Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative: Causes And Solutions
Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative warnings can be concerning, but CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through understanding and resolving them. This comprehensive guide explores the causes of ESP malfunctions, diagnostic steps, and effective repair solutions, ensuring your Mercedes C-Class delivers optimal performance and safety. Let’s explore troubleshooting, electronic stability program (ESP) resets and ABS issues.
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP Inoperative
Mercedes-Benz vehicles integrate advanced technologies to enhance the driving experience, and the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a critical component. ESP maintains vehicle stability by preventing skidding and ensuring directional control, particularly in adverse conditions. When a “Mercedes-Benz ESP Inoperative” warning appears, it signals a potential issue within this system that needs prompt attention. Addressing this warning light is essential for maintaining vehicle safety and performance.
 Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
2. How ESP Works in Your Mercedes C-Class
ESP’s primary function is to prevent loss of tire traction and wheel spin, which are common causes of instability. It utilizes data from various sensors, including wheel speed and tire pressure, to make real-time adjustments.
2.1 Key Functions of ESP
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during braking by pulsing the brakes, ensuring optimal stopping force.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Limits wheel spin during acceleration, particularly on slippery surfaces.
- Yaw Control: Corrects oversteer or understeer by applying brakes to individual wheels, keeping the vehicle on its intended path.
ESP calculates and makes adjustments hundreds of times per second, ensuring the vehicle maintains stability.
3. Common Causes of Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative Message
Identifying the root cause is crucial for resolving ESP issues effectively. Several factors can trigger the “Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative” message.
3.1 ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Explanation: Damaged or faulty ABS wheel speed sensors are a frequent cause of ESP malfunctions. These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide critical data to the ESP system.
Impact: Inaccurate readings from these sensors can confuse the ESP system, leading it to shut down as a preventive measure.
3.2 Battery and Voltage Problems
Explanation: A weak or dead 12-volt battery or a malfunctioning alternator can disrupt the optimal performance of the ESP system.
Impact: ESP components require a steady voltage supply. Voltage irregularities can affect sensor accuracy and overall system function. According to a study by AAA, automotive batteries typically last between 3 to 5 years, and voltage drops can occur due to age or extreme temperatures, affecting ESP performance.
3.3 Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
Explanation: The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel, providing essential data for the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction.
Impact: If this sensor is misaligned or needs replacement, it can cause ESP errors. Calibration ensures the sensor provides accurate readings, which is vital for ESP to function correctly.
3.4 Brake Light Switch Malfunction
Explanation: The brake light switch signals when the driver applies the brakes.
Impact: A faulty switch can send incorrect signals to the ESP system, causing it to deactivate.
3.5 Additional Potential Causes
- Faulty Solenoids or Worn Hydraulic Valves: These components are crucial for the proper functioning of the braking system.
- Corrupted Software or Faulty Connectors: Software glitches or connection issues can disrupt communication within the ESP system.
- Low Tire Pressure or Incorrect Wheel Alignment: These factors can affect vehicle stability and trigger ESP warnings. Studies by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) show that maintaining proper tire pressure and wheel alignment can significantly enhance vehicle stability and safety.
 Mercedes ESP Inoperative
Mercedes ESP Inoperative
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing the ESP Issue
Diagnosing a Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative issue involves a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause. Here’s a detailed guide:
4.1 Initial Inspection
Step 1: Check the Warning Light
Action: Note when the ESP warning light illuminates. Does it appear immediately upon starting the car, or does it come on during driving?
Expected Result: Understanding the conditions under which the warning light appears can provide clues about the possible causes.
Step 2: Review Recent Maintenance
Action: Check if any recent maintenance or repairs might be related to the ESP issue.
Expected Result: Identifying recent work can help pinpoint whether a specific repair could have triggered the problem.
4.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner
Step 1: Connect the Scanner
Action: Plug an OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard.
Expected Result: The scanner powers on and establishes a connection with the vehicle’s computer.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality OBD-II scanners perfect for diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the best tool for your needs.
Step 2: Read the Error Codes
Action: Use the scanner to read any stored error codes related to the ESP system.
Expected Result: The scanner displays a list of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that provide specific information about the issue.
