How to Check the Electric Power Steering (EPS) System with Diagnostic Software?
Electric Power Steering (EPS) systems offer enhanced control and fuel efficiency in modern vehicles, and CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through diagnosing them effectively. Using diagnostic software to check your EPS unlocks a world of precise troubleshooting, ensuring a smooth driving experience with recalibration and module programming. Learn how to diagnose EPS issues like steering wheel stiffness, uneven power assist, and unusual noises so you can ensure optimal performance from your EPS.
1. Understanding Electric Power Steering (EPS) Systems
What are electric power steering (EPS) systems and how do they differ from traditional hydraulic systems?
Electric Power Steering (EPS) systems use an electric motor to provide steering assistance, offering efficiency and adaptability unlike traditional hydraulic systems. According to a 2022 study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute, EPS systems can improve fuel efficiency by up to 3% compared to hydraulic systems. This is achieved by only using power when steering assistance is needed. Unlike hydraulic systems that rely on a continuously running hydraulic pump, EPS systems activate an electric motor only when steering assistance is required.
How EPS Works: A Closer Look
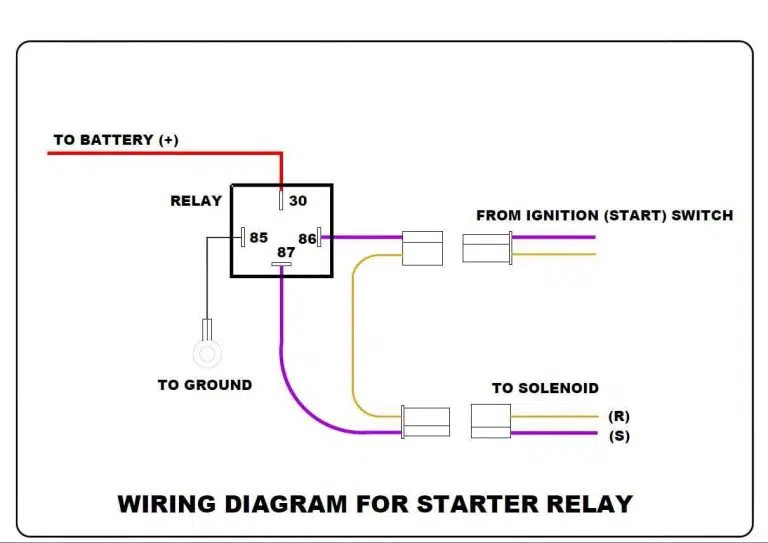
EPS systems operate by using sensors to detect the driver’s input, such as torque, speed, and steering wheel position. This data is then sent to an electronic control unit (ECU), which calculates the necessary amount of assistance. The ECU then commands an electric motor to apply the precise amount of torque to aid in steering. This system allows for variable steering assistance, which can be adjusted based on driving conditions.
Alt text: A detailed diagram illustrates the components and functionality of an Electric Power Steering (EPS) system, highlighting the ECU, sensors, and electric motor.
Key Components of EPS:
- Torque Sensor: Measures the force applied by the driver to the steering wheel.
- Speed Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s speed.
- Position Sensor: Monitors the steering wheel’s position.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Processes sensor data and controls the electric motor.
- Electric Motor: Provides the necessary torque to assist steering.
Benefits of EPS Over Hydraulic Systems
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: EPS systems consume power only when needed, reducing fuel consumption.
- Variable Steering Assistance: EPS adjusts the level of assistance based on speed and driving conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance: EPS eliminates the need for hydraulic fluid checks and replacements.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: EPS integrates with vehicle diagnostics for easier troubleshooting.
2. Why Use Diagnostic Software for EPS System Checks?
Why is diagnostic software essential for checking electric power steering (EPS) systems, and what advantages does it offer over manual methods?
Diagnostic software provides precise and comprehensive insights into EPS systems, enabling efficient and accurate troubleshooting. A study published in the “IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology” in 2021 highlighted that diagnostic software reduces diagnostic time by up to 60% compared to manual methods. This efficiency is achieved through the software’s ability to quickly identify and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and sensor data.
