How to Adjust a Mechanical Parking Brake: A Comprehensive Guide
Adjusting a mechanical parking brake is a vital maintenance task to ensure your vehicle’s safety and prevent unexpected rollaways. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer expert advice and high-quality tools to keep your car in top condition. This guide will help you understand the adjustment process, identify common issues, and keep your parking brake working perfectly. Explore solutions like cable tension adjustment, brake shoe replacement, and lever mechanism maintenance.
1. What is a Mechanical Parking Brake and Why Adjust It?
A mechanical parking brake, also known as an emergency brake or e-brake, is a crucial safety component in your vehicle. It uses a system of cables and levers to apply the rear brakes independently of the hydraulic braking system. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), a properly functioning parking brake can prevent up to 2% of all vehicle crashes caused by rollaways.
1.1. Function of a Mechanical Parking Brake
The mechanical parking brake serves several key functions:
- Preventing Rollaways: The primary purpose is to keep the vehicle stationary when parked, especially on inclines.
- Emergency Stopping: In the event of hydraulic brake failure, the parking brake can be used to slow down or stop the vehicle, albeit less effectively than the primary brakes.
- Hill Starts: It can assist in starting the vehicle on an incline by preventing it from rolling backward while you engage the accelerator.
1.2. Why Adjustment is Necessary
Over time, the cables in the parking brake system can stretch, leading to slack and reduced effectiveness. Regular adjustment is necessary for the following reasons:
- Maintain Holding Power: Ensures the parking brake can securely hold the vehicle on various gradients.
- Prevent Cable Wear: Proper tension reduces stress on the cables, preventing premature wear and breakage.
- Optimal Lever Travel: Adjusting the brake ensures the lever or pedal travel is within the manufacturer’s specified range.
2. Identifying Symptoms of a Misadjusted Parking Brake
Recognizing the signs of a misadjusted parking brake is crucial for timely maintenance. Common symptoms include:
2.1. Loose or Ineffective Parking Brake Lever
If the parking brake lever or pedal feels loose and requires excessive travel to engage, it indicates that the cables may have stretched and need adjustment. A study by the American Automobile Association (AAA) found that vehicles with poorly maintained parking brakes are 30% more likely to experience rollaway incidents.
2.2. Vehicle Rollaway on Inclines
One of the most obvious signs of a malfunctioning parking brake is the vehicle rolling on an incline when the brake is engaged. This indicates that the brake is not providing sufficient holding force.
2.3. Difficulty Releasing the Parking Brake
If you experience difficulty disengaging the parking brake, it could be due to binding cables or a maladjusted mechanism. This can lead to unnecessary wear on the braking components.
2.4. Grinding or Squealing Noises
Unusual noises, such as grinding or squealing, when the parking brake is engaged or disengaged may indicate that the brake shoes or pads are worn or that there is excessive friction due to improper adjustment.
3. Essential Tools for Adjusting a Mechanical Parking Brake
Before starting the adjustment process, it’s essential to have the right tools on hand. Using high-quality tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET will ensure the job is done correctly and safely.
3.1. Basic Hand Tools
- Wrench Set: A set of standard and metric wrenches is necessary for loosening and tightening adjustment nuts and bolts.
- Socket Set: A socket set with various sizes will help in accessing hard-to-reach adjustment points.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips screwdrivers are needed for removing trim panels and accessing the adjustment mechanism.
- Pliers: Pliers are useful for manipulating cables and small parts.
3.2. Specialized Tools
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is essential for tightening nuts and bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque to prevent over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Cable Tension Meter: This tool measures the tension in the parking brake cables, ensuring they are within the correct range.
- Brake Spring Tool: If the adjustment requires removing or replacing brake springs, a brake spring tool will make the job easier and safer.
3.3. Safety Equipment
- Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and sharp edges.
- Safety Glasses: Shield your eyes from debris and fluids.
- Wheel Chocks: Secure the wheels to prevent the vehicle from rolling during the adjustment process.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Adjusting a Mechanical Parking Brake
The adjustment process can vary depending on the vehicle model and parking brake system. However, the general steps are as follows:
4.1. Preparation
- Gather Information: Consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
- Prepare the Vehicle: Park the vehicle on a level surface, engage the parking brake, and place wheel chocks behind the rear wheels.