Step 3: Interpret the Codes
Action: Research each error code to understand its meaning and potential causes. Common codes related to ESP issues include:
- C1000: ABS control module malfunction
- C1100: ABS wheel speed sensor electrical fault
- C1120: ESP control unit fault
- C1140: Steering angle sensor fault
Expected Result: A clear understanding of the error codes and their implications for the ESP system.
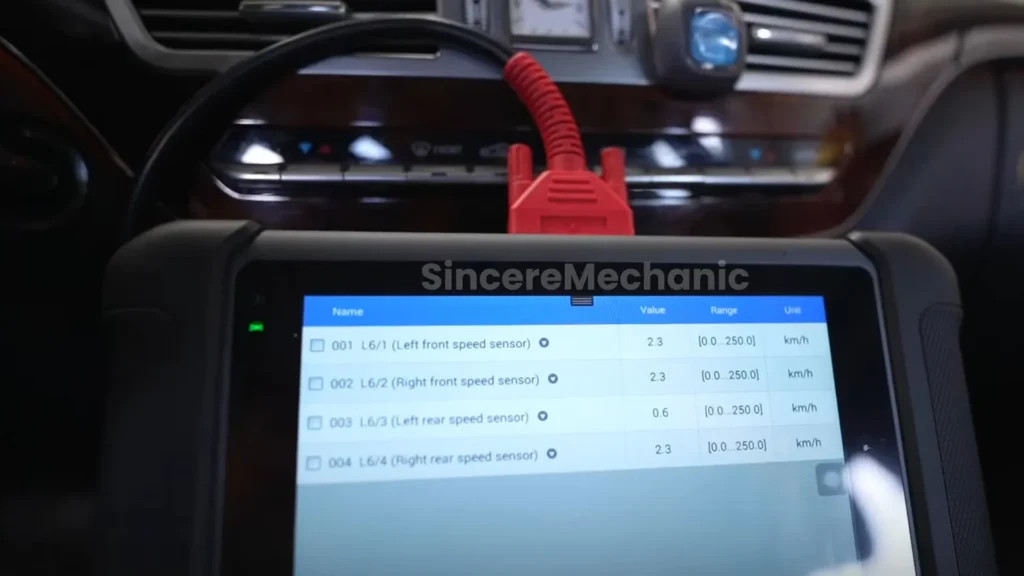
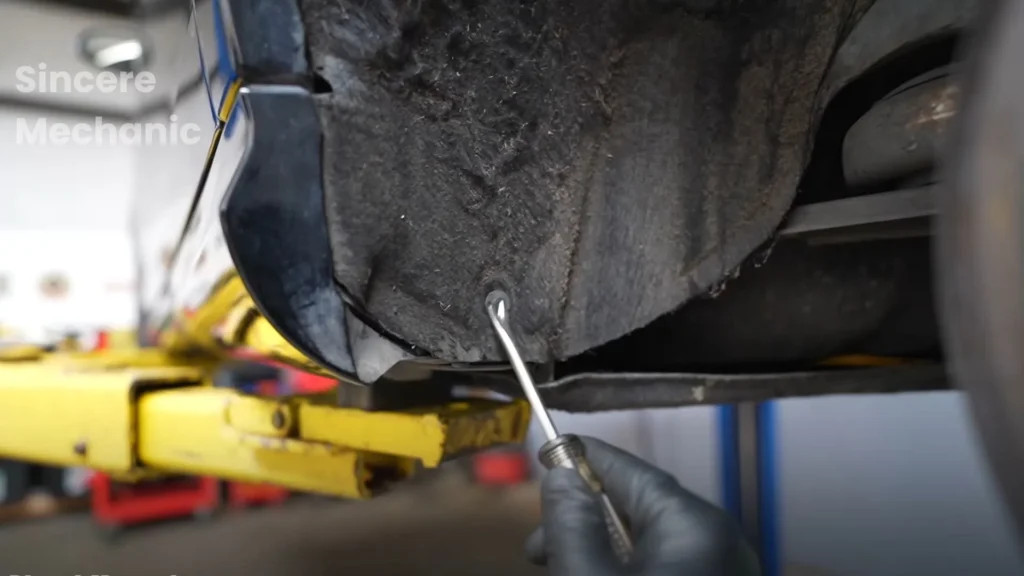
4.3 Inspecting the ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
Step 1: Locate the Sensors
Action: Find the ABS wheel speed sensors on each wheel hub.
