What is the Operating Principle of an Air Conditioning System in a Car?
The operating principle of an air conditioning system in a car involves a cyclical process of refrigerant phase changes, pressure adjustments, and heat exchange to deliver cool air into the cabin, and at CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing top-notch tools for maintaining these intricate systems. This process, vital for passenger comfort, relies on key components like the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve to efficiently remove heat and humidity from the vehicle’s interior. Explore high-quality A/C diagnostic tools and equipment at CARDIAGTECH.NET to ensure optimal performance and comfort, while staying ahead in automotive climate control technology with our latest offerings and expert insights.
1. Understanding the Core Principle: How Car AC Works
How does a car’s air conditioning system manage to keep you cool on a hot day? The core operating principle of an air conditioning system in a car relies on the magic of refrigerant. This special substance cycles between liquid and gaseous states, strategically absorbing heat and humidity from the vehicle’s interior and releasing cool, dry air into the cabin. It’s all about manipulating the refrigerant to create a refreshing environment inside your car. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2022, efficient refrigerant management can improve fuel economy by up to 5%, highlighting the importance of a well-maintained AC system.
2. The Refrigerant: The Heart of the Cooling Process
2.1. Historical Overview of Automotive Refrigerants
What types of refrigerants have been used in car AC systems over the years? Automotive air conditioning systems have seen a fascinating evolution in refrigerant types. Initially, R-12, also known as Freon, was the go-to choice, lauded for its effectiveness as a CFC-based refrigerant that was neither flammable nor poisonous. However, the late 1980s brought a turning point when scientists discovered its detrimental impact on the Earth’s ozone layer.
In the mid-1990s, manufacturers shifted to R-134a, an HFC-based refrigerant that addressed the ozone-depletion issue. Today, the newest refrigerant on the block is R-1234yf, designed to minimize greenhouse gas emissions. Europe has already embraced R-1234yf, and it’s poised to become the new standard in the United States. As the industry evolves, CARDIAGTECH.NET remains committed to providing the latest tools and equipment to handle these advancements.
2.2. R-12 (Freon): The Initial Coolant
What made R-12 the original choice for car AC systems? R-12, or Freon, initially gained favor in car AC systems due to its exceptional cooling efficiency and stability. According to a 1970 report by DuPont, a major manufacturer of Freon, R-12 offered superior thermodynamic properties, making it ideal for automotive applications. Its non-flammable and non-toxic nature further solidified its popularity. However, its high ozone depletion potential led to its eventual phase-out under the Montreal Protocol.
2.3. R-134a: The Transitional Coolant
Why was R-134a adopted as a replacement for R-12? R-134a stepped in as the successor to R-12 because it lacks chlorine, thereby eliminating the risk of ozone depletion. A 1994 study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) confirmed that R-134a has zero ozone depletion potential, making it an environmentally sound alternative. While it is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and a greenhouse gas, its global warming potential is significantly lower than that of R-12. This transition marked a significant step towards more sustainable automotive air conditioning.
2.4. R-1234yf: The Modern, Eco-Friendly Coolant
What advantages does R-1234yf offer over previous refrigerants? R-1234yf represents the latest advancement in automotive refrigerants, distinguished by its dramatically reduced global warming potential (GWP). A 2015 study by the European Commission highlighted that R-1234yf has a GWP of less than 1, compared to R-134a’s GWP of 1430. This eco-friendly refrigerant breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, minimizing its environmental impact. While it is mildly flammable, modern vehicle AC systems are designed with safety features to mitigate any risks, making it a sustainable choice for the future.
2.5. Recharging Your AC System
How do you know when it’s time to recharge your car’s AC system? If your car’s AC system is blowing warm air or not cooling as efficiently as it used to, it may be time for a recharge. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that can help you assess your system’s refrigerant levels. A technician can safely recharge the system with the appropriate refrigerant, ensuring your AC performs optimally. Regular maintenance and timely recharges can extend the life of your AC system and keep you comfortable on the road. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and top-quality AC service tools.
