What Are the Types of Pressure Sensors (e.g., Manifold Absolute Pressure)?
Pressure sensors play a vital role in modern automotive technology, and CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to illuminate the diverse world of these essential components. Understanding the different types of pressure sensors, from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensors to others, is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics and repair. Let’s explore the various kinds of pressure sensors and their specific applications in automotive systems, providing you with the knowledge to keep your clients’ vehicles running smoothly and efficiently, and prompting you to consider how CARDIAGTECH.NET can supply you with the tools to do so.
1. Understanding Pressure Sensors: An Overview
What exactly is a pressure sensor? Pressure sensors, sometimes called pressure transducers, measure the pressure of a gas or liquid. They convert this physical quantity into an electrical signal that a vehicle’s computer (ECU) can interpret. This data is crucial for controlling various engine and vehicle functions.
Pressure sensors are essential components of modern vehicle systems, and according to a study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute in 2022, they provide critical data for engine management, safety systems, and overall vehicle performance.
2. Key Pressure Sensor Types in Automotive Applications
What are the most common types of pressure sensors used in automobiles? Let’s delve into the four primary pressure sensor types you’ll encounter in automotive repair:
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensors
- Barometric Pressure Sensors
- Brake Pressure Sensors
- Fuel Pressure Sensors
2.1. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensors
What is a MAP sensor and what does it do? Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors measure the pressure inside the intake manifold of an engine. This information is used by the ECU to determine the engine’s air intake, which is critical for calculating the correct fuel injection amount and ignition timing.
According to a 2021 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), accurate MAP sensor readings are vital for optimizing engine performance and reducing emissions.
2.1.1. How MAP Sensors Work
How do MAP sensors function? MAP sensors typically use a diaphragm that flexes in response to pressure changes in the intake manifold. This flexing alters the resistance of a strain gauge, producing an electrical signal proportional to the pressure. The ECU reads this signal and adjusts the air-fuel mixture accordingly.
A study conducted by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering in 2020 highlighted the importance of MAP sensor accuracy in achieving optimal combustion efficiency.
2.1.2. Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor
What are the signs of a failing MAP sensor? A failing MAP sensor can cause several noticeable symptoms, including:
- Poor fuel economy
- Rough idling
- Hesitation during acceleration
- Black smoke from the exhaust
- Check engine light illumination
If you observe these symptoms, using diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET to check the MAP sensor is a great idea.
2.1.3. Diagnosing MAP Sensor Issues
How do you diagnose MAP sensor problems? Diagnosing MAP sensor issues typically involves:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the sensor or its wiring.
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to read MAP sensor data and check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage output at different manifold pressures.
- Vacuum Testing: Use a vacuum gauge to verify the manifold vacuum matches the MAP sensor reading.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that can help you accurately diagnose MAP sensor problems.
2.1.4. MAP Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
How do you maintain or replace a MAP sensor? Replacing a MAP sensor is generally straightforward:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Ensure the vehicle is powered off.
- Locate the MAP Sensor: Typically found on the intake manifold.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully detach the connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Unbolt or unclip the sensor from the manifold.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated and secured.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reattach the connector.
- Reconnect the Battery: Restore power to the vehicle.
- Clear DTCs: Use a scan tool to clear any diagnostic trouble codes.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of faulty MAP sensors can prevent more significant engine problems. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality replacement MAP sensors to ensure reliable performance.
2.2. Barometric Pressure Sensors
What is a barometric pressure sensor? Barometric pressure sensors measure the ambient atmospheric pressure. The ECU uses this information to adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing based on altitude. This ensures optimal engine performance regardless of the vehicle’s location.
According to a 2019 study by Bosch, barometric pressure sensors are crucial for maintaining consistent engine performance in varying altitudes.
2.2.1. How Barometric Pressure Sensors Work
How do barometric pressure sensors operate? These sensors typically use a sealed chamber that contains a reference vacuum. A pressure-sensitive diaphragm measures the difference between the reference vacuum and the outside atmospheric pressure. This difference is converted into an electrical signal that the ECU interprets.
The accuracy of barometric pressure sensors directly impacts the precision of the air-fuel mixture calculation, as noted in a 2022 technical paper by Continental Automotive.
2.2.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Barometric Pressure Sensor
What are the symptoms of a bad barometric pressure sensor? A malfunctioning barometric pressure sensor can lead to:
- Poor engine performance at high altitudes
- Incorrect air-fuel mixture
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Check engine light illumination
Identifying these symptoms early can prevent further engine complications.
2.2.3. Diagnosing Barometric Pressure Sensor Issues
How do you diagnose barometric pressure sensor problems? Diagnosing barometric pressure sensor issues involves:
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to read the sensor’s data and check for any DTCs.
- Voltage Testing: Check the sensor’s voltage output using a multimeter to ensure it is within the specified range.
