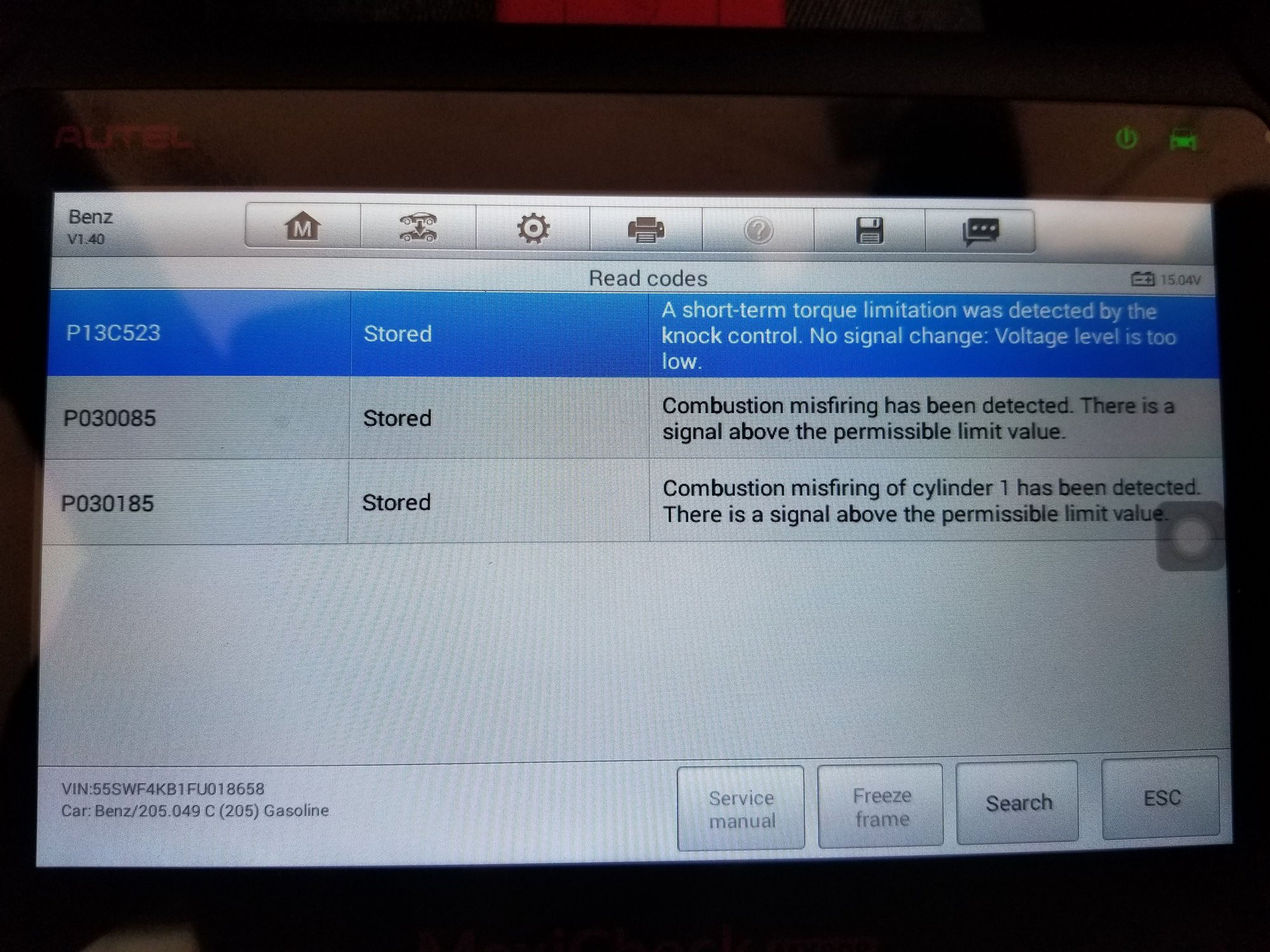
P13C523 Mercedes Fault Code Symptoms: Expert Troubleshooting Guide

Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and resolving the P13C523 Mercedes fault code, brought to you by CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our aim is to provide clear solutions, assisting you in diagnosing and fixing the issue, while highlighting the diagnostic tools and equipment we offer to make the process seamless.
