How to Clear OBD-II Fault Codes After Repair: A Comprehensive Guide

Clearing OBD-II fault codes after a repair is crucial for ensuring your vehicle’s optimal performance and verifying the effectiveness of the fix. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to accomplish this using an OBD-II scanner, ensuring you can confidently maintain your vehicle. This guide covers everything from understanding fault codes to the actual clearing process, and also highlights the importance of proper diagnostics and repairs.
1. Understanding OBD-II Fault Codes
What are OBD-II fault codes, and why are they important?
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) fault codes are standardized codes used to identify issues within a vehicle’s engine, transmission, and other systems. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD-II systems were mandated in all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 in the United States to monitor and report on vehicle emissions. These codes are crucial because they provide valuable information for diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems. Without them, technicians would have a much harder time pinpointing the source of a problem.
- Importance of OBD-II Codes:
- Emission Control: Ensures vehicles meet emission standards, helping to reduce air pollution.
- Early Problem Detection: Identifies minor issues before they become major, costly repairs.
- Standardized Diagnostics: Provides a consistent method for technicians to diagnose issues across different vehicle makes and models.
2. Identifying Search Intent
What are the common reasons people search for information on clearing OBD-II fault codes?
Understanding the search intent behind “How to clear OBD-II fault codes after repair?” is essential for providing relevant and helpful content. Here are five common search intents:
- DIY Repair Verification: Users want to confirm that their self-performed repairs have successfully resolved the issue and that the check engine light will stay off.
- Post-Repair Reset: After a professional repair, users want to clear the codes themselves to avoid additional charges from the mechanic for this simple task.
- Understanding Code Meanings: Users are curious about what specific fault codes mean and whether clearing them is appropriate after addressing the underlying issue.
- Tool Usage Guidance: Novice users seek step-by-step instructions on how to use an OBD-II scanner to clear codes effectively.
- Preventing Recurring Issues: Users want to learn how to ensure the fault codes don’t reappear by properly diagnosing and fixing the root cause of the problem.
3. Essential Tools for Clearing OBD-II Codes
What tools do you need to clear OBD-II codes effectively?
To effectively clear OBD-II fault codes, you’ll need the right tools. Here’s a breakdown:
- OBD-II Scanner: This is the primary tool for reading and clearing fault codes. Ensure the scanner supports both reading and clearing functions.
- Vehicle Repair Manual: A repair manual specific to your vehicle’s make and model can provide detailed information about fault codes and repair procedures.
- Basic Hand Tools: Depending on the repair needed, you may require tools like wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Safety Gear: Always wear safety glasses and gloves when working on your vehicle.
A reliable OBD-II scanner, such as the CGSULIT SC301 available at CARDIAGTECH.NET, is an invaluable tool for any car owner or technician. It allows you to diagnose and clear codes efficiently.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing OBD-II Fault Codes
How do you clear OBD-II fault codes after completing a repair?
Clearing OBD-II fault codes involves a series of steps that require careful attention. Here’s a detailed guide:
4.1. Verify the Repair
Before attempting to clear any codes, ensure that the underlying issue has been properly diagnosed and repaired. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), prematurely clearing codes without addressing the root cause can lead to recurring problems and potentially more severe damage.
- Check Engine Light: Confirm that the check engine light is no longer illuminated after the repair.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to see if the issue reappears under normal driving conditions.
- Monitor System Data: Use the OBD-II scanner to monitor relevant system data to ensure it is within normal operating parameters.
