Do You Have Knowledge of EV Charging Systems (AC and DC)?

Do you have knowledge of EV charging systems (AC and DC)? Absolutely. This article delves into the essentials of EV charging systems, contrasting AC and DC charging methods, and highlighting the significance of Level 2 chargers, all designed to empower you with practical knowledge and insights. Ready to elevate your understanding and potentially boost your automotive repair capabilities? Let’s explore the world of EV charging and discover how you can stay ahead in this rapidly evolving field, focusing on EV charging infrastructure, Level 2 charging solutions, and electric vehicle service equipment.
1. What Sets Level 2 Chargers Apart in EV Charging Systems?
Level 2 chargers provide faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 chargers, utilizing alternating current (AC) power, making them ideal for home, workplace, and public charging stations. Level 2 chargers are the most common chargers installed globally, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- AC Power Utilization: Level 2 chargers use alternating current, which is standard in most homes and businesses, facilitating straightforward installation.
- Compatibility: They are compatible with almost all electric vehicles, ensuring versatility for EV owners.
- Installation: Level 2 chargers can be wall-mounted or attached to a pedestal, providing flexibility for different locations.
 Various Level 2 EV charger designs
Various Level 2 EV charger designs
2. AC vs. DC Charging: Understanding the Core Differences
AC and DC charging represent the two primary methods for charging electric vehicles, each with unique characteristics and applications. Alternating Current (AC) changes direction periodically, while Direct Current (DC) flows in one direction.
2.1. Alternating Current (AC)
AC is the standard electricity from the grid, powering homes and offices. According to a study by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), AC electricity is efficient for long-distance transport, making it ideal for power distribution networks.
- Standard: AC is universally available in residential and commercial outlets.
- Level 2 Charging: Level 2 chargers use AC power, which is then converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard converter.
- Efficiency: AC power is easily transmitted over long distances, making it a practical choice for widespread use.
2.2. Direct Current (DC)
DC is stored in EV batteries and used to power electronic devices directly. When an EV charges using Level 2, AC power is converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard converter.
- Battery Storage: EVs store energy as DC power in their batteries.
- Direct Use: DC power is used directly by the vehicle’s motor and other components.
- Fast Charging: DC fast charging stations bypass the onboard converter, delivering DC power directly to the battery for faster charging.
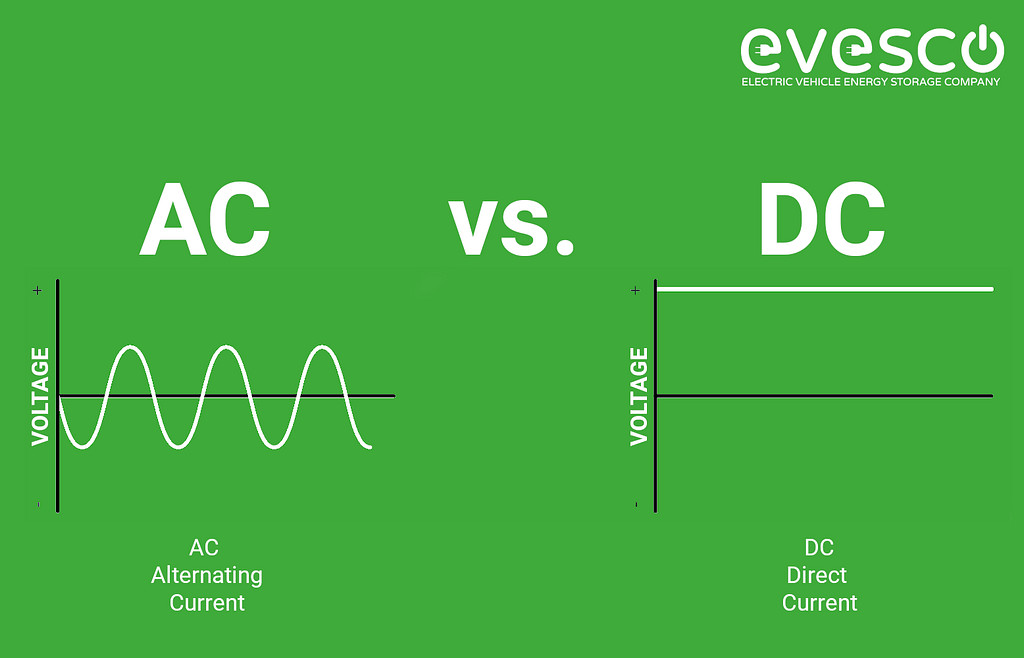 Visual representation of AC versus DC charging
Visual representation of AC versus DC charging
2.3. The Power Conversion Process
Electric vehicles must convert AC power from Level 2 chargers into DC power. This conversion is handled by the vehicle’s onboard converter.
