How to Check the Oil Pump: A Comprehensive Guide
Is your vehicle’s engine not running as smoothly as it should? Are you concerned that the engine might not be pumping oil correctly? At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide a detailed guide on how to check the oil pump effectively. Understanding the signs of oil pump failure and knowing how to test the system can prevent severe engine damage. Read on to learn the essential steps and ensure your engine stays well-lubricated and in optimal condition. Explore how to diagnose issues, maintain oil pressure, and potentially save on costly repairs with our expert advice.
1. Understanding the Vital Role of the Oil Pump
Why is the oil pump so critical to your engine’s health? The oil pump is the heart of your engine’s lubrication system. Its primary role is to circulate oil from the oil pan to various engine components, ensuring they are adequately lubricated. According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Department of Mechanical Engineering in 2022, effective lubrication reduces friction, dissipates heat, and prevents wear and tear on critical engine parts. Without a properly functioning oil pump, engine components can suffer severe damage, leading to costly repairs or even complete engine failure. Understanding the importance of the oil pump is the first step in ensuring your vehicle’s longevity and performance. Regular checks and maintenance can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
1.1. Lubrication: The Engine’s Lifeblood
Why is lubrication considered the lifeblood of an engine? Lubrication minimizes friction between moving parts, reducing heat and wear. Insufficient lubrication can lead to rapid engine degradation, potentially causing irreversible damage. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), proper lubrication can extend the lifespan of engine components by up to 50%. Key benefits of effective lubrication include:
- Reduced Friction: Minimizes wear and tear on moving parts.
- Heat Dissipation: Helps regulate engine temperature.
- Prevention of Corrosion: Protects against rust and corrosion.
- Removal of Contaminants: Cleans and filters out harmful particles.
1.2. Common Types of Oil Pumps
What are the different types of oil pumps used in vehicles? Several types of oil pumps are used in vehicles, each designed with specific advantages and applications. According to a study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), the most common types include:
- Gear Pumps: Simple and reliable, used in many older vehicles.
- Rotor Pumps: More efficient and compact, often found in modern engines.
- Vane Pumps: Provide variable oil flow, optimizing performance under different conditions.
Understanding the type of oil pump in your vehicle can aid in proper diagnosis and maintenance. Each type has unique characteristics and potential failure points that require specific attention.
1.3. Consequences of Oil Pump Failure
What happens when an oil pump fails? The consequences of oil pump failure can be severe and lead to significant engine damage. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2023 found that oil pump failure is a leading cause of catastrophic engine failures. The primary consequences include:
- Engine Seizure: Lack of lubrication can cause moving parts to seize, resulting in complete engine failure.
- Bearing Damage: Insufficient oil flow can damage critical bearings, leading to engine knocking and reduced performance.
- Overheating: Friction from unlubricated parts can cause the engine to overheat rapidly, potentially causing warping or cracking of engine components.
- Increased Wear and Tear: Accelerated wear on engine parts can significantly shorten the engine’s lifespan.
2. Recognizing the Signs of a Failing Oil Pump
How can you tell if your oil pump is failing? Recognizing the signs of a failing oil pump early can save you from costly repairs. According to a report by AAA, addressing minor engine issues promptly can prevent up to 80% of major breakdowns. Be vigilant for these key symptoms:
2.1. Low Oil Pressure Warning Light
Why does the oil pressure light come on? The oil pressure warning light is a critical indicator of potential problems within the engine’s lubrication system. This light illuminates when the oil pressure drops below a safe level, signaling that the engine is not receiving adequate lubrication. A study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Transportation Sustainability Research Center in 2022 found that ignoring the oil pressure light can lead to severe engine damage within a short period. Possible causes for the light turning on include:
- Low Oil Level: Insufficient oil in the system.
- Faulty Oil Pump: The pump is not generating enough pressure.
- Clogged Oil Filter: Restrictions in the oil flow.
- Oil Leak: Loss of oil from the system.
- Defective Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor providing false readings.
When the oil pressure light activates, it’s crucial to investigate immediately to prevent further engine damage. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers diagnostic tools to help you pinpoint the issue accurately.