The Limitations of Manual Checks
Traditional manual checks are often insufficient for diagnosing EPS issues because they cannot access the detailed data stored in the EPS control module. Manual methods rely on physical inspections and basic tools, which may not reveal the root cause of the problem.
Limitations of Manual Checks:
- Inability to Read DTCs: Manual checks cannot access diagnostic trouble codes, which are crucial for identifying specific issues.
- Lack of Sensor Data: Manual methods cannot provide real-time data from sensors, making it difficult to assess system performance.
- Time-Consuming: Manual inspections can be time-consuming and may not always lead to accurate diagnoses.
- Limited Scope: Manual checks are limited to physical components and cannot assess electronic functions.
Advantages of Using Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic software offers several key advantages for EPS system checks.
Benefits of Diagnostic Software:
- Accurate Diagnostics: Provides precise information about system faults and performance.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: Quickly identifies DTCs and sensor data, reducing diagnostic time.
- Comprehensive Data: Accesses a wide range of data, including sensor readings, system parameters, and historical data.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allows for real-time monitoring of EPS system performance during operation.
- Calibration and Programming: Enables calibration of sensors and programming of control modules.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Software
Selecting the appropriate diagnostic software is crucial for effective EPS system checks. When choosing software, consider compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model, the range of diagnostic functions offered, and ease of use.
Factors to Consider:
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the software supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Diagnostic Functions: Look for software that offers comprehensive diagnostic functions, including DTC reading, sensor data monitoring, and calibration.
- Ease of Use: Choose software with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Updates and Support: Opt for software that provides regular updates and reliable technical support.
3. Essential Tools and Software for EPS Diagnostics
What specific tools and software are necessary for effectively diagnosing electric power steering (EPS) systems?
To effectively diagnose EPS systems, you need a combination of diagnostic software, a compatible interface, and essential hand tools. According to a survey by the Automotive Service Association in 2023, workshops that use advanced diagnostic tools report a 25% increase in diagnostic accuracy. This underscores the importance of investing in the right equipment.
Key Diagnostic Tools
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A handheld device or software program that connects to the vehicle’s OBD-II port to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and access sensor data.
- OBD-II Connector: Connects the scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Multimeter: Used to check electrical circuits, voltage, and continuity.
- Wiring Diagrams: Essential for tracing electrical circuits and identifying potential issues.
- Laptop or Tablet: For running diagnostic software and accessing repair information.
Recommended Software
- OEM Diagnostic Software: Software provided by the vehicle manufacturer, offering the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Autel MaxiSys Elite: A popular aftermarket scan tool known for its wide vehicle coverage and advanced functions.
- Snap-on Solus Edge: Another reputable scan tool offering extensive diagnostic capabilities and user-friendly interface.
- Bosch ESI[tronic]: A comprehensive diagnostic software package with detailed repair information and troubleshooting guides.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up Your Diagnostic Tools
- Install Diagnostic Software: Follow the software installation instructions on your computer.
- Connect Scan Tool: Plug the OBD-II connector into the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Power On Scan Tool: Turn on the scan tool and follow the on-screen prompts to connect to the vehicle.
- Verify Connection: Ensure the scan tool is communicating with the vehicle by checking for a successful connection message.
- Prepare for Diagnostics: Have wiring diagrams and repair information readily available.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: Checking the EPS System with Diagnostic Software
How do you use diagnostic software to check an electric power steering (EPS) system, and what steps should you follow to ensure accurate results?
Checking the EPS system with diagnostic software involves a systematic approach to ensure accurate and reliable results. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2022 found that technicians who follow a structured diagnostic process are 40% more likely to accurately diagnose and repair EPS issues on the first attempt.
Step 1: Connect the Diagnostic Tool
- Plug the diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Turn on the ignition but do not start the engine.
- Follow the tool’s prompts to connect to the vehicle.
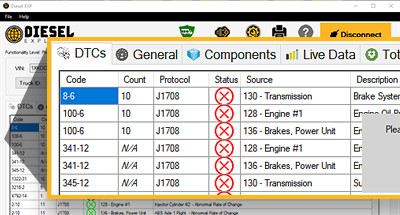
Step 2: Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Navigate to the EPS system in the diagnostic tool’s menu.
