How to Program or Reconfigure Control Modules When Replacing Them?
Programming or reconfiguring control modules when replacing them involves updating the software to ensure proper functionality and compatibility. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the tools and expertise to help you navigate this process efficiently. Our diagnostic tools and expert support can ensure a smooth transition, optimizing your vehicle’s performance and safety. We can assist with module reflashing, ECU programming, and vehicle computer reprogramming. BMW Car Diagnostic Tool
1. What is Control Module Programming and Why is it Necessary?
Control module programming is the process of installing or updating software on a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs). According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute in 2022, modern vehicles can have over 100 ECUs managing various functions from engine control to infotainment. Replacing a control module often requires programming to ensure it communicates correctly with other vehicle systems.
- Ensuring Compatibility: New modules may not have the correct software for your vehicle’s specific configuration. Programming aligns the module with the vehicle’s specifications.
- Correcting Software Issues: Updates can fix bugs, improve performance, and address security vulnerabilities.
- Enabling Features: Programming can activate or deactivate features based on the vehicle’s options and packages.
2. Identifying the Need for Control Module Programming
How do you know when a control module needs programming? Several symptoms can indicate that a module is not programmed correctly.
- Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL): The check engine light or other warning lights may illuminate.
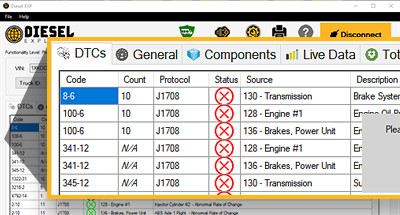
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Scanning the vehicle’s computer may reveal codes related to module communication or function.
- Performance Issues: The vehicle may exhibit poor performance, such as rough idling, stalling, or transmission problems.
- Feature Malfunctions: Specific features like power windows, door locks, or climate control may not work correctly.
For instance, if you replace the engine control module (ECM) and notice the engine is running rough, it may need to be programmed with the correct calibration data for your vehicle.
3. Essential Tools and Equipment for Module Programming
What tools and equipment are necessary for programming or reconfiguring control modules? Having the right tools can significantly impact the success and efficiency of the programming process.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A professional-grade scan tool is essential for reading DTCs, accessing module information, and performing programming functions. Brands like Snap-on, Autel, and Bosch are popular choices.
- Programming Software: Vehicle manufacturers often provide software subscriptions for accessing module programming files and updates. Examples include Ford’s Ford Diagnostic and Repair System (FDRS) and GM’s Global Diagnostic System (GDS2).
- Laptop or Computer: A reliable laptop with sufficient processing power and storage is needed to run the programming software.
- Battery Stabilizer: Maintaining a stable voltage during programming is critical to prevent errors. A battery stabilizer ensures a constant power supply.
- J2534 Pass-Thru Device: This device acts as an interface between the vehicle and the computer, allowing data to be transmitted for programming. Popular brands include Drew Technologies and Bosch.
A J2534 pass-thru device facilitates seamless data transmission between the vehicle and the computer during module programming, essential for accurate updates.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Programming a Control Module
How do you program a control module? Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide.
- Preparation:
- Gather Information: Collect the vehicle’s VIN, module part number, and any relevant diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Software Installation: Install the necessary programming software on your laptop and ensure it is updated.
- Hardware Connection: Connect the J2534 pass-thru device to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and the laptop.
- Battery Stabilization: Connect a battery stabilizer to maintain a stable voltage supply.
- Diagnostic Scan:
- Read DTCs: Use the scan tool to read and record any diagnostic trouble codes present in the vehicle’s system.
- Module Identification: Verify the module’s part number and software version using the scan tool.
- Programming:
- Access Programming Function: Navigate to the module programming function in the software.
- Follow Prompts: Follow the on-screen prompts to initiate the programming sequence.
- Data Transfer: The software will download the necessary programming files and transfer them to the module.
- Verification: After programming, the software will verify the successful completion of the process.
