How to Use Diagnostic Software to Read and Clear Fault Codes?
Using diagnostic software to read and clear fault codes from control modules is crucial for efficient vehicle maintenance and repair, and CARDIAGTECH.NET offers top-tier solutions. This article delves into how to effectively use diagnostic software, enhancing your automotive repair capabilities and streamlining workflows, ultimately saving time and boosting productivity. Discover innovative tools and strategies that revolutionize how you approach vehicle diagnostics.
1. What is Diagnostic Software and How Does it Work?
Diagnostic software is a specialized tool that allows technicians to communicate with a vehicle’s onboard computer, read fault codes, and assess the overall health of various systems. It works by translating complex data from the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) into understandable information, enabling precise diagnostics and efficient repairs.
1.1 The Core Functionality of Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic software allows users to perform a variety of essential tasks, including:
- Reading Fault Codes: Identifies problems stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Clearing Fault Codes: Erases codes after repairs are made.
- Live Data Streaming: Monitors real-time data from sensors and systems.
- Component Testing: Actuates components to verify their functionality.
- Vehicle Health Reports: Generates comprehensive reports on the vehicle’s condition.
1.2 How Diagnostic Software Interfaces with Vehicle Modules
Diagnostic software interfaces with a vehicle’s modules via a diagnostic port, typically an OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) port. The software communicates with the vehicle’s ECUs using standardized protocols like CAN (Controller Area Network) or J1939. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2022, modern diagnostic tools use advanced algorithms to quickly interpret data, providing technicians with accurate and timely insights.
2. Identifying the Right Diagnostic Software for Your Needs
Choosing the right diagnostic software is critical for any automotive repair professional. The best software depends on the types of vehicles you service and the depth of diagnostics you require. Here are key considerations to help you select the most suitable software.
2.1 Compatibility with Vehicle Makes and Models
Ensure the diagnostic software supports the makes and models of vehicles you commonly work on. Some software is designed for specific manufacturers, while others offer broader coverage. According to a 2023 report by Automotive Engineering International, comprehensive coverage is a top priority for technicians to avoid using multiple tools.
2.2 Essential Features to Look For in Diagnostic Software
Look for software that offers:
- Extensive Fault Code Database: A comprehensive library of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Bi-Directional Controls: Capability to command vehicle components for testing.
- Live Data Display: Real-time monitoring of sensor data.
- Regular Updates: Frequent updates to support new models and features.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive design for ease of use.
2.3 Evaluating Subscription Options: Basic vs. Professional
Many diagnostic software providers offer different subscription levels. A basic subscription typically includes essential functions like reading and clearing fault codes, while a professional subscription adds advanced features like bi-directional controls and detailed data analysis. Evaluate your diagnostic needs to determine the most cost-effective option. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers flexible subscription models to suit various requirements.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading Fault Codes
Reading fault codes is a fundamental task in automotive diagnostics. This step-by-step guide outlines the process using diagnostic software, ensuring accurate and efficient troubleshooting.
3.1 Connecting the Diagnostic Tool to the Vehicle
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Diagnostic Tool: Connect the tool to the OBD-II port securely.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Launch the Diagnostic Software: Open the software on your computer or tablet.
3.2 Navigating the Software Interface to Access Diagnostic Functions
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Choose Diagnostic Mode: Select the option to read fault codes or run a diagnostic scan.
- Initiate the Scan: Start the diagnostic process and wait for the software to retrieve fault codes.
3.3 Interpreting Fault Codes: Understanding Severity and Potential Causes
Once the scan is complete, the software will display any stored fault codes. Each code corresponds to a specific issue within the vehicle.
- Identify the Code: Note the alphanumeric code (e.g., P0300).
- Consult the Database: Use the software’s built-in database or online resources to look up the code’s description.
- Assess Severity: Determine the severity of the issue based on the code description.
- Consider Potential Causes: Investigate possible causes for the fault code, such as faulty sensors or wiring issues.
 OBD II Port
OBD II Port
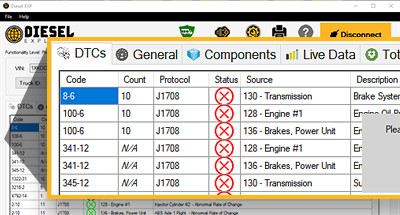
Understanding DTCs: The diagnostic software from CARDIAGTECH.NET displays detailed information about diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), helping technicians quickly identify and address vehicle issues.