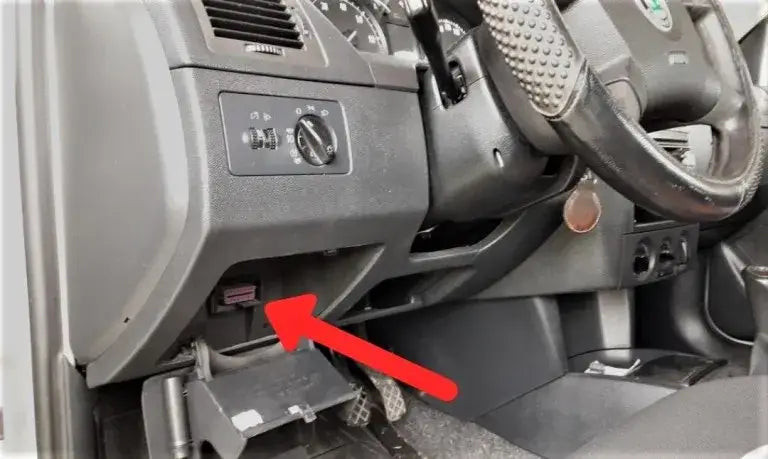
4.2. Locate the OBD-II Port
The OBD-II port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include near the steering column, in the center console, or behind a small panel.
- Standard Location: Most vehicles adhere to the standard location for ease of access.
- Check Your Manual: If you’re having trouble finding the port, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
 Locate the OBDII port in your car
Locate the OBDII port in your car
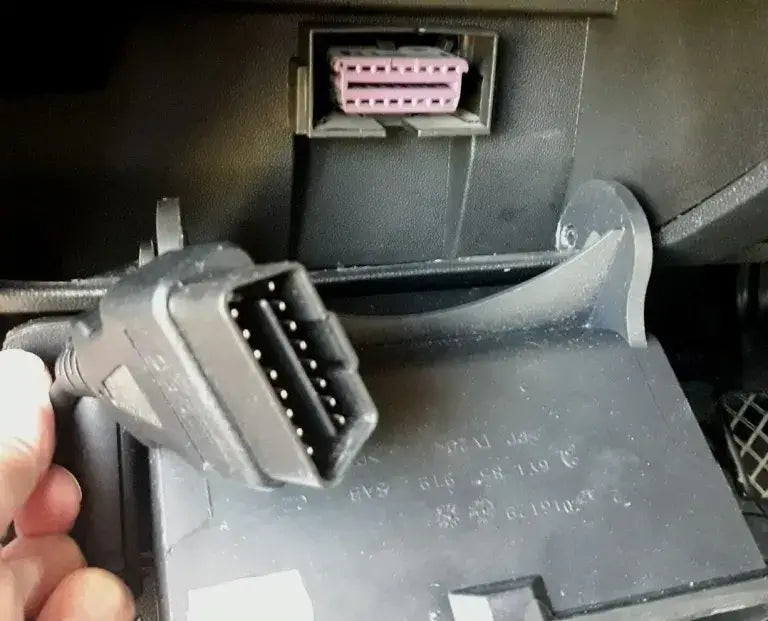
4.3. Connect the OBD-II Scanner
With the ignition off, plug the OBD-II scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Proper Connection: A secure connection is vital for accurate data transmission.
- Check for Power: Some scanners will power on automatically, while others may require you to turn them on manually.
 Connect the OBD code reader to your car's OBDII port
Connect the OBD code reader to your car's OBDII port
4.4. Turn On the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s computer and allows the scanner to communicate with it.
- Avoid Starting the Engine: Starting the engine can interfere with the scanning process.
- Check Scanner Display: Ensure the scanner is powered on and displaying information.
 Turn On the Ignition to access the car's computer
Turn On the Ignition to access the car's computer
4.5. Read the Fault Codes
Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored fault codes. The scanner will display a list of codes, each corresponding to a specific issue.
- Note the Codes: Record each code for future reference and troubleshooting.
- Interpret the Codes: Use the scanner’s built-in database or a reliable online resource to interpret the meaning of each code.
 Allow the OBD code reader to scan your car for fault codes
Allow the OBD code reader to scan your car for fault codes
4.6. Clear the Fault Codes
Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. Follow the prompts to clear the stored fault codes.
- Confirmation Prompt: The scanner may ask for confirmation before clearing the codes.
- Verify Clearing: After clearing, re-read the codes to ensure they have been successfully cleared.