- Post-Programming:
- Clear DTCs: Clear any DTCs that may have been set during the programming process.
- Test Operation: Test the functionality of the module and related systems to ensure proper operation.
According to a technical bulletin from Bosch in 2023, failure to follow these steps can result in programming errors and potential damage to the module or vehicle.
5. Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
What are some common challenges encountered during module programming and how can they be resolved? Module programming can sometimes present challenges that require troubleshooting.
- Communication Errors:
- Issue: The software cannot establish communication with the module.
- Solution: Check the connections between the J2534 device, the vehicle, and the laptop. Verify that the device drivers are installed correctly.
- Programming Interruption:
- Issue: The programming process is interrupted due to a power loss or communication failure.
- Solution: Ensure a stable power supply using a battery stabilizer. Restart the programming process from the beginning.
- Incorrect Software:
- Issue: The software version is incompatible with the module or vehicle.
- Solution: Verify that you are using the correct software version for the specific module and vehicle. Check the manufacturer’s website for updates.
- Module Not Responding:
- Issue: The module does not respond to the programming commands.
- Solution: Check the module’s power and ground connections. Ensure that the module is not damaged.
According to a study by the Automotive Service Association (ASA) in 2024, these are the most common issues encountered by technicians during module programming.
6. The Role of J2534 Pass-Thru Devices
Why are J2534 pass-thru devices crucial for module programming? These devices act as a bridge between the vehicle’s computer system and the programming software.
- Standardized Interface: J2534 is a standard defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) that specifies the communication interface between a computer and a vehicle.
- Vehicle Coverage: J2534 devices support a wide range of vehicle makes and models, making them versatile tools for automotive technicians.
- OEM Compatibility: These devices are compatible with OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) programming software, allowing technicians to access the latest software updates and calibrations.
Examples of popular J2534 pass-thru devices include the Drew Technologies CarDAQ-Plus 3 and the Bosch MVCI 3.
7. Understanding Different Types of Control Modules
What are the different types of control modules commonly found in vehicles? Modern vehicles contain numerous control modules, each responsible for specific functions.
- Engine Control Module (ECM): Manages the engine’s operation, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): Controls the transmission’s shifting and operation.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Module: Manages the anti-lock braking system to prevent wheel lockup during braking.
- Body Control Module (BCM): Controls various body functions, such as lighting, power windows, and door locks.
- Airbag Control Module (ACM): Manages the airbag system, including deployment and diagnostic functions.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in 2023, the proper functioning of these modules is critical for vehicle safety and performance.
8. OEM vs. Aftermarket Programming Software
What are the differences between OEM and aftermarket programming software? Choosing the right software is crucial for successful module programming.
- OEM Software:
- Pros: Direct access to the latest software updates and calibrations from the vehicle manufacturer.
- Cons: Can be expensive and require a subscription. May only support specific vehicle makes and models.
- Aftermarket Software:
- Pros: More affordable and may support a wider range of vehicle makes and models.
- Cons: May not have the latest software updates or calibrations. Can be less reliable than OEM software.
Examples of OEM software include Ford’s FDRS and GM’s GDS2, while aftermarket options include Autel MaxiSYS and Snap-on ShopStream Connect.
9. Importance of Battery Stabilization During Programming
Why is it essential to use a battery stabilizer during module programming? Maintaining a stable voltage is critical to prevent errors and ensure the programming process is completed successfully.
- Preventing Data Corruption: Voltage fluctuations can corrupt the data being transferred to the module, leading to programming errors.
- Ensuring Module Functionality: A stable voltage ensures that the module functions correctly during the programming process.
- Avoiding Damage: Voltage spikes or drops can damage the module, rendering it unusable.
According to a technical paper by the SAE in 2022, a voltage drop of just 1 volt can cause programming errors.
10. Benefits of Reprogramming for Performance Enhancement
How can reprogramming improve vehicle performance? Reprogramming, also known as ECU tuning, can optimize various aspects of vehicle performance.