4. Clearing Fault Codes Safely and Effectively
Clearing fault codes is necessary after performing repairs to ensure the vehicle’s computer accurately reflects its current condition. However, it’s essential to follow a proper procedure to avoid potential problems.
4.1 Verifying Repairs Before Clearing Codes
Before clearing any codes, verify that the underlying issues have been properly addressed. Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only result in the codes reappearing.
4.2 Step-by-Step Instructions for Clearing Codes
- Access the Clearing Function: In the diagnostic software, navigate to the option for clearing fault codes.
- Confirm Your Selection: The software may ask for confirmation before proceeding.
- Clear the Codes: Initiate the clearing process and wait for confirmation that the codes have been successfully cleared.
- Verify the Result: Perform another scan to ensure no new codes have appeared.
4.3 Potential Risks of Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Underlying Issue
Clearing codes without fixing the problem can mask symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose future issues. It can also lead to:
- False Sense of Security: The driver may believe the vehicle is repaired when it is not.
- Delayed Repairs: Delaying necessary repairs can lead to more severe and costly problems.
- Failed Emissions Tests: The vehicle may fail emissions tests if underlying issues are not resolved.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures with Specialized Software
Specialized diagnostic software offers advanced capabilities beyond basic fault code reading and clearing. These procedures can help diagnose complex issues and perform necessary maintenance tasks.
5.1 Using Bi-Directional Controls for Component Testing
Bi-directional controls allow technicians to command vehicle components to perform specific actions, verifying their functionality. This can be useful for testing:
- Fuel Injectors: Activating injectors to check for proper fuel delivery.
- Cooling Fans: Turning on cooling fans to ensure they operate correctly.
- Actuators: Testing the operation of various actuators in the engine and transmission.
5.2 Live Data Streaming: Monitoring Real-Time Sensor Information
Live data streaming provides real-time information from the vehicle’s sensors, allowing technicians to monitor critical parameters such as:
- Engine Temperature: Monitoring coolant temperature to diagnose overheating issues.
- O2 Sensor Readings: Assessing oxygen sensor performance to diagnose fuel mixture problems.
- Throttle Position: Monitoring throttle position to diagnose acceleration issues.
5.3 Performing Module Programming and Calibrations
Some diagnostic software allows for module programming and calibrations, which are necessary when replacing or updating vehicle components. This can include:
- ECU Programming: Updating the engine control unit software.
- Transmission Calibration: Calibrating the transmission after repairs.
- Sensor Calibration: Calibrating sensors to ensure accurate readings.
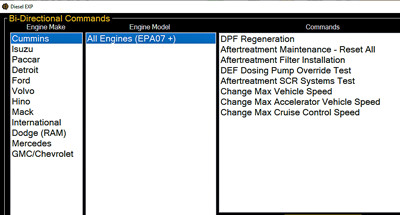 Bi-Directional Commands
Bi-Directional Commands
Control at Your Fingertips: The professional version of CARDIAGTECH.NET’s diagnostic software enables bi-directional commands, such as DPF regenerations and aftertreatment resets, enhancing your diagnostic capabilities.
6. Maximizing the Benefits of Diagnostic Software
To fully leverage the capabilities of diagnostic software, it’s important to stay updated with the latest advancements and best practices.
6.1 Staying Updated with Software Updates and Training
Regularly update your diagnostic software to ensure you have the latest features, vehicle coverage, and bug fixes. Additionally, invest in training to improve your diagnostic skills and stay current with industry best practices.
6.2 Integrating Diagnostic Software with Other Shop Tools and Resources
Integrate your diagnostic software with other shop tools and resources to streamline your workflow. This can include:
- Repair Information Databases: Linking diagnostic software with repair information databases for quick access to troubleshooting guides and wiring diagrams.
- Shop Management Systems: Integrating diagnostic data with shop management systems for efficient record-keeping and billing.
- Online Forums and Communities: Participating in online forums and communities to share knowledge and learn from other technicians.
6.3 Utilizing Cloud-Based Diagnostic Platforms for Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms offer enhanced collaboration by allowing technicians to share diagnostic data and collaborate on complex issues. This can improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce repair times. CARDIAGTECH.NET’s cloud-based solutions provide seamless integration and enhanced collaboration capabilities.