2.2. Engine Overheating
How does a failing oil pump cause engine overheating? A failing oil pump can lead to engine overheating because it reduces the engine’s ability to regulate temperature effectively. When the oil pump doesn’t circulate enough oil, friction between moving parts increases dramatically. This friction generates excessive heat, which the oil is supposed to dissipate. According to research from Texas A&M University’s Engineering Department in 2023, insufficient lubrication can raise engine temperatures by as much as 30-40 degrees Fahrenheit, leading to overheating and potential engine damage.
2.3. Unusual Engine Noises
What types of noises indicate oil pump problems? Unusual engine noises can be a telltale sign of oil pump issues. These noises often result from inadequate lubrication, causing increased friction between moving parts. According to a study by the National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF) in 2022, common noises associated with oil pump failure include:
- Ticking or Tapping: Caused by lifters and valves not receiving enough oil.
- Knocking: Indicates severe friction and potential damage to bearings and connecting rods.
- Whining: May suggest a worn or failing oil pump struggling to maintain pressure.
2.4. Metallic Shavings in the Oil
Why are metallic shavings a concern? Metallic shavings in the oil are a serious concern, indicating significant wear and tear within the engine. These particles are often the result of metal-on-metal contact due to inadequate lubrication. A study by the Argonne National Laboratory’s Center for Transportation Research in 2023 found that the presence of metallic shavings can accelerate engine damage and reduce its lifespan. Key reasons for concern include:
- Increased Friction: Shavings act as abrasives, increasing friction and wear.
- Clogging: Metallic particles can clog oil passages, further reducing lubrication.
- Bearing Damage: Shavings can embed in bearings, causing premature failure.
2.5. Decreased Engine Performance
How does oil pump failure affect performance? Oil pump failure significantly impacts engine performance by reducing lubrication to critical components. This leads to increased friction, heat, and wear, all of which degrade the engine’s efficiency and power output. A report by the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in 2022 highlighted that inadequate lubrication can decrease engine horsepower by as much as 15-20%. Key effects on performance include:
- Reduced Power: Insufficient lubrication leads to increased friction, reducing the engine’s ability to generate power.
- Poor Fuel Economy: The engine has to work harder to overcome friction, consuming more fuel.
- Hesitation and Stalling: Lack of lubrication can cause the engine to run rough, leading to hesitation and stalling.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Your Oil Pump
How do you check your oil pump? Testing your oil pump involves several steps to ensure accurate diagnosis. Follow this guide to assess your oil pump’s performance effectively.
3.1. Gather Necessary Tools and Equipment
What tools do you need to check an oil pump? To accurately check your oil pump, you’ll need specific tools and equipment. Here’s a list to get you started:
| Tool/Equipment | Description | Why You Need It |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Pressure Gauge Kit | Measures the oil pressure in your engine. | Essential for determining if the oil pump is producing adequate pressure. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers reliable pressure gauge kits. |
| Socket Set | Used to remove and install the oil pressure sensor or sending unit. | Necessary for accessing the oil pressure port. |
| Wrench Set | Provides additional options for removing and installing components. | Versatile for various tasks during the process. |
| Screwdrivers (Various Sizes) | Used for removing and installing screws and fasteners. | Useful for accessing components and removing covers. |
| Multimeter | Tests electrical connections and wiring. | Helps diagnose electrical issues related to the oil pressure sensor. |
| Oil Filter Wrench | Removes the oil filter to inspect for debris. | Important for checking the oil filter for metallic shavings or other contaminants. |
| Drain Pan | Catches oil when removing the oil filter or other components. | Prevents spills and keeps your workspace clean. |
| Jack and Jack Stands | Lifts the vehicle safely to access the oil pump or related components. | Provides safe and stable access to the underside of the vehicle. |
| Safety Glasses and Gloves | Protects your eyes and hands from oil and other fluids. | Ensures safety during the process. |
| Shop Rags or Paper Towels | Cleans up spills and wipes down tools and components. | Essential for maintaining a clean workspace. |
| Service Manual for Your Vehicle | Provides specific instructions and diagrams for your vehicle model. | Offers detailed guidance and torque specifications for your specific vehicle. |
| Diagnostic Scanner (OBD-II) | Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). | Helps identify any error codes related to the oil pressure or other engine issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic scanners for accurate and efficient diagnostics. |
| Inspection Light or Flashlight | Provides light in dark areas for better visibility. | Useful for inspecting the oil pump and related components. |
| Torque Wrench | Ensures bolts and nuts are tightened to the correct specifications. | Prevents over-tightening or under-tightening, ensuring components are properly secured. |
| Penetrating Oil | Helps loosen rusted or stuck bolts and nuts. | Makes disassembly easier and prevents damage to components. |
| Camera or Smartphone | Takes pictures of components before disassembly. | Helps with reassembly and ensures everything goes back in the correct place. |
3.2. Check the Oil Level and Condition
Why is checking the oil level important? Checking the oil level and condition is crucial for diagnosing potential oil pump issues. Low oil levels can cause the oil pump to suck air, leading to reduced pressure and potential damage. According to Mobil Oil, maintaining the correct oil level ensures proper lubrication and cooling of engine components. To check the oil level:
- Park your vehicle on a level surface.