Expected Result: The sensors are typically mounted near the brake rotors.
Step 2: Check for Damage
Action: Visually inspect the sensors and their wiring for any signs of damage, such as cracks, frayed wires, or corrosion.
Expected Result: Identification of any physical damage that could affect sensor performance.
Step 3: Test the Sensors
Action: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Expected Result: Confirmation of whether the sensors are functioning within the acceptable range. A reading outside the specified range indicates a faulty sensor.
4.4 Checking the Battery and Alternator
Step 1: Test the Battery Voltage
Action: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off and running.
Expected Result: A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when off and between 13.7 to 14.7 volts when the engine is running. Readings outside these ranges indicate a potential issue.
Step 2: Inspect the Alternator
Action: Check the alternator for any signs of damage or wear.
Expected Result: Identification of any visible damage that could affect alternator performance.
Step 3: Perform a Load Test
Action: Conduct a load test on the battery and alternator to ensure they can handle the electrical demands of the vehicle.
Expected Result: Confirmation of whether the battery and alternator are functioning correctly under load.
4.5 Evaluating the Steering Angle Sensor
Step 1: Access the Sensor Data
Action: Use an OBD-II scanner to access the live data from the steering angle sensor.
Expected Result: Real-time data on the steering angle, which can be compared to the actual steering wheel position.
Step 2: Check for Accuracy
Action: Turn the steering wheel and observe the sensor readings. Ensure the readings match the actual steering angle.
Expected Result: Confirmation of whether the sensor is providing accurate data. Discrepancies indicate a need for calibration or replacement.
4.6 Brake Light Switch Assessment
Step 1: Locate the Switch
Action: Find the brake light switch, typically located near the brake pedal.
Expected Result: The switch is accessible for inspection and testing.
Step 2: Test the Switch
Action: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the switch. The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and no continuity when the pedal is released.
Expected Result: Confirmation of whether the switch is functioning correctly.
4.7 Additional Checks
Action: Inspect other potential causes, such as faulty solenoids, worn hydraulic valves, corrupted software, and low tire pressure.
Expected Result: Comprehensive assessment of all possible factors contributing to the ESP issue.
By following this step-by-step diagnostic process, you can systematically identify the root cause of the Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative message and take appropriate corrective actions.
5. Resetting the Mercedes-Benz ESP Warning Light
After addressing the underlying issue, resetting the ESP warning light is essential. The reset process may vary slightly depending on your specific model.
5.1 Manual Reset Procedure
- Locate the ESP Button: Find the “ESP Off” button on your dashboard.
- Press and Hold: Press and hold the button for approximately five seconds.
- Restart Vehicle: Turn off the vehicle, wait a few seconds, and then restart it.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides detailed repair guides and diagnostic tools to help you resolve ESP issues efficiently. Contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
5.2 Using a Diagnostic Scanner
- Connect the Scanner: Plug an OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port.
- Clear Error Codes: Use the scanner to clear any stored error codes related to the ESP system.
- Verify Reset: Restart the vehicle and check if the ESP warning light has been reset.
If the manual reset or scanner method does not work, consult a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair.
6. Advanced Troubleshooting and Repairs
In some cases, the ESP issue may require more complex troubleshooting and repairs.
6.1 Replacing ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
- Symptoms: Erratic ABS or ESP behavior, ABS warning light, error codes indicating sensor failure.
- Procedure: Replace the faulty sensor with a new one, ensuring proper installation and connection.
- Tools Needed: Socket set, wrench, multimeter.
6.2 Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
- Symptoms: ESP warning light after wheel alignment or steering system work, inaccurate ESP corrections.
- Procedure: Use a diagnostic scanner to recalibrate the steering angle sensor, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Tools Needed: OBD-II scanner with calibration function.
6.3 Addressing Electrical Issues
- Symptoms: Intermittent ESP warning lights, voltage irregularities, sensor malfunctions.
- Procedure: Inspect and repair any damaged wiring, replace faulty connectors, and ensure proper grounding.
- Tools Needed: Multimeter, wire strippers, crimping tool.
7. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of your ESP system.
7.1 Regular Inspections
- Schedule: Inspect ABS wheel speed sensors, wiring, and connectors during routine maintenance.
- Benefits: Early detection of potential issues can prevent major problems and costly repairs.