1. What Exactly Does the P13C523 Mercedes Fault Code Mean?
The P13C523 Mercedes fault code indicates “Combustion Misfiring has occurred – Cylinder 1 has an implausible signal.” Essentially, your car’s engine is experiencing misfires in cylinder 1, and the data being reported is not within expected parameters. This can lead to rough idling, reduced engine power, and potentially damage to the catalytic converter if left unaddressed.
-
Misfire: When one or more cylinders in an engine fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly, it leads to a misfire. This results in incomplete combustion, reducing engine efficiency and causing noticeable performance issues.
-
Implausible Signal: The engine control unit (ECU) receives signals from various sensors to monitor engine performance. An implausible signal means that the data received from the cylinder 1 sensors is inconsistent or outside the acceptable range, indicating a problem.
2. What Are the Common Symptoms of the P13C523 Fault Code?
Experiencing any of these symptoms? Here’s what you might notice if your Mercedes is throwing the P13C523 code:
- Rough Idling: The engine may vibrate or shake excessively when the car is stationary.
- Reduced Engine Power: The car may feel sluggish, especially when accelerating.
- Check Engine Light: The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the dashboard will illuminate.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Misfires can lead to inefficient combustion, resulting in lower miles per gallon.
- Stalling: The engine may stall, particularly at low speeds or when stopped.
- Unusual Noises: You may hear popping or banging sounds from the engine compartment.
- Hesitation During Acceleration: The car might hesitate or stumble when you press the accelerator pedal.
- Vibration: Increased vibration, especially at certain speeds.
3. What Causes the P13C523 Error Code in Mercedes Vehicles?
Several factors can trigger the P13C523 fault code. Let’s explore the primary causes:
-
Faulty Ignition Coil:
- Issue: The ignition coil is responsible for providing the high-voltage spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture in cylinder 1. A failing coil can lead to misfires and an implausible signal.
- Solution: Test the ignition coil using a multimeter to check for proper resistance. If it fails the test, replace it.
-
Bad Spark Plug:
- Issue: A worn, fouled, or damaged spark plug in cylinder 1 can cause incomplete combustion and misfires.
- Solution: Inspect the spark plug for signs of wear, carbon buildup, or damage. Replace if necessary, ensuring the new plug is properly gapped.
-
Fuel Injector Problems:
- Issue: A malfunctioning fuel injector can disrupt the proper fuel delivery to cylinder 1, leading to misfires. This could be due to a clogged injector, electrical issues, or mechanical failure.
- Solution: Use a fuel injector cleaner to clear potential blockages. If the issue persists, test the injector’s electrical resistance and spray pattern. Replace if faulty.
-
Vacuum Leaks:
- Issue: Vacuum leaks can alter the air-fuel mixture in cylinder 1, causing misfires. Leaks can occur in intake manifold gaskets, vacuum hoses, or other engine seals.
- Solution: Inspect all vacuum lines and intake components for cracks, leaks, or loose connections. Use a smoke machine to identify hard-to-find leaks. Replace any damaged components.
-
Compression Issues:
- Issue: Low compression in cylinder 1 can prevent proper combustion. This can be caused by worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket.
- Solution: Perform a compression test on all cylinders. If cylinder 1 shows significantly lower compression compared to others, further investigate the internal engine components.
-
Wiring and Connector Issues:
- Issue: Damaged or corroded wiring and connectors to the ignition coil, fuel injector, or other sensors can disrupt the signal to the ECU.
- Solution: Inspect all wiring and connectors for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean or replace as necessary, and ensure proper connections.
-
Faulty Oxygen Sensor:
- Issue: Although less common, a faulty oxygen sensor can provide incorrect data to the ECU, leading to improper adjustments in the air-fuel mixture and subsequent misfires.
- Solution: Test the oxygen sensor’s performance using a scan tool. Replace if it’s not functioning within specified parameters.
-
Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems:
- Issue: In rare cases, the ECU itself may be faulty, leading to incorrect interpretations of sensor data and misfires.
- Solution: This is the least common cause and should be considered after ruling out all other possibilities. Consult with a professional to diagnose and potentially reprogram or replace the ECU.
4. How to Diagnose the P13C523 Mercedes Fault Code
Diagnosing the P13C523 fault code requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you pinpoint the issue:
-
Initial Scan:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to confirm the presence of the P13C523 code and check for any other related fault codes.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality OBD-II scanners that provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information.
-
Visual Inspection:
- Carefully inspect the engine bay, focusing on cylinder 1. Look for any obvious signs of damage, such as cracked hoses, loose connections, or frayed wires.