- Wait for the engine to cool down.
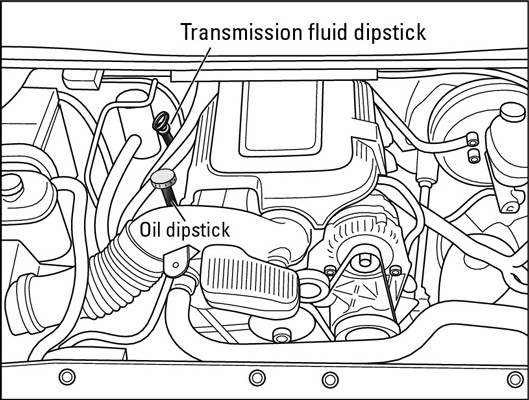
- Locate the dipstick, usually marked with an oil can symbol.
- Remove the dipstick and wipe it clean.
- Reinsert the dipstick fully, then remove it again.
- Check the oil level against the “min” and “max” markings.
If the oil level is low, add the recommended type of oil until it reaches the “max” mark. Also, inspect the oil’s condition. Clean oil should be amber in color. Dark, sludgy oil indicates contamination or degradation, which can affect oil pump performance.
3.3. Inspect the Oil Pressure Sensor
What does the oil pressure sensor do? The oil pressure sensor monitors the oil pressure in your engine and sends a signal to the dashboard gauge or warning light. A faulty sensor can provide inaccurate readings, leading to false alarms or a failure to detect low oil pressure. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), a malfunctioning oil pressure sensor can lead to unnecessary repairs or, conversely, failure to address critical engine issues. To inspect the sensor:
- Locate the oil pressure sensor, typically near the oil filter or on the engine block.
- Check the wiring for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s electrical continuity and voltage.
- Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications.
If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one from CARDIAGTECH.NET to ensure accurate readings and proper engine monitoring.
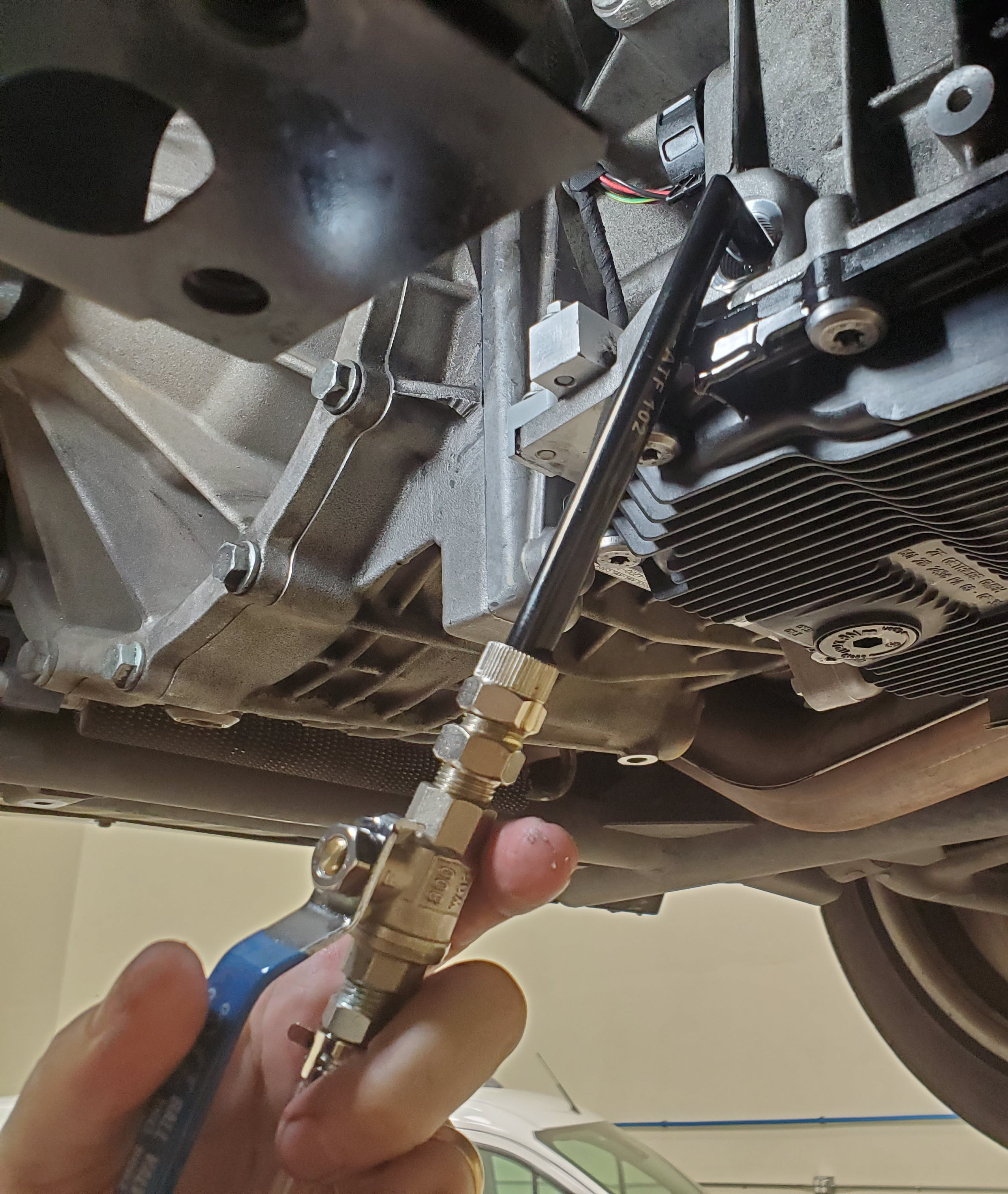
3.4. Use an Oil Pressure Gauge
How do you use an oil pressure gauge? Using an oil pressure gauge is essential for accurately assessing your oil pump’s performance. This tool provides a direct reading of the oil pressure, helping you determine if the pump is functioning correctly. Follow these steps:
- Locate the oil pressure sending unit on your engine.
- Remove the sending unit using a wrench.
- Install the oil pressure gauge in place of the sending unit.
- Start the engine and let it idle.
- Observe the gauge reading.
