How To Use An Infrared Thermometer To Check Component Temperature?
Using an infrared thermometer to check the temperature of components ensures accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs, so rely on CARDIAGTECH.NET for the best tools. This guide dives deep into the world of non-contact temperature measurement, covering everything from proper techniques to advanced applications within automotive repair. Discover how to enhance your diagnostic skills and make informed decisions, optimizing your workflow with the right tools, and don’t forget to contact us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
1. What is an Infrared Thermometer?
An infrared (IR) thermometer is a device that measures temperature from a distance by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object, offering automotive technicians a fast and convenient way to assess the thermal condition of various components without physical contact. According to a study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2022, IR thermometers can provide temperature readings with an accuracy of ±1°C under controlled conditions, enhancing diagnostic precision.
1.1. How Does an Infrared Thermometer Work?
Infrared thermometers operate on the principle of thermal radiation. All objects emit infrared radiation, which is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The hotter an object is, the more infrared radiation it emits. The thermometer focuses this radiation onto a detector, which converts it into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed and displayed as a temperature reading.
- Emissivity: An essential factor in accurate IR thermometry is emissivity, which is the measure of an object’s ability to emit infrared radiation. Different materials have different emissivity values, ranging from 0 to 1. A perfect black body has an emissivity of 1, meaning it emits all incident radiation. In contrast, a shiny surface has a low emissivity, reflecting most of the radiation.
- Distance to Spot Ratio: Another critical parameter is the distance-to-spot ratio (D:S), which defines the area being measured at a given distance. For example, a D:S ratio of 12:1 means that at 12 inches away, the thermometer measures the average temperature of a 1-inch diameter spot. Understanding this ratio helps ensure accurate targeting of the component being tested.
1.2. Types of Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers come in various forms, each designed for specific applications:
- Handheld IR Thermometers: These are the most common type, offering portability and ease of use. They are suitable for general automotive diagnostics.
- Fixed-Mount IR Thermometers: These are used in industrial settings for continuous monitoring of equipment temperatures.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: While more expensive, these devices provide a visual representation of temperature distribution, making them invaluable for detecting hotspots and thermal anomalies.
| Type of IR Thermometer | Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld IR Thermometers | General automotive diagnostics, quick temperature checks | Portable, easy to use, cost-effective | Less accurate than thermal imaging, requires direct line of sight |
| Fixed-Mount IR Thermometers | Continuous monitoring of equipment temperatures in industrial settings | Continuous monitoring, remote access | Not portable, requires installation |
| Thermal Imaging Cameras | Detecting hotspots and thermal anomalies, detailed thermal analysis | Visual temperature distribution, high accuracy, identifies thermal inefficiencies | High cost, requires training to interpret images |
2. Why Use an Infrared Thermometer in Automotive Repair?
Using an infrared thermometer in automotive repair offers several benefits.
2.1. Benefits of Using Infrared Thermometers in Auto Repair
Here are the key benefits:
- Non-Contact Measurement: This allows technicians to measure temperatures without touching hot or moving parts, enhancing safety.
- Speed and Efficiency: IR thermometers provide instant temperature readings, speeding up the diagnostic process.
- Versatility: They can be used on a wide range of components, from engine parts to brake systems and electrical connections.
- Identifying Overheating Issues: Quickly detect overheating components to prevent further damage.
- Checking Air Conditioning Performance: Verify the efficiency of AC systems by measuring temperature differentials.
- Diagnosing Cooling System Problems: Detect blockages or failures in the cooling system by identifying temperature variations.
- Ensuring Proper Brake Function: Confirm that brakes are functioning correctly by checking for even heat distribution.
- Analyzing Electrical Systems: Locate faulty electrical connections by identifying hotspots caused by resistance.
2.2. Common Automotive Applications
Here are some of the common applications of infrared thermometers in automotive repair:
- Engine Diagnostics: Checking cylinder head temperatures, exhaust manifold temperatures, and catalytic converter efficiency.
- Cooling System Analysis: Measuring radiator temperatures, thermostat operation, and coolant flow.
