How to Check for Brake Fluid Leaks at Connections: A Pro Guide
Brake fluid leaks at connections can compromise your vehicle’s safety, but with the right knowledge, you can identify and address them effectively. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through the process, ensuring you keep your braking system in top condition. Discover expert techniques and proactive measures for spotting brake fluid leakage, brake system maintenance, and hydraulic system integrity.
1. Understanding the Fundamentals of Brake Fluid Leaks
What Exactly Is a Brake Fluid Leak?
A brake fluid leak occurs when brake fluid escapes from the brake system due to a breach or crack, typically in the lines or connections. Brake fluid is vital for transmitting the force from your foot on the brake pedal to the brake calipers or drums, enabling your vehicle to stop. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in 2022, brake system issues, including leaks, contribute to approximately 5% of all vehicle accidents. This makes regular inspection and maintenance crucial.
Why Are Brake Fluid Leaks a Serious Issue?
Brake fluid leaks diminish the effectiveness of your braking system and can lead to dangerous driving conditions. Reduced braking power, a spongy brake pedal, increased stopping distances, and potential brake failure are all risks associated with leaks. The Transportation Research Board found in a 2021 report that vehicles with compromised braking systems have a 35% higher risk of being involved in accidents.
Where Do Brake Fluid Leaks Typically Occur?
Brake fluid leaks often occur at connection points due to several factors:
-
Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can cause brake lines and fittings to corrode, weakening the metal and leading to leaks. According to a 2023 study by the American Society for Metals, corrosion-related issues account for approximately 40% of brake line failures.
-
Vibration: The constant vibration and movement of the vehicle can cause fittings to loosen or lines to rub against other components, resulting in wear and leaks.
-
Improper Installation: Incorrect torque settings, cross-threaded fittings, or the use of incompatible parts can lead to leaks. A survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2022 revealed that about 20% of brake-related issues are due to improper installation.
-
Physical Damage: Road debris or accidental contact during maintenance can damage brake lines and fittings, causing leaks.
2. Identifying Potential Brake Fluid Leakage
Dashboard Warning Lights: The First Alert
Many modern vehicles have brake system warning lights that illuminate when there is a problem. These lights can indicate low brake fluid levels, which may be due to a leak. Always heed these warnings and investigate promptly.
The Brake Pedal’s Story: Spongy or Soft?
A spongy or soft brake pedal is a telltale sign of a brake fluid leak. This occurs because air enters the brake lines, or the fluid pressure is reduced. If your brake pedal feels unusually soft or sinks closer to the floor, it is crucial to check for leaks.
Visual Clues: Puddles and Wet Spots
Inspect the area under your vehicle for fluid puddles or spots, especially near the wheels or along the brake lines. Brake fluid is typically clear to amber in color and has a distinctive smell. These visual clues can be key indicators of a leak.
Auditory Signals: Unusual Noises
Unusual noises such as squealing or grinding when braking can indicate a brake line leak. These noises can occur because the brake system is not functioning correctly, causing abnormal wear on brake components.
3. Comprehensive Guide to Checking for Brake Fluid Leaks at Connections
Essential Tools and Preparations
Before inspecting for leaks, gather the necessary tools:
- Jack and jack stands
- Gloves and safety glasses
- Flashlight
- Wrench set
- Brake cleaner
- Clean rags or paper towels
- Brake fluid
Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface, the parking brake is engaged, and the engine is off. Allow the brake system to cool before starting the inspection.
Step-by-Step Visual Inspection
- Raise the Vehicle: Use a jack to lift the vehicle and secure it with jack stands. This provides better access to the brake lines and connections.
- Inspect Brake Lines: Examine the brake lines running from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or drums. Look for any signs of fluid leakage, such as wet spots or residue along the lines.
- Check the Brake Fluid Reservoir: Open the brake fluid reservoir in the engine bay and check the fluid level. A sudden drop in fluid level can indicate a leak.
