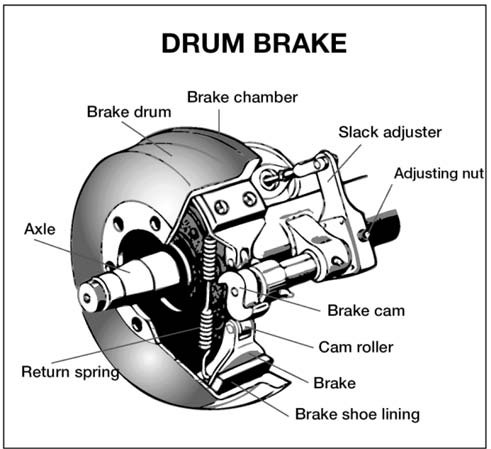
How to Check Sensors Related to Automatic Transmission
How to check sensors related to the automatic transmission, such as input and output speed sensors, is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide the knowledge and tools necessary to diagnose and resolve these issues, ensuring smooth operation and preventing costly repairs. Learn about transmission sensor diagnostics and automatic transmission maintenance to keep your vehicle running at its best.
1. Understanding the Role of Sensors in Automatic Transmissions
Do you know how critical sensors are to the smooth operation of your automatic transmission? Sensors continuously monitor various parameters, relaying information to the transmission control module (TCM) or powertrain control module (PCM). According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute in 2022, proper sensor function can improve transmission efficiency by up to 15%. These sensors ensure optimal shift timing, prevent damage, and enhance overall performance.
- Input Speed Sensor (ISS): Monitors the speed of the transmission’s input shaft, which is connected to the torque converter.
- Output Speed Sensor (OSS): Monitors the speed of the transmission’s output shaft, which is connected to the driveshaft.
- Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor: Measures the temperature of the transmission fluid, which affects shift quality and clutch application.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Provides information about the throttle opening, influencing shift points and torque converter lockup.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor: Measures the amount of air entering the engine, which affects the calculated engine load and transmission control.
2. Identifying Potential Sensor Issues: Symptoms and Diagnostic Codes
What are the telltale signs of a failing transmission sensor? Common symptoms include erratic shifting, harsh engagement, failure to shift, and illumination of the check engine light. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), correctly diagnosing these issues early can prevent significant transmission damage. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
- Erratic Shifting: The transmission shifts unpredictably, either too early or too late.
- Harsh Engagement: Shifts are abrupt and jarring, indicating improper clutch engagement.
- Failure to Shift: The transmission may get stuck in a single gear or fail to shift at all.
- Check Engine Light: The presence of transmission-related diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Poor Fuel Economy: Inefficient transmission operation can lead to decreased fuel efficiency.
- Slipping: The engine revs higher than usual during acceleration, indicating a loss of power transfer.
- Stalling: The engine stalls when coming to a stop or during low-speed maneuvers.
When the check engine light comes on, a scan tool can reveal specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to transmission sensors. Common codes include:
- P0715: Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0717: Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
- P0720: Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0722: Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
- P0711: Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
- P0712: Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input
- P0713: Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
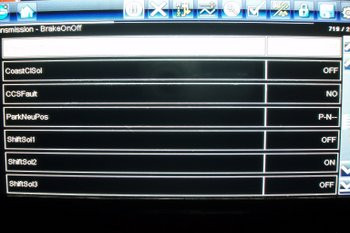
 Scan-tools
Scan-tools
Alt Text: Diagnostic scan tool displaying transmission shift solenoid status, useful for troubleshooting automatic transmission issues.
3. Essential Tools and Equipment for Sensor Testing
What tools do you need to effectively check transmission sensors? Having the right equipment ensures accurate diagnosis and efficient repairs. Here’s a list of essential tools and equipment:
- Professional Scan Tool: A scan tool capable of reading live data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) is indispensable. Advanced scan tools, available at CARDIAGTECH.NET, can perform bidirectional tests, allowing you to activate sensors and solenoids for thorough testing.