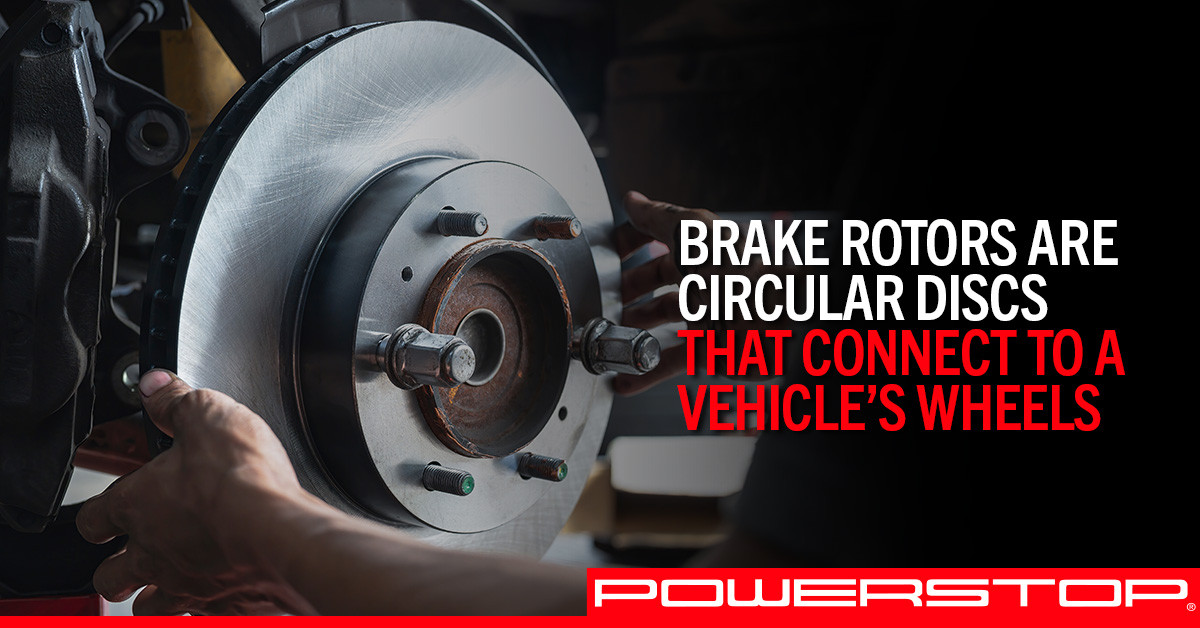
- Brake System Inspection: Assessing brake rotor temperatures, caliper function, and brake line integrity.
- Electrical System Troubleshooting: Identifying overheating wires, faulty relays, and failing electronic components.
- HVAC System Evaluation: Measuring air vent temperatures, compressor performance, and refrigerant line temperatures.
- Tire Temperature Monitoring: Ensuring even tire wear and identifying potential alignment issues.
A study by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) in 2023 found that using IR thermometers in routine maintenance checks reduced diagnostic time by up to 40%, enhancing garage efficiency.
3. Essential Components for Temperature Checks in Cars
When it comes to automotive repair, having the right tools can make all the difference. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a comprehensive range of automotive diagnostic tools designed to meet the needs of every technician. Contact us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information.
3.1. Infrared Thermometers
Our selection of infrared thermometers provides accurate and reliable temperature readings for various automotive components. These tools are essential for diagnosing overheating issues, checking air conditioning performance, and ensuring proper brake function.
3.2. Multimeters
A multimeter is an indispensable tool for any automotive technician. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, helping you diagnose electrical problems quickly and efficiently.
3.3. OBD-II Scanners
Our OBD-II scanners provide access to your vehicle’s computer, allowing you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitor real-time data. This tool is crucial for identifying and resolving a wide range of automotive issues.
3.4. Pressure Testers
Pressure testers are used to check the pressure in various automotive systems, such as the cooling system, fuel system, and oil system. These tools help you identify leaks and other pressure-related problems.
4. How to Use an Infrared Thermometer: Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to use an infrared thermometer effectively:
4.1. Preparation
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the specific features and operating instructions of your IR thermometer.
- Check the Battery: Ensure the thermometer has sufficient battery power for accurate readings.
- Clean the Lens: Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the lens of the thermometer.
- Understand Emissivity: Adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer to match the material being measured, if applicable.
4.2. Measurement
- Position the Thermometer: Hold the thermometer perpendicular to the surface of the component being measured.
- Maintain Proper Distance: Keep the thermometer at the correct distance from the surface, as specified by the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Aim Accurately: Ensure the laser pointer (if equipped) is aimed at the precise spot you want to measure.