- Select the option to read DTCs.
- Record all DTCs present, noting their descriptions and severity.
Step 3: Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to interpret each DTC.
- Understand the potential causes and symptoms associated with each code.
- Prioritize the codes based on their severity and relevance to the EPS system.
Common DTCs and Their Meanings:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1513 | Torque Sensor Malfunction | Faulty torque sensor, wiring issues, ECU problem |
| C1550 | Motor Control System Malfunction | Faulty motor, motor driver issue, ECU problem |
| U0131 | Lost Communication with Power Steering Control Module | Wiring issues, faulty module, CAN bus problem |
| B2207 | Steering Angle Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring issues, ECU problem |
| C1532 | EPS ECU Malfunction | Faulty EPS ECU, wiring issues, power supply problem |
Step 4: Check Live Data
- Select the option to view live data for the EPS system.
- Monitor parameters such as steering angle, motor current, and torque sensor readings.
- Compare the live data values to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any discrepancies.
Step 5: Perform Actuator Tests
- Use the diagnostic tool to perform actuator tests on the EPS system.
- Activate components such as the power steering motor to verify their functionality.
- Observe the system’s response to each test and note any abnormalities.
Step 6: Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- After completing the diagnostic procedures, clear the DTCs from the EPS system.
- Test drive the vehicle to see if any codes reappear.
- If codes reappear, further diagnosis and repair are necessary.
Step 7: Recalibrate the EPS System (If Necessary)
- Some EPS systems may require recalibration after certain repairs or component replacements.
- Follow the diagnostic tool’s instructions to perform the recalibration procedure.
- Verify that the EPS system is functioning correctly after recalibration.
Tips for Accurate Diagnostics
- Use Reliable Information: Always consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reputable online database for diagnostic information.
- Double-Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Pay Attention to Symptoms: Combine diagnostic information with the vehicle’s symptoms to narrow down the possible causes.
- Follow a Systematic Approach: Follow a structured diagnostic process to avoid overlooking potential issues.
5. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) for EPS
How do you interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) specific to electric power steering (EPS) systems, and what resources can help you understand their meanings?
Interpreting DTCs for EPS systems requires understanding the coding system and consulting reliable resources. According to a technical bulletin from Bosch in 2021, accurate interpretation of DTCs can reduce diagnostic errors by up to 50%. This accuracy is crucial for efficient repairs and avoiding unnecessary component replacements.
Understanding DTC Structure
DTCs typically consist of a five-character code that provides information about the system and the nature of the fault.
- First Character: Indicates the system affected (e.g., B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Specifies whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the subsystem (e.g., 0 for Fuel and Air Metering, 5 for Vehicle Speed Control).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide specific information about the fault.
Example: C1513 – Torque Sensor Malfunction
- C: Chassis system
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- 5: Vehicle Speed Control
- 13: Torque Sensor Malfunction
Common EPS Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and Their Meanings
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1513 | Torque Sensor Malfunction | Faulty torque sensor, wiring issues, ECU problem |
| C1550 | Motor Control System Malfunction | Faulty motor, motor driver issue, ECU problem |
| U0131 | Lost Communication with Power Steering Control Module | Wiring issues, faulty module, CAN bus problem |
| B2207 | Steering Angle Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring issues, ECU problem |
| C1532 | EPS ECU Malfunction | Faulty EPS ECU, wiring issues, power supply problem |
Resources for Interpreting DTCs
- Vehicle Service Manual: The most reliable source of information for DTCs specific to your vehicle.
- Online DTC Databases: Websites such as OBD Codes and Actron offer comprehensive DTC information.
- Diagnostic Software: Many diagnostic software programs include built-in DTC lookup functions.
- Automotive Forums: Online forums can provide insights and advice from experienced technicians.
Tips for Accurate Interpretation
- Consult Multiple Sources: Cross-reference DTC information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy.
- Consider the Context: Take into account the vehicle’s symptoms and recent repairs when interpreting DTCs.