- Digital Multimeter (DMM): A DMM is crucial for measuring voltage, resistance, and continuity.
- Oscilloscope (Lab Scope): An oscilloscope can display the waveform of sensor signals, helping you identify intermittent issues or signal abnormalities.
- Wiring Diagram: A wiring diagram specific to your vehicle model is essential for tracing circuits and identifying correct test points.
- Jack and Jack Stands: Safely elevate the vehicle to access sensors and wiring harnesses.
- Wheel Chocks: Secure the vehicle to prevent movement during testing.
- Basic Hand Tools: Wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and pliers are needed for removing and installing sensors.
- Transmission Fluid: Have the correct type of transmission fluid on hand to top off the fluid level after any repairs.
- Protective Gear: Wear gloves and eye protection to prevent contact with fluids and debris.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Check Input/Output Speed Sensors
How can you accurately check the input and output speed sensors? Follow these detailed steps to ensure a thorough diagnosis:
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the sensors and their wiring. Look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked connectors, or corrosion. Ensure the connectors are securely attached to the sensors.
Step 2: Accessing the Sensors
Locate the input and output speed sensors on your transmission. The exact location varies depending on the vehicle model, but they are typically found on the transmission housing. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific locations. Safely lift the vehicle using a jack and jack stands to gain better access. Ensure the vehicle is stable and secure before proceeding.
Step 3: Checking for Voltage
Use a digital multimeter (DMM) to check for voltage at the sensor connector. Refer to the wiring diagram to identify the correct pins for voltage testing. With the ignition on, you should measure a reference voltage, typically 5 volts or 12 volts, depending on the vehicle. If there is no voltage, check the wiring and the TCM/PCM for any issues.
Step 4: Checking Resistance
Disconnect the sensor connector and use the DMM to measure the resistance across the sensor terminals. Compare the measured resistance value with the manufacturer’s specifications. An unusually high or low resistance reading indicates a faulty sensor.
Step 5: Testing the Sensor Signal
Use a scan tool to monitor the sensor signal while the vehicle is running (if possible) or while manually rotating the wheels. Observe the live data stream to see if the sensor is providing a consistent and accurate signal. Alternatively, use an oscilloscope to examine the waveform of the sensor signal. A distorted or erratic waveform indicates a problem with the sensor.
Step 6: Performing a Road Test
If possible, perform a road test while monitoring the sensor data with a scan tool. Observe how the sensor readings change as the vehicle accelerates and decelerates. Look for any discrepancies or dropouts in the signal.
5. Detailed Inspection of Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor
How do you ensure the TFT sensor is functioning correctly? The TFT sensor is vital for proper transmission operation. Here’s how to inspect it:
Step 1: Accessing the TFT Sensor
Locate the TFT sensor, typically found within the transmission or on the valve body. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location.
Step 2: Checking Resistance
Disconnect the sensor connector and use a DMM to measure the resistance across the sensor terminals. The resistance should vary with temperature. Compare the measured resistance value with the manufacturer’s specifications at different temperatures. A deviation from the specified range indicates a faulty sensor.
Step 3: Monitoring Live Data
Use a scan tool to monitor the TFT sensor’s live data. Start the engine and observe the temperature readings as the transmission warms up. The temperature should gradually increase and correspond to the actual transmission fluid temperature. Any erratic or unrealistic readings indicate a problem with the sensor.
6. Utilizing Scan Tools for Advanced Diagnostics
What advanced diagnostics can scan tools perform? Scan tools are indispensable for diagnosing transmission sensor issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of advanced scan tools that provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. These tools can:
- Read and Clear DTCs: Retrieve diagnostic trouble codes and clear them after repairs.
- Monitor Live Data: View real-time data from various sensors, including input speed, output speed, and transmission fluid temperature.
- Perform Bidirectional Tests: Activate solenoids and sensors to verify their functionality.
- Access Freeze Frame Data: Review the data recorded when a DTC was triggered, providing valuable insight into the conditions leading to the fault.