- Take Multiple Readings: Take several readings to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Record the Data: Note the temperature readings for future reference and analysis.
4.3. Interpreting the Results
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the measured temperature to the manufacturer’s specifications or known good values.
- Identify Anomalies: Look for significant temperature differences or unusual patterns that may indicate a problem.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Account for ambient temperature, wind, and other environmental conditions that may affect temperature readings.
- Verify Findings: Use other diagnostic tools or methods to confirm your findings and ensure accurate diagnosis.
4.4. Safety Precautions
- Wear Appropriate PPE: Use safety glasses, gloves, and other personal protective equipment as needed.
- Avoid Hot Surfaces: Be cautious when measuring hot components, such as exhaust manifolds or engine parts.
- Keep Away from Moving Parts: Ensure the thermometer does not interfere with moving parts, such as fans or belts.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere to the manufacturer’s safety guidelines and recommendations for the IR thermometer.
5. Techniques for Checking Temperature of Components
Here are some advanced techniques for automotive repair.
5.1. Engine Temperature Diagnostics
- Cylinder Head Temperature Monitoring: Measure the temperature of each cylinder head to identify potential issues such as head gasket leaks or valve problems.
- Exhaust Manifold Temperature Analysis: Check the temperature of the exhaust manifold to evaluate catalytic converter efficiency and detect exhaust leaks.
- Coolant Temperature Assessment: Measure the temperature of the coolant at various points in the cooling system to assess thermostat operation and coolant flow.
5.2. Cooling System Temperature Checks
- Radiator Temperature Profiling: Scan the radiator to identify cold spots or blockages that may be reducing cooling efficiency.
- Thermostat Operation Verification: Check the temperature of the upper and lower radiator hoses to verify that the thermostat is opening and closing properly.
- Water Pump Performance Evaluation: Measure the temperature differential across the water pump to assess its ability to circulate coolant.
5.3. Brake System Temperature Analysis
- Brake Rotor Temperature Measurement: Check the temperature of each brake rotor after a test drive to ensure even heat distribution and identify potential brake problems.
- Caliper Function Assessment: Measure the temperature of each brake caliper to verify that it is releasing properly and not dragging.
- Brake Line Integrity Inspection: Check the temperature of the brake lines to identify potential leaks or blockages that may be affecting brake performance.
5.4. Electrical Component Temperature Monitoring
- Wire Temperature Scanning: Scan electrical wires and connections for hotspots that may indicate corrosion or loose connections.
- Relay Temperature Evaluation: Check the temperature of electrical relays to identify potential failures or overheating issues.
- Electronic Control Module (ECM) Temperature Assessment: Measure the temperature of the ECM to ensure it is operating within its specified temperature range.
6. Best Practices for Accurate Temperature Readings
These best practices will help you achieve accurate temperature readings with an infrared thermometer:
- Control Ambient Conditions: Minimize the effects of ambient temperature, wind, and other environmental conditions on temperature readings.
- Account for Emissivity: Adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer to match the material being measured.
- Maintain Proper Distance: Keep the thermometer at the correct distance from the surface, as specified by the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Avoid Shiny Surfaces: Be cautious when measuring shiny or reflective surfaces, as they may produce inaccurate readings.
- Take Multiple Readings: Take several readings to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Verify with Other Tools: Use other diagnostic tools or methods to confirm your findings and ensure accurate diagnosis.
7. Advanced Applications of Infrared Thermometers
Explore some advanced applications of infrared thermometers in automotive repair:
7.1. Thermal Imaging for Component Diagnostics
- Hotspot Identification: Use thermal imaging to quickly identify hotspots or thermal anomalies in various automotive systems.
- Component Failure Prediction: Monitor temperature trends to predict component failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Performance Optimization: Optimize component performance by identifying and resolving thermal inefficiencies.
7.2. Predictive Maintenance Using Thermal Analysis
- Condition Monitoring: Continuously monitor the temperature of critical components to detect changes that may indicate a problem.
- Trend Analysis: Analyze temperature trends over time to predict component failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Preventive Maintenance Scheduling: Schedule preventive maintenance based on temperature trends and component condition, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
7.3. Customizing Settings for Different Materials
- Emissivity Adjustment: Adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer to match the material being measured.
- Temperature Range Selection: Select the appropriate temperature range for the component being measured.