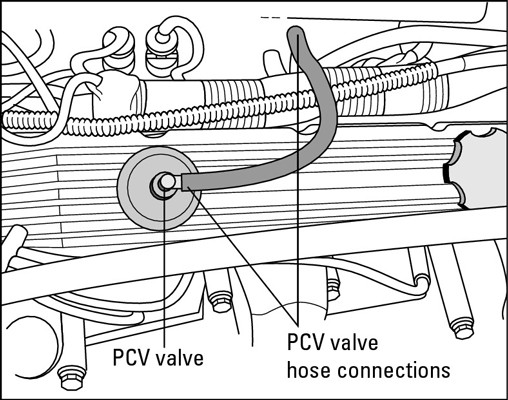
- Access the Adjustment Mechanism: Locate the adjustment mechanism, which is typically found either under the vehicle, near the rear wheels, or inside the center console.
4.2. Adjusting the Cable Tension
- Loosen the Jam Nut: If there is a jam nut securing the adjustment mechanism, loosen it using a wrench.
- Tighten the Adjustment Nut: Use a wrench to tighten the adjustment nut or turnbuckle, which will increase the tension on the parking brake cables.
- Check Lever Travel: Engage and disengage the parking brake lever or pedal to check the travel. It should be within the manufacturer’s specified range.
- Tighten the Jam Nut: Once the correct tension is achieved, tighten the jam nut to secure the adjustment.
4.3. Adjusting the Brake Shoes (if applicable)
- Remove the Rear Wheels: If the adjustment requires access to the brake shoes, remove the rear wheels.
- Locate the Adjustment Star Wheel: Find the adjustment star wheel, which is typically located on the backing plate of the brake assembly.
- Adjust the Star Wheel: Use a brake adjustment tool or screwdriver to turn the star wheel, which will either expand or retract the brake shoes.
- Check Brake Drag: Rotate the wheel hub to check for brake drag. The shoes should have a slight drag against the drum or rotor.
- Reinstall the Wheels: Once the adjustment is complete, reinstall the rear wheels and torque the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specification.
4.4. Final Checks
- Test the Parking Brake: Test the parking brake on a slight incline to ensure it holds the vehicle securely.
- Verify Release: Make sure the parking brake releases completely when disengaged, without any binding or dragging.
- Inspect Cables: Inspect the parking brake cables for any signs of damage, such as fraying or corrosion.
5. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
During the adjustment process, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
5.1. Rusted or Seized Cables
If the parking brake cables are rusted or seized, they may not move freely, making adjustment difficult.
- Solution: Apply penetrating oil to the cables and allow it to soak for several hours. Gently work the cables back and forth to loosen them. If the cables are severely corroded, they may need to be replaced. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of replacement cables to ensure your parking brake system functions optimally.
5.2. Stripped Adjustment Nuts
Over-tightening the adjustment nuts can strip the threads, making it impossible to achieve the correct tension.
- Solution: Replace the stripped nuts with new ones. Ensure you use the correct size and thread pitch. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality replacement hardware for various parking brake systems.
5.3. Worn Brake Shoes or Pads
If the brake shoes or pads are worn, the parking brake may not hold effectively, even after adjustment.
- Solution: Replace the worn brake shoes or pads with new ones. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of brake components to restore your parking brake’s performance.
5.4. Binding or Sticking Brakes
Binding or sticking brakes can be caused by corrosion, debris, or a maladjusted mechanism.
- Solution: Clean and lubricate the brake components. Check the adjustment mechanism for any signs of damage or misalignment. If necessary, replace the affected parts.
6. Advanced Techniques for Optimal Parking Brake Performance
For those looking to fine-tune their parking brake system, here are some advanced techniques:
6.1. Cable Lubrication
Regular lubrication of the parking brake cables can prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation.
- How-to: Use a cable lubricator tool to force lubricant into the cable housing. Apply a high-quality cable lubricant that is resistant to water and heat.
6.2. Brake Shoe Bedding
When replacing brake shoes, it’s essential to bed them in properly to ensure optimal performance.
- How-to: After installing new brake shoes, perform a series of light to moderate stops to allow the shoes to conform to the drum or rotor surface. Avoid hard stops during the bedding-in process.
6.3. Lever Ratio Optimization
Adjusting the lever ratio can affect the amount of force required to engage the parking brake.