 Read and interpret the error codes displayed by the OBD2 code reader
Read and interpret the error codes displayed by the OBD2 code reader
4.7. Verify the Check Engine Light
After clearing the codes, start the engine and check if the check engine light remains off. If it comes back on, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been fully resolved.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to the vehicle’s performance during a test drive to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Check for Pending Codes: Some scanners can show pending codes, which indicate potential future issues.
4.8. Disconnect the Scanner
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the OBD-II scanner from the port.
- Proper Removal: Gently remove the scanner to avoid damaging the port.
- Store the Scanner: Keep the scanner in a safe place for future use.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
What are the common pitfalls when clearing OBD-II codes?
Clearing OBD-II codes can be straightforward, but several common mistakes can lead to further complications. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
- Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Issue: The most common mistake is clearing the codes without addressing the underlying problem. This will only result in the check engine light coming back on.
- Using a Faulty Scanner: Ensure your OBD-II scanner is functioning correctly and compatible with your vehicle. A faulty scanner can provide inaccurate readings or fail to clear codes properly.
- Ignoring Pending Codes: Pending codes indicate potential future issues. Ignoring them can lead to more significant problems down the road.
- Forgetting to Verify the Repair: Always verify that the repair has been successful before clearing the codes. This includes test driving the vehicle and monitoring system data.
- Damaging the OBD-II Port: Be gentle when connecting and disconnecting the scanner to avoid damaging the OBD-II port.
6. Understanding Different Types of OBD-II Codes
What are the various types of OBD-II codes?
OBD-II codes are categorized into different types, each indicating the system affected. Here’s a breakdown:
- P (Powertrain) Codes: These relate to the engine, transmission, and associated components. Examples include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) and P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1).
- B (Body) Codes: These pertain to systems like airbags, power windows, and seats. An example is B1000 (ECU Malfunction).
- C (Chassis) Codes: These codes involve systems such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and suspension. An example is C0040 (Front Right Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction).
- U (Network) Codes: These relate to the communication network between different vehicle systems. An example is U0100 (Lost Communication With ECM/PCM).
Understanding these categories can help you narrow down the potential issue and perform more targeted diagnostics.
7. The Importance of Proper Diagnostics
Why is accurate diagnosis crucial before clearing OBD-II codes?
Proper diagnostics are paramount before clearing any OBD-II codes. Clearing codes without identifying and fixing the underlying issue is akin to treating the symptom without addressing the disease. According to a study by AAA, faulty diagnostics account for a significant percentage of repeat repairs.
- Preventing Recurring Issues: Accurate diagnostics ensure that the root cause of the problem is addressed, preventing the issue from recurring.
- Avoiding Further Damage: Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary repairs and potentially cause further damage to the vehicle.
- Saving Time and Money: Proper diagnostics can save time and money by identifying the correct repair procedure the first time.
8. Choosing the Right OBD-II Scanner
How do you select the best OBD-II scanner for your needs?
Selecting the right OBD-II scanner is crucial for effective diagnostics and code clearing. Here are some factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Functionality: Look for a scanner that supports both reading and clearing codes. Advanced scanners may also offer features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bidirectional control.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Update Capability: Select a scanner that can be updated with the latest vehicle information and code definitions.
- Price: Scanners range in price from basic models to advanced professional tools. Consider your budget and the features you need.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of OBD-II scanners to suit different needs and budgets. The CGSULIT SC301 is a popular choice for its reliability and ease of use.
9. Understanding Freeze Frame Data
What is freeze frame data, and how can it aid in diagnostics?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a fault code was triggered. This data can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), freeze frame data can significantly reduce diagnostic time.
- Key Parameters: Freeze frame data typically includes parameters such as engine speed, engine load, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Analyzing the Data: By analyzing the freeze frame data, technicians can gain insights into the conditions that led to the fault code, helping them pinpoint the root cause.
- Using with an OBD-II Scanner: Most advanced OBD-II scanners can display freeze frame data, providing technicians with a more comprehensive picture of the issue.
10. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD-II Diagnostics
How do oxygen sensors affect OBD-II diagnostics?