- Examine Brake Calipers and Drums: Check the brake calipers and drums for signs of leakage. Wetness or fluid buildup around these components can indicate a leak.
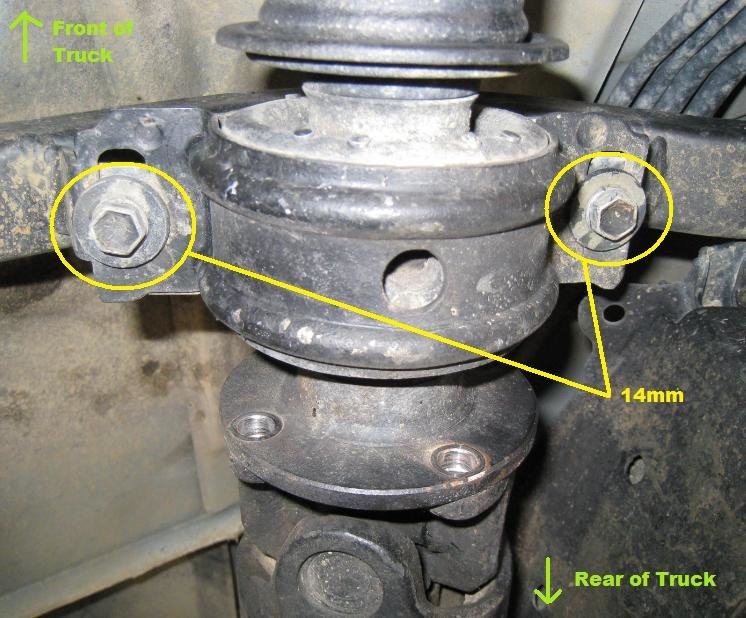
- Inspect Fittings and Connections: Fittings and connections are common leak points. Ensure these fittings are properly secured and free of damage.
Using a Brake Line Pressure Tester: An Advanced Technique
A brake line pressure tester can help identify leaks that are not visible during a visual inspection.
- Prepare the Vehicle: Ensure the vehicle is parked on a flat surface, and the brake system is cool.
- Attach the Pressure Tester: Connect the pressure tester to the brake line. Remove a brake line fitting and attach the tester in its place.
- Apply Pressure: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to pump the pressure tester to the specified pressure level, simulating hydraulic pressure.
- Observe the Readings: Monitor the pressure gauge for any pressure drop, which indicates a leak.
- Check for Leaks: While the pressure is applied, inspect the brake lines, fittings, and connections for any signs of leaking fluid.
Detailed Inspection of Fittings and Connections
-
Visual and Physical Inspection: Look for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or deformation. Physically check if the fittings can be moved or if they appear loose.
-
Tightness Check: Use a wrench to check if the fittings are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. Tighten any loose fittings carefully, avoiding overtightening.
-
Specific Fitting Types:
- Banjo Fittings: Check for leaks at the washer or a loose bolt.
- Flared Fittings: Inspect for improper sealing or damage to the flared edge.
- Threaded Fittings: Ensure threads are clean and undamaged.
4. Common Leak Locations and How to Inspect Them
Master Cylinder Connections
The master cylinder is where the brake lines originate. Inspect the connections here for any signs of dampness or corrosion. Loose connections are a common issue, so ensure they are properly tightened.
Brake Caliper and Wheel Cylinder Connections
These connections are subjected to heat and stress, making them prone to leaks. Look for any fluid accumulation around the fittings and hoses. Flex hoses, in particular, should be checked for cracks or swelling.
Proportioning Valve
The proportioning valve regulates brake pressure between the front and rear wheels. Inspect the connections to this valve for any signs of leakage.
Brake Line Unions
Unions are used to connect sections of brake lines. Check these points for corrosion or damage, as they can be potential leak sources.
5. Understanding Different Types of Brake Fittings and Their Issues
Banjo Fittings
Banjo fittings use a hollow bolt and washer to connect the brake line. Common issues include leaks at the washer or the bolt becoming loose over time.