- Comparison with Known Values: Compare the sensor’s reading with known atmospheric pressure values for your current altitude.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers diagnostic tools that provide accurate and reliable readings for barometric pressure sensors.
2.2.4. Barometric Pressure Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
How do you maintain or replace a barometric pressure sensor? Replacement involves:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Ensure the vehicle is powered off.
- Locate the Sensor: Typically found near the ECU or on the firewall.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully detach the connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Unbolt or unclip the sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated and secured.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reattach the connector.
- Reconnect the Battery: Restore power to the vehicle.
- Clear DTCs: Use a scan tool to clear any diagnostic trouble codes.
Replacing a faulty barometric pressure sensor ensures optimal engine performance across varying altitudes. CARDIAGTECH.NET supplies high-quality barometric pressure sensors for reliable and accurate readings.
2.3. Brake Pressure Sensors
What are brake pressure sensors? Brake pressure sensors measure the pressure within the brake lines of a vehicle’s braking system. These sensors are critical for advanced safety systems like Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC).
According to a 2020 report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), brake pressure sensors are integral to the proper functioning of modern vehicle safety systems.
2.3.1. How Brake Pressure Sensors Work
How do brake pressure sensors work? Brake pressure sensors typically use a strain gauge that measures the pressure applied to the brake fluid. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the pressure increases, and the sensor converts this pressure into an electrical signal. The ECU uses this signal to modulate the braking force at each wheel, preventing wheel lockup and maintaining vehicle stability.
Research from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) in 2021 underscores the importance of accurate brake pressure readings for effective ABS and ESC performance.
2.3.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Brake Pressure Sensor
What are the symptoms of a failing brake pressure sensor? A malfunctioning brake pressure sensor can cause:
- ABS light illumination
- ESC light illumination
- Reduced braking performance
- Erratic braking behavior
- Brake pedal feels spongy or hard
Addressing these issues promptly is vital for maintaining vehicle safety.
2.3.3. Diagnosing Brake Pressure Sensor Issues
How do you diagnose brake pressure sensor problems? Diagnosing brake pressure sensor issues involves:
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to read the sensor’s data and check for any DTCs related to the ABS or ESC systems.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor the brake pressure sensor readings in real-time while applying the brakes to check for inconsistencies or abnormal values.
- Physical Inspection: Inspect the sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Hydraulic System Check: Check the hydraulic system for leaks or air, which can affect brake pressure readings.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools that offer comprehensive analysis of brake system performance.
2.3.4. Brake Pressure Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
How do you maintain or replace a brake pressure sensor? Replacing a brake pressure sensor requires caution due to the hydraulic brake system:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Ensure the vehicle is powered off.
- Locate the Sensor: Typically found on the brake master cylinder or near the ABS module.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully detach the connector from the sensor.
- Relieve Brake Pressure: Use a bleeder wrench to carefully relieve pressure from the brake lines.
- Remove the Sensor: Unscrew the sensor, being careful to catch any leaking brake fluid.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated and tightened.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reattach the connector.
- Bleed the Brakes: Bleed the brake lines to remove any air that may have entered the system.
- Reconnect the Battery: Restore power to the vehicle.
- Clear DTCs: Use a scan tool to clear any diagnostic trouble codes.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of faulty brake pressure sensors are essential for maintaining the integrity of the vehicle’s safety systems. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of reliable replacement brake pressure sensors.
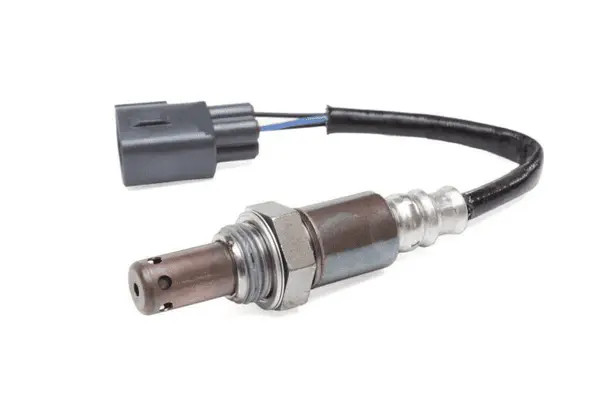
2.4. Fuel Pressure Sensors
What is a fuel pressure sensor? Fuel pressure sensors measure the pressure of the fuel in the fuel rail. The ECU uses this information to ensure the correct amount of fuel is injected into the engine’s cylinders. Accurate fuel pressure is crucial for engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
According to a 2023 report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), precise fuel pressure management is vital for meeting stringent emissions standards.
