenance | Real-Time Data, Prevents Breakdowns, Proactive Maintenance |
| EV Applications | Optimized Belts for EVs, Increased Efficiency | Specialized Belts, Efficient Operation, Maximized Vehicle Range |
Understanding how to fix a car belt, including identifying issues, performing replacements, and maintaining belts, empowers you to keep your vehicle running smoothly. For high-quality tools and expert advice, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET. Proper car belt maintenance can save you money and ensure your vehicle’s reliability. Remember, regular inspections and timely replacements are key to preventing breakdowns and costly repairs.
Are you facing car belt problems? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States for expert advice and premium auto repair tools. Our team is ready to assist you with your auto repair needs. Don’t let car belt issues slow you down; reach out today for reliable solutions and quality products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should I replace my car belt?
It is recommended to replace your car belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, or as specified in your vehicle’s manual.
2. What are the signs of a failing car belt?
Common signs include squealing noises, visible cracks, power steering problems, overheating engine, and battery warning light.
3. Can I replace a car belt myself?
Yes, if you have the necessary tools and experience, you can replace a car belt yourself. However, professional service is recommended for complex systems.
4. What tools do I need to replace a car belt?
Essential tools include a socket set, wrenches, belt tensioner tool, pry bar, and a new replacement belt.
5. How do I check the tension of a car belt?
You can check the tension using a belt tension gauge. Refer to your vehicle’s manual for the recommended tension specifications.
6. What happens if a car belt breaks while driving?
If a car belt breaks, you may lose power steering, air conditioning, and the engine could overheat. Pull over safely and call for assistance.
7. Can I use any type of car belt for my vehicle?
No, you must use the correct size and type of belt specified for your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
8. How do I prevent my car belt from failing prematurely?
Regularly inspect the belt for wear, check the tension, keep it clean, and avoid oil and chemical contamination.
9. What is the difference between a V-belt and a serpentine belt?
A V-belt is trapezoidal and drives specific accessories, while a serpentine belt is longer and drives all engine accessories.
10. Where can I buy high-quality car belts and tools?
You can purchase high-quality car belts and tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET, your trusted source for automotive repair solutions.