Compare the reading to your vehicle’s manufacturer specifications. For example, many engines should have an oil pressure of 20-60 PSI at idle. Low pressure indicates a potential issue with the oil pump. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality oil pressure gauges for accurate testing.
3.5. Check for Clogged Oil Filter
Why does a clogged oil filter affect oil pressure? A clogged oil filter restricts oil flow, reducing oil pressure and potentially damaging the engine. The oil filter removes contaminants from the oil, and over time, it can become clogged with dirt, debris, and sludge. According to research from the American Petroleum Institute (API), a clogged oil filter can decrease oil pressure by as much as 5-10 PSI. Here’s how to check for a clogged oil filter:
- Locate the oil filter on your engine.
- Remove the oil filter using an oil filter wrench.
- Inspect the filter for excessive dirt, debris, or sludge.
- Cut open the old filter and examine the pleats for contaminants.
If the oil filter is clogged, replace it with a new one. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of high-quality oil filters to ensure proper oil flow and engine protection.
3.6. Inspect the Oil Pump Itself
How do you inspect the oil pump? Inspecting the oil pump directly involves removing it from the engine and examining its components for wear or damage. This process requires some mechanical skill and should be done carefully. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Drain the Oil: Remove the oil drain plug and drain all the engine oil into a drain pan.
- Remove the Oil Pan: Unbolt the oil pan and carefully remove it. You may need to disconnect other components to access the oil pan.
- Access the Oil Pump: The oil pump is typically located inside the oil pan, attached to the engine block.
- Remove the Oil Pump: Unbolt the oil pump and carefully remove it.
- Inspect the Pump:
- Check the pump housing for cracks or damage.
- Examine the gears or rotors for wear, damage, or excessive play.
- Look for any signs of blockage or debris inside the pump.