2.4.1. How Fuel Pressure Sensors Work
How do fuel pressure sensors operate? Fuel pressure sensors typically use a diaphragm that flexes in response to changes in fuel pressure. This flexing alters the resistance of a strain gauge, producing an electrical signal proportional to the pressure. The ECU uses this signal to adjust the fuel pump speed and injector pulse width, maintaining the optimal fuel pressure.
A study by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 2022 highlighted the impact of fuel pressure sensor accuracy on fuel economy and engine longevity.
2.4.2. Symptoms of a Faulty Fuel Pressure Sensor
What are the symptoms of a bad fuel pressure sensor? A malfunctioning fuel pressure sensor can cause:
- Poor fuel economy
- Engine misfires
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Rough idling
- Check engine light illumination
Addressing these symptoms promptly can prevent more severe engine damage.
2.4.3. Diagnosing Fuel Pressure Sensor Issues
How do you diagnose fuel pressure sensor problems? Diagnosing fuel pressure sensor issues involves:
- Scan Tool Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to read the sensor’s data and check for any DTCs related to the fuel system.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor the fuel pressure sensor readings in real-time to check for inconsistencies or abnormal values.
- Pressure Testing: Use a fuel pressure gauge to verify the sensor’s readings match the actual fuel pressure in the fuel rail.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect the sensor’s wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers professional-grade diagnostic tools that provide accurate and reliable fuel system analysis.
2.4.4. Fuel Pressure Sensor Maintenance and Replacement
How do you maintain or replace a fuel pressure sensor? Replacing a fuel pressure sensor requires care due to the presence of fuel:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Ensure the vehicle is powered off.
- Locate the Sensor: Typically found on the fuel rail.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully detach the connector from the sensor.
- Relieve Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure relief tool to carefully relieve pressure from the fuel system.
- Remove the Sensor: Unscrew the sensor, being careful to catch any leaking fuel.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated and tightened.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reattach the connector.
- Reconnect the Battery: Restore power to the vehicle.
- Clear DTCs: Use a scan tool to clear any diagnostic trouble codes.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of faulty fuel pressure sensors are crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality replacement fuel pressure sensors for reliable and accurate readings.
3. Additional Types of Pressure Sensors
Beyond the primary types, other pressure sensors are used in specific automotive applications:
- Transmission Pressure Sensors: Monitor hydraulic pressure in automatic transmissions to ensure proper shifting.
- Power Steering Pressure Sensors: Measure the pressure in the power steering system to assist with steering control.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Sensors: Monitor tire pressure to improve safety and fuel efficiency.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Pressure Sensors: Monitor refrigerant pressure in the A/C system to ensure proper cooling.
Understanding these specialized sensors can help you address a wider range of automotive issues.
4. The Importance of Accurate Pressure Sensor Readings
Why are accurate pressure sensor readings so important? Accurate pressure sensor readings are crucial for:
- Engine Performance: Ensuring the correct air-fuel mixture and ignition timing for optimal power and efficiency.
- Fuel Efficiency: Optimizing fuel delivery to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Safety Systems: Enabling the proper functioning of ABS, ESC, and other safety features.
- Emissions Control: Meeting stringent emissions standards by precisely controlling engine parameters.
- Vehicle Diagnostics: Identifying and resolving issues quickly and accurately.
Investing in high-quality pressure sensors and diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET ensures reliable and accurate readings, enhancing your ability to service vehicles effectively.
5. Choosing the Right Pressure Sensor
How do you choose the right pressure sensor for a specific application? Selecting the appropriate pressure sensor depends on several factors:
- Pressure Range: Ensure the sensor can measure the expected pressure range for the application.
- Accuracy: Choose a sensor with the required accuracy for the specific system.
- Operating Temperature: Select a sensor that can withstand the operating temperatures of the environment.
- Durability: Opt for a sensor that is robust and resistant to vibration, shock, and chemical exposure.
- Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with the vehicle’s ECU and diagnostic systems.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of pressure sensors to meet diverse automotive needs, backed by expert advice to help you make the right choice.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Pressure Sensors
What are some advanced diagnostic techniques for pressure sensors? In addition to basic diagnostic procedures, consider these advanced techniques:
- Waveform Analysis: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the sensor’s output waveform, which can reveal subtle issues not apparent with standard voltage testing.
- Frequency Testing: Measure the sensor’s output frequency, which can indicate signal integrity and sensor health.
- Dynamic Testing: Perform tests under varying engine loads and driving conditions to assess sensor performance in real-world scenarios.
- Simulation: Use a sensor simulator to mimic sensor signals and verify the ECU’s response.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic equipment and training to help you master these techniques.
7. The Role of Pressure Sensors in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
How are pressure sensors used in electric and hybrid vehicles? Pressure sensors are also crucial in electric and hybrid vehicles for:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Monitoring coolant pressure to ensure optimal battery temperature and performance.
- Brake Systems: Providing feedback for regenerative braking systems, which recover energy during deceleration.