Oxygen sensors play a vital role in monitoring the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Faulty oxygen sensors can trigger OBD-II codes related to fuel trim, efficiency, and emissions. According to Bosch, a leading supplier of automotive components, malfunctioning oxygen sensors can reduce fuel efficiency by as much as 40%.
- Monitoring Air-Fuel Ratio: Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture.
- Common Codes: Common codes related to oxygen sensors include P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 1 Sensor 1) and P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1).
- Testing Oxygen Sensors: Use an OBD-II scanner with live data capabilities to monitor the performance of oxygen sensors. Look for values that are within the normal operating range.
11. Clearing Codes on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Are there any special considerations when clearing codes on hybrid and electric vehicles?
Clearing OBD-II codes on hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) requires some special considerations due to their unique systems.
- High Voltage Systems: Hybrid and EVs have high-voltage systems that can be dangerous. Always disconnect the high-voltage battery before performing any repairs or diagnostics.
- Specific Codes: Hybrid and EVs have unique fault codes related to their electric drive systems. Ensure your OBD-II scanner is compatible with these codes.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Pay attention to codes related to the BMS, as these can indicate issues with the battery pack.
- Regenerative Braking: Codes related to regenerative braking systems can also be unique to hybrid and EVs.
12. The Impact of Aftermarket Parts on OBD-II Systems
How can aftermarket parts affect OBD-II system performance?
Aftermarket parts can sometimes interfere with the OBD-II system, leading to false fault codes or reduced performance.
- Sensors: Low-quality aftermarket sensors may not meet OEM specifications, triggering fault codes.
- ECU Tuning: Modified ECU tuning can alter the way the engine operates, leading to unexpected OBD-II codes.
- Exhaust Systems: Aftermarket exhaust systems can affect the performance of oxygen sensors and catalytic converters, triggering emissions-related codes.
- Air Intakes: Modified air intakes can change the air-fuel mixture, leading to lean or rich conditions.
13. Maintaining Your Vehicle to Prevent Fault Codes
What maintenance steps can you take to minimize the occurrence of OBD-II fault codes?
Regular maintenance is key to preventing OBD-II fault codes and ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly.
- Regular Oil Changes: Changing your engine oil at the recommended intervals helps keep the engine clean and reduces wear.
- Air Filter Replacement: A clean air filter ensures proper airflow to the engine, improving performance and fuel efficiency.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replacing spark plugs at the recommended intervals helps maintain proper ignition and reduces the risk of misfires.
- Fuel System Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the fuel system helps remove deposits and ensures proper fuel delivery.
- Checking and Replacing Fluids: Check and replace fluids such as coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid at the recommended intervals.
14. Addressing Recurring Fault Codes
What steps should you take if a fault code reappears after being cleared?
If a fault code reappears after being cleared, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been fully resolved.
- Repeat Diagnostics: Perform a more thorough diagnostic process to identify the root cause of the problem.
- Check for Intermittent Issues: Intermittent issues can be difficult to diagnose. Use freeze frame data and live data streaming to monitor the vehicle’s performance under various conditions.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unable to diagnose the issue yourself, consult a qualified technician.
15. The Importance of Keeping Your OBD-II Scanner Updated
Why should you keep your OBD-II scanner’s software up to date?
Keeping your OBD-II scanner’s software up to date is essential for accurate diagnostics and code clearing.
- New Codes: Updates include definitions for new fault codes, ensuring you can accurately diagnose the latest vehicle models.
- Improved Functionality: Updates can improve the scanner’s functionality, adding new features and capabilities.
- Bug Fixes: Updates address any bugs or issues that may be present in the scanner’s software.
- Compatibility: Updates ensure the scanner remains compatible with the latest vehicle models and protocols.
 Return to the Homepage of the OBD2 code reader
Return to the Homepage of the OBD2 code reader
16. Potential Risks of Ignoring OBD-II Fault Codes
What are the potential consequences of neglecting to address OBD-II fault codes?
Ignoring OBD-II fault codes can lead to a variety of negative consequences:
- Increased Emissions: Fault codes related to emissions can result in higher levels of pollution, harming the environment.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Engine problems can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, costing you more money at the pump.