- Check the ignition coil and fuel injector for any visible damage or wear.
-
Ignition Coil Testing:
- Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the ignition coil. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the resistance is outside the specified range, replace the ignition coil.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers digital multimeters designed for automotive diagnostics, providing precise measurements and durability.
-
Spark Plug Inspection:
- Remove the spark plug from cylinder 1 and inspect it for signs of wear, carbon buildup, or damage.
- Note: The correct size for the 2015 C300 is a thin-walled 14mm socket.
- If the spark plug is fouled or damaged, replace it. Ensure the new plug is properly gapped according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality spark plug sockets and gapping tools to ensure proper installation and optimal performance.
 Spark plug socket for mercedes benz
Spark plug socket for mercedes benz
- Remove the spark plug from cylinder 1 and inspect it for signs of wear, carbon buildup, or damage.
-
Fuel Injector Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the fuel injector. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Listen to the fuel injector using a stethoscope while the engine is running. You should hear a clicking sound, indicating that it is functioning.
- If the fuel injector is suspected to be clogged, use a fuel injector cleaner or have it professionally cleaned.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers fuel injector testing kits and cleaning solutions to help you maintain optimal fuel delivery.
-
Compression Test:
- Perform a compression test on all cylinders, including cylinder 1.
- If the compression in cylinder 1 is significantly lower than the other cylinders, this indicates a potential issue with the piston rings, valves, or head gasket.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides compression testing kits that are easy to use and provide accurate results.
-
Vacuum Leak Test:
- Inspect all vacuum lines and intake components for cracks, leaks, or loose connections.
- Use a smoke machine to identify any hard-to-find leaks.
- Replace any damaged components and ensure all connections are secure.
- Tool Recommendation: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers smoke machines designed for automotive diagnostics, making it easier to locate vacuum leaks.
-
Wiring and Connector Inspection:
- Inspect all wiring and connectors related to the ignition coil, fuel injector, and other sensors.
- Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean or replace any damaged components and ensure proper connections.
-
Oxygen Sensor Testing:
- Use a scan tool to monitor the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Ensure that the sensors are functioning within the specified parameters.
- If an oxygen sensor is faulty, replace it.
-
ECU Diagnosis:
- If all other components have been tested and ruled out, the ECU may be the cause of the problem.
- Consult with a professional to diagnose and potentially reprogram or replace the ECU.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing the P13C523 Fault Code
Once you’ve identified the root cause, here’s how to address the P13C523 fault code:
-
Replacing a Faulty Ignition Coil:
- Step 1: Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 2: Locate the ignition coil for cylinder 1.
- Step 3: Disconnect the electrical connector from the ignition coil.
- Step 4: Remove the mounting bolts or screws securing the ignition coil.
- Step 5: Remove the old ignition coil and install the new one.
- Step 6: Reconnect the electrical connector and secure the mounting bolts or screws.
- Step 7: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 8: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
 Coil Pack replacement mercedes benz
Coil Pack replacement mercedes benz
-
Replacing a Bad Spark Plug:
- Step 1: Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 2: Locate the spark plug for cylinder 1.
- Step 3: Disconnect the spark plug wire or ignition coil from the spark plug.
- Step 4: Use a spark plug socket to remove the old spark plug.
- Step 5: Install the new spark plug, ensuring it is properly gapped according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Step 6: Reconnect the spark plug wire or ignition coil.
- Step 7: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 8: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Addressing Fuel Injector Problems:
- Step 1: Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 2: Locate the fuel injector for cylinder 1.
- Step 3: Disconnect the electrical connector from the fuel injector.
- Step 4: Remove the fuel line from the fuel injector.
- Step 5: Remove the mounting bolts or clips securing the fuel injector.
- Step 6: Remove the old fuel injector and install the new one.
- Step 7: Reconnect the fuel line and electrical connector.
- Step 8: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Step 9: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Fixing Vacuum Leaks:
- Step 1: Locate the vacuum leak using a smoke machine or visual inspection.
- Step 2: Replace any cracked or damaged vacuum lines or intake components.
- Step 3: Ensure all connections are secure.
- Step 4: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Resolving Compression Issues:
- Step 1: Perform a compression test on all cylinders to confirm the issue.
- Step 2: Depending on the cause of the low compression, you may need to replace the piston rings, valves, or head gasket.
- Step 3: Reassemble the engine and ensure all components are properly installed.