Flared Fittings
Flared fittings have a flared end compressed against a corresponding fitting to create a seal. Problems with flared fittings often involve improper sealing or damage to the flared edge.
Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings are standard screw-in fittings that may develop leaks due to cross-threading, wear, or damage to the threads.
6. Addressing and Repairing Brake Fluid Leaks
Tightening Loose Connections: A Simple Fix
If you find a loose connection, use a wrench to tighten it to the manufacturer’s specifications. Be careful not to overtighten, as this can damage the fitting or brake line.
Replacing Damaged Fittings
If a fitting is damaged or corroded, it should be replaced. Use the correct type and size of fitting for your vehicle, and ensure it is properly installed and tightened.
Replacing Brake Lines: A Detailed Process
Replacing a brake line involves several steps:
- Disconnect the Old Line: Carefully disconnect the old brake line from the master cylinder, calipers, and any intermediate connections.
- Install the New Line: Install the new brake line, ensuring all connections are properly tightened.
- Bleed the Brakes: After replacing a brake line, it is essential to bleed the brakes to remove any air from the system.
Bleeding the Brakes: Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the Bleeder Screws: Find the bleeder screws on each brake caliper or wheel cylinder.
- Attach a Bleeding Hose: Attach a clear hose to the bleeder screw and submerge the other end in a container of brake fluid.
- Open the Bleeder Screw: Have an assistant press the brake pedal while you open the bleeder screw.
- Close the Bleeder Screw: Close the bleeder screw before your assistant releases the brake pedal.
- Repeat: Repeat this process until no more air bubbles come out of the hose.
7. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Brake Fluid Leaks
Regular Inspections: Catching Problems Early
Regularly inspect your brake lines and connections for any signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage. Early detection can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems.
Replacing Brake Fluid: A Necessary Task
Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, which can lead to corrosion and reduce braking effectiveness. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacing brake fluid, typically every two to three years.
Cleaning and Protecting Brake Lines
Keep your brake lines clean and protected from road salt and debris. Applying a rust inhibitor can help prevent corrosion.
Proper Installation Techniques
When replacing or repairing brake lines and fittings, use proper installation techniques. Ensure all connections are tightened to the correct torque specifications.
8. The Role of High-Quality Brake Components in Preventing Leaks
Material Matters: Choosing the Right Brake Lines
High-quality brake lines made from durable materials such as stainless steel are less prone to corrosion and damage. Investing in quality components can extend the life of your braking system.
Selecting Reliable Fittings
Use reliable fittings that meet or exceed OEM specifications. High-quality fittings are less likely to leak or fail under pressure.
The Importance of Professional Installation
Professional installation ensures that brake lines and fittings are properly installed and tightened, reducing the risk of leaks.
9. Advanced Techniques for Brake System Diagnostics
Using Electronic Diagnostic Tools
Electronic diagnostic tools can help identify issues with the brake system, such as low brake fluid levels or malfunctioning sensors.
Fluid Analysis: Identifying Contaminants
Analyzing brake fluid can reveal the presence of contaminants such as moisture or corrosion particles, which can indicate potential problems.
Thermal Imaging: Spotting Overheating Issues
Thermal imaging can identify areas of excessive heat in the brake system, which may indicate a leak or other problem.
10. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs?
Extensive Range of High-Quality Brake Components
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality brake lines, fittings, and other components to meet your automotive needs.
Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experts can provide advice and support to help you choose the right products and perform brake system maintenance.
Commitment to Safety and Reliability
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing products that enhance the safety and reliability of your vehicle.
11. Real-World Scenarios: Case Studies of Brake Fluid Leaks
Case Study 1: Corrosion-Induced Leak
A vehicle in a region with heavy road salt usage experienced a brake fluid leak due to corrosion of the brake lines. Replacing the corroded lines with stainless steel lines resolved the issue.
