Mercedes SLK BAS ESP Light: Diagnosis And Solutions
The Mercedes SLK BAS ESP light can be a troubling sign, indicating potential issues within your vehicle’s braking and stability systems. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the urgency of addressing such warnings. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and resolving Mercedes SLK BAS ESP light issues, offering solutions that leverage advanced diagnostic tools to ensure optimal vehicle performance and safety and address concerns like faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor malfunctions, or brake light switch failures. We will explore common causes, diagnostic procedures, and effective repair strategies, all while highlighting how CARDIAGTECH.NET can equip you with the necessary tools and knowledge to tackle these challenges head-on.
1. Understanding the BAS ESP System in Your Mercedes SLK
1.1. What is BAS and ESP?
The Brake Assist System (BAS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP) are crucial safety features in your Mercedes SLK. BAS enhances braking power during emergency stops, potentially reducing stopping distances. ESP helps maintain vehicle control by detecting and reducing skidding, especially in adverse driving conditions. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP can reduce accidents by up to 40%. Both systems work together to provide a safer driving experience.
1.2. How Do These Systems Work Together?
BAS monitors the speed and force with which you apply the brake pedal. If it detects an emergency braking situation, it applies maximum braking force, even if you haven’t fully pressed the pedal. ESP uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, ESP selectively applies brakes to individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course. These systems integrate seamlessly to enhance both braking efficiency and vehicle stability.
1.3. Why Is the BAS ESP Light Illuminated?
The BAS ESP light illuminates when the system detects a fault. This could be due to a variety of reasons, ranging from sensor malfunctions to issues with the hydraulic unit. Common causes include:
- Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: Faulty sensors can disrupt the accuracy of readings, triggering the warning light.
- Steering Angle Sensor Malfunctions: Incorrect readings can affect the ESP’s ability to accurately assess the vehicle’s direction.
- Brake Light Switch Problems: A malfunctioning switch can prevent the BAS from functioning correctly.
- Hydraulic Unit Problems: Issues within the hydraulic unit can impact both BAS and ESP functionality.
- Low Battery Voltage: Insufficient voltage can cause erratic sensor behavior, leading to false alerts.
Alt text: Illuminated BAS ESP light on a Mercedes-Benz SLK dashboard, signaling potential brake assist and stability system malfunctions requiring diagnostic attention.
1.4. Potential Consequences of Ignoring the Warning Light
Ignoring the BAS ESP light can have serious consequences. Your vehicle’s braking and stability systems may not function correctly, increasing the risk of accidents, especially in emergency braking situations or slippery conditions. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), vehicles with malfunctioning stability control systems are significantly more likely to be involved in accidents. Addressing the issue promptly is crucial for your safety and the safety of others on the road.
2. Common Causes of the Mercedes SLK BAS ESP Light
2.1. Wheel Speed Sensor Problems
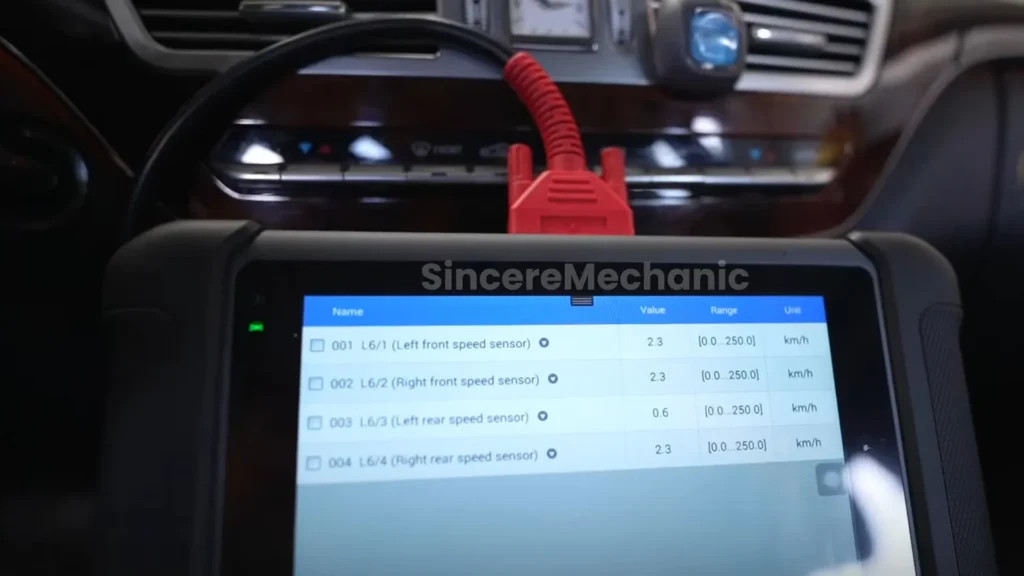
Wheel speed sensors are vital components of the ABS and ESP systems. They monitor the speed of each wheel and transmit this data to the control unit. If a sensor fails or provides inaccurate readings, the BAS ESP light may illuminate.