- Engine Damage: Ignoring fault codes can lead to more severe engine damage, requiring costly repairs.
- Safety Issues: Some fault codes can indicate safety-related issues, such as problems with the braking system or airbags.
- Failed Inspections: Vehicles with active fault codes may fail emissions inspections, preventing you from registering or operating the vehicle legally.
17. How to Handle Complex or Unusual Fault Codes
What should you do when faced with a complex or unusual fault code?
Dealing with complex or unusual fault codes can be challenging. Here are some steps to take:
- Research: Conduct thorough research to understand the code’s meaning and potential causes.
- Consult Technical Resources: Consult technical service bulletins (TSBs) and online forums for additional information.
- Use Advanced Diagnostics: Employ advanced diagnostic techniques such as oscilloscope testing and circuit analysis.
- Seek Expert Advice: If you’re unable to resolve the issue yourself, seek advice from a qualified technician with experience in diagnosing complex problems.
18. Using Live Data for Advanced Diagnostics
How can live data from an OBD-II scanner help in diagnosing vehicle issues?
Live data provides real-time information about the vehicle’s operating conditions, allowing technicians to monitor various parameters as the engine runs.
- Sensor Readings: Monitor sensor readings such as oxygen sensor voltage, mass airflow (MAF) sensor values, and throttle position.
- Fuel Trim: Analyze fuel trim data to identify lean or rich conditions.
- Engine Performance: Monitor engine performance parameters such as engine speed, load, and ignition timing.
- Identifying Intermittent Issues: Live data can help identify intermittent issues by allowing technicians to observe how the vehicle’s systems respond under different conditions.
19. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Clearing OBD-II Fault Codes
Here are some frequently asked questions about clearing OBD-II fault codes:
- Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
Driving with the check engine light on is not recommended, as it could indicate a serious issue that could lead to further damage or safety risks. - Will clearing the fault codes fix my car?
Clearing the fault codes will not fix the car. It only clears the symptom of the underlying issue. The problem must be properly diagnosed and repaired first. - How often should I check for OBD-II fault codes?
You should check for OBD-II fault codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms in your vehicle’s performance. - Can I clear the fault codes myself, or do I need a mechanic?
You can clear the fault codes yourself using an OBD-II scanner, but it’s important to ensure that the underlying issue has been properly diagnosed and repaired first. - What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the codes?
If the check engine light comes back on after clearing the codes, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been fully resolved. Further diagnostics are needed. - Are all OBD-II scanners the same?
No, OBD-II scanners vary in terms of compatibility, functionality, and ease of use. Choose a scanner that meets your specific needs and budget. - Can aftermarket parts cause OBD-II fault codes?
Yes, low-quality or incompatible aftermarket parts can sometimes interfere with the OBD-II system, leading to false fault codes or reduced performance. - How can I find out what a specific OBD-II code means?
You can use the scanner’s built-in database or a reliable online resource to interpret the meaning of each code. - What is freeze frame data, and how is it helpful?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a fault code was triggered. It can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues. - What are the potential risks of ignoring OBD-II fault codes?
Ignoring OBD-II fault codes can lead to increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, engine damage, safety issues, and failed inspections.
20. Conclusion
Mastering how to clear OBD-II fault codes after a repair is an invaluable skill for any car owner or technician. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your vehicle is running smoothly and efficiently. Remember, proper diagnostics and repairs are essential for preventing recurring issues and maintaining your vehicle’s performance. For all your OBD-II scanning needs, trust CARDIAGTECH.NET to provide you with reliable tools and expert support.
 Disconnect the OBD Code Reader from the vehicle's port
Disconnect the OBD Code Reader from the vehicle's port
Don’t let vehicle troubles slow you down. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and the best OBD-II scanners on the market. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET and take the first step toward worry-free vehicle maintenance. Our team is ready to assist you with your diagnostic tools, ensuring you have the right equipment to keep your vehicle in top condition. Reach out now and experience the CARDIAGTECH.NET difference.
 Turn Off the Ignition in your car
Turn Off the Ignition in your car