7.2 Battery Maintenance
- Schedule: Regularly check the battery voltage and condition.
- Benefits: A healthy battery ensures stable voltage for all ESP components.
7.3 Tire Care
- Schedule: Maintain proper tire pressure and alignment.
- Benefits: Optimal tire conditions contribute to vehicle stability and ESP performance. According to research by the National Tire Safety Board, maintaining proper tire inflation can improve fuel efficiency by up to 3.3% and extend tire life.
8. The Importance of Professional Assistance
While many ESP issues can be resolved with DIY methods, certain situations require professional expertise.
8.1 When to Seek a Professional
- Complex Issues: If the ESP warning light persists after basic troubleshooting and resets.
- Unfamiliarity: If you are uncomfortable performing diagnostic tests or repairs.
- Advanced Tools: When specialized tools or diagnostic equipment are required.
8.2 Benefits of Professional Service
- Accurate Diagnosis: Certified technicians have the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose complex ESP issues.
- Quality Repairs: Professional service ensures high-quality repairs and reliable performance.
- Warranty Protection: Many repair shops offer warranties on their work, providing added peace of mind.
Table: Common ESP Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Causes | DIY Solutions | Professional Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESP Warning Light On | Faulty ABS wheel speed sensor, low battery | Check and clean sensors, charge or replace battery | Diagnose and replace faulty sensors, perform electrical system diagnostics |
| ABS and ESP Inoperative | Steering angle sensor calibration, brake switch | Reset ESP system, check brake light switch | Calibrate steering angle sensor, replace faulty brake light switch |
| Intermittent ESP Malfunction | Wiring issues, faulty connectors | Inspect and repair wiring, clean connectors | Diagnose and repair electrical issues, replace faulty connectors |
| Loss of Traction Control | Low tire pressure, incorrect wheel alignment | Inflate tires to proper pressure, perform wheel alignment | Diagnose and repair suspension issues, ensure proper tire fitment |
| ESP System Failure | Corrupted software, control module failure | Reset ESP system, check for software updates | Reflash or replace ESP control module, perform advanced system diagnostics |
9. Real-World Examples and Scenarios
Understanding how ESP issues manifest in real-world scenarios can help you better diagnose and address problems.
9.1 Scenario 1: ESP Light After Battery Replacement
Situation: A driver replaces their Mercedes C-Class battery and then notices the ESP warning light is illuminated.
Possible Cause: The steering angle sensor may need recalibration after the battery replacement. The ESP system relies on accurate steering angle data, and voltage fluctuations during the battery change can disrupt the sensor’s calibration.
Solution: Use an OBD-II scanner to recalibrate the steering angle sensor. Follow the scanner’s instructions to perform the calibration procedure, ensuring the sensor provides accurate readings.
9.2 Scenario 2: ESP Light During Wet Weather
Situation: A driver notices the ESP warning light comes on intermittently during heavy rain.
Possible Cause: Moisture may be affecting the ABS wheel speed sensors or their wiring. Water intrusion can cause corrosion and electrical shorts, leading to inaccurate sensor readings and ESP malfunctions.
Solution: Inspect the ABS wheel speed sensors and their wiring for signs of moisture or corrosion. Clean the sensors and apply dielectric grease to the connectors to prevent further moisture intrusion. If the problem persists, consider replacing the sensors.
9.3 Scenario 3: ESP Light After Wheel Alignment
Situation: A driver has a wheel alignment performed on their Mercedes C-Class and then sees the ESP warning light.
Possible Cause: The wheel alignment process may have affected the steering angle sensor. Adjustments to the steering system can misalign the sensor, causing it to provide incorrect data to the ESP system.
Solution: Use an OBD-II scanner to check the steering angle sensor readings. If the readings are inaccurate, recalibrate the sensor using the scanner’s calibration function.
9.4 Scenario 4: ESP Light with Brake Issues
Situation: A driver experiences both the ESP warning light and issues with the braking system, such as longer stopping distances or uneven braking.
Possible Cause: There may be a problem with the brake light switch or ABS system. A faulty brake light switch can send incorrect signals to the ESP system, while issues with the ABS system can directly affect ESP performance.
Solution: Test the brake light switch to ensure it is functioning correctly. Check the ABS system for any error codes and perform a thorough inspection of the brake components, including the brake pads, rotors, and calipers.