2.1.1. How Wheel Speed Sensors Work
Wheel speed sensors typically use a magnetic encoder ring and a sensor head to generate a signal proportional to the wheel’s speed. As the wheel rotates, the encoder ring passes by the sensor head, creating a pulse signal. The control unit interprets this signal to determine the wheel’s speed.
2.1.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Illuminated BAS ESP Light: The most common symptom.
- ABS Light On: Often accompanies the BAS ESP light.
- Traction Control Issues: Reduced or non-existent traction control.
- Erratic Braking: Uneven or unpredictable braking performance.
- Speedometer Problems: Inaccurate or fluctuating speedometer readings.
2.1.3. Diagnosing Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor and wiring for damage.
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool like those available at CARDIAGTECH.NET to read fault codes related to wheel speed sensors.
- Multimeter Testing: Test the sensor’s resistance and signal output.
- Oscilloscope Analysis: Analyze the sensor’s signal waveform to identify irregularities.
2.1.4. Repairing or Replacing Wheel Speed Sensors
- Cleaning: Clean the sensor and encoder ring of any debris or corrosion.
- Wiring Repair: Repair or replace damaged wiring.
- Sensor Replacement: Replace the faulty sensor with a new one. Ensure it is compatible with your Mercedes SLK model.
2.2. Steering Angle Sensor Malfunctions
The steering angle sensor monitors the position of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP system. This data is crucial for determining the driver’s intended direction and initiating corrective actions.
2.2.1. How the Steering Angle Sensor Works
The steering angle sensor typically uses optical or magnetic encoders to measure the steering wheel’s angle. This information is transmitted to the ESP control unit, allowing it to accurately assess the vehicle’s intended path.
2.2.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Steering Angle Sensor
- Illuminated BAS ESP Light: A primary indicator of a problem.
- ESP Inactivity: The ESP system may not engage when needed.
- Erratic ESP Engagement: The ESP system may activate unnecessarily.
- Steering Issues: Stiff or unresponsive steering.
2.2.3. Diagnosing Steering Angle Sensor Problems
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a diagnostic tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET to read fault codes related to the steering angle sensor.
- Live Data Analysis: Monitor the sensor’s readings in real-time to identify any discrepancies.
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor and wiring for damage.
2.2.4. Calibrating or Replacing the Steering Angle Sensor
- Calibration: Recalibrate the sensor using a diagnostic tool. This may be necessary after replacing the sensor or performing certain repairs.
- Replacement: Replace the faulty sensor with a new, compatible unit.
2.3. Brake Light Switch Issues
The brake light switch signals when the brake pedal is pressed. This information is used by both the BAS and ESP systems to initiate braking assistance and stability control.
2.3.1. How the Brake Light Switch Functions
The brake light switch is typically located near the brake pedal. When the pedal is pressed, the switch closes, activating the brake lights and signaling the control units.
2.3.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Brake Light Switch
- Illuminated BAS ESP Light: A common symptom.
- Brake Lights Not Working: The brake lights may not illuminate when the pedal is pressed.
- Cruise Control Problems: The cruise control may not engage or disengage properly.
- Difficulty Shifting: The transmission may be difficult to shift out of park.
2.3.3. Diagnosing Brake Light Switch Problems
- Visual Inspection: Check the switch for damage or loose connections.
- Multimeter Testing: Test the switch for continuity when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to check for fault codes related to the brake light switch.
2.3.4. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
- Replacement: Replace the faulty switch with a new, compatible unit. Ensure proper adjustment after installation.
2.4. Hydraulic Unit Problems
The hydraulic unit is a critical component of the ABS, BAS, and ESP systems. It controls the distribution of brake fluid to individual wheels, allowing for precise braking and stability control.
2.4.1. How the Hydraulic Unit Operates
The hydraulic unit uses a series of valves and pumps to regulate brake pressure to each wheel. This allows the system to apply brakes selectively, preventing skidding and maintaining vehicle control.