If you find significant wear or damage, the oil pump needs to be replaced. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality oil pumps to keep your engine running smoothly.
4. Interpreting the Results of Your Oil Pump Check
What do the different readings mean? Understanding the results of your oil pump check is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. Different readings indicate various issues that need to be addressed. Here’s how to interpret the results:
4.1. Understanding Normal Oil Pressure Readings
What is considered normal oil pressure? Normal oil pressure varies depending on the vehicle and engine type, but generally falls within a specific range. According to data from various automotive manufacturers, typical oil pressure readings are:
- At Idle: 20-30 PSI (pounds per square inch)
- At 2,000 RPM: 40-60 PSI
- During Cold Start: Can be higher, but should stabilize within the normal range once the engine warms up.
Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the specific oil pressure specifications for your make and model. Staying within these ranges ensures adequate lubrication and optimal engine performance.
4.2. Identifying Low Oil Pressure Causes
What causes low oil pressure? Low oil pressure can result from several underlying issues, each requiring specific attention. Understanding these causes is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective repair. Common causes include:
- Low Oil Level: Insufficient oil in the system, preventing the pump from drawing enough oil.
- Worn Oil Pump: A worn pump may not generate sufficient pressure due to internal wear.
- Clogged Oil Filter: Restrictions in the filter can impede oil flow and reduce pressure.
- Oil Leaks: Leaks in the system can reduce the overall oil volume and pressure.
- Worn Engine Bearings: Excessive clearance in the bearings can cause a drop in oil pressure.
- Faulty Oil Pressure Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor can provide inaccurate low-pressure readings.
- Incorrect Oil Viscosity: Using the wrong type of oil can affect its ability to maintain pressure.
4.3. Diagnosing High Oil Pressure Issues
What causes high oil pressure? High oil pressure can also indicate problems within the engine’s lubrication system. While less common than low oil pressure, it can still cause significant damage if left unaddressed. Common causes of high oil pressure include:
- Clogged Oil Passages: Blockages in the oil lines can cause pressure to build up.
- Faulty Oil Pressure Regulator: A malfunctioning regulator can prevent the system from relieving excess pressure.
- Incorrect Oil Filter: Using the wrong type of oil filter can restrict oil flow and increase pressure.
- Cold Weather: Cold temperatures can increase oil viscosity, leading to higher pressure readings, especially during startup.
4.4. Using Diagnostic Codes for Oil Pump Problems
How can diagnostic codes help? Diagnostic codes, retrieved using an OBD-II scanner, can provide valuable insights into oil pump problems. These codes can help pinpoint specific issues within the lubrication system, saving time and effort in the diagnostic process. Common codes related to oil pressure include:
- P0520: Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Circuit Malfunction
- P0521: Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Range/Performance
- P0522: Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Low Voltage
- P0523: Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch High Voltage
- P06DD: Dual Stage Oil Pump Control Circuit Performance/Stuck Off
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic scanners to help you read and interpret these codes accurately.
5. Repairing or Replacing a Faulty Oil Pump
When is it time to replace the oil pump? If your oil pump is failing, deciding whether to repair or replace it depends on the extent of the damage and the overall condition of the engine. In many cases, replacement is the most reliable option to ensure long-term engine health.
5.1. Steps for Replacing an Oil Pump
How do you replace an oil pump? Replacing an oil pump is a detailed process that requires careful attention to ensure proper installation and function. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Tools and Equipment: Ensure you have all necessary tools, including a socket set, wrench set, screwdrivers, oil filter wrench, drain pan, jack, jack stands, safety glasses, and gloves.
- Drain the Oil: Remove the oil drain plug and drain all the engine oil into a drain pan.
- Remove the Oil Pan: Unbolt the oil pan and carefully remove it. You may need to disconnect other components to access the oil pan.
- Access the Oil Pump: The oil pump is typically located inside the oil pan, attached to the engine block.
- Remove the Old Oil Pump: Unbolt the old oil pump and carefully disconnect any lines or electrical connectors.
- Install the New Oil Pump:
- Ensure the new oil pump is the correct part for your vehicle. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality oil pumps.
- Install the new oil pump in the reverse order of removal, ensuring all bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect any lines or electrical connectors.
- Reinstall the Oil Pan: Clean the oil pan and install a new gasket. Bolt the oil pan back onto the engine, tightening the bolts to the specified torque.