- How-to: Consult your vehicle’s service manual for instructions on adjusting the lever ratio. Be careful not to over-adjust, as this can lead to premature wear or damage.
7. The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your vehicle’s parking brake system is essential for safety and reliability. Here are some maintenance tips:
7.1. Regular Inspections
Inspect the parking brake cables, levers, and components for any signs of damage or wear. Check the cable tension and lever travel.
7.2. Lubrication
Lubricate the parking brake cables and mechanism regularly to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation.
7.3. Adjustment Intervals
Adjust the parking brake every 12 months or 12,000 miles, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
7.4. Professional Service
If you are not comfortable performing the adjustment yourself, seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic. CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with trusted service providers in your area.
8. Choosing the Right Parking Brake Components from CARDIAGTECH.NET
Selecting the correct parking brake components is vital for ensuring optimal performance and safety. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality parts to meet your needs.
8.1. Types of Parking Brake Components Available
- Cables: High-strength steel cables designed for durability and precise operation.
- Shoes and Pads: Premium-grade friction materials for superior holding power and longevity.
- Hardware Kits: Comprehensive kits including springs, adjusters, and clips for a complete overhaul.
- Levers and Handles: Ergonomically designed levers and handles for comfortable and reliable engagement.
8.2. Factors to Consider When Selecting Components
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the components are specifically designed for your vehicle’s make and model.
- Material Quality: Opt for parts made from durable materials that can withstand harsh conditions.
- Performance Requirements: Consider your vehicle’s usage and choose components that meet or exceed OEM specifications.
- Warranty: Look for components with a solid warranty to protect against defects and premature failure.
8.3. Benefits of Purchasing from CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Wide Selection: A vast inventory of parking brake components for various vehicle types.
- High-Quality Products: Parts sourced from reputable manufacturers known for their reliability.
- Expert Advice: Knowledgeable staff to assist you in selecting the right components for your needs.
- Competitive Pricing: Affordable prices on premium-grade parking brake parts.
9. Parking Brake System Variations Across Different Vehicle Types
Parking brake systems can vary significantly depending on the vehicle type. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper adjustment and maintenance.
9.1. Passenger Cars
- Cable-Operated Systems: Most passenger cars use cable-operated parking brakes, which can be adjusted at the lever or near the rear wheels.
- Integrated Systems: Some modern cars feature electronically controlled parking brakes integrated with the ABS system.
9.2. Trucks and SUVs
- Drum Brake Systems: Many trucks and SUVs use drum brakes with an internal parking brake mechanism.
- External Shoe Systems: Some heavy-duty trucks employ external shoe systems that clamp onto the driveshaft.
9.3. Performance Vehicles
- High-Performance Pads: Performance vehicles often require high-performance brake pads and rotors to handle increased braking demands.
- Adjustable Levers: Some performance vehicles feature adjustable parking brake levers for precise control.
9.4. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
- Regenerative Braking: Electric and hybrid vehicles use regenerative braking, which can affect the wear of the mechanical parking brake system.
- Electronic Actuation: Many electric and hybrid vehicles use electronically actuated parking brakes for enhanced convenience and safety.
10. The Role of Parking Brakes in Vehicle Safety Inspections
Parking brakes are a critical component in vehicle safety inspections. A properly functioning parking brake is essential for passing inspection and ensuring vehicle safety.
10.1. Inspection Criteria
- Holding Power: The parking brake must be able to hold the vehicle securely on a specified incline.
- Lever Travel: The lever or pedal travel must be within the manufacturer’s specified range.
- Cable Condition: The parking brake cables must be free from damage, corrosion, and excessive slack.
- Brake Shoe Condition: The brake shoes or pads must have sufficient friction material and be free from contamination.
10.2. Consequences of Failing Inspection
- Vehicle Rejection: Vehicles that fail the parking brake inspection may be rejected and require repairs before being re-inspected.
- Safety Concerns: A faulty parking brake can pose a significant safety risk, potentially leading to rollaway accidents.
- Legal Implications: Operating a vehicle with a defective parking brake may result in fines or other legal consequences.
10.3. Tips for Passing Inspection
- Pre-Inspection Check: Perform a thorough inspection of the parking brake system before taking the vehicle for inspection.