2.4.2. Symptoms of Hydraulic Unit Issues
- Illuminated BAS ESP Light: A common symptom.
- ABS Light On: Often accompanies the BAS ESP light.
- Braking Problems: Reduced braking performance or uneven braking.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding or squealing noises during braking.
2.4.3. Diagnosing Hydraulic Unit Problems
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a diagnostic tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET to read fault codes related to the hydraulic unit.
- Visual Inspection: Check the unit for leaks or damage.
- Pressure Testing: Test the hydraulic pressure at various points in the system.
2.4.4. Repairing or Replacing the Hydraulic Unit
- Repair: Minor issues may be repairable, such as replacing faulty valves.
- Replacement: In more severe cases, the entire hydraulic unit may need to be replaced.
2.5. Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can cause a variety of electrical problems in your Mercedes SLK, including issues with the BAS and ESP systems.
2.5.1. How Low Voltage Affects the BAS ESP System
Low voltage can cause sensors to provide inaccurate readings, leading to false alerts and system malfunctions.
2.5.2. Symptoms of Low Battery Voltage
- Illuminated BAS ESP Light: May appear intermittently.
- Difficulty Starting: The engine may crank slowly or fail to start.
- Dimming Lights: Headlights and interior lights may appear dim.
- Electrical Issues: Various electrical systems may malfunction.
2.5.3. Diagnosing Low Battery Voltage
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Load Testing: Perform a load test to assess the battery’s ability to hold a charge under load.
2.5.4. Resolving Low Battery Voltage Issues
- Charging: Charge the battery using a battery charger.
- Replacement: If the battery is old or damaged, replace it with a new one.
- Alternator Check: Ensure the alternator is charging the battery properly.
3. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures for the BAS ESP Light
3.1. Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
Before starting any diagnostic work, ensure you have the necessary tools and equipment. These may include:
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A tool like those from CARDIAGTECH.NET that is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles to read and clear fault codes.
- Multimeter: For testing voltage, continuity, and resistance.
- Socket Set: For removing and installing sensors and other components.
- Wrench Set: For various mechanical tasks.
- Jack and Jack Stands: For safely lifting the vehicle.
- Wheel Chocks: For securing the vehicle.
- Service Manual: A reference guide specific to your Mercedes SLK model.
3.2. Performing a Visual Inspection
Start with a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle. Check the following:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Look for damage to the sensors and wiring.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Inspect the sensor and connections.
- Brake Light Switch: Check the switch for proper operation and damage.
- Hydraulic Unit: Look for leaks or damage.
- Wiring Harnesses: Inspect all wiring harnesses for damage or corrosion.
3.3. Using a Diagnostic Scan Tool
A diagnostic scan tool is essential for reading fault codes and gathering information about the BAS ESP system.
3.3.1. Connecting the Scan Tool to the Vehicle
- Locate the OBD-II port in your Mercedes SLK. It is typically located under the dashboard.
- Plug the scan tool into the OBD-II port.
- Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Follow the scan tool’s instructions to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
3.3.2. Reading and Interpreting Fault Codes
- Select the “Read Codes” or “Trouble Codes” option on the scan tool.
- The scan tool will display any stored fault codes related to the BAS ESP system.
- Record the fault codes and research their meaning using a service manual or online resources. Common codes include:
- C1000: Control Unit Fault
- C1100 – C1106: Wheel Speed Sensor Faults
- C1140: Steering Angle Sensor Fault
- C1175: Brake Light Switch Fault
- Interpret the codes to identify the likely cause of the problem.
3.3.3. Clearing Fault Codes
After addressing the identified issues, clear the fault codes using the scan tool.
- Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scan tool.
- Follow the scan tool’s instructions to clear the codes.
- Start the engine and drive the vehicle to see if the BAS ESP light illuminates again. If it does, further diagnosis may be necessary.
3.4. Testing Individual Components
3.4.1. Testing Wheel Speed Sensors with a Multimeter
- Disconnect the wheel speed sensor.
- Set the multimeter to the resistance setting.
- Measure the resistance between the sensor terminals. Refer to the service manual for the correct resistance value.
- Check the sensor’s signal output by connecting the multimeter to the sensor terminals and spinning the wheel. The multimeter should display a fluctuating voltage.
3.4.2. Testing the Steering Angle Sensor
- Connect the scan tool to the vehicle.
- Select the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the scan tool.
- Monitor the steering angle sensor’s readings as you turn the steering wheel. The readings should change smoothly and accurately.