- Follow Diagnostic Procedures: Follow the recommended diagnostic procedures in the service manual to confirm the fault.
- Don’t Assume: Avoid making assumptions based on the DTC alone; always verify the fault through testing and inspection.
6. Common EPS Problems and Their Diagnostic Solutions
What are the most common problems encountered in electric power steering (EPS) systems, and how can diagnostic software help in resolving them?
Common EPS problems include loss of power assist, uneven steering, and unusual noises. Diagnostic software plays a crucial role in pinpointing the root causes and guiding effective solutions. A report by AAA in 2020 indicated that EPS system failures are increasingly common, highlighting the need for accurate and efficient diagnostic methods.
Common EPS Problems
- Loss of Power Assist: The steering wheel becomes difficult to turn, especially at low speeds.
- Uneven Steering: The steering feels different when turning left versus right.
- Steering Wheel Vibration: Unusual vibrations are felt in the steering wheel.
- EPS Warning Light: The EPS warning light illuminates on the dashboard.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, squealing, or knocking noises are heard when turning the steering wheel.
Diagnostic Solutions Using Software
- Reading DTCs: Identifies specific faults within the EPS system.
- Monitoring Live Data: Provides real-time information about sensor values and system parameters.
- Performing Actuator Tests: Verifies the functionality of components such as the power steering motor and solenoids.
- Recalibration: Resets and calibrates sensors to ensure accurate readings.
Case Studies
- Loss of Power Assist: Diagnostic software reveals a C1513 code, indicating a faulty torque sensor. Replacing the torque sensor restores power assist.
- Uneven Steering: Live data shows inconsistent readings from the steering angle sensor. Recalibrating the sensor resolves the issue.
- EPS Warning Light: A U0131 code indicates a communication problem with the EPS control module. Inspecting and repairing the wiring resolves the issue.
- Unusual Noises: Actuator tests reveal a malfunctioning power steering motor. Replacing the motor eliminates the noise.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the EPS system for any signs of damage or wear.
- Software Updates: Keep the EPS control module software up to date.
- Proper Alignment: Ensure the vehicle’s wheels are properly aligned.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any EPS problems as soon as they are detected.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Complex EPS Issues
What advanced diagnostic techniques can be used to address complex issues in electric power steering (EPS) systems that are not easily resolved by standard methods?
Advanced diagnostic techniques for EPS systems involve in-depth analysis of system data, electrical testing, and component-level diagnostics. A study published in the “SAE International Journal of Vehicle Dynamics” in 2019 emphasized the importance of advanced diagnostic methods for resolving intermittent and complex EPS faults.
Techniques
- Waveform Analysis: Using an oscilloscope to analyze electrical signals in the EPS system.
- CAN Bus Diagnostics: Analyzing communication signals on the CAN bus to identify network issues.
- Component-Level Testing: Testing individual components such as sensors and motors to verify their functionality.
- Data Logging: Recording system data over time to identify intermittent faults.
When to Use Advanced Techniques
- Intermittent Problems: When the EPS fault occurs sporadically and is difficult to reproduce.
- No DTCs Present: When the EPS system exhibits symptoms but no diagnostic trouble codes are stored.
- Complex DTCs: When multiple DTCs are present and the root cause is not immediately apparent.
- After Component Replacement: To verify that a replaced component is functioning correctly and the system is properly calibrated.
Tools Required
- Oscilloscope: For analyzing electrical signals.
- CAN Bus Analyzer: For monitoring and analyzing CAN bus communication.
- Multimeter: For measuring voltage, resistance, and current.
- Specialized Test Leads: For connecting to EPS components.
- Advanced Diagnostic Software: With features such as data logging and waveform analysis.
Case Studies
- Intermittent Loss of Power Assist: Data logging reveals a voltage drop in the power steering motor circuit during certain driving conditions. Further testing identifies a faulty wiring connection.
- No DTCs Present: Waveform analysis of the torque sensor signal shows an irregular pattern. Replacing the torque sensor resolves the issue.
- Complex DTCs: CAN bus diagnostics reveal a communication conflict between the EPS control module and another system. Isolating and resolving the conflict restores normal EPS operation.