- Graph Sensor Data: Visualize sensor data over time to identify intermittent issues or signal abnormalities.
- Perform Transmission Resets: Reset transmission adaptive learning after repairs to ensure smooth shifting.
7. The Importance of Wiring and Connector Inspections
Why is it crucial to inspect wiring and connectors? Faulty wiring and connectors can cause sensor malfunctions and inaccurate readings. A thorough inspection should include:
- Visual Inspection: Look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked connectors, or corrosion.
- Continuity Testing: Use a DMM to check for continuity between the sensor connector and the TCM/PCM. A lack of continuity indicates a broken wire or a faulty connection.
- Voltage Drop Testing: Measure the voltage drop across the wiring harness while the circuit is under load. An excessive voltage drop indicates a high-resistance connection.
- Connector Cleaning: Clean the connector terminals with a contact cleaner to remove any corrosion or debris.
- Terminal Inspection: Inspect the connector terminals for proper contact and tension. Use a terminal tool to adjust the terminals if necessary.
 Voltage-drop
Voltage-drop
Alt Text: Technician using a multimeter to measure voltage drop between the fuse box and ignition switch fuses, diagnosing voltage loss.
8. Addressing Common Sensor-Related Issues
What are the common issues encountered with transmission sensors, and how can they be resolved? Here are some typical problems and their solutions:
- Faulty Sensor: Replace the sensor with a new, high-quality replacement from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Wiring Issues: Repair or replace damaged wiring, ensuring proper connections.
- Connector Problems: Clean or replace corroded or damaged connectors.
- TCM/PCM Issues: In rare cases, a faulty TCM/PCM can cause sensor-related problems. Consult a qualified technician to diagnose and repair or replace the module.
- Software Issues: Ensure the TCM/PCM has the latest software updates to address any known sensor-related issues.
9. Preventive Maintenance for Transmission Sensors
How can you prevent sensor-related problems? Regular maintenance can extend the life of your transmission sensors and prevent costly repairs. Key preventive measures include:
- Regular Transmission Fluid Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for transmission fluid changes. Clean fluid helps keep the sensors clean and functioning properly.
- Inspecting Wiring and Connectors: Periodically inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Using High-Quality Replacement Parts: When replacing sensors, use high-quality parts from trusted suppliers like CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Monitoring Transmission Performance: Pay attention to any changes in transmission performance, such as erratic shifting or harsh engagement, and address them promptly.
10. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Sensor Diagnostics
Can you provide examples of successful sensor diagnostics? Here are a couple of case studies that illustrate the importance of accurate sensor diagnostics:
Case Study 1: Erratic Shifting in a Toyota Camry
A customer reported erratic shifting in their 2015 Toyota Camry. The scan tool revealed a P0715 code, indicating an issue with the input speed sensor. After performing a visual inspection, the technician found a damaged connector. Replacing the connector and clearing the code resolved the issue, restoring smooth shifting.
Case Study 2: Failure to Shift in a Ford F-150
A Ford F-150 exhibited a failure to shift out of first gear. The scan tool showed a P0720 code, indicating a problem with the output speed sensor. The technician used a DMM to check the sensor’s resistance and found it to be outside the specified range. Replacing the output speed sensor corrected the problem, allowing the transmission to shift normally.
11. Advanced Techniques: Using an Oscilloscope for Sensor Analysis
What advanced techniques can be used for sensor analysis? An oscilloscope, or lab scope, is a valuable tool for analyzing sensor signals in detail. Here’s how it can be used:
- Visualizing Waveforms: An oscilloscope displays the waveform of the sensor signal, allowing you to see its shape, amplitude, and frequency.
- Identifying Signal Abnormalities: By examining the waveform, you can identify issues such as signal dropouts, noise, or distortion.
- Diagnosing Intermittent Problems: An oscilloscope can capture intermittent sensor problems that may not be apparent with a scan tool or DMM.
- Comparing Signals: You can compare the waveforms of different sensors to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
- Analyzing PWM Signals: An oscilloscope is essential for analyzing pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals, which are commonly used in modern transmissions.