3.4.3. Testing the Brake Light Switch
- Disconnect the brake light switch.
- Set the multimeter to the continuity setting.
- Check for continuity between the switch terminals when the brake pedal is pressed and released. The switch should show continuity only when the pedal is pressed.
3.5. Checking Wiring and Connections
Poor wiring and loose connections can cause a variety of electrical problems, including issues with the BAS ESP system.
3.5.1. Inspecting Wiring Harnesses
- Visually inspect all wiring harnesses related to the BAS ESP system.
- Look for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Pay close attention to areas where the wiring harnesses are exposed to the elements or subject to vibration.
3.5.2. Cleaning and Securing Connections
- Disconnect any corroded or loose connections.
- Clean the terminals with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
- Reassemble the connections and ensure they are secure.
- Apply dielectric grease to protect the connections from corrosion.
4. Repairing and Replacing Components
4.1. Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor
- Loosen the wheel lug nuts.
- Jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the wheel.
- Disconnect the wheel speed sensor connector.
- Remove the sensor mounting bolts.
- Remove the old sensor.
- Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Tighten the mounting bolts to the specified torque.
- Reconnect the sensor connector.
- Reinstall the wheel.
- Lower the vehicle.
- Tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque.
4.2. Calibrating a Steering Angle Sensor
- Connect the scan tool to the vehicle.
- Select the “Steering Angle Sensor Calibration” or “SAS Calibration” option on the scan tool.
- Follow the scan tool’s instructions to calibrate the sensor. This typically involves turning the steering wheel to specific positions.
- Verify the calibration by monitoring the sensor’s readings in real-time.
4.3. Replacing a Brake Light Switch
- Locate the brake light switch near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the switch connector.
- Remove the switch from its mounting bracket.
- Install the new switch, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Reconnect the switch connector.
- Adjust the switch as necessary to ensure proper operation.
4.4. Addressing Hydraulic Unit Issues
- Determine if the hydraulic unit can be repaired or if it needs to be replaced. Minor issues like faulty valves may be repairable.
- If replacing the unit, disconnect the brake lines and electrical connectors.
- Remove the old unit.
- Install the new unit, ensuring all connections are secure.
- Bleed the brake system to remove any air.
- Test the system to ensure proper operation.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
5.1. Using Oscilloscopes for Sensor Analysis
An oscilloscope can provide valuable insights into sensor performance by displaying the sensor’s signal waveform.
5.1.1. Setting Up the Oscilloscope
- Connect the oscilloscope to the sensor signal wire and ground.
- Set the oscilloscope to the appropriate voltage and time scales.
- Start the engine and observe the sensor’s waveform.
5.1.2. Analyzing Sensor Waveforms
- Compare the sensor’s waveform to a known good waveform.
- Look for irregularities such as dropouts, spikes, or distortions.
- Use the waveform to diagnose sensor problems such as intermittent failures or signal degradation.
5.2. Utilizing Advanced Scan Tool Functions
Advanced scan tools like those from CARDIAGTECH.NET offer a variety of functions that can aid in diagnosing BAS ESP system problems.
5.2.1. Actuation Tests
Actuation tests allow you to activate individual components of the BAS ESP system, such as the ABS pump or individual brake valves. This can help you identify problems with specific components.
5.2.2. Data Logging
Data logging allows you to record sensor data over time. This can be useful for identifying intermittent problems that may not be apparent during a static test.
5.2.3. System Programming and Coding
Some BAS ESP system components may require programming or coding after replacement. This ensures that the new component is properly integrated into the vehicle’s computer system.
6. Preventative Maintenance Tips for the BAS ESP System
6.1. Regular Brake System Inspections
Regular brake system inspections can help prevent problems with the BAS ESP system.
6.1.1. Checking Brake Pad and Rotor Condition
Inspect the brake pads and rotors for wear and damage. Replace them as needed to ensure optimal braking performance.
6.1.2. Monitoring Brake Fluid Levels and Condition
Check the brake fluid level and condition. Replace the brake fluid every two years to prevent corrosion and maintain optimal performance.
6.2. Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of the BAS ESP system.
6.2.1. Maintaining Correct Tire Pressure
Maintain the correct tire pressure as specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual.
6.2.2. Ensuring Even Tire Wear
Ensure even tire wear by rotating the tires regularly.
6.3. Battery Maintenance
Proper battery maintenance can help prevent electrical problems that can affect the BAS ESP system.
6.3.1. Keeping Battery Terminals Clean
Keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion.