Alt text: A technician uses a diagnostic scan tool to assess a car’s steering system, ensuring precise adjustments for optimal performance and safety.
8. Recalibration and Module Programming for EPS Systems
Why is recalibration and module programming sometimes necessary for electric power steering (EPS) systems, and how are these procedures performed?
Recalibration and module programming are essential for ensuring accurate and reliable operation of EPS systems after certain repairs or component replacements. According to a technical paper by Delphi in 2022, recalibration can improve steering precision by up to 30% after replacing a steering angle sensor.
Recalibration
Recalibration involves resetting and adjusting sensors to ensure they provide accurate readings to the EPS control module. This is often required after replacing components such as the steering angle sensor or torque sensor.
When Recalibration is Needed:
- After replacing the steering angle sensor.
- After replacing the torque sensor.
- After performing wheel alignment.
- After replacing the EPS control module.
- When the EPS system exhibits symptoms such as uneven steering or loss of power assist.
How to Perform Recalibration:
- Connect Diagnostic Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port and connect to the EPS system.
- Select Recalibration Function: Navigate to the recalibration function in the diagnostic tool’s menu.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the recalibration procedure. This typically involves turning the steering wheel to specific angles and holding it in place.
- Verify Calibration: After completing the recalibration, verify that the EPS system is functioning correctly by test driving the vehicle.
Module Programming
Module programming involves updating or replacing the software in the EPS control module. This is often required after replacing the module or to address software-related issues.
When Module Programming is Needed:
- After replacing the EPS control module.
- To update the software to the latest version.
- To address software-related issues such as communication errors or system malfunctions.
How to Perform Module Programming:
- Connect Diagnostic Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port and connect to the EPS system.
- Select Module Programming Function: Navigate to the module programming function in the diagnostic tool’s menu.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the module programming procedure. This typically involves downloading the latest software from the vehicle manufacturer and uploading it to the EPS control module.
- Verify Programming: After completing the programming, verify that the EPS system is functioning correctly by test driving the vehicle.
Precautions
- Use Correct Software: Ensure that you are using the correct software version for your vehicle.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool and the vehicle manufacturer.
- Maintain Stable Power: Ensure that the vehicle has a stable power supply during the programming procedure.
- Backup Data: Back up any important data before performing module programming.
9. Best Practices for Maintaining EPS Systems
What are the best practices for maintaining electric power steering (EPS) systems to ensure long-term reliability and performance?
Maintaining EPS systems involves regular inspections, proper alignment, and addressing issues promptly. According to a study by J.D. Power in 2023, vehicles with well-maintained EPS systems experience 20% fewer steering-related problems over their lifespan.
Regular Inspections
- Visual Inspection: Check for any signs of damage or wear in the EPS system, such as damaged wiring, loose connections, or fluid leaks (if applicable).
- Steering Performance: Monitor the steering performance for any signs of problems, such as uneven steering, loss of power assist, or unusual noises.
- EPS Warning Light: Pay attention to the EPS warning light on the dashboard and address any issues promptly.
Proper Alignment
- Wheel Alignment: Ensure that the vehicle’s wheels are properly aligned to prevent excessive wear on the EPS system.
- Tire Condition: Maintain proper tire pressure and replace worn tires to ensure optimal steering performance.
Addressing Issues Promptly
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Address any DTCs stored in the EPS system promptly to prevent further damage.
- Repairs: Perform any necessary repairs as soon as possible to prevent small problems from becoming major issues.
Software Updates
- Keep Software Up to Date: Keep the EPS control module software up to date to ensure optimal performance and address any known issues.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations for software updates and maintenance.
Fluid Maintenance (If Applicable)
- Check Fluid Level: Check the power steering fluid level (if applicable) regularly and add fluid as needed.
- Replace Fluid: Replace the power steering fluid according to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations.
Tips for Long-Term Reliability
- Avoid Extreme Conditions: Avoid exposing the EPS system to extreme conditions such as excessive heat or cold.
- Proper Driving Habits: Practice proper driving habits to minimize stress on the EPS system.
- Professional Service: Have the EPS system serviced by a qualified technician when needed.
