**What Is the Operating Principle of the ABS Braking System?**

The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) operates by preventing wheel lock-up during braking, thus maintaining traction and steering control; the system utilizes speed sensors to detect wheel deceleration, valves to modulate brake pressure, a pump to restore pressure, and a controller to manage these components. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to ensure optimal ABS performance, keeping you safe on the road. Explore our range of automotive solutions including brake system diagnostics and wheel speed sensor calibration tools, designed to enhance vehicle safety.
1. Understanding the Fundamental Principle of ABS
1.1. What is the Core Idea Behind ABS?
The core idea behind ABS is to prevent wheels from locking up during braking, ensuring maximum traction and steering control. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), vehicles equipped with ABS have a 35% lower risk of being involved in a crash. This is achieved by modulating brake pressure to each wheel independently, allowing the driver to maintain control and reduce stopping distances.
1.2. Why is Preventing Wheel Lock-Up So Important?
Preventing wheel lock-up is critical because a skidding wheel has significantly less traction than a rolling one. When a wheel locks, it loses its ability to provide both braking force and steering control. This can lead to longer stopping distances and an increased risk of losing control of the vehicle, especially on slippery surfaces.
1.3. How Does ABS Enhance Vehicle Safety?
ABS enhances vehicle safety by:
- Maintaining Steering Control: By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS allows drivers to steer around obstacles during emergency braking.
- Reducing Stopping Distances: ABS can significantly reduce stopping distances on slippery surfaces like wet roads, ice, or snow.
- Improving Stability: ABS helps maintain vehicle stability during hard braking, reducing the risk of skidding or spinning out.
- Optimizing Braking Force: ABS modulates brake pressure to each wheel individually, ensuring maximum braking force is applied without causing lock-up.
According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ABS is one of the most important safety technologies in modern vehicles, contributing to a significant reduction in crash rates.
2. Key Components of the ABS System
2.1. What are the Essential Parts of ABS?
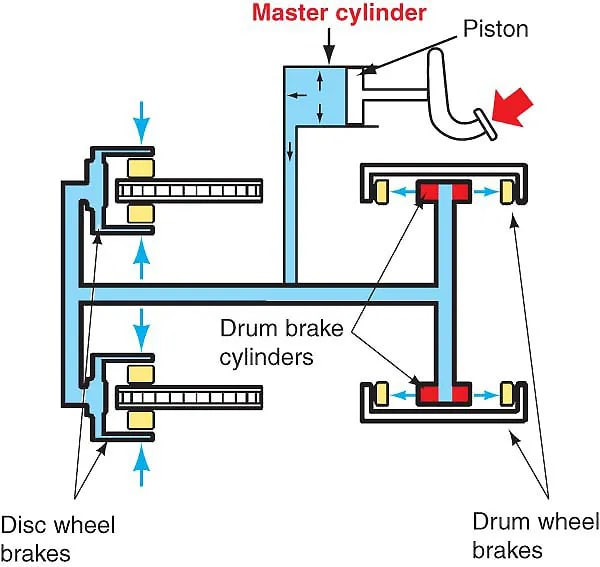
The essential parts of an ABS system include:
- Speed Sensors: These monitor the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Valves: These control the brake pressure to each wheel.
- Pump: This restores brake pressure when the valves release it.
- Controller (ECU): This processes sensor data and controls the valves and pump.
2.2. How Do Speed Sensors Work in ABS?
Speed sensors, typically located at each wheel, monitor the rotational speed and send this data to the ABS controller. These sensors are crucial for detecting when a wheel is about to lock up. There are two main types of speed sensors:
- Reluctor Ring Sensors: These use a toothed ring and a magnetic sensor to generate a signal proportional to wheel speed.
- Hall Effect Sensors: These use a slotted ring and a semiconductor sensor to produce a digital signal indicating wheel speed.
According to Bosch, a leading supplier of automotive components, wheel speed sensors must be highly accurate and reliable to ensure the ABS system functions correctly.
2.3. What Role Do Valves Play in Regulating Brake Pressure?
Valves play a critical role in regulating brake pressure to each wheel independently. These valves can either increase, decrease, or maintain the brake pressure based on signals from the ABS controller. A typical ABS valve has three positions:
- Open: Allows full brake pressure from the master cylinder to the wheel.
- Blocking: Isolates the wheel from the master cylinder, preventing further pressure increase.
- Release: Reduces brake pressure at the wheel to prevent lock-up.