- Onboard Converter: This component changes AC power to DC, allowing the battery to store and use the energy.
- Level 3 Charging: DC fast charging stations have their own AC to DC converters, bypassing the vehicle’s onboard system for quicker charging.
- Charging Efficiency: Understanding this process helps optimize charging practices and choose the appropriate charging level for specific needs.
2.4. Different Levels of EV Chargers
Level 1 and Level 2 chargers use AC power, while Level 3 chargers deliver DC power directly. By understanding the differences, technicians can better service and maintain EV charging systems, increasing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Level 1: Uses standard household outlets, offering the slowest charging speed.
- Level 2: Requires a 240V outlet and provides significantly faster charging than Level 1.
- Level 3 (DC Fast Charging): Offers the quickest charging but requires specialized equipment and higher voltage.
 Illustrative comparison of AC and DC fast charging
Illustrative comparison of AC and DC fast charging
3. Charging Speed: How Fast Is Level 2 EV Charging?
Level 2 charging speeds vary from 3 to 19.2 kilowatts (kW) in the United States and up to 22 kW in Europe, providing 10 to 75 miles (16 – 120 km) of range per hour. The actual speed depends on the charger’s power output and the vehicle’s charge acceptance rate. Level 2 chargers can be up to 19 times faster than Level 1 chargers, offering a significant upgrade for EV owners.
- Kilowatt Range: Chargers in the US range from 3 kW to 19.2 kW.
- Range Per Hour: Provides 10 to 75 miles of range per hour.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Charging speed depends on the vehicle’s onboard charging capabilities.
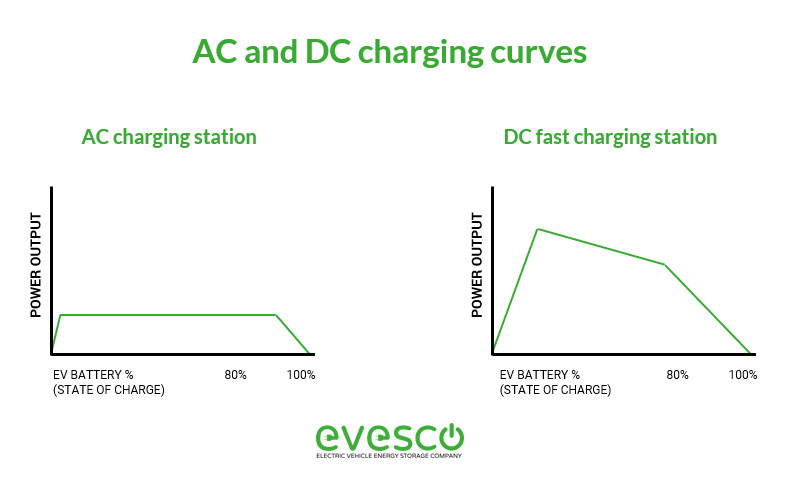 Illustration of Level 2 and Level 3 charging curves
Illustration of Level 2 and Level 3 charging curves
4. Delving into Charging Times for Level 2 Chargers
Charging time depends on several factors, including the charger’s power output, the EV’s charge acceptance rate, and the battery size. The table below provides rough estimates based on an EV with a 40 kWh battery capacity, a common size for electric vehicle batteries.
| Level 2 Charger Output Power | Charge Time (hours) |
|---|---|
| 3 kW | 13.3 |
| 7 kW | 5.7 |
| 11 kW | 3.6 |
| 19.2 kW | 2.1 |
| 22 kW | 1.8 |
- Estimates: Times can vary based on the specific EV model.
- Battery Size: Assumes a 40 kWh battery capacity.
- Variables: Real-world charging times can be influenced by weather conditions, battery age, and initial state of charge.