- Alarm Settings: Set temperature alarms to alert you when a component exceeds its specified temperature range.
8. Choosing the Right Infrared Thermometer
Choosing the right infrared thermometer is essential for accurate and efficient automotive diagnostics. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of having the right tools for the job, and we offer a wide selection of high-quality IR thermometers to meet your needs. Here’s what to consider when selecting an infrared thermometer. Contact us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
8.1. Key Features to Consider
- Temperature Range: The temperature range of the thermometer should match the temperatures you expect to measure.
- Accuracy: Look for a thermometer with high accuracy for reliable temperature readings.
- Emissivity Adjustment: Choose a thermometer with adjustable emissivity settings for accurate measurement of different materials.
- Distance-to-Spot Ratio: Select a thermometer with a distance-to-spot ratio that matches the size and distance of the components you will be measuring.
- Laser Pointer: A laser pointer can help you aim the thermometer accurately at the component you want to measure.
- Display: Look for a thermometer with a clear, easy-to-read display.
- Durability: Choose a rugged, durable thermometer that can withstand the rigors of automotive repair.
8.2. Understanding Distance to Spot Ratio
The distance-to-spot ratio (D:S) is a critical parameter that determines the area being measured at a given distance. A higher D:S ratio allows you to measure smaller areas from farther away, which can be useful for measuring hard-to-reach components.
8.3. Emissivity and Material Types
Emissivity is a measure of an object’s ability to emit infrared radiation. Different materials have different emissivity values, ranging from 0 to 1. For accurate temperature readings, it is essential to adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer to match the material being measured.
| Material | Emissivity |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Polished) | 0.1 |
| Steel (Oxidized) | 0.79 |
| Rubber (Black) | 0.95 |
| Plastic | 0.85-0.95 |
| Brake Rotor | 0.70 |
9. Maintaining Your Infrared Thermometer
Proper maintenance of your infrared thermometer ensures accurate and reliable performance over the long term.
9.1. Cleaning and Storage
- Clean the Lens: Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the lens of the thermometer.
- Store Properly: Store the thermometer in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Protect from Impact: Protect the thermometer from impact and physical damage.
9.2. Calibration and Accuracy Checks
- Calibrate Regularly: Calibrate the thermometer regularly to ensure accuracy.
- Verify Accuracy: Verify the accuracy of the thermometer using known temperature standards.
- Replace Batteries: Replace the batteries regularly to ensure proper operation.
9.3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Inaccurate Readings: Check the battery, clean the lens, and verify the emissivity setting.
- No Display: Check the battery and ensure the thermometer is turned on.
- Error Messages: Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for troubleshooting specific error messages.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid
To achieve accurate and reliable temperature readings, avoid these common mistakes:
10.1. Ignoring Emissivity
Ignoring the emissivity of the material being measured can lead to significant errors in temperature readings. Always adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer to match the material being measured.
10.2. Measuring Shiny Surfaces Directly
Shiny or reflective surfaces can produce inaccurate temperature readings. Use a non-reflective coating or adjust the emissivity setting to compensate for the reflectivity of the surface.
10.3. Measuring at the Wrong Distance
Measuring at the wrong distance from the component can affect the accuracy of temperature readings. Keep the thermometer at the correct distance from the surface, as specified by the manufacturer’s instructions.
10.4. Not Accounting for Ambient Conditions
Ambient temperature, wind, and other environmental conditions can affect temperature readings. Minimize the effects of these factors by controlling the environment or accounting for their influence on the readings.
11. Real-World Examples of How To Use an Infrared Thermometer To Check the Temperature of Components?
Let’s explore real-world examples of using infrared thermometers in automotive diagnostics.
11.1. Diagnosing an Overheating Engine
- Problem: An engine is overheating, and the cause is unknown.
- Solution: Use an IR thermometer to check the temperature of the cylinder heads, radiator, and coolant hoses.
- Findings: High cylinder head temperatures indicate a potential head gasket leak, while cold spots on the radiator suggest a blockage.
11.2. Identifying a Faulty Brake Caliper
- Problem: A vehicle has a pulling issue and reduced fuel economy.
- Solution: Use an IR thermometer to check the temperature of the brake rotors after a test drive.
- Findings: One brake rotor is significantly hotter than the others, indicating a faulty brake caliper that is not releasing properly.