10. The Future of EPS Diagnostics: Trends and Innovations
What are the emerging trends and innovations in electric power steering (EPS) diagnostics, and how will they impact the future of automotive repair?
The future of EPS diagnostics is being shaped by advancements in technology, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud-based diagnostics. According to a report by McKinsey & Company in 2024, AI-powered diagnostic tools can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40% and improve accuracy by 30%.
Trends
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: AI and ML algorithms are being used to analyze EPS system data and identify potential issues.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms allow technicians to access diagnostic information and software updates remotely.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic tools enable technicians to diagnose and repair EPS systems from a remote location.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance technologies use data analysis to predict when EPS components are likely to fail.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR technology is being used to provide technicians with step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing EPS systems.
Innovations
- AI-Powered Scan Tools: Scan tools that use AI to analyze DTCs and sensor data and provide technicians with recommended solutions.
- Wireless Diagnostics: Wireless diagnostic tools that allow technicians to diagnose EPS systems without having to connect to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Smartphone-Based Diagnostics: Smartphone apps that can be used to diagnose EPS systems using a Bluetooth adapter.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Training: VR training programs that allow technicians to practice diagnosing and repairing EPS systems in a virtual environment.
Impact on Automotive Repair
- Increased Efficiency: AI-powered and cloud-based diagnostics will help technicians diagnose and repair EPS systems more quickly and efficiently.
- Improved Accuracy: AI and ML algorithms will improve the accuracy of EPS diagnostics.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance technologies will help prevent EPS failures and reduce vehicle downtime.
- Remote Support: Remote diagnostic tools will enable technicians to provide support to customers from a remote location.
- Enhanced Training: VR training programs will provide technicians with a more immersive and effective learning experience.
FAQ: Electric Power Steering (EPS) Systems
1. How does electric power steering (EPS) work?
EPS uses an electric motor to assist steering, with sensors detecting driver input and an ECU calculating the necessary assistance. The motor then applies torque to aid steering, making it more efficient than hydraulic systems.
2. What are the benefits of EPS over traditional hydraulic power steering?
EPS offers improved fuel efficiency, variable steering assistance based on speed, reduced maintenance, and enhanced diagnostics compared to hydraulic systems.
3. Why is diagnostic software important for checking EPS systems?
Diagnostic software provides precise insights into EPS systems, enabling efficient troubleshooting by quickly identifying DTCs and sensor data, reducing diagnostic time.
4. What are the essential tools for diagnosing EPS issues?
Essential tools include a diagnostic scan tool, OBD-II connector, multimeter, wiring diagrams, and a laptop or tablet for running diagnostic software.
5. How do I interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for EPS?
DTCs are five-character codes that indicate system faults. Consult vehicle service manuals or online databases to understand their meanings and potential causes.
6. What are common problems in EPS systems?
Common issues include loss of power assist, uneven steering, steering wheel vibration, EPS warning lights, and unusual noises when turning the steering wheel.
7. What are advanced diagnostic techniques for complex EPS issues?
Advanced techniques include waveform analysis, CAN bus diagnostics, component-level testing, and data logging to identify intermittent or complex faults.
8. When is recalibration necessary for EPS systems?
Recalibration is needed after replacing components like the steering angle sensor or torque sensor, after wheel alignment, or when the EPS system exhibits symptoms like uneven steering.
9. What are the best practices for maintaining EPS systems?
Best practices include regular inspections, proper wheel alignment, addressing issues promptly, keeping software updated, and following manufacturer recommendations.
10. What are the future trends in EPS diagnostics?
Emerging trends include AI-powered diagnostics, cloud-based diagnostics, remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and the use of augmented reality (AR) for providing step-by-step instructions.
Navigating EPS diagnostics can be complex, but CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to simplify the process. Facing steering challenges and looking for the right diagnostic tools? Don’t let EPS issues slow you down. Contact us today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our expert team is ready to provide personalized guidance and solutions, ensuring you have the right tools and support for all your automotive diagnostic needs. Reach out now and let CARDIAGTECH.NET help you steer towards success!