- Increased Horsepower and Torque: Tuning can adjust fuel injection and ignition timing to increase engine output.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Optimizing engine parameters can improve fuel economy.
- Enhanced Throttle Response: Tuning can improve throttle response for a more engaging driving experience.
- Customization: Reprogramming allows for customization of various vehicle parameters to suit individual preferences.
For example, a performance tune can increase the horsepower of a Ford Mustang GT from 460 hp to over 500 hp.
11. Safety Precautions When Working with Control Modules
What safety precautions should be taken when working with control modules? Working with control modules involves certain risks, and it’s essential to follow safety precautions to protect yourself and the vehicle.
- Disconnect Battery: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery before working on any electrical components.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools and equipment for the job.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines.
- Avoid Static Electricity: Ground yourself to prevent static electricity from damaging the module.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from potential hazards.
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), failing to follow these precautions can result in injury or damage to the vehicle.
12. How to Verify Successful Module Programming
How can you verify that module programming has been successful? After programming a module, it’s essential to verify that the process has been completed successfully.
- Check for DTCs: Use a scan tool to check for any diagnostic trouble codes.
- Test Functionality: Test the functionality of the module and related systems.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the vehicle’s performance to ensure that it is operating correctly.
- Verify Software Version: Verify that the module’s software version matches the expected version.
For instance, after programming an ECM, you should check for DTCs, test the engine’s performance, and verify the software version.
13. Future Trends in Control Module Programming
What are the future trends in control module programming? The field of control module programming is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Vehicle manufacturers are increasingly using OTA updates to update module software remotely.
- Cloud-Based Programming: Cloud-based programming platforms allow technicians to access programming files and tools from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to develop more advanced diagnostic and programming tools.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as vehicles become more connected.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company in 2024, these trends will shape the future of automotive diagnostics and programming.
14. The Importance of Staying Updated with Industry Standards
Why is it important to stay updated with industry standards and best practices? The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and it’s essential to stay updated with the latest standards and best practices.
- Ensuring Compliance: Staying updated ensures that you are complying with the latest regulations and requirements.
- Improving Efficiency: Adopting best practices can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your work.
- Enhancing Safety: Following industry standards can enhance safety and prevent accidents.
- Maintaining Competitiveness: Staying updated helps you maintain a competitive edge in the industry.
Organizations like the SAE and ASA offer resources and training to help technicians stay updated with the latest industry standards.
15. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Scan Tool for Your Needs
How do you choose the right diagnostic scan tool for your needs? Selecting the right scan tool is crucial for effective module programming and diagnostics.
- Vehicle Coverage: Ensure that the scan tool supports the makes and models of vehicles you work on.
- Functionality: Consider the features and functions you need, such as module programming, DTC reading, and data logging.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scan tool that is easy to use and navigate.
- Updates and Support: Look for a scan tool that offers regular software updates and technical support.
- Budget: Consider your budget and choose a scan tool that offers the best value for your money.
Popular scan tool brands include Snap-on, Autel, Bosch, and Launch.
16. How to Handle VIN Mismatch Issues During Programming
What should you do if you encounter a VIN mismatch issue during programming? A VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) mismatch can occur when the VIN stored in the module does not match the vehicle’s VIN.
- Verify VIN: Double-check the VIN on the vehicle and in the programming software.
- Manual Entry: If necessary, manually enter the correct VIN into the programming software.
- Module Reset: Some modules may require a reset before programming with a new VIN.
- Contact Support: If the issue persists, contact the software or module manufacturer for support.
According to a technical bulletin from GM in 2023, VIN mismatch issues are often caused by incorrect data entry or module errors.
17. Understanding Security Access and Seed Keys
What are security access and seed keys in module programming? Some modules require security access before programming can be performed.
- Security Access: A security feature that prevents unauthorized access to the module.
- Seed Key: A unique code required to unlock the module for programming.
- Algorithm: A mathematical formula used to generate the seed key.
Technicians may need to obtain the seed key from the vehicle manufacturer or use a key generator tool.