- Address Issues Promptly: Repair any identified issues, such as worn cables or brake shoes, before the inspection.
- Professional Adjustment: Have the parking brake professionally adjusted to ensure it meets inspection requirements.
11. Maintaining Parking Brakes in Different Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can significantly impact the performance and longevity of parking brake systems. Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring reliable operation in various climates.
11.1. Hot Weather
- Heat Expansion: High temperatures can cause the parking brake cables to expand, leading to reduced tension.
- Brake Fade: Extreme heat can cause brake fade, reducing the holding power of the parking brake.
11.2. Cold Weather
- Cable Contraction: Cold temperatures can cause the parking brake cables to contract, leading to excessive tension.
- Freezing: Moisture can freeze inside the parking brake cables, causing them to seize or break.
11.3. Wet Weather
- Corrosion: Wet weather can accelerate corrosion of the parking brake cables and components.
- Reduced Friction: Moisture can reduce the friction between the brake shoes and drums, affecting holding power.
11.4. Preventative Measures
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate the parking brake cables and mechanism to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation.
- Cable Adjustment: Adjust the parking brake cables as needed to compensate for temperature-related changes in tension.
- Component Protection: Apply a protective coating to the parking brake components to prevent corrosion in wet climates.
12. DIY vs. Professional Parking Brake Adjustment: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to adjust your parking brake yourself or seek professional assistance depends on your mechanical skills, available tools, and comfort level.
12.1. DIY Adjustment
- Pros:
- Cost Savings: Save on labor costs by performing the adjustment yourself.
- Convenience: Adjust the parking brake at your own pace and on your own schedule.
- Learning Opportunity: Gain valuable experience and knowledge about your vehicle’s braking system.
- Cons:
- Requires Mechanical Skills: Requires a basic understanding of automotive mechanics and braking systems.
- Specialized Tools Needed: May require specialized tools, such as a torque wrench and cable tension meter.
- Risk of Errors: Potential for errors that could compromise the parking brake’s performance or safety.
12.2. Professional Adjustment
- Pros:
- Expertise: Benefit from the knowledge and experience of a qualified mechanic.
- Proper Tools and Equipment: Professionals have access to specialized tools and equipment for accurate adjustment.
- Warranty: Professional service often comes with a warranty, providing peace of mind.
- Cons:
- Higher Cost: Professional service typically costs more than DIY adjustment.
- Scheduling Constraints: May need to schedule an appointment and wait for the service to be completed.
- Potential for Inconvenience: May need to drop off and pick up the vehicle at the service center.
12.3. Factors to Consider
- Mechanical Skills: Assess your mechanical skills and comfort level with automotive repairs.
- Available Tools: Determine if you have the necessary tools or if you need to purchase them.
- Cost: Compare the cost of DIY adjustment versus professional service.
- Safety: Prioritize safety and choose the option that ensures the parking brake is adjusted correctly.
13. How to Inspect and Maintain Parking Brake Cables
The parking brake cables are a critical part of the system, and their condition directly affects the brake’s performance. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent failures and ensure reliable operation.
13.1. Inspecting Cables for Damage
- Visual Inspection: Look for signs of fraying, corrosion, or kinks along the length of the cables.
- Flexibility Test: Check the cables’ flexibility by bending them gently. Stiff or binding cables may need replacement.
- Sheath Condition: Inspect the cable sheaths for cracks, tears, or other damage that could allow moisture and debris to enter.
13.2. Maintaining Cable Integrity
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable cable lubricant to keep the cables moving smoothly within their sheaths.
- Adjust Tension: Regularly adjust the cable tension to compensate for stretching or wear.
- Replace Worn Cables: Replace any cables that show signs of significant wear, damage, or corrosion.
13.3. Proper Cable Routing
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Ensure the cables are routed smoothly without any sharp bends or kinks that could restrict movement.
- Secure Mounting: Secure the cables properly to prevent them from rubbing against other components.
- Check Clearance: Verify that the cables have adequate clearance from exhaust pipes, suspension parts, and other moving components.
14. Understanding Automatic Parking Brake Systems
While this guide primarily focuses on mechanical systems, many modern vehicles use automatic parking brakes, which offer enhanced convenience and safety features.