- Step 4: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Repairing Wiring and Connector Issues:
- Step 1: Inspect all wiring and connectors related to the ignition coil, fuel injector, and other sensors.
- Step 2: Clean or replace any damaged or corroded wiring and connectors.
- Step 3: Ensure all connections are secure.
- Step 4: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Replacing a Faulty Oxygen Sensor:
- Step 1: Locate the faulty oxygen sensor.
- Step 2: Disconnect the electrical connector from the oxygen sensor.
- Step 3: Use an oxygen sensor socket to remove the old sensor.
- Step 4: Install the new oxygen sensor and reconnect the electrical connector.
- Step 5: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
-
Addressing ECU Problems:
- Step 1: Consult with a professional to diagnose and potentially reprogram or replace the ECU.
- Step 2: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for replacing the ECU.
- Step 3: Clear the fault codes using an OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle.
6. Tools and Equipment Recommended by CARDIAGTECH.NET
To effectively diagnose and repair the P13C523 fault code, CARDIAGTECH.NET recommends the following tools and equipment:
| Tool/Equipment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanner | A diagnostic tool used to read and clear fault codes, as well as monitor engine performance. | Provides accurate diagnostic information, helps identify the root cause of the problem, and allows you to clear fault codes after repairs. |
| Digital Multimeter | A tool used to measure voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. | Essential for testing ignition coils, fuel injectors, and other electrical components. Offers precise measurements and helps identify faulty components. |
| Spark Plug Socket Set | A set of sockets designed specifically for removing and installing spark plugs. | Ensures proper installation of spark plugs, preventing damage and ensuring optimal performance. |
| Compression Testing Kit | A kit used to measure the compression in each cylinder of the engine. | Helps identify issues with piston rings, valves, or head gasket, providing valuable information for diagnosing compression-related problems. |
| Vacuum Leak Smoke Machine | A device used to introduce smoke into the intake system to identify vacuum leaks. | Simplifies the process of locating vacuum leaks, which can be difficult to find using traditional methods. |
| Fuel Injector Testing Kit | A kit used to test the performance of fuel injectors, including spray pattern and flow rate. | Helps identify clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors, ensuring proper fuel delivery and optimal engine performance. |
| Oxygen Sensor Socket | A specialized socket designed for removing and installing oxygen sensors. | Prevents damage to the oxygen sensor during removal and installation, ensuring proper fit and function. |
| Mechanic’s Tool Set | A comprehensive set of tools including sockets, wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. | Provides a wide range of tools necessary for performing various automotive repairs, ensuring you have the right tool for the job. |
| Diagnostic Software | Software that provides detailed information about vehicle systems and components. | Offers advanced diagnostic capabilities, allowing you to access detailed information about the engine and other systems. |
| Protective Gear (Gloves/Eye Wear) | Gloves and eye protection to ensure safety while working on the vehicle. | Protects hands and eyes from potential hazards such as chemicals, sharp objects, and debris. |
These tools are available at CARDIAGTECH.NET, ensuring you have access to high-quality equipment for effective and efficient repairs.
7. Preventive Measures to Avoid P13C523 Fault Code
Preventing the P13C523 fault code involves regular maintenance and care. Here are some preventive measures to keep your Mercedes running smoothly:
- Regular Spark Plug Replacement: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for spark plug replacement.
- Fuel Injector Cleaning: Use a fuel injector cleaner periodically to prevent clogs and maintain optimal fuel delivery.
- Inspect Vacuum Lines: Regularly inspect vacuum lines for cracks or leaks and replace them as needed.
- Maintain Ignition System: Ensure the ignition system components, such as coils and wires, are in good condition and replace them as needed.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel to prevent deposits and maintain optimal engine performance.
- Regular Oil Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for oil changes.
- Check Engine Compression: Periodically check engine compression to identify potential issues early.
- Monitor Oxygen Sensors: Keep an eye on the performance of oxygen sensors and replace them as needed.
- Keep the Engine Clean: Regularly clean the engine bay to prevent dirt and debris from damaging components.