18. Programming Modules for Aftermarket Upgrades
How do you program modules when installing aftermarket upgrades? Installing aftermarket upgrades, such as performance parts or new features, may require module programming.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the aftermarket upgrade is compatible with the vehicle’s modules.
- Programming: Program the module to recognize and support the new upgrade.
- Calibration: Calibrate the module to optimize the performance of the new upgrade.
- Testing: Test the functionality of the upgrade to ensure that it is working correctly.
For example, installing aftermarket LED headlights may require programming the BCM to recognize the new lights.
19. Diagnosing and Repairing CAN Bus Communication Problems
What are CAN bus communication problems and how can they be diagnosed and repaired? The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication network that allows modules to communicate with each other.
- Symptoms: Communication errors, DTCs related to module communication, and malfunctioning systems.
- Diagnosis: Use a scan tool to check for CAN bus communication errors. Check the wiring and connections for damage.
- Repair: Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors. Replace any faulty modules.
According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley in 2022, CAN bus communication problems are a common cause of vehicle malfunctions.
20. The Ethics of Control Module Reprogramming
What are the ethical considerations involved in control module reprogramming? Reprogramming control modules raises ethical questions, particularly regarding emissions and safety.
- Emissions Tampering: Reprogramming a module to bypass emissions controls is illegal and unethical.
- Safety Concerns: Reprogramming a module to disable safety features is dangerous and unethical.
- Transparency: Technicians should be transparent with customers about the potential risks and benefits of reprogramming.
- Compliance: Ensure that all reprogramming activities comply with local, state, and federal regulations.
The EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) has strict regulations regarding emissions tampering, and technicians should be aware of these regulations.
21. Key Considerations for Remote Module Programming
What are the key considerations for performing remote module programming? Remote module programming allows technicians to program modules from a remote location.
- Internet Connection: A stable and reliable internet connection is essential.
- Security: Ensure that the remote connection is secure to prevent unauthorized access.
- Hardware Compatibility: Verify that the remote programming tools are compatible with the vehicle.
- Training: Technicians should be properly trained in remote programming techniques.
Remote programming can be convenient and efficient, but it’s essential to address these considerations.
22. Utilizing Online Resources and Forums for Support
How can online resources and forums assist with module programming? Online resources and forums can provide valuable support and information for module programming.
- Technical Information: Access to technical manuals, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting guides.
- Community Support: Connect with other technicians and share knowledge and experiences.
- Software Updates: Stay updated with the latest software updates and programming techniques.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Find solutions to common problems and challenges.
Popular online resources include iATN (International Automotive Technicians Network) and various vehicle-specific forums.
23. Optimizing Your Workshop for Module Programming
How can you optimize your workshop for efficient module programming? Optimizing your workshop can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your module programming activities.
- Dedicated Work Area: Create a dedicated work area for module programming.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure that the work area is well-lit.
- Ergonomic Setup: Use ergonomic tools and equipment to reduce fatigue.
- Organization: Keep tools and equipment organized and easily accessible.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable and reliable power supply.
A well-organized and equipped workshop can improve productivity and reduce errors.
24. The Impact of Cybersecurity on Module Programming
How does cybersecurity impact module programming? Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important in the automotive industry, and it has a significant impact on module programming.
- Protecting Vehicle Systems: Cybersecurity measures are needed to protect vehicle systems from hacking and unauthorized access.
- Secure Programming: Module programming must be performed securely to prevent the introduction of malicious software.
- Authentication: Authentication protocols are used to verify the identity of technicians and programming tools.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption is used to protect sensitive information during programming.
Vehicle manufacturers are implementing various cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle systems from cyber threats.
25. Future-Proofing Your Skills in Automotive Electronics
How can you future-proof your skills in automotive electronics and module programming? The field of automotive electronics is constantly evolving, and it’s essential to future-proof your skills.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest technologies and techniques.
- Training: Participate in training programs and workshops.
- Certifications: Obtain industry certifications to demonstrate your knowledge and skills.