7. Understanding Fault Code Severity and Prioritization
Effective fault code management involves understanding the severity of different codes and prioritizing repairs accordingly. This approach ensures critical issues are addressed promptly, minimizing potential damage and maximizing vehicle safety.
7.1 Classifying Fault Codes by Severity (Critical, Major, Minor)
Fault codes can be classified into three main categories based on their severity:
- Critical: These codes indicate severe issues that require immediate attention to prevent further damage or safety risks. Examples include engine misfires (P0300 series) and brake system malfunctions (C0200 series).
- Major: These codes represent significant problems that should be addressed as soon as possible to avoid potential long-term damage. Examples include issues with the transmission (P0700 series) or fuel system (P0100 series).
- Minor: These codes indicate less severe issues that may not require immediate attention but should be monitored and addressed during routine maintenance. Examples include minor sensor malfunctions (e.g., ambient air temperature sensor) or non-critical emissions issues.
7.2 Prioritizing Repairs Based on Diagnostic Findings
Prioritize repairs based on the severity of the fault codes and their potential impact on vehicle safety and performance. Critical issues should be addressed first, followed by major and minor issues. Consider the following factors when prioritizing repairs:
- Safety: Prioritize issues that affect vehicle safety, such as brake system malfunctions or steering problems.
- Performance: Address issues that significantly impact vehicle performance, such as engine misfires or transmission problems.
- Emissions: Address emissions-related issues to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Customer Concerns: Take into account any specific concerns or complaints from the vehicle owner.
7.3 Documenting Diagnostic Results and Repair Actions
Proper documentation is essential for effective fault code management. Record all diagnostic results, fault codes, and repair actions in a clear and organized manner. This documentation can be useful for:
- Tracking Repair History: Maintaining a detailed record of all repairs performed on the vehicle.
- Identifying Recurring Issues: Spotting patterns or recurring problems that may require further investigation.
- Supporting Warranty Claims: Providing documentation to support warranty claims.
- Improving Diagnostic Accuracy: Learning from past experiences and improving diagnostic skills.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Diagnostic Software
Even experienced technicians can make mistakes when using diagnostic software. Avoiding these common pitfalls can improve diagnostic accuracy and prevent potential damage to the vehicle.
8.1 Ignoring Additional Symptoms and Relying Solely on Fault Codes
Fault codes provide valuable information, but they should not be the sole basis for diagnosis. Always consider additional symptoms and perform a thorough inspection of the vehicle to identify potential issues that may not be indicated by fault codes. According to a 2022 study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), relying solely on fault codes can lead to misdiagnosis in up to 30% of cases.
8.2 Neglecting to Verify Repairs After Clearing Codes
After clearing fault codes, it’s essential to verify that the underlying issues have been resolved and that no new codes have appeared. Perform another diagnostic scan and monitor the vehicle’s performance to ensure the repairs were successful.
8.3 Failing to Keep Software Updated
Diagnostic software is constantly evolving, with new features, vehicle coverage, and bug fixes being added regularly. Failing to keep your software updated can limit its capabilities and lead to inaccurate diagnoses. Make sure to install updates as soon as they become available.
 Software Updates
Software Updates
Stay Current: CARDIAGTECH.NET regularly updates its Diesel Explorer software with new features, improvements, and commands to ensure you have the latest tools at your disposal.
9. The Future of Diagnostic Software and Automotive Repair
The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends shaping the future of repair. Staying informed about these advancements can help you stay ahead of the curve and provide the best possible service to your customers.
9.1 Advancements in AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing an increasingly important role in automotive diagnostics. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from vehicle sensors and systems to identify potential issues before they become major problems. Predictive diagnostics can help technicians:
- Anticipate Failures: Identify components that are likely to fail in the near future.
- Optimize Maintenance Schedules: Recommend maintenance tasks based on actual vehicle conditions.
- Reduce Downtime: Prevent breakdowns by addressing issues before they occur.
9.2 Integration with Telematics and Remote Diagnostics
Telematics and remote diagnostics allow technicians to access vehicle data and perform diagnostic tests remotely. This can be useful for:
- Fleet Management: Monitoring the health of a fleet of vehicles and identifying potential issues.
- Remote Assistance: Providing remote diagnostic assistance to technicians in the field.