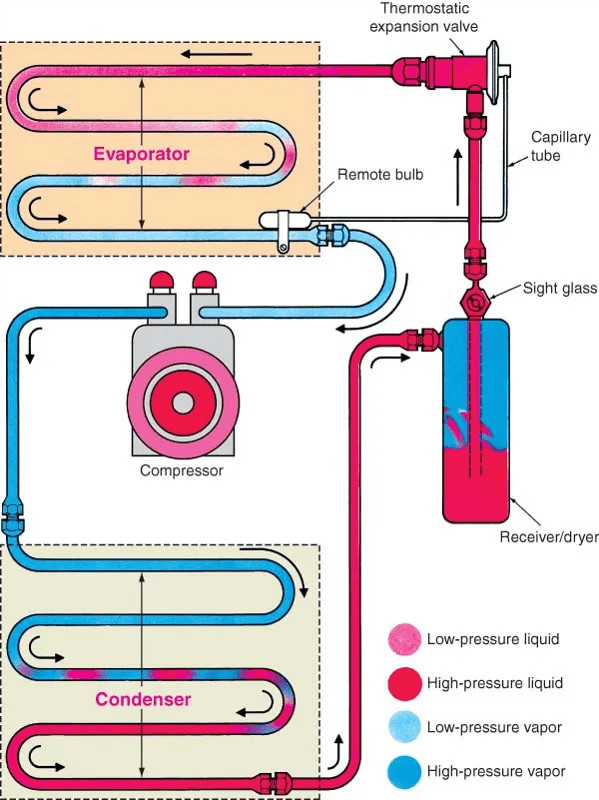
3. Essential Components of a Car AC System
3.1. The Compressor: The System’s Powerhouse
What is the role of the compressor in the AC system? The compressor is the heart of your car’s AC system. It acts as the power unit, separating the low-pressure side from the high-pressure side. The compressor takes in low-pressure gas and squeezes it into high-temperature, high-pressure gas. It’s usually mounted to the front of the engine and driven by the serpentine belt. According to a 2020 study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), a well-maintained compressor can improve the overall efficiency of the AC system by up to 20%.
 AC Compressor
AC Compressor
The main components used and how they’re connected in AC system.
3.2. The Condenser: Cooling the Refrigerant
How does the condenser cool the high-pressure refrigerant? The condenser works to cool down the refrigerant while keeping it at high pressure. As the refrigerant cools, it transforms from a gaseous state to a liquid state. Like the engine radiator, the condenser uses forced air (from a fan or vehicle movement) to transfer heat. It’s typically mounted in front of the vehicle, behind the grill. Research from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in 2018 indicates that an efficient condenser design can reduce energy consumption by up to 10%.
3.3. The Dryer: Removing Moisture
Why is it important to remove water from the refrigerant? The dryer is crucial for removing water from the refrigerant using a desiccant, a drying agent. It also acts as a filter for the system. The dryer is mounted on the high-pressure side, between the condenser and the metering device. According to a study by the Japan Automobile Research Institute (JARI) in 2019, moisture in the refrigerant can lead to corrosion and reduced cooling efficiency, emphasizing the dryer’s importance in maintaining system integrity.
3.4. The Metering Device: Controlling Refrigerant Flow
What are the types and functions of metering devices in an AC system? The metering device, either an expansion valve or a fixed orifice tube, is responsible for lowering the refrigerant pressure, which rapidly drops the refrigerant temperature. The refrigerant remains in liquid form after exiting the metering device. It’s mounted on the high-pressure side, between the dryer and the firewall. A 2017 report by the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA) highlights that precise refrigerant flow control can significantly improve cooling performance and energy efficiency.
3.5. The Evaporator: Providing the Cooling Effect
How does the evaporator produce cool air inside the car? The evaporator is where the refrigerant turns back into a gas, creating a cooling effect. Cabin air is cooled and dehumidified as it blows across the evaporator. This component is the only one located inside the passenger compartment, behind the dashboard. A study by the Center for Environmental Energy Engineering (CEEE) at the University of Maryland in 2021 found that the design and efficiency of the evaporator core directly impact the cooling capacity and dehumidification effectiveness of the AC system.