14.1. How Automatic Systems Work
- Electronic Actuation: Automatic parking brakes use electronic actuators to engage and disengage the brakes.
- Sensor Integration: These systems are often integrated with sensors that detect vehicle inclination and automatically apply the parking brake when needed.
- Push-Button Operation: Instead of a lever or pedal, automatic parking brakes are typically controlled by a push button or switch.
14.2. Benefits of Automatic Systems
- Convenience: Automatic engagement and disengagement simplify parking and starting on inclines.
- Safety: Automatic engagement on inclines prevents rollaway accidents.
- Reduced Wear: Precise electronic control can reduce wear on the braking components.
14.3. Maintenance Considerations
- Software Updates: Automatic parking brake systems may require periodic software updates to ensure proper operation.
- Sensor Calibration: Sensors may need to be calibrated to maintain accurate readings.
- Professional Service: Complex diagnostic and repair procedures typically require professional service.
15. The Future of Parking Brake Technology
Parking brake technology continues to evolve, with advancements in electronic control, sensor integration, and material science.
15.1. Integration with ADAS
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Future parking brake systems will be more closely integrated with ADAS features, such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist.
15.2. Predictive Maintenance
- Sensor-Based Monitoring: Sensors will monitor the condition of the parking brake components and predict maintenance needs.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics will allow technicians to identify and address potential issues before they lead to failures.
15.3. Lightweight Materials
- Composite Materials: The use of lightweight composite materials will reduce the weight of the parking brake system, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
- High-Strength Alloys: High-strength alloys will provide improved durability and corrosion resistance.
16. Safety Precautions When Working on Parking Brakes
Working on parking brakes involves certain risks, and it’s essential to take appropriate safety precautions to prevent injuries.
16.1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from dirt, grease, and sharp edges.
- Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and fluids.
- Closed-Toe Shoes: Wear closed-toe shoes to protect your feet from falling objects and sharp objects on the ground.
16.2. Vehicle Stabilization
- Level Surface: Park the vehicle on a level surface before starting any work.
- Wheel Chocks: Use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
- Jack Stands: Use jack stands to support the vehicle if you need to lift it.
16.3. Hazardous Materials
- Brake Cleaner: Use brake cleaner in a well-ventilated area and avoid contact with skin and eyes.
- Brake Fluid: Brake fluid can damage painted surfaces and cause skin irritation. Clean up any spills immediately.
- Asbestos: Some older brake components may contain asbestos. Take appropriate precautions to avoid inhaling asbestos fibers.
17. Eco-Friendly Parking Brake Maintenance Practices
Maintaining your parking brake system with environmentally friendly practices can reduce your carbon footprint and protect the environment.
17.1. Use Eco-Friendly Products
- Brake Cleaners: Use brake cleaners that are free from harmful chemicals, such as chlorinated solvents.
- Lubricants: Use lubricants that are biodegradable and non-toxic.
- Recycled Components: Consider using recycled or remanufactured parking brake components.
17.2. Proper Disposal of Waste
- Brake Fluid: Dispose of used brake fluid properly at a designated recycling center.
- Brake Pads: Some brake pad manufacturers offer recycling programs for used brake pads.
- Packaging: Recycle all packaging materials from new parking brake components.
17.3. Prevent Leaks
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the parking brake system regularly for leaks.
- Tighten Connections: Tighten any loose connections to prevent leaks.
- Replace Seals: Replace any worn or damaged seals to prevent leaks.
18. Finding a Reputable Mechanic for Parking Brake Services
If you prefer to have a professional handle your parking brake maintenance, finding a reputable mechanic is crucial.
18.1. Research and Reviews
- Online Reviews: Check online reviews to see what other customers have to say about the mechanic’s service.
- Referrals: Ask friends, family, and colleagues for referrals to trusted mechanics.
- BBB Rating: Check the mechanic’s rating with the Better Business Bureau (BBB).
18.2. Certifications and Affiliations
- ASE Certification: Look for mechanics who are certified by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
- Manufacturer Affiliations: Some mechanics are affiliated with specific vehicle manufacturers, indicating specialized training and expertise.
18.3. Service Guarantees
- Warranty: Ask about the mechanic’s warranty on parts and labor.
- Satisfaction Guarantee: Look for a mechanic who offers a satisfaction guarantee.