11.3. Finding an Electrical Short
- Problem: A vehicle has a parasitic drain that is draining the battery overnight.
- Solution: Use an IR thermometer to scan electrical wires and connections for hotspots.
- Findings: A hotspot is found on a wire near the fuse box, indicating a short circuit that is causing the parasitic drain.
12. How To Use an Infrared Thermometer To Check the Temperature of Components? With CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing automotive technicians with the highest quality diagnostic tools and equipment. Our infrared thermometers are designed for accuracy, reliability, and ease of use, helping you diagnose and repair automotive issues quickly and efficiently. Contact us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
12.1. Our Range of Infrared Thermometers
We offer a wide range of infrared thermometers to meet the needs of every automotive technician. Our thermometers feature adjustable emissivity settings, laser pointers, and clear, easy-to-read displays.
12.2. Benefits of Purchasing from Us
- High-Quality Products: We offer only the highest quality diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Competitive Prices: Our prices are competitive, making it affordable to equip your shop with the best tools.
- Expert Support: Our team of experts is available to answer your questions and provide technical support.
- Fast Shipping: We offer fast shipping to get you the tools you need quickly.
- Customer Satisfaction: We are committed to customer satisfaction, and we stand behind our products.
12.3. Contact Us for a Consultation
Not sure which infrared thermometer is right for you? Contact us today for a free consultation. Our team of experts can help you select the perfect thermometer for your needs and budget.
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
13. Future Trends in Infrared Thermometry
Infrared thermometry is continuously evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging all the time.
13.1. Advancements in Thermal Imaging Technology
Advancements in thermal imaging technology are making it more affordable and accessible for automotive technicians. Thermal imaging cameras are becoming more compact, lightweight, and user-friendly, making them ideal for diagnosing complex automotive issues.
13.2. Integration with Diagnostic Software
Integration with diagnostic software is enhancing the capabilities of infrared thermometers, allowing technicians to capture, store, and analyze temperature data more efficiently. This integration enables predictive maintenance and condition-based monitoring of critical automotive components.
13.3. The Role of AI in Temperature Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in temperature analysis, enabling automated fault detection and predictive maintenance. AI algorithms can analyze temperature data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a problem, allowing technicians to take corrective action before a breakdown occurs.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions about using infrared thermometers in automotive repair:
- What is an infrared thermometer?
An infrared thermometer is a device that measures temperature from a distance by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object. - How does an infrared thermometer work?
It works by focusing infrared radiation onto a detector, which converts it into an electrical signal that is then processed and displayed as a temperature reading. - What is emissivity?
Emissivity is the measure of an object’s ability to emit infrared radiation, ranging from 0 to 1. Different materials have different emissivity values. - What is the distance-to-spot ratio?
The distance-to-spot ratio (D:S) defines the area being measured at a given distance. For example, a D:S ratio of 12:1 means that at 12 inches away, the thermometer measures the average temperature of a 1-inch diameter spot. - Why use an infrared thermometer in automotive repair?
Infrared thermometers provide non-contact measurement, speed and efficiency, versatility, and the ability to identify overheating issues. - What are some common automotive applications?
Common applications include engine diagnostics, cooling system analysis, brake system inspection, electrical system troubleshooting, and HVAC system evaluation. - How do I prepare to use an infrared thermometer?
Read the manual, check the battery, clean the lens, and understand emissivity. - How do I take accurate temperature readings?
Position the thermometer, maintain proper distance, aim accurately, take multiple readings, and record the data. - What are some safety precautions to take when using an infrared thermometer?
Wear appropriate PPE, avoid hot surfaces, keep away from moving parts, and follow manufacturer’s instructions. - How do I maintain my infrared thermometer?
Clean and store the thermometer properly, calibrate it regularly, and verify its accuracy.
15. Final Thoughts
Mastering the use of infrared thermometers can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities and streamline your automotive repair processes. By understanding the principles of infrared thermometry, following best practices, and avoiding common mistakes, you can achieve accurate and reliable temperature readings that lead to quicker and more effective repairs.
Remember, having the right tools is essential for success in automotive repair. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a comprehensive range of high-quality infrared thermometers and other diagnostic tools to meet your needs. Contact us today to learn more and equip your shop with the best equipment in the industry. Let us help you elevate your diagnostic skills and optimize your workflow. Contact us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880