3.6. Refrigerant’s Journey: A Step-by-Step Path
What happens to the refrigerant as it moves through the AC system?
- Low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant (gas) enters the compressor.
- High-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant (gas) exits the compressor.
- Refrigerant cools and becomes liquid in the condenser, remaining under high pressure.
- The receiver/dryer removes water from the refrigerant.
- The expansion valve reduces refrigerant pressure.
- Refrigerant reverts to a gaseous state in the evaporator.
- Heat is absorbed, and air blowing across the evaporator becomes cool and dry.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides comprehensive diagnostic tools to monitor each stage of this process, ensuring optimal performance.
4. Common Issues in Car AC Systems
4.1. Identifying and Addressing Leaks
Why is it important to fix AC system leaks promptly? Because automotive air conditioning systems operate under pressure, maintaining a complete seal is crucial. Any breach that allows refrigerant to escape or contaminants to enter can lead to system failure. A study by the Mobile Air Conditioning Society (MACS) in 2022 revealed that refrigerant leaks are the primary cause of AC system failures, accounting for over 60% of reported issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced leak detection tools to help you quickly identify and resolve these problems.
If a leak is present in any component, simply recharging the system with new refrigerant is, at best, a temporary solution. The proper approach involves identifying the leak, replacing the faulty component, and then evacuating and recharging the system. Ignoring leaks can lead to more severe damage and costly repairs. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice on leak detection and repair.
4.2. Compressor Overheating
What happens if the compressor runs with insufficient refrigerant? A system leak can not only stop the AC from cooling but also damage the compressor. The compressor can overheat and damage itself by operating with too little refrigerant. Compressors are generally not serviceable and can be expensive to replace. A 2018 report by the Automotive Air Conditioning Council (AACC) indicated that compressor failure is often linked to low refrigerant levels, underscoring the importance of addressing leaks promptly.
4.3. Condenser Blockage
How does a blocked condenser affect AC performance? For the AC condenser to function correctly, it needs a consistent flow of air through its fins. Road debris and dirt can reduce airflow, causing system malfunctions. The condenser is mounted directly behind the vehicle grill, making it vulnerable to partial blockage. Research from the SAE in 2020 showed that a 25% blockage of the condenser can reduce AC cooling efficiency by up to 15%. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the condenser are essential for optimal performance.
5. The Importance of AC System Maintenance
5.1. Regular Inspections
Why should you regularly inspect your car’s AC system? Regular inspections of your car’s AC system can help prevent major issues and ensure optimal performance. Check for any unusual noises, reduced cooling efficiency, and visible signs of leaks. Early detection of problems can save you time and money in the long run. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a variety of diagnostic tools to help you conduct thorough inspections and identify potential issues before they escalate.
5.2. Filter Replacement
How often should you replace the cabin air filter? Replacing the cabin air filter is a simple yet effective maintenance task. A dirty or clogged filter can restrict airflow, reducing the efficiency of the AC system and potentially leading to musty odors. Most manufacturers recommend replacing the cabin air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or at least once a year. A clean filter ensures better air quality inside the car and improves the overall performance of the AC system.
5.3. Professional Servicing
When should you seek professional AC service? While some AC maintenance tasks can be done at home, professional servicing is essential for more complex issues. If you notice significant cooling problems, refrigerant leaks, or compressor issues, it’s best to consult a qualified technician. Professional servicing includes refrigerant recharging, leak detection, component replacement, and system diagnostics. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools and equipment for professional AC servicing, ensuring technicians can provide top-notch service.