9.5 Scenario 5: ESP Light with Tire Problems
Situation: A driver notices the ESP warning light is on, and their tires are worn unevenly.
Possible Cause: Uneven tire wear can cause the ESP system to activate unnecessarily, as the system detects variations in wheel speed. Low or uneven tire pressure can also affect ESP performance.
Solution: Ensure that the tires are inflated to the correct pressure and have a wheel alignment performed to correct the uneven wear. Replace the tires if they are excessively worn.
10. Tools and Equipment for ESP Diagnosis and Repair
Having the right tools and equipment is essential for effective ESP diagnosis and repair.
10.1 Essential Tools
- OBD-II Scanner: For reading and clearing error codes, accessing live data, and performing system resets.
- Multimeter: For testing electrical components, such as sensors and wiring.
- Socket Set: For removing and installing sensors and other components.
- Wrench Set: For tightening and loosening bolts and nuts.
- Torque Wrench: For ensuring components are tightened to the correct specifications.
- Wire Strippers and Crimpers: For repairing and replacing wiring.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive selection of tools and equipment for diagnosing and repairing ESP systems. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the perfect tools for your needs.
10.2 Diagnostic Equipment
- ABS Scan Tool: For advanced diagnostics of the ABS system.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration Tool: For calibrating the steering angle sensor.
- Battery Tester: For testing the battery voltage and condition.
- Alternator Tester: For testing the alternator output and performance.
10.3 Safety Equipment
- Safety Glasses: For protecting your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Gloves: For protecting your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Jack and Jack Stands: For safely lifting and supporting the vehicle.
11. ESP System Components and Their Functions
Understanding the various components of the ESP system and their functions can aid in effective diagnosis and repair.
11.1 ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
- Function: Measure the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Location: Mounted near the brake rotors on each wheel hub.
- Importance: Provide critical data for the ESP system to detect wheel slippage and loss of traction.
11.2 Steering Angle Sensor
- Function: Measures the position of the steering wheel.
- Location: Typically located on the steering column.
- Importance: Provides essential data for the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction.
11.3 Yaw Rate Sensor
- Function: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Location: Usually located near the center of the vehicle.
- Importance: Helps the ESP system detect oversteer and understeer.
11.4 Lateral Acceleration Sensor
- Function: Measures the vehicle’s acceleration perpendicular to its direction of travel.
- Location: Often located near the yaw rate sensor.
- Importance: Helps the ESP system detect sideways movement and loss of stability.
11.5 ESP Control Module
- Function: Processes data from the various sensors and controls the ABS and traction control systems.
- Location: Typically located in the engine compartment or under the dashboard.
- Importance: The brain of the ESP system, responsible for making real-time adjustments to maintain vehicle stability.
11.6 Hydraulic Control Unit
- Function: Modulates the brake pressure at each wheel.
- Location: Usually located near the ABS control module.
- Importance: Allows the ESP system to apply brakes to individual wheels to correct oversteer or understeer.
11.7 Brake Light Switch
- Function: Signals when the driver applies the brakes.
- Location: Located near the brake pedal.
- Importance: Informs the ESP system when the driver is braking, which can affect how the system responds.
12. Safety Precautions When Working on ESP Systems
Working on ESP systems involves handling electrical and mechanical components, so it is crucial to follow safety precautions to prevent injury and damage.
12.1 General Safety Guidelines
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Wear Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job to prevent damage to components.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for diagnosis and repair.
12.2 Specific Precautions for ESP Systems
- Handle Sensors Carefully: ABS wheel speed sensors and other sensors are sensitive and can be easily damaged.
- Avoid Static Electricity: Static electricity can damage electronic components. Use an anti-static wrist strap when handling sensors and control modules.
- Check Wiring Carefully: Inspect wiring for damage before making any connections.
- Tighten Connections Securely: Ensure all connections are tight to prevent electrical shorts.
By following these safety precautions, you can work on ESP systems safely and effectively.
13. Long-Term Benefits of Maintaining Your ESP System
Maintaining your ESP system provides numerous long-term benefits, including improved safety, enhanced vehicle performance, and reduced repair costs.