6.3.2. Monitoring Battery Voltage
Monitor the battery voltage and replace the battery as needed.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Diagnosing and Repairing BAS ESP Issues
7.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools can help you quickly and accurately diagnose BAS ESP system problems.
7.2. Expert Support and Training
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides expert support and training to help you get the most out of your diagnostic tools. Our team of experienced technicians can answer your questions and provide guidance on diagnosing and repairing BAS ESP system problems.
7.3. Comprehensive Repair Solutions
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive repair solutions, including replacement parts and repair procedures. We can help you find the parts you need to repair your Mercedes SLK and provide guidance on how to perform the repairs correctly.
8. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of BAS ESP Light Issues
8.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
A Mercedes SLK owner reported that the BAS ESP light was illuminated. Using a diagnostic scan tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET, a technician identified a fault code related to the left front wheel speed sensor. Upon further inspection, the technician found that the sensor wiring was damaged. After repairing the wiring, the BAS ESP light turned off, and the system functioned normally.
8.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
A Mercedes SLK owner reported that the ESP system was activating erratically. Using a diagnostic scan tool, a technician identified a problem with the steering angle sensor. After calibrating the sensor using the scan tool, the ESP system functioned correctly.
8.3. Case Study 3: Brake Light Switch Replacement
A Mercedes SLK owner reported that the BAS ESP light was illuminated and the brake lights were not working. Upon inspection, a technician found that the brake light switch was faulty. After replacing the switch, the BAS ESP light turned off, and the brake lights functioned normally.
9. The Importance of Professional Diagnosis and Repair
While some BAS ESP system problems can be diagnosed and repaired by a skilled DIY mechanic, others require professional expertise. It is important to seek professional diagnosis and repair if you are not comfortable working on your vehicle or if the problem is complex. A professional technician has the tools, knowledge, and experience to accurately diagnose and repair BAS ESP system problems, ensuring your safety and the proper functioning of your vehicle.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Mercedes SLK BAS ESP Light
10.1. What does the BAS ESP light mean on my Mercedes SLK?
The BAS ESP light indicates a problem with the Brake Assist System (BAS) or Electronic Stability Program (ESP). These systems are crucial for your vehicle’s braking and stability.
10.2. Can I drive my Mercedes SLK with the BAS ESP light on?
While you can drive with the light on, it’s not recommended. The BAS and ESP systems may not function correctly, reducing your vehicle’s safety, especially in emergency braking or slippery conditions.
10.3. How do I reset the BAS ESP light on my Mercedes SLK?
Resetting the light requires addressing the underlying issue. Use a diagnostic scan tool to read and clear fault codes after repairing the problem.
10.4. What are common causes of the BAS ESP light illuminating?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor malfunctions, brake light switch problems, hydraulic unit issues, and low battery voltage.
10.5. How can I diagnose the cause of the BAS ESP light?
Start with a visual inspection, then use a diagnostic scan tool to read fault codes. Test individual components like wheel speed sensors and the brake light switch.
10.6. Can low battery voltage trigger the BAS ESP light?
Yes, low battery voltage can cause sensors to provide inaccurate readings, triggering the BAS ESP light.
10.7. Is it safe to ignore the BAS ESP light?
No, ignoring the BAS ESP light can compromise your vehicle’s safety and increase the risk of accidents.
10.8. Do I need special tools to diagnose BAS ESP issues?
Yes, a diagnostic scan tool compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles is essential. A multimeter, socket set, and wrench set are also helpful. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers these tools and more.
10.9. How often should I have my BAS ESP system checked?
Include the BAS ESP system in your regular brake system inspections, typically every 6 months or as part of your vehicle’s scheduled maintenance.
10.10. Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools for my Mercedes SLK?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools, expert support, and comprehensive repair solutions for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
11. Conclusion: Ensuring Your Mercedes SLK’s Safety with Proper BAS ESP System Maintenance
The Mercedes SLK BAS ESP light is a critical warning that should not be ignored. By understanding the BAS and ESP systems, diagnosing the cause of the warning light, and performing the necessary repairs, you can ensure your vehicle’s safety and optimal performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner in diagnosing and repairing BAS ESP system problems, offering high-quality diagnostic tools, expert support, and comprehensive repair solutions.
Don’t let a warning light compromise your safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert assistance and top-of-the-line diagnostic tools. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your Mercedes SLK running smoothly and safely, ensuring every drive is a pleasure.