5. Tethered vs. Untethered: Types of Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers come in tethered and untethered versions. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the best option for various needs and preferences.
5.1. Tethered EV Chargers
Tethered chargers have a permanently attached charging cable, offering convenience and ease of use. They are prevalent in North America.
- Convenience: No need to carry a separate charging cable.
- Ease of Use: Always ready for charging, simplifying the process.
- Popularity: Commonly used in North America.
5.1.1. Benefits of Tethered EV Chargers
Tethered chargers provide a hassle-free experience, ideal for those who value convenience and ease of use.
- Hassle-Free: The cable is always ready, saving time and effort.
- Price Transparency: The cost of the cable is included in the charger’s price.
5.1.2. Things to Consider with Tethered EV Chargers
Tethered chargers have limitations such as cable length restrictions and potential wear and tear.
- Limited Length: Cable length is fixed, potentially requiring additional costs for longer cables.
- Space Requirements: The attached cable may require more space and additional cable management solutions.
- Cable Theft: Risk of cable theft for scrap value.
- Wear and Tear: Cables are subject to wear and may need replacement.
5.2. Untethered EV Chargers
Untethered chargers do not have an attached cable, requiring users to supply their own. These are popular in Europe.
- Flexibility: Users can choose their preferred cable length and type.
- Maintenance: Easier to maintain due to fewer components.
- Prevalence: Common throughout Europe.
5.2.1. Benefits of Untethered EV Chargers
Untethered chargers are easier to maintain and can be less expensive than tethered options.
- Easier to Maintain: Fewer parts mean less potential for damage and wear.
- Less Expensive: Generally cheaper as they do not include a cable.
- Flexibility: Allows the use of upgraded charging cables as technology advances.
5.2.2. Things to Consider with Untethered EV Chargers
Untethered chargers require users to remember and attach their charging cables.
- Inconvenience: Requires manual attachment and detachment of the charging cable.
- Dependency: Useless without a compatible charging cable.
6. Exploring Level 2 Charging Connectors and Plugs
Different regions use different connectors and plugs for Level 2 charging. Key types include Type 1 (J1772), Type 2 (Mennekes), GB/T (AC), and NACS (North American Charging Standard).
6.1. Type 1 (J1772)
The Type 1 connector is mainly used in North America and Japan. It can deliver up to 19.2 kW with 80 amps using a single-phase 240-volt input. Almost every battery electric car and plug-in hybrid in North America, except for Tesla, uses this connector.
- Regions: North America and Japan.
- Power: Up to 19.2 kW.
- Compatibility: Used by most non-Tesla EVs in North America.
6.2. Type 2 (Mennekes)
The Type 2 connector is used in Europe, Australia, and parts of the Middle East and Africa. It can deliver up to 7.6 kW with 32 amps at single-phase 230-volt and 22 kW with 32 amps utilizing a three-phase 400-volt input.
- Regions: Europe, Australia, and parts of the Middle East and Africa.
- Power: Up to 22 kW.
- Voltage: Supports both single-phase and three-phase inputs.
6.3. GB/T (AC)
GB/T is the standard EV connector for AC charging in China, providing up to 7.4 kW with a single-phase input. While it looks similar to the Type 2 connector, the wiring configuration is different, making them incompatible.
- Region: China.
- Power: Up to 7.4 kW.
- Compatibility: Exclusive to China.
6.4. NACS (North American Charging Standard)
NACS, developed by Tesla, is used in North America and can provide both AC and DC charging. The AC version, classified as Level 2, can deliver up to 48 Amps on a single-phase 240-volt input.
- Region: North America.
- Developer: Tesla.
- Functionality: Supports both AC and DC charging.
7. Pinpointing Ideal Locations for Installing Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers are versatile and efficient in various locations, providing convenience for EV users. Optimal locations include homes, workplaces, public charging stations, and commercial properties.
7.1. Home Charging
Home installations are perfect for overnight charging, providing sufficient range for daily commutes and short journeys.
- Convenience: Easy access for overnight charging.
- Cost-Effective: Lower electricity rates during off-peak hours.
- Accessibility: Always available for homeowners.
7.2. Workplace Charging
Workplaces are strategic locations, allowing employees to recharge during work hours. Installing chargers can attract and retain environmentally conscious staff, offering an employee benefit.