- HVAC Systems: Monitoring refrigerant pressure to maintain efficient climate control.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Systems: Measuring hydrogen pressure for safe and efficient operation.
As electric and hybrid vehicles become more prevalent, understanding the role of pressure sensors in these systems will become increasingly important.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with Pressure Sensors
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with pressure sensors? Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Incorrect Installation: Ensure the sensor is properly seated and tightened to prevent leaks and inaccurate readings.
- Damaged Wiring: Check for damaged or corroded wiring, which can cause signal degradation.
- Using the Wrong Sensor: Verify that the sensor is the correct type and specification for the application.
- Ignoring DTCs: Always investigate and resolve diagnostic trouble codes related to pressure sensors.
- Neglecting Calibration: Calibrate the sensor if required to ensure accurate readings.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure reliable and accurate pressure sensor performance.
9. The Future of Pressure Sensor Technology
What does the future hold for pressure sensor technology? The future of pressure sensor technology includes:
- Miniaturization: Smaller, more compact sensors that can be integrated into tighter spaces.
- Wireless Sensors: Wireless sensors that transmit data wirelessly, reducing wiring complexity.
- Self-Calibration: Sensors that automatically calibrate themselves to maintain accuracy over time.
- Advanced Materials: Sensors made from advanced materials that are more durable and resistant to harsh environments.
- Integration with AI: Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive maintenance and advanced diagnostics.
Staying abreast of these advancements will help you remain at the forefront of automotive technology.
10. How CARDIAGTECH.NET Can Help You
Looking for the right tools and equipment for diagnosing and repairing pressure sensor issues? CARDIAGTECH.NET is your one-stop shop for high-quality automotive diagnostic tools and equipment. Here’s how we can assist you:
- Comprehensive Range of Products: We offer a wide selection of pressure sensors, diagnostic tools, and replacement parts to meet all your automotive needs.
- Expert Advice: Our knowledgeable team can provide expert advice and guidance to help you choose the right products for your specific applications.
- Competitive Prices: We offer competitive prices on all our products, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
- Fast Shipping: We provide fast and reliable shipping to get you the tools and equipment you need quickly.
- Excellent Customer Service: Our dedicated customer service team is available to answer your questions and provide support whenever you need it.
Don’t let pressure sensor issues slow you down. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our extensive range of products and services. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your clients’ vehicles running smoothly and safely.
FAQ: All About Pressure Sensors
1. What is the primary function of a pressure sensor in a car?
A pressure sensor measures the pressure of a gas or liquid and converts it into an electrical signal that a vehicle’s computer (ECU) can interpret. This data is crucial for controlling various engine and vehicle functions, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and brake performance.
2. How does a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor improve engine efficiency?
A MAP sensor measures the pressure inside the intake manifold, allowing the ECU to determine the engine’s air intake. This information is used to calculate the correct fuel injection amount and ignition timing, optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
3. What are the main symptoms of a failing barometric pressure sensor?
Symptoms of a failing barometric pressure sensor include poor engine performance at high altitudes, incorrect air-fuel mixture, difficulty starting the engine, and illumination of the check engine light.
4. Why are brake pressure sensors important for vehicle safety?
Brake pressure sensors are critical for advanced safety systems like Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC). They measure the pressure within the brake lines, allowing the ECU to modulate braking force at each wheel, preventing wheel lockup and maintaining vehicle stability.
5. How does a fuel pressure sensor contribute to fuel efficiency?
A fuel pressure sensor measures the pressure of the fuel in the fuel rail, ensuring the correct amount of fuel is injected into the engine’s cylinders. Accurate fuel pressure is crucial for engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
6. Can a faulty pressure sensor cause the check engine light to come on?
Yes, a faulty pressure sensor can cause the check engine light to illuminate. The ECU detects abnormal readings from the sensor and triggers the check engine light to alert the driver to a potential issue.
7. What tools are needed to diagnose pressure sensor problems?
Diagnosing pressure sensor problems typically requires a scan tool to read sensor data and check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage output, and a vacuum or pressure gauge to verify the sensor’s readings.
8. How often should pressure sensors be inspected and replaced?
Pressure sensors should be inspected regularly as part of routine vehicle maintenance. Replacement is typically recommended when the sensor fails or exhibits symptoms of malfunction, such as poor engine performance or illumination of the check engine light.
9. Are pressure sensors used in electric and hybrid vehicles?
Yes, pressure sensors are also crucial in electric and hybrid vehicles for monitoring battery coolant pressure, providing feedback for regenerative braking systems, managing HVAC systems, and measuring hydrogen pressure in fuel cell systems.
10. Where can I find high-quality pressure sensors and diagnostic tools?
High-quality pressure sensors and diagnostic tools can be found at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide selection of products, expert advice, competitive prices, and excellent customer service to meet all your automotive needs. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.