2.4. Why is a Pump Needed in the ABS System?
A pump is needed in the ABS system to restore brake pressure after the valves have released it. When the ABS controller detects a wheel about to lock up, it signals the valve to release pressure. The pump then works to quickly restore this pressure, allowing the system to cycle rapidly and maintain optimal braking performance.
2.5. What is the Function of the ABS Controller (ECU)?
The ABS controller, also known as the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), is the brain of the ABS system. It performs several critical functions:
- Data Processing: Receives and processes data from the wheel speed sensors.
- Lock-Up Detection: Detects when a wheel is about to lock up based on rapid deceleration.
- Valve Control: Controls the valves to modulate brake pressure to each wheel.
- Pump Activation: Activates the pump to restore brake pressure as needed.
- Diagnostic Monitoring: Monitors the ABS system for faults and alerts the driver if a problem is detected.
According to Continental Automotive, a major supplier of automotive electronics, the ABS controller uses sophisticated algorithms to ensure optimal braking performance in various driving conditions.
 ABS Components
ABS Components
3. The ABS Operating Principle Explained
3.1. How Does ABS Prevent Wheel Lock-Up in Real-Time?
ABS prevents wheel lock-up in real-time through a rapid cycle of monitoring, detecting, and modulating brake pressure. The ABS controller continuously monitors the speed sensors at each wheel. If it detects a wheel decelerating rapidly, indicating an imminent lock-up, it signals the valve to reduce brake pressure to that wheel. Once the wheel begins to regain speed, the controller increases the pressure again, repeating this cycle multiple times per second.
3.2. What Happens During an Emergency Braking Situation?
During an emergency braking situation, the driver typically applies maximum force to the brake pedal. Without ABS, this would likely cause the wheels to lock up, resulting in a loss of steering control and increased stopping distance. However, with ABS, the system takes over to prevent lock-up:
- Maximum Brake Force: The driver applies maximum brake force.
- Lock-Up Detection: The ABS controller detects any wheel that is about to lock up.
- Pressure Modulation: The controller modulates brake pressure to each wheel individually, preventing lock-up.
- Steering Control: The driver maintains steering control and can steer around obstacles.
- Optimal Braking: The system ensures optimal braking force is applied without causing lock-up, reducing stopping distance.
3.3. How Does the System Adapt to Different Road Conditions?
The ABS system adapts to different road conditions by continuously monitoring wheel speeds and adjusting brake pressure accordingly. For example, on a slippery surface like ice or snow, the ABS system will be more active, cycling more frequently to prevent lock-up. On dry pavement, the system may be less active, allowing for more direct braking force.
3.4. What is the Role of the Pulsing Sensation in the Brake Pedal?
The pulsing sensation felt in the brake pedal during ABS operation is a direct result of the rapid opening and closing of the valves. This pulsing is normal and indicates that the ABS system is actively working to prevent wheel lock-up. According to studies, some ABS systems can cycle up to 15-20 times per second.
3.5. How Does ABS Differ from Traditional Braking Systems?
ABS differs significantly from traditional braking systems in its ability to prevent wheel lock-up and maintain steering control. In a traditional braking system, applying too much brake force can easily cause the wheels to lock, leading to skidding and loss of control. ABS, on the other hand, modulates brake pressure to each wheel, allowing the driver to maintain control and reduce stopping distances.
| Feature | Traditional Braking Systems | ABS Braking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Wheel Lock-Up | Prone to lock-up | Prevents lock-up |
| Steering Control | Lost during lock-up | Maintained |
| Stopping Distance | Longer | Shorter |
| Driver Skill Required | Higher | Lower |
4. Advantages and Limitations of ABS
4.1. What are the Key Benefits of Having ABS in a Vehicle?
The key benefits of having ABS in a vehicle include:
- Enhanced Safety: ABS significantly reduces the risk of accidents by preventing wheel lock-up and maintaining steering control.
- Shorter Stopping Distances: ABS can reduce stopping distances, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Improved Vehicle Stability: ABS helps maintain vehicle stability during hard braking, reducing the risk of skidding or spinning out.
- Greater Driver Control: ABS allows drivers to maintain steering control and maneuver around obstacles during emergency braking.
4.2. Are There Any Drawbacks to Using ABS?
While ABS offers numerous benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Increased Complexity: ABS systems are more complex than traditional braking systems, which can lead to higher maintenance and repair costs.
- Pulsing Sensation: The pulsing sensation in the brake pedal can be disconcerting for some drivers who may not be familiar with ABS operation.
- Performance on Loose Surfaces: On very loose surfaces like gravel or sand, ABS can sometimes increase stopping distances compared to traditional braking systems.