- Professional Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a qualified mechanic to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
8. The Cost of Repairing the P13C523 Fault Code
The cost of repairing the P13C523 fault code can vary depending on the cause and the extent of the damage. Here’s a general breakdown of potential costs:
| Repair | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Ignition Coil Replacement | $150 – $300 (including parts and labor). The cost of a new ignition coil can range from $50 to $150, and labor costs typically range from $100 to $150. |
| Spark Plug Replacement | $80 – $200 (including parts and labor). The cost of a new spark plug can range from $10 to $30 per plug, and labor costs typically range from $60 to $140 for replacing all spark plugs. |
| Fuel Injector Replacement | $200 – $500 (including parts and labor). The cost of a new fuel injector can range from $100 to $300, and labor costs typically range from $100 to $200. |
| Vacuum Leak Repair | $100 – $400 (including parts and labor). The cost of vacuum lines and intake components can range from $20 to $100, and labor costs typically range from $80 to $300, depending on the location and complexity of the leak. |
| Compression Issues | $500 – $3000+ (including parts and labor). This depends on the severity of the issue. Minor repairs like piston ring replacement can cost around $500 to $1500, while major repairs like valve or head gasket replacement can cost $1500 to $3000 or more. |
| Wiring/Connector Repair | $50 – $200 (including parts and labor). The cost of wiring and connectors can range from $10 to $50, and labor costs typically range from $40 to $150. |
| Oxygen Sensor Replacement | $100 – $300 (including parts and labor). The cost of a new oxygen sensor can range from $50 to $150, and labor costs typically range from $50 to $150. |
| ECU Repair/Replacement | $500 – $2000+ (including parts and labor). ECU repairs can range from $300 to $800, while ECU replacements can cost $800 to $2000 or more. |
Note: These costs are estimates and may vary based on your location, the specific model of your Mercedes, and the repair shop you choose.
9. Can I Drive My Mercedes with the P13C523 Fault Code?
While it is technically possible to drive your Mercedes with the P13C523 fault code, it is not recommended. Driving with a misfiring cylinder can lead to several potential issues:
- Catalytic Converter Damage: Unburnt fuel entering the catalytic converter can cause it to overheat and fail, leading to costly repairs.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Misfires reduce engine efficiency, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Engine Damage: Prolonged misfires can cause damage to the piston rings, valves, and other engine components.
- Reduced Performance: The car will experience reduced power and acceleration, making it less safe to drive.
It is best to address the P13C523 fault code as soon as possible to prevent further damage and ensure your Mercedes remains in optimal condition.
10. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics and Repair
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges you face when dealing with complex automotive issues like the P13C523 fault code. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you quickly and accurately identify and resolve these problems.
- High-Quality Products: We provide top-of-the-line OBD-II scanners, multimeters, spark plug tools, compression testing kits, and more.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide guidance and support, ensuring you get the most out of your diagnostic tools.
- Competitive Pricing: We offer competitive pricing on all our products, making professional-grade diagnostic equipment accessible to everyone.
Don’t let the P13C523 fault code keep you off the road. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our wide range of diagnostic solutions. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your Mercedes running at its best!
Ready to get your Mercedes back on the road? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET now for expert advice and top-quality diagnostic tools!
11. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Mercedes-Benz, like other modern vehicles, utilizes an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system to monitor various vehicle systems and components. When the system detects a malfunction, it stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the vehicle’s computer. Understanding these codes is crucial for diagnosing and repairing issues.
OBD-II System
The OBD-II system is a standardized system used in most vehicles sold in the United States since 1996. It provides a wealth of information about the vehicle’s performance and can help technicians pinpoint problems quickly.
Structure of a DTC
A DTC consists of five characters:
-
First Character: Indicates the system the code refers to:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, lighting)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
-
Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1, 2, or 3: Manufacturer-specific code
-
Third Character: Indicates the sub-system:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering – injector circuit
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific fault number.
Example: P13C523
In the case of the P13C523 code:
- P: Powertrain
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- C523: Specific fault number
12. Common Mercedes-Benz Fault Codes Related to Misfires
Besides P13C523, several other fault codes are related to misfires in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Understanding these codes can help you diagnose the issue more effectively.