- Replace the Oil Filter: Remove the old oil filter and install a new one.
- Add Oil: Refill the engine with the recommended type and amount of oil.
- Check for Leaks: Start the engine and check for any oil leaks around the oil pan and oil filter.
- Test the Oil Pressure: Use an oil pressure gauge to ensure the oil pump is functioning correctly and providing adequate pressure.
5.2. Choosing the Right Replacement Oil Pump
What should you look for in a new oil pump? Selecting the right replacement oil pump is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. Consider these factors when choosing a new oil pump:
- Compatibility: Ensure the oil pump is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and engine type. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of oil pumps designed for various vehicles.
- Quality: Choose a high-quality oil pump from a reputable manufacturer. Look for pumps made from durable materials with precise engineering.
- Type: Determine the type of oil pump your vehicle requires (e.g., gear, rotor, vane) and select the appropriate replacement.
- Reviews: Read reviews and ratings from other customers to gauge the reliability and performance of the oil pump.
- Warranty: Check the warranty offered by the manufacturer. A longer warranty indicates greater confidence in the product’s quality and durability.
5.3. Essential Maintenance Tips to Extend Oil Pump Life
How can you extend the life of your oil pump? Maintaining your vehicle’s lubrication system is crucial for extending the life of the oil pump and preventing costly repairs. Follow these essential maintenance tips:
| Maintenance Tip | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Oil Changes | Change your engine oil and filter at the manufacturer-recommended intervals. | Ensures clean oil is circulating through the engine, reducing wear and tear on the oil pump and other components. |
| Use the Correct Oil | Use the oil viscosity and type recommended for your vehicle. | Ensures proper lubrication and oil pressure, preventing excessive wear on the oil pump. |
| Check Oil Level Regularly | Monitor the oil level and top off as needed to maintain the correct level. | Prevents the oil pump from sucking air, which can reduce pressure and damage the pump. |
| Inspect for Leaks | Regularly check for oil leaks around the engine, oil pan, and oil filter. | Addresses leaks promptly to maintain adequate oil pressure and prevent oil pump starvation. |
| Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions | Minimize harsh acceleration, high RPMs, and excessive idling. | Reduces stress on the engine and lubrication system, prolonging the life of the oil pump. |
| Use High-Quality Oil Filters | Use high-quality oil filters to trap contaminants and prevent them from circulating through the engine. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of premium oil filters to keep your engine running smoothly. | Ensures clean oil is supplied to the engine, reducing wear on the oil pump and other components. |
| Monitor Oil Pressure | Keep an eye on the oil pressure gauge or warning light. | Alerts you to potential issues early, allowing you to address them before they cause significant damage. |
| Perform Regular Engine Tune-Ups | Ensure the engine is properly tuned, including the fuel system and ignition system. | Helps the engine run efficiently and smoothly, reducing stress on the lubrication system. |
| Keep the Engine Clean | Regularly clean the engine to remove dirt and debris, which can cause overheating and stress on the oil pump. | Helps maintain proper engine temperature and reduces strain on the lubrication system. |
| Address Issues Promptly | If you notice any signs of oil pump problems, such as low oil pressure or unusual engine noises, address them promptly to prevent further damage. | Prevents minor issues from escalating into major problems, saving you time and money in the long run. |
6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Oil Pump Maintenance
How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help you? CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. We offer a wide range of high-quality tools and equipment to help you maintain your vehicle’s oil pump and lubrication system effectively.
6.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
What diagnostic tools does CARDIAGTECH.NET offer? CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a variety of advanced diagnostic tools to help you accurately assess your oil pump’s performance. Our selection includes:
- Oil Pressure Gauge Kits: Measure the oil pressure in your engine with precision.
- OBD-II Scanners: Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to oil pressure and other engine issues.
- Multimeters: Test electrical connections and wiring to diagnose sensor problems.
6.2. Premium Oil Pumps and Components
What oil pump components are available? CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of premium oil pumps and components to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity. Our selection includes:
- Replacement Oil Pumps: High-quality oil pumps designed for various vehicle makes and models.
- Oil Filters: Premium oil filters to keep your oil clean and free from contaminants.
- Oil Pressure Sensors: Accurate and reliable sensors to monitor oil pressure effectively.
- Oil Pan Gaskets: Durable gaskets to prevent oil leaks and maintain proper sealing.