6. The Role of Automotive Technicians
6.1. Diagnosing AC Problems
What skills do automotive technicians need to diagnose AC issues? Automotive technicians play a crucial role in diagnosing and repairing AC systems. They need a strong understanding of AC system components, refrigerant types, and diagnostic procedures. Technicians use specialized tools and equipment to identify leaks, measure refrigerant pressure, and assess component performance. Skilled technicians can quickly pinpoint the root cause of AC problems and recommend appropriate solutions.
6.2. Repairing and Replacing Components
What are the common AC components that technicians repair or replace? Technicians are often responsible for repairing or replacing faulty AC components. Common repairs include fixing refrigerant leaks, replacing compressors, condensers, evaporators, and expansion valves. They also handle tasks like flushing the system, replacing filters, and recharging the refrigerant. Proper repair and replacement procedures are essential for restoring the AC system to optimal performance.
6.3. Staying Updated with New Technologies
How do technicians keep up with advancements in AC technology? The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and AC technology is no exception. Technicians must stay updated with the latest advancements in refrigerant types, system designs, and diagnostic tools. Continuous training and education are essential for technicians to effectively service modern AC systems. CARDIAGTECH.NET supports technicians by providing access to the latest tools, equipment, and training resources.
7. Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Car AC Operation
7.1. Initial State: Low-Pressure Gas
Where does the AC process begin, and what is the initial state of the refrigerant? The AC process starts with low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas entering the compressor. This is the beginning of the cooling cycle, where the refrigerant is prepared for its transformation. Ensuring the refrigerant is in the correct state at this stage is crucial for the entire system’s efficiency.
7.2. Compression Stage: Increasing Pressure and Temperature
What happens to the refrigerant as it goes through the compressor? As the refrigerant moves through the compressor, it is compressed, significantly increasing its pressure and temperature. The refrigerant exits the compressor as a high-pressure, high-temperature gas, ready to release heat in the next stage. According to a study by the U.S. Department of Energy in 2019, efficient compression can reduce overall energy consumption by up to 15%.
7.3. Condensation Stage: Releasing Heat
How does the condenser help cool the high-pressure refrigerant? In the condenser, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas is cooled, causing it to condense into a high-pressure liquid. This process releases heat to the outside air, facilitated by the condenser fan or vehicle movement. Effective condensation is essential for the AC system to efficiently remove heat from the vehicle’s interior.
7.4. Filtration Stage: Removing Impurities
Why is filtration important in the AC system? The receiver/dryer filters the high-pressure liquid refrigerant, removing moisture and contaminants. This ensures that only clean, dry refrigerant proceeds to the next stage, protecting the system from corrosion and damage. A clean system operates more efficiently and has a longer lifespan.
7.5. Expansion Stage: Reducing Pressure and Temperature
How does the expansion valve reduce the refrigerant’s pressure? The expansion valve lowers the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, causing it to rapidly cool. This low-pressure, low-temperature liquid refrigerant is now ready to absorb heat inside the vehicle. The precise control of refrigerant flow at this stage is crucial for optimal cooling performance.
7.6. Evaporation Stage: Absorbing Heat and Cooling Air
How does the evaporator cool the air inside the car? In the evaporator, the low-pressure, low-temperature liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the air blowing across it, turning back into a gas. This process cools and dehumidifies the air, which is then circulated into the vehicle cabin. The efficiency of the evaporator directly impacts the cooling capacity and comfort level inside the car.
7.7. Cycle Completion: Returning to the Compressor
What happens to the refrigerant after it passes through the evaporator? The refrigerant, now a low-pressure, low-temperature gas, returns to the compressor to begin the cycle again. This continuous loop ensures constant cooling and dehumidification, keeping the vehicle interior comfortable. Maintaining the correct refrigerant charge and system integrity is vital for sustained performance.
8. Optimizing Your Car AC System
8.1. Using AC Efficiently
What are some tips for using your car AC more efficiently? To use your car AC efficiently, start by parking in the shade to reduce initial heat buildup. Open windows briefly to vent hot air before turning on the AC. Use the recirculation mode to cool the cabin faster and reduce the load on the system. Regularly check and clean the condenser to ensure proper airflow. These simple steps can improve cooling performance and save fuel.