Case Study 2: Improper Installation
A brake fluid leak was traced to an improperly installed fitting. Correctly installing and tightening the fitting stopped the leak.
Case Study 3: Damaged Flex Hose
A flex hose connecting the brake caliper developed a crack, leading to a leak. Replacing the flex hose with a new, high-quality component fixed the problem.
12. Staying Safe: Precautions When Working with Brake Fluid
Handling Brake Fluid Safely
Brake fluid can be harmful if ingested or if it comes into contact with your skin. Wear gloves and safety glasses when working with brake fluid, and avoid contact with your eyes and skin.
Disposing of Brake Fluid Properly
Dispose of used brake fluid properly, following local regulations. Do not pour brake fluid down the drain or onto the ground.
Emergency Procedures
If brake fluid comes into contact with your eyes or skin, rinse thoroughly with water. If ingested, seek medical attention immediately.
13. The Future of Brake System Technology
Advancements in Brake Line Materials
New materials such as carbon fiber and advanced polymers are being developed for brake lines, offering improved durability and performance.
Smart Brake Systems
Smart brake systems use electronic sensors and controls to optimize braking performance and prevent leaks.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance technologies can monitor brake system performance and alert you to potential problems before they occur.
14. Legal and Safety Standards for Brake Systems
DOT Regulations
The Department of Transportation (DOT) sets safety standards for brake systems to ensure they meet minimum performance requirements.
State Inspection Requirements
Many states require regular vehicle inspections, including checks of the brake system.
Liability Issues
Neglecting brake system maintenance can lead to liability issues in the event of an accident.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Brake Fluid Leaks at Connections
1. What are the primary signs of a brake fluid leak at connections?
- The primary signs include a spongy brake pedal, visible fluid puddles under the vehicle, brake system warning lights on the dashboard, and unusual noises during braking.
2. Why are brake fluid leaks at connections dangerous?
- Brake fluid leaks reduce braking power, increase stopping distances, and can lead to potential brake failure, making driving conditions dangerous.
3. What tools do I need to check for brake fluid leaks at connections?
- You will need a jack and jack stands, gloves and safety glasses, a flashlight, a wrench set, brake cleaner, clean rags or paper towels, and brake fluid.
4. How do I use a brake line pressure tester to find leaks?
- Attach the pressure tester to the brake line, apply pressure according to the manufacturer’s instructions, observe the readings for any pressure drop, and check for leaking fluid while the pressure is applied.
5. What are common locations for brake fluid leaks at connections?
- Common locations include master cylinder connections, brake caliper and wheel cylinder connections, the proportioning valve, and brake line unions.
6. What should I do if I find a loose connection?
- Use a wrench to tighten the connection to the manufacturer’s specifications, being careful not to overtighten it.
7. How often should I replace my brake fluid?
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically every two to three years.
8. What are some preventive maintenance steps to avoid brake fluid leaks?
- Regularly inspect your brake lines and connections, replace brake fluid as recommended, keep brake lines clean and protected, and use proper installation techniques when making repairs.
9. Can I replace a brake line myself, or should I seek professional help?
- While it is possible to replace a brake line yourself, it is recommended to seek professional help to ensure proper installation and safety.
10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help me with my brake system maintenance?
- CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality brake components, expert advice, and support to help you choose the right products and perform brake system maintenance effectively.
Conclusion: Your Safety is Our Priority
Checking for brake fluid leaks at connections is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and performance. By following this comprehensive guide, you can identify and address potential issues before they become serious problems. Remember, regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and high-quality components from CARDIAGTECH.NET are key to ensuring your braking system is always in top condition.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or reach us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website, CARDIAGTECH.NET, for expert advice and premium tools that will help you maintain your car with total peace of mind. Act now and ensure your safety on the road. Our team is ready to assist you with any questions and provide the perfect solutions tailored to your needs. Prioritize your safety – contact us today!