- Employee Benefit: Attracts and retains talent.
- Convenience: Allows charging during work hours.
- Sustainability: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility.
7.3. Public Charging Stations
Public charging stations provide accessible charging solutions for EV drivers away from home or work. Locations include community centers, parks, and roadside rest stops.
- Accessibility: Essential for those without home charging options.
- Convenience: Supports longer journeys and unexpected needs.
- Infrastructure: Contributes to a robust charging network.
7.4. Commercial Properties
Retail parks, restaurants, long-stay car parks, and hotels benefit from Level 2 chargers. They support EV fleets, encourage longer customer stays, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
- Customer Attraction: Encourages longer visits and spending.
- Fleet Support: Supports commercial EV fleets.
- Sustainability: Enhances the property’s image as environmentally conscious.
8. Unveiling Incentives for Installing Level 2 Chargers
Many governments offer financial incentives to encourage EV adoption and the installation of charging infrastructure. Incentives include tax credits, rebates, and grants. In the United States, various states offer incentives for Level 2 and DC fast chargers, including rebates from utility companies.
- Tax Credits: Reduces the overall cost of installation.
- Rebates: Provides partial refunds on charger and installation expenses.
- Grants: Offers financial aid for infrastructure development.
9. Leveraging Media Screens on Level 2 Charging Stations
Level 2 charging stations with media screens enhance the charging experience by providing entertainment, information, and communication. These stations offer a dynamic digital platform that elevates the user experience.
- Entertainment: Displays engaging content during charging.
- Information: Provides updates and relevant news.
- Communication: Offers a platform for advertising and public service announcements.
10. Addressing Customer Challenges and Needs with CARDIAGTECH.NET
Understanding the challenges faced by automotive technicians, CARDIAGTECH.NET offers tools and equipment that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety in EV repairs. We provide solutions that address the specific needs of the modern auto repair shop, ensuring you stay competitive and profitable.
- Efficiency: Tools that reduce repair times.
- Accuracy: Equipment that ensures precise diagnostics and repairs.
- Safety: Products designed to protect technicians during EV servicing.
Are you ready to enhance your EV repair capabilities? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and solutions tailored to your needs. Visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Explore our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information.
FAQ: Your Questions About EV Charging Systems Answered
1. What is the primary difference between AC and DC charging for EVs?
AC charging uses alternating current converted to direct current by the vehicle, while DC charging delivers direct current directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard converter for faster charging.
2. How much faster is Level 2 charging compared to Level 1?
Level 2 charging can be up to 19 times faster than Level 1 charging, significantly reducing charging times for electric vehicles.
3. What factors influence the charging time of a Level 2 charger?
Charging time depends on the charger’s power output, the EV’s charge acceptance rate, and the battery size. Additional variables like weather and initial state of charge also play a role.
4. What are the key advantages of using a tethered Level 2 charger?
Tethered chargers offer convenience and ease of use with a permanently attached cable, eliminating the need to carry a separate charging cable and ensuring it is always ready for use.
5. What should I consider when choosing between tethered and untethered Level 2 chargers?
Consider convenience, cable length limitations, and potential wear and tear with tethered chargers. Untethered chargers offer flexibility and easier maintenance but require users to supply their own cable.
6. Which Level 2 charging connector is most common in North America?
The Type 1 (J1772) connector is most common in North America for Level 2 charging, used by almost every non-Tesla battery electric car and plug-in hybrid vehicle.
7. What incentives are available for installing Level 2 chargers?
Incentives include tax credits, rebates, and grants offered by various countries, states, and local governments to encourage EV adoption and charging infrastructure development.
8. Where are the ideal locations for installing Level 2 chargers?
Ideal locations include homes, workplaces, public charging stations, and commercial properties like retail parks and hotels, ensuring accessibility and convenience for EV users.
9. How do Level 2 charging stations with media screens enhance the charging experience?
These stations provide entertainment, information, and communication, creating a dynamic digital platform that improves the user experience and offers additional benefits like advertising opportunities.
10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with EV repair and maintenance?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers specialized tools and equipment that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety in EV repairs, addressing the unique needs of modern auto repair shops to ensure competitiveness and profitability.