8.2. Maintaining Optimal Refrigerant Levels
Why is maintaining the correct refrigerant level important? Maintaining the correct refrigerant level is crucial for optimal AC performance. Low refrigerant levels can reduce cooling efficiency and damage the compressor. Regular checks and timely recharges can prevent these issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of tools for monitoring refrigerant levels and performing recharges safely and efficiently. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and high-quality equipment.
8.3. Preventing Common Issues
How can you prevent common AC system problems? Preventing common AC issues involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Keep the condenser clean, replace the cabin air filter regularly, and inspect the system for leaks. Address any unusual noises or reduced cooling performance promptly. By taking these steps, you can extend the life of your AC system and avoid costly repairs.
9. AC Systems FAQs
9.1. How does a car air conditioner work?
The AC in a car cools the air by cycling refrigerant through a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, which then releases heat in the condenser. The refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve, lowering its pressure and temperature. Finally, the cold refrigerant absorbs heat in the evaporator, cooling the air blown into the cabin.
9.2. What are the main components of a car air conditioning system?
The main components of an AC system include the compressor, condenser, evaporator, receiver-dryer, and expansion valve. Each component plays a crucial role in the cooling process, from compressing the refrigerant to cooling and dehumidifying the air.
9.3. How does the refrigerant in a car air conditioner cool the air?
The refrigerant cools the air by changing from a liquid to a gaseous state in the evaporator. This process absorbs heat from the air passing through the evaporator, resulting in cooler and drier air being circulated into the vehicle.
9.4. What causes a car AC to stop working?
A car AC can stop working due to various reasons, including refrigerant leaks, a faulty compressor, a clogged condenser, or a malfunctioning expansion valve. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help prevent these issues.
9.5. How often should I service my car’s AC system?
It is recommended to service your car’s AC system every one to two years. Regular servicing includes checking refrigerant levels, inspecting components, and replacing the cabin air filter.
9.6. Can I recharge my car AC myself?
While it is possible to recharge your car AC yourself, it is generally recommended to have it done by a professional. Improper handling of refrigerants can be harmful to the environment and can damage the AC system.
9.7. What is the difference between R-134a and R-1234yf refrigerants?
R-134a and R-1234yf are both refrigerants used in car AC systems. R-1234yf is more environmentally friendly due to its lower global warming potential compared to R-134a.
9.8. How do I know if my car AC has a refrigerant leak?
Signs of a refrigerant leak include reduced cooling performance, hissing sounds from the AC system, and visible leaks of oily residue. A professional inspection can confirm the presence of a leak.
9.9. What is the purpose of the cabin air filter in the AC system?
The cabin air filter removes dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air entering the vehicle cabin. Replacing the cabin air filter regularly improves air quality and AC system performance.
9.10. How can I improve the efficiency of my car’s AC system?
To improve the efficiency of your car’s AC system, park in the shade, use the recirculation mode, keep the condenser clean, and maintain the correct refrigerant level. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can also enhance efficiency.
10. Conclusion: Ensuring Optimal AC Performance with CARDIAGTECH.NET
Understanding the operating principle of an air conditioning system in a car is crucial for maintaining optimal comfort and performance. From the compressor to the evaporator, each component plays a vital role in the cooling process. Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and the use of high-quality tools are essential for keeping your AC system in top condition.
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are dedicated to providing automotive technicians and car owners with the best diagnostic tools and equipment for AC system maintenance. Whether you need leak detectors, refrigerant gauges, or component replacement tools, we have you covered. Our products are designed to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety, ensuring you can tackle any AC system challenge with confidence.
Don’t let a malfunctioning AC system ruin your driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our extensive range of AC service tools. Our expert team is ready to assist you with any questions and help you find the perfect solutions for your needs. Located at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, we are your trusted partner for automotive excellence. Invest in CARDIAGTECH.NET and experience the difference in quality, performance, and customer satisfaction.