12. Reprogramming and Relearning Procedures
When are reprogramming and relearning procedures necessary? After replacing certain transmission components, such as the TCM or solenoids, it may be necessary to perform reprogramming or relearning procedures. These procedures help the TCM adapt to the new components and ensure optimal performance. Common procedures include:
- TCM Reprogramming: Updating the TCM software to the latest version.
- Quick Learn Procedure: Allowing the TCM to quickly learn the characteristics of the new components.
- Adaptive Learning Reset: Resetting the TCM’s adaptive learning to start fresh.
Refer to your vehicle’s service manual or a qualified technician for specific reprogramming and relearning procedures.
13. Understanding Default Strategies and Limp Mode
What happens when a sensor fails and the transmission enters limp mode? When a transmission sensor fails, the TCM typically enters a default strategy, often referred to as “limp mode.” In this mode, the transmission is limited to a single gear or a restricted range of gears to prevent further damage. This can result in reduced performance and fuel economy. Understanding limp mode is crucial for diagnosing and addressing transmission issues promptly.
14. The Role of Transmission Fluid Quality
How does transmission fluid quality affect sensor performance? The quality of the transmission fluid plays a critical role in the performance and longevity of transmission sensors. Contaminated or degraded fluid can cause sensors to malfunction or provide inaccurate readings. Regular transmission fluid changes, using the correct type of fluid, are essential for maintaining sensor health.
15. Selecting the Right Replacement Sensors
How do you choose the right replacement sensors for your vehicle? When replacing transmission sensors, it’s important to choose high-quality parts that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of premium replacement sensors to ensure reliable performance and durability. Consider the following factors when selecting replacement sensors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Quality: Choose sensors from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and reliability.
- Warranty: Look for sensors that come with a warranty to protect against defects.
- Reviews: Read customer reviews to get an idea of the sensor’s performance and durability.
16. Tips for Avoiding Common Diagnostic Mistakes
What are the common diagnostic mistakes to avoid when checking transmission sensors? Here are some tips to help you avoid common pitfalls:
- Verify the Code: Always verify the diagnostic trouble code before starting any repairs.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Don’t skip the visual inspection; it can often reveal obvious issues.
- Check Wiring and Connectors: Always check the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Use the Right Tools: Use the appropriate tools for the job, including a scan tool, DMM, and oscilloscope.
- Consult the Service Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and specifications.
- Don’t Assume: Don’t assume the sensor is faulty without performing thorough testing.
- Test Before Replacing: Always test the sensor before replacing it to confirm that it is indeed the problem.
- Follow the Procedures: Follow the diagnostic procedures outlined in the service manual carefully.
- Double-Check Your Work: Double-check your work to ensure that everything is properly connected and functioning correctly.
17. The Future of Transmission Sensor Technology
How is transmission sensor technology evolving? Transmission sensor technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Some emerging trends include:
- Smarter Sensors: Sensors with built-in processing capabilities that can perform more advanced diagnostics and provide more accurate data.
- Wireless Sensors: Wireless sensors that eliminate the need for wiring harnesses, reducing complexity and improving reliability.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors that can predict potential problems before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Integration with AI: Integration of sensor data with artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize transmission performance and efficiency.
18. DIY vs. Professional Diagnostics: Making the Right Choice
Should you attempt to diagnose and repair transmission sensor issues yourself, or should you seek professional help? The decision depends on your skill level, experience, and the complexity of the problem. DIY diagnostics can save you money, but they also carry the risk of misdiagnosis or further damage if not performed correctly. Professional diagnostics offer accuracy and expertise, but they can be more expensive. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Skill Level: Do you have the knowledge and experience to perform the necessary tests and repairs?
- Tools and Equipment: Do you have access to the necessary tools and equipment, such as a scan tool, DMM, and oscilloscope?
- Complexity of the Problem: Is the problem a simple sensor replacement, or is it a more complex issue requiring advanced diagnostics?
- Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with the risk of misdiagnosis or further damage?
- Cost: Compare the cost of DIY diagnostics with the cost of professional diagnostics.
19. Resources for Further Learning
Where can you find more information about transmission sensor diagnostics? Here are some valuable resources for further learning:
- Vehicle Service Manuals: Your vehicle’s service manual contains detailed information about transmission sensor diagnostics and repair procedures.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to automotive repair can provide valuable insights and advice from experienced technicians.
- Training Courses: Automotive training courses can provide hands-on experience and in-depth knowledge of transmission sensor diagnostics.
- Technical Articles: Technical articles published by automotive magazines and websites can offer valuable tips and techniques.
- CARDIAGTECH.NET: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wealth of information about transmission sensor diagnostics and repair, as well as a wide selection of high-quality tools and equipment.
20. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Transmission Diagnostics
Why choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for your transmission diagnostic needs? CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your transmission diagnostic needs. We offer:
- Wide Selection of Tools and Equipment: We carry a wide selection of high-quality scan tools, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and other tools and equipment needed for transmission sensor diagnostics.
- Expert Advice and Support: Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert advice and support to help you diagnose and repair transmission sensor issues.
- Competitive Prices: We offer competitive prices on all our products, so you can get the tools you need at a price you can afford.
- Fast Shipping: We offer fast shipping on all orders, so you can get your tools quickly and get back to work.
- Excellent Customer Service: We are committed to providing excellent customer service and ensuring your satisfaction.
Don’t let transmission sensor issues keep you off the road. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 and let us help you diagnose and repair your transmission problems quickly and efficiently. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our extensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment. Address your customer’s challenges by providing them with solutions that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Contact us now for a consultation on how our tools can elevate your garage’s performance.
FAQ: How to Check Sensors Related to the Automatic Transmission
1. What are the main sensors related to automatic transmission?
The main sensors include the Input Speed Sensor (ISS), Output Speed Sensor (OSS), Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor, Throttle Position Sensor (TPS), and Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor. These sensors monitor various parameters to ensure optimal transmission operation.
2. What symptoms indicate a failing transmission sensor?
Common symptoms include erratic shifting, harsh engagement, failure to shift, the check engine light illuminating, poor fuel economy, slipping, and stalling.
3. What tools are essential for checking transmission sensors?
Essential tools include a professional scan tool, digital multimeter (DMM), oscilloscope, wiring diagram, jack and jack stands, wheel chocks, and basic hand tools.
4. How do I check the input/output speed sensors?
Visually inspect the sensors and wiring, check for voltage at the sensor connector, measure the resistance across the sensor terminals, test the sensor signal with a scan tool or oscilloscope, and perform a road test while monitoring sensor data.
5. How do I inspect the Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor?
Access the TFT sensor, check the resistance across the sensor terminals, and monitor live data using a scan tool to ensure temperature readings correspond to the actual transmission fluid temperature.
6. What advanced diagnostics can scan tools perform?
Scan tools can read and clear DTCs, monitor live data, perform bidirectional tests, access freeze frame data, graph sensor data, and perform transmission resets.
7. Why is it important to inspect wiring and connectors?
Faulty wiring and connectors can cause sensor malfunctions and inaccurate readings. Inspect for damage, test for continuity, measure voltage drop, clean connector terminals, and inspect terminals for proper contact.
8. What are common sensor-related issues and their solutions?
Common issues include faulty sensors, wiring problems, connector issues, and TCM/PCM problems. Solutions include replacing the sensor, repairing or replacing wiring, cleaning or replacing connectors, and consulting a qualified technician for TCM/PCM issues.
9. How can I prevent sensor-related problems?
Preventive measures include regular transmission fluid changes, inspecting wiring and connectors, using high-quality replacement parts, and monitoring transmission performance for any changes.
10. When is reprogramming or relearning necessary?
Reprogramming or relearning procedures may be necessary after replacing certain transmission components, such as the TCM or solenoids, to help the TCM adapt to the new components and ensure optimal performance.