| Fault Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression. |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 1. |
| P0302 | Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 2. |
| P0303 | Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 3. |
| P0304 | Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 4. |
| P0305 | Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 5. |
| P0306 | Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 6. |
| P0307 | Cylinder 7 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 7. |
| P0308 | Cylinder 8 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, vacuum leak, low compression in cylinder 8. |
| P0316 | Misfire Detected on Startup (First 1000 Revolutions) | Fuel delivery issues, faulty spark plugs, ignition coils. |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, faulty fuel injector. |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, faulty fuel injector. |
| P0172 | System Too Rich (Bank 1) | Faulty fuel injector, high fuel pressure, faulty oxygen sensor, restricted air filter. |
| P0175 | System Too Rich (Bank 2) | Faulty fuel injector, high fuel pressure, faulty oxygen sensor, restricted air filter. |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks. |
| P0430 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2) | Faulty catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks. |
| P0011 | A Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil control valve, timing chain. |
| P0014 | B Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil control valve, timing chain. |
| P0016 | Crankshaft Position – Camshaft Position Correlation (Bank 1 Sensor A) | Faulty crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, timing chain. |
13. How to Clear the P13C523 Fault Code
After addressing the underlying issue causing the P13C523 fault code, it’s essential to clear the code from your vehicle’s computer. Here’s how to do it:
-
Use an OBD-II Scanner:
- Connect the OBD-II scanner to the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” menu on the scanner.
- Confirm that the P13C523 code is present, along with any other related codes.
-
Clear the Fault Codes:
- Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scanner.
- The scanner will prompt you to confirm that you want to clear the codes. Confirm the action.
- Wait for the scanner to complete the process.
- Turn off the ignition and disconnect the scanner.
-
Verify the Repair:
- Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the issue is resolved and the P13C523 code does not return.
- Use the OBD-II scanner again to check for any new or pending fault codes.
14. Benefits of Using Professional Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
Investing in professional diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET offers numerous benefits:
- Accuracy: Our tools provide precise and reliable diagnostic information, helping you pinpoint the root cause of the problem quickly.
- Efficiency: With the right tools, you can diagnose and repair issues more efficiently, saving time and money.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Our tools support a wide range of vehicle makes and models, including Mercedes-Benz.
- User-Friendly Interface: Our tools feature intuitive interfaces that make them easy to use, even for beginners.
- Expert Support: We provide expert technical support to help you get the most out of your diagnostic tools.
- Cost-Effective: Investing in professional diagnostic tools can save you money in the long run by allowing you to perform your own repairs and avoid costly trips to the mechanic.
- Preventive Maintenance: Our tools can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems, allowing you to perform preventive maintenance and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
15. Stay Ahead with Regular Vehicle Diagnostics
Regular vehicle diagnostics are crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your Mercedes-Benz. By performing routine checks with a professional diagnostic tool, you can:
- Identify Issues Early: Detect potential problems before they cause significant damage.
- Improve Fuel Efficiency: Ensure that the engine is running optimally, maximizing fuel economy.
- Extend Vehicle Life: Keep your vehicle in good condition, extending its lifespan and resale value.
- Ensure Safety: Address safety-related issues promptly, ensuring the vehicle is safe to drive.
- Reduce Repair Costs: Prevent costly repairs by addressing minor issues before they escalate.
- Maintain Performance: Keep your vehicle running at its best, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable driving experience.
16. FAQ About P13C523 Mercedes Fault Code
Here are some frequently asked questions about the P13C523 Mercedes fault code:
- What does the P13C523 code mean for my Mercedes?
The P13C523 code indicates a combustion misfire in cylinder 1 with an implausible signal, meaning the engine is misfiring, and the data reported is inconsistent. - Can I fix the P13C523 code myself, or do I need a professional?
You can attempt to diagnose and fix the issue yourself if you have mechanical knowledge and the right tools. However, if you’re not comfortable, a professional mechanic is recommended. - What are the most common causes of the P13C523 code?
Common causes include a faulty ignition coil, bad spark plug, fuel injector problems, vacuum leaks, and compression issues. - How much does it cost to fix the P13C523 code?
The cost varies depending on the cause, ranging from $80 for a spark plug replacement to over $500 for fuel injector issues or ECU repairs. - Is it safe to drive my Mercedes with the P13C523 code?
It is not recommended, as driving with a misfiring cylinder can damage the catalytic converter and other engine components. - What tools do I need to diagnose the P13C523 code?
An OBD-II scanner, digital multimeter, spark plug socket set, compression testing kit, and vacuum leak smoke machine are helpful. - How do I clear the P13C523 code after fixing the issue?
Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the fault codes after addressing the underlying problem. - Can regular maintenance prevent the P13C523 code?
Yes, regular maintenance such as spark plug replacement, fuel injector cleaning, and vacuum line inspections can help prevent this code. - Where can I buy high-quality diagnostic tools for my Mercedes?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website. - What should I do if the P13C523 code returns after I’ve fixed the issue?
Recheck the components you previously fixed and ensure they are functioning correctly. If the code persists, consult a professional mechanic for further diagnosis.