13.1 Enhanced Safety
- Improved Stability: A properly functioning ESP system helps maintain vehicle stability in adverse driving conditions, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Reduced Risk of Skidding: ESP helps prevent skidding and loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Better Traction: ESP improves traction during acceleration and braking, enhancing overall vehicle safety.
13.2 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
- Smoother Ride: ESP helps maintain a smoother and more controlled ride, especially during cornering and sudden maneuvers.
- Improved Handling: ESP enhances vehicle handling, making it more responsive and predictable.
- Optimal Braking: ESP ensures optimal braking performance, reducing stopping distances and improving safety.
13.3 Reduced Repair Costs
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance can prevent major ESP issues and costly repairs.
- Early Detection: Early detection of ESP problems can allow for minor repairs before they escalate into more significant issues.
- Prolonged Component Life: Proper maintenance can extend the life of ESP components, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
14. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of maintaining your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. That’s why we offer a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment to help you diagnose and repair ESP issues effectively.
14.1 High-Quality Products
We offer a comprehensive selection of OBD-II scanners, ABS scan tools, steering angle sensor calibration tools, and other diagnostic equipment from top brands. Our products are designed to provide accurate and reliable results, ensuring you can diagnose ESP problems quickly and efficiently.
14.2 Expert Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance. Whether you need help choosing the right diagnostic tool or troubleshooting an ESP issue, we are here to assist you.
14.3 Competitive Prices
We offer competitive prices on all our products, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
14.4 Convenient Shopping
Our online store makes it easy to browse and purchase the diagnostic tools and equipment you need. We offer fast shipping and hassle-free returns, ensuring a convenient and enjoyable shopping experience.
Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to learn more about our products and services. We are here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz ESP system functioning at its best.
15. Conclusion
The Mercedes C Class ESP Inoperative warning can be a cause for concern, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can effectively diagnose and resolve the issue. From understanding the function of ESP to diagnosing common causes and performing necessary repairs, this comprehensive guide provides you with the information you need to maintain your vehicle’s stability and safety. Remember, addressing ESP issues promptly ensures a smooth, efficient, and safe driving experience. If you encounter complex problems or are unsure about performing repairs, seeking professional assistance is always a wise choice.
For all your diagnostic and repair needs, trust CARDIAGTECH.NET. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website. Our expert team is ready to assist you in maintaining the optimal performance and safety of your Mercedes-Benz.
16. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
16.1 What does ESP stand for in a Mercedes-Benz?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It is a safety system designed to help maintain vehicle stability by preventing skidding and loss of control.
16.2 How do I know if my ESP is not working?
If your ESP is not working, the ESP warning light will illuminate on your dashboard. You may also experience a loss of traction control or stability, especially in slippery conditions.
16.3 Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP light on?
While it is generally safe to drive with the ESP light on, it is not recommended. The ESP system is designed to enhance safety, and driving without it can increase the risk of accidents, especially in adverse conditions.
16.4 How do I reset the ESP light on my Mercedes-Benz?
You can try resetting the ESP light by locating the “ESP Off” button on your dashboard, pressing and holding it for five seconds, and then restarting the vehicle. If this does not work, you may need to use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored error codes.
16.5 What are the common causes of ESP malfunction in a Mercedes-Benz C-Class?
Common causes of ESP malfunction include faulty ABS wheel speed sensors, a weak or dead battery, a malfunctioning alternator, a misaligned steering angle sensor, and a faulty brake light switch.
16.6 How often should I have my ESP system checked?
It is recommended to have your ESP system checked during routine maintenance, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles.
16.7 Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system. The system relies on accurate wheel speed data, and low tire pressure can cause variations in wheel speed, leading to ESP malfunctions.
16.8 Is it possible to disable ESP in a Mercedes-Benz?
Yes, it is possible to disable ESP in most Mercedes-Benz models. However, it is generally not recommended to disable the system unless necessary, as it is designed to enhance safety.
16.9 How much does it cost to repair an ESP system in a Mercedes-Benz?
The cost to repair an ESP system can vary depending on the cause of the malfunction. Minor repairs, such as replacing a faulty sensor, may cost a few hundred dollars, while more complex repairs, such as replacing the ESP control module, can cost several thousand dollars.
16.10 Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools for my Mercedes-Benz ESP system?
You can find reliable diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz ESP system at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide range of high-quality OBD-II scanners and other diagnostic equipment from top brands.