6.3. Expert Advice and Support
How can CARDIAGTECH.NET support you? At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing expert advice and support to help you maintain your vehicle’s oil pump and lubrication system. Our team of experienced technicians can assist you with:
- Troubleshooting: Diagnosing oil pump problems and identifying the root cause.
- Product Selection: Recommending the right tools and components for your vehicle.
- Installation Guidance: Providing step-by-step instructions for replacing or repairing oil pump components.
- Maintenance Tips: Offering essential maintenance tips to extend the life of your oil pump and engine.
Is your engine showing signs of oil pump failure? Don’t wait until it’s too late! Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and high-quality diagnostic tools and components. Our team is ready to help you diagnose and fix any oil pump issues, ensuring your engine stays well-lubricated and running smoothly.
Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your partner in maintaining a healthy and efficient engine.
7. FAQs About Oil Pump Checks
7.1. How Often Should I Check My Oil Pump?
How often should you check your oil pump? Ideally, you should check your oil pump every time you perform an oil change. This allows you to monitor the oil’s condition, check for any unusual noises, and ensure the oil pressure is within the normal range. According to recommendations from automotive experts, a visual inspection during each oil change can help catch potential issues early.
7.2. Can I Drive with a Failing Oil Pump?
Is it safe to drive with a failing oil pump? No, it is not safe to drive with a failing oil pump. A failing oil pump can lead to severe engine damage due to inadequate lubrication. Driving with low oil pressure can cause engine overheating, bearing damage, and even complete engine seizure. If you suspect your oil pump is failing, stop driving immediately and address the issue.
7.3. What Is the Lifespan of an Oil Pump?
How long does an oil pump last? The lifespan of an oil pump varies depending on the vehicle, driving conditions, and maintenance practices. However, most oil pumps are designed to last for at least 100,000 to 150,000 miles. Regular oil changes and proper maintenance can help extend the lifespan of your oil pump.
7.4. Can Low Oil Level Damage the Oil Pump?
Can low oil levels affect the oil pump? Yes, low oil levels can damage the oil pump. When the oil level is too low, the pump may suck air, leading to reduced pressure and potential damage to the pump’s internal components. Maintaining the correct oil level is crucial for ensuring proper lubrication and protecting the oil pump.
7.5. How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Oil Pump?
What is the average cost to replace an oil pump? The cost to replace an oil pump can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, as well as the labor costs in your area. On average, the cost ranges from $300 to $1,000, including parts and labor. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for high-quality replacement oil pumps at competitive prices.
7.6. Can I Replace the Oil Pump Myself?
Is it a DIY job to replace the oil pump? Replacing an oil pump is a complex task that requires mechanical skill and specific tools. If you are experienced with automotive repairs and have the necessary tools, you may be able to replace the oil pump yourself. However, if you are not comfortable with this type of repair, it is best to have a professional mechanic do the job.
7.7. How Do I Know If My Oil Pressure Sensor Is Bad?
How can you tell if the oil pressure sensor is faulty? Signs of a bad oil pressure sensor include:
- Inaccurate oil pressure readings on the dashboard gauge.
- The oil pressure warning light turning on and off intermittently.
- The engine running rough or stalling.
- Diagnostic trouble codes related to the oil pressure sensor.
Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s electrical continuity and voltage. If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
7.8. What Is the Difference Between an Oil Pump and a Water Pump?
What is the function of an oil pump compared to a water pump? The oil pump and water pump serve different functions in the engine. The oil pump circulates oil to lubricate engine components, while the water pump circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature. Both are essential for maintaining engine health and performance.
7.9. Can a Bad Oil Filter Cause Low Oil Pressure?
How does the oil filter affect oil pressure? Yes, a clogged or faulty oil filter can cause low oil pressure. A restricted oil filter can impede oil flow, reducing the overall pressure in the lubrication system. Regularly replacing the oil filter helps maintain proper oil pressure and protects the engine from damage.
7.10. What Are the Symptoms of a Clogged Oil Pickup Tube?
What happens if the oil pickup tube is clogged? Symptoms of a clogged oil pickup tube include:
- Low oil pressure.
- Engine overheating.
- Unusual engine noises.
- Metallic shavings in the oil.
A clogged oil pickup tube restricts oil flow to the oil pump, leading to these issues. Clean or replace the oil pickup tube to restore proper oil flow.