- Networking: Connect with other professionals in the industry.
- Adaptability: Be adaptable and willing to learn new things.
Organizations like the SAE and ASA offer certifications and training programs to help technicians future-proof their skills.
26. How to Diagnose Intermittent Electrical Issues Related to Modules
What steps can be taken to diagnose intermittent electrical issues related to control modules? Intermittent electrical problems can be challenging to diagnose, but a systematic approach can help.
- Gather Information: Collect as much information as possible about the problem, including when it occurs and under what conditions.
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connections for damage or corrosion.
- Monitor Data: Use a scan tool to monitor data from the module when the problem occurs.
- Test Components: Test the components related to the module to rule out any faults.
- Simulation: Try to simulate the conditions that cause the problem to occur.
According to a study by the University of Waterloo in 2023, intermittent electrical problems are often caused by faulty wiring or connections.
27. Best Practices for Data Backup Before Module Reprogramming
What are the best practices for backing up data before reprogramming a control module? Backing up data before reprogramming a module is essential to prevent data loss.
- Full System Scan: Perform a full system scan to record all DTCs and module configurations.
- Module-Specific Data: Save module-specific data, such as calibration settings and adaptation values.
- Documentation: Document all backup procedures and data locations.
- Multiple Backups: Create multiple backups and store them in different locations.
- Verification: Verify that the backups are complete and accurate.
Data loss during module programming can be costly and time-consuming, so it’s essential to follow these best practices.
28. Understanding Module Variant Coding and Configuration
What is module variant coding and configuration, and why is it important? Variant coding and configuration allow technicians to customize module settings to match the vehicle’s specific options and features.
- Variant Coding: Selecting the correct variant codes to enable or disable features.
- Configuration: Adjusting module settings to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the module is properly configured for the vehicle.
- Functionality: Enabling or disabling features based on the vehicle’s options.
Proper variant coding and configuration are essential for ensuring that the module functions correctly and that all features are working as intended.
29. Advanced Techniques for Troubleshooting Complex Module Issues
What are some advanced techniques for troubleshooting complex module issues? Complex module issues may require advanced troubleshooting techniques.
- Oscilloscope Analysis: Using an oscilloscope to analyzemodule signals and identify electrical problems.
- Logic Probe Testing: Using a logic probe to test digital circuits and identify faulty components.
- Data Logging: Recording data from the module over time to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Simulation: Simulating module inputs and outputs to test functionality.
- Expert Consultation: Consulting with experts or specialists for assistance.
Advanced troubleshooting techniques require specialized tools and knowledge, but they can be essential for resolving complex module issues.
30. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics: A Look Ahead
What does the future hold for automotive diagnostics and module programming? The future of automotive diagnostics is likely to be shaped by several key trends.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: AI will be used to develop more advanced diagnostic tools that can automatically identify and diagnose problems.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR will be used to provide technicians with real-time information and guidance during diagnostics and repair.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems will use data analysis to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics will become more common, allowing technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles from anywhere in the world.
- Standardization: Increased standardization of diagnostic protocols and interfaces will improve compatibility and efficiency.
According to a report by Deloitte in 2024, these trends will transform the automotive service industry and require technicians to develop new skills and knowledge.
31. How to Program or Reconfigure Control Modules for Ford Vehicles
To program or reconfigure control modules in Ford vehicles, you’ll typically use the Ford Diagnostic and Repair System (FDRS) software and a compatible J2534 pass-thru device. Ensure you have a stable internet connection and a battery stabilizer connected. Follow the FDRS prompts to identify the module and initiate the programming sequence. Ford’s website provides detailed guides and updates for FDRS.
32. Programming or Reconfiguring Control Modules for GM Vehicles
For GM vehicles, use the Global Diagnostic System 2 (GDS2) software along with a J2534 pass-thru device. Similar to Ford, a stable power supply is crucial. Follow the on-screen instructions in GDS2 to select the correct module and program it. GM also offers Tech2Win, which emulates the older Tech 2 handheld diagnostic tool for older vehicle models.