- Preventive Maintenance: Scheduling preventive maintenance based on actual vehicle usage and conditions.
9.3 The Role of Augmented Reality in Diagnostic Procedures
Augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a valuable tool for automotive diagnostics. AR applications can overlay digital information onto the real world, providing technicians with step-by-step instructions, wiring diagrams, and other helpful resources directly in their field of vision. This can improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce repair times.
10. Real-World Examples of Diagnostic Software in Action
To illustrate the practical benefits of diagnostic software, let’s explore a few real-world examples of how it can be used to diagnose and repair common vehicle issues.
10.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing Intermittent Engine Misfires
A customer complains of intermittent engine misfires in their vehicle. The technician connects a diagnostic tool and retrieves the fault code P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected). Using live data streaming, the technician monitors the engine’s performance and notices that the misfires occur primarily when the engine is under load. After further investigation, the technician discovers a faulty ignition coil and replaces it, resolving the issue.
10.2 Case Study 2: Identifying ABS Issues Using Diagnostic Software
A vehicle’s ABS warning light is illuminated. The technician uses diagnostic software to retrieve the fault code C0265 (ABS Motor Relay Circuit Malfunction). The technician uses bi-directional controls to test the ABS motor relay and confirms that it is not functioning correctly. The technician replaces the ABS motor relay, clears the fault code, and verifies that the ABS system is now functioning properly.
10.3 Case Study 3: Resetting Service Intervals on a Modern Vehicle
A customer brings in their vehicle for routine maintenance, including an oil change. The vehicle’s service interval indicator is illuminated. The technician uses diagnostic software to reset the service interval, ensuring that the vehicle’s computer accurately reflects the current maintenance status.
FAQ: Your Questions About Diagnostic Software Answered
1. What is the primary function of diagnostic software in automotive repair?
Diagnostic software enables technicians to communicate with a vehicle’s computer, read and clear fault codes, monitor live data, and perform component testing, facilitating precise diagnostics and efficient repairs.
2. How do I choose the right diagnostic software for my shop?
Consider compatibility with the makes and models you service, essential features like bi-directional controls, and subscription options that align with your diagnostic needs.
3. What are the key steps in reading fault codes using diagnostic software?
Connect the diagnostic tool to the OBD-II port, select vehicle information, choose diagnostic mode, and initiate the scan to retrieve fault codes.
4. Is it safe to clear fault codes after repairing a vehicle?
Yes, clearing fault codes is safe after verifying the underlying issues have been properly addressed to ensure the vehicle’s computer accurately reflects its condition.
5. What are bi-directional controls and how are they useful?
Bi-directional controls allow technicians to command vehicle components for testing, such as activating fuel injectors or turning on cooling fans to verify their functionality.
6. How important is it to keep my diagnostic software updated?
Regular software updates ensure you have the latest features, vehicle coverage, and bug fixes, improving diagnostic accuracy and preventing potential issues.
7. What is the role of AI in future diagnostic software?
AI and machine learning can analyze vehicle sensor data to predict potential issues, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce downtime.
8. How can cloud-based diagnostic platforms enhance collaboration among technicians?
Cloud-based platforms allow technicians to share diagnostic data and collaborate on complex issues, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing repair times.
9. What is the significance of understanding fault code severity?
Understanding fault code severity helps prioritize repairs, ensuring critical issues are addressed promptly, minimizing potential damage and maximizing vehicle safety.
10. What are some common mistakes to avoid when using diagnostic software?
Avoid relying solely on fault codes, neglecting to verify repairs after clearing codes, and failing to keep the software updated to ensure accurate diagnoses.
Diagnostic software is an indispensable tool for modern automotive repair, offering capabilities that streamline workflows, improve diagnostic accuracy, and enhance overall efficiency. By understanding how to effectively use diagnostic software to read and clear fault codes from control modules, you can provide superior service to your customers and stay ahead in a competitive industry. CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing cutting-edge diagnostic solutions that meet the evolving needs of automotive professionals.
Are you ready to elevate your automotive diagnostic capabilities? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, to explore our range of diagnostic tools and find the perfect solution for your needs. Don’t let outdated tools hold you back—discover the CARDIAGTECH.NET advantage and revolutionize your approach to vehicle diagnostics today!