19. How Parking Brake Use Affects Overall Vehicle Health
The way you use your parking brake can have a significant impact on its longevity and the overall health of your vehicle.
19.1. Regular Use vs. Neglect
- Regular Use: Using the parking brake regularly, even on level surfaces, can help keep the cables and mechanism from corroding or seizing.
- Neglect: Neglecting to use the parking brake can lead to corrosion, cable stretch, and reduced effectiveness.
19.2. Avoiding Abuse
- Gentle Engagement: Engage the parking brake gently to avoid stressing the cables and mechanism.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Avoid over-tightening the parking brake, which can lead to premature wear.
- Release Before Driving: Always release the parking brake fully before driving to prevent damage to the braking system.
19.3. Monitoring Performance
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the parking brake regularly for signs of wear or damage.
- Listen for Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises when engaging or disengaging the parking brake.
- Test Holding Power: Test the parking brake’s holding power on an incline to ensure it’s functioning properly.
20. The Legal Aspects of Parking Brake Maintenance
In many jurisdictions, having a functioning parking brake is a legal requirement. Neglecting parking brake maintenance can have legal consequences.
20.1. Vehicle Safety Regulations
- Inspection Requirements: Many states require vehicles to pass a safety inspection, which includes checking the parking brake’s functionality.
- Legal Mandates: Some states have specific legal mandates regarding parking brake maintenance and repair.
20.2. Liability Issues
- Rollaway Accidents: If a vehicle rolls away due to a faulty parking brake and causes damage or injury, the owner may be held liable.
- Negligence: Neglecting to maintain the parking brake could be considered negligence, increasing liability in the event of an accident.
20.3. Insurance Implications
- Coverage Denials: Some insurance companies may deny coverage for accidents caused by a faulty parking brake.
- Increased Premiums: Having a history of parking brake-related incidents could lead to increased insurance premiums.
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Is your parking brake giving you trouble? Don’t wait until it’s too late. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and high-quality parking brake components. Our team of experienced professionals can help you diagnose the problem and find the right solution to keep your vehicle safe and reliable. Whether you need a simple adjustment or a complete overhaul, we have the tools and expertise to get the job done right. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Let us help you keep your vehicle in top condition.
FAQ: How to Adjust a Mechanical Parking Brake?
1. What is the primary function of a mechanical parking brake?
The primary function of a mechanical parking brake is to prevent the vehicle from rolling away when parked, especially on inclines, ensuring safety and stability.
2. How often should I adjust my mechanical parking brake?
It is recommended to adjust your mechanical parking brake every 12 months or 12,000 miles, or as specified by your vehicle’s manufacturer, to maintain its effectiveness.
3. What are the signs that my parking brake needs adjustment?
Signs include a loose or ineffective lever, vehicle rollaway on inclines, difficulty releasing the brake, and unusual noises like grinding or squealing when engaged or disengaged.
4. Can I adjust the parking brake myself, or should I seek professional help?
Whether you adjust it yourself or seek professional help depends on your mechanical skills, available tools, and comfort level with automotive repairs.
5. What tools are essential for adjusting a mechanical parking brake?
Essential tools include a wrench set, socket set, screwdrivers, pliers, torque wrench, cable tension meter, and brake spring tool, along with safety equipment like gloves and safety glasses.
6. What should I do if the parking brake cables are rusted or seized?
Apply penetrating oil to the cables and allow it to soak for several hours. Gently work the cables back and forth to loosen them. If severely corroded, consider replacement with high-quality cables from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
7. How do I adjust the cable tension in a mechanical parking brake?
Loosen the jam nut, tighten the adjustment nut to increase cable tension, check the lever travel, and then tighten the jam nut to secure the adjustment.
8. Why is it important to use a torque wrench when adjusting a parking brake?
A torque wrench ensures that nuts and bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque, preventing over-tightening or under-tightening, which can compromise the brake’s performance.
9. What are some common issues encountered during parking brake adjustment?
Common issues include rusted or seized cables, stripped adjustment nuts, worn brake shoes or pads, and binding or sticking brakes.
10. How does regular maintenance of the parking brake system contribute to vehicle safety?
Regular maintenance ensures the parking brake can securely hold the vehicle, prevents cable wear, optimizes lever travel, and ultimately reduces the risk of rollaway accidents, enhancing overall vehicle safety.