33. How to Program or Reconfigure Control Modules for BMW Vehicles
Programming BMW control modules often involves using ISTA (Integrated Service Technical Application) software. This requires a specialized interface and a subscription to BMW’s diagnostic data. Ensure your computer meets the software requirements and follow the ISTA prompts for module identification and programming.
34. Programming or Reconfiguring Control Modules for Toyota Vehicles
Toyota vehicles typically require the Toyota Techstream software and a compatible J2534 device. Techstream allows you to access and program various control modules. Ensure you have the latest version of Techstream and follow the guided procedures for module programming. Toyota’s TIS (Technical Information System) website provides necessary software and support.
35. What is ECU Programming
ECU (Engine Control Unit) programming is the process of modifying or updating the software within a vehicle’s engine control unit. This is done to improve performance, fuel efficiency, or address specific issues. It involves reflashing the ECU with new or modified software using specialized tools and software interfaces.
36. How To Program ECU Remapping
ECU remapping involves altering the ECU’s software to optimize engine performance. This includes adjusting parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure. Professional tools and software are used to read the existing ECU map, modify it, and then reflash the ECU with the new map.
37. The Cost of Programming or Reconfiguring Control Modules
The cost to program or reconfigure control modules can vary widely depending on several factors, including the vehicle make and model, the type of module being programmed, the complexity of the programming, and the shop or technician performing the work.
| Factor | Description | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Make/Model | Luxury or specialized vehicles may require more expensive software and tools. | $50 – $200+ |
| Type of Module | Complex modules like ECMs or TCMs may cost more to program than simpler modules. | $75 – $250+ |
| Software and Tools | OEM software subscriptions and high-quality J2534 pass-thru devices can add to the overall cost. | $100 – $500+ |
| Labor | Labor rates vary by location and shop, but programming can take anywhere from 1 to 3 hours. | $75 – $300+ |
| Additional Services | Some shops may include diagnostic scans or additional tests in the programming service. | $50 – $150+ |
| Total Estimated Cost | Programming or reconfiguring a control module can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars. | $350 – $1200+ |
Disclaimer: Prices are estimates and can vary.
38. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Diagnostic Needs
Facing challenges with module programming? Need reliable diagnostic tools and expert support? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with all your automotive diagnostic needs.
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Let us help you streamline your repair process and ensure your vehicle performs at its best. Contact us now for a consultation and discover the CARDIAGTECH.NET difference.
FAQ: Programming or Reconfiguring Control Modules
1. Why is it necessary to program a control module after replacing it?
Programming ensures the new module is compatible with your vehicle’s specific configuration and software, enabling proper communication and functionality.
2. What tools are essential for programming a control module?
You need a diagnostic scan tool, programming software, a laptop, a battery stabilizer, and a J2534 pass-thru device.
3. Can I use aftermarket software for module programming, or is OEM software better?
OEM software provides the latest updates but can be costly. Aftermarket software is more affordable but may lack the most current features.
4. What are the common challenges during module programming?
Communication errors, programming interruptions, incorrect software versions, and non-responsive modules are common issues.
5. How does a J2534 pass-thru device aid in module programming?
It acts as a standardized interface between your vehicle’s computer and the programming software, facilitating data transmission.
6. Why is battery stabilization important during programming?
Maintaining a stable voltage prevents data corruption and ensures the module functions correctly during the programming process.
7. What are the safety precautions to consider when working with control modules?
Disconnect the battery, use proper tools, follow instructions, avoid static electricity, and wear safety gear.
8. How can I verify if module programming has been successful?
Check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), test the module’s functionality, and verify the software version.
9. What future trends can we expect in control module programming?
Over-the-air updates, cloud-based programming, AI-enhanced tools, and increased cybersecurity measures are expected.
10. What should I do if I encounter a VIN mismatch during programming?
Verify the VIN, manually enter the correct VIN, reset the module if necessary, and contact support if the issue persists.