- Reliance on Technology: Over-reliance on ABS can lead to complacency and a decrease in safe driving habits.
4.3. How Does ABS Perform on Different Road Surfaces?
ABS performance can vary depending on the road surface:
- Dry Pavement: ABS provides excellent braking performance on dry pavement, reducing stopping distances and maintaining steering control.
- Wet Roads: ABS is particularly effective on wet roads, where it can significantly reduce stopping distances compared to traditional braking systems.
- Ice and Snow: ABS helps maintain control on ice and snow by preventing wheel lock-up, although stopping distances may still be longer than on dry pavement.
- Gravel and Sand: On loose surfaces like gravel and sand, ABS can sometimes increase stopping distances, as the wheels need to dig into the surface to provide effective braking.
4.4. Can ABS Prevent All Accidents?
No, ABS cannot prevent all accidents. While ABS can significantly enhance vehicle safety, it is not a substitute for safe driving habits. Drivers should still maintain a safe following distance, drive at appropriate speeds for the conditions, and avoid distractions. According to the NHTSA, driver behavior is a critical factor in most accidents.
4.5. How Does the Effectiveness of ABS Vary Among Different Vehicles?
The effectiveness of ABS can vary among different vehicles depending on factors such as vehicle weight, tire condition, and the specific ABS system design. Newer vehicles typically have more advanced ABS systems that are better able to adapt to different driving conditions. Additionally, well-maintained tires are essential for optimal ABS performance.
5. Maintaining and Troubleshooting ABS
5.1. What are the Common Issues That Can Affect ABS Performance?
Common issues that can affect ABS performance include:
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: Damaged or dirty wheel speed sensors can provide inaccurate data to the ABS controller.
- Malfunctioning Valves: Valves that are stuck or leaking can prevent the ABS system from properly modulating brake pressure.
- Defective Pump: A failing pump can prevent the ABS system from restoring brake pressure.
- Controller Problems: Issues with the ABS controller, such as software glitches or hardware failures, can disrupt the entire system.
- Hydraulic Issues: Leaks or blockages in the hydraulic lines can affect ABS performance.
5.2. How Can I Tell if My Vehicle’s ABS is Not Working Properly?
Signs that your vehicle’s ABS may not be working properly include:
- ABS Warning Light: The ABS warning light on the dashboard remains illuminated.
- Lack of Pulsing Sensation: The brake pedal does not pulse during hard braking.
- Increased Stopping Distance: The vehicle takes longer to stop than usual.
- Wheel Lock-Up: The wheels lock up during braking, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Unusual Noises: Strange noises coming from the brakes during ABS operation.
5.3. What are the Steps for Diagnosing ABS Problems?
The steps for diagnosing ABS problems typically involve:
- Visual Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage or wear, such as broken wires or leaking hydraulic lines.
- Diagnostic Scan: Use a diagnostic scanner to read ABS trouble codes stored in the controller.
- Component Testing: Test individual components, such as wheel speed sensors and valves, to verify their functionality.
- Hydraulic System Check: Inspect the hydraulic system for leaks, blockages, or other issues.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to observe ABS performance under various driving conditions.
5.4. Can I Repair ABS Myself, or Should I Seek Professional Help?
While some minor ABS issues, such as cleaning wheel speed sensors, can be addressed by experienced DIYers, most ABS repairs should be performed by a qualified mechanic. ABS systems are complex and require specialized knowledge, tools, and diagnostic equipment. Attempting to repair ABS without proper training can be dangerous.
5.5. What Maintenance Tasks are Recommended to Keep ABS in Good Condition?
Recommended maintenance tasks to keep ABS in good condition include:
- Regular Brake Inspections: Have your brakes inspected regularly by a qualified mechanic.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Cleaning: Keep wheel speed sensors clean and free of debris.
- Brake Fluid Flushes: Perform regular brake fluid flushes to remove contaminants and maintain hydraulic system performance.
- Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire inflation and replace worn tires promptly.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any ABS issues promptly to prevent further damage.
6. The Future of ABS Technology
6.1. How is ABS Technology Evolving?
ABS technology is continually evolving, with advancements focused on:
- Integration with Stability Control Systems: Modern vehicles often integrate ABS with electronic stability control (ESC) systems to provide even greater control and stability.
- Improved Sensor Technology: New sensor technologies, such as high-resolution sensors and radar-based sensors, are enhancing the accuracy and responsiveness of ABS systems.
- Advanced Control Algorithms: Sophisticated control algorithms are being developed to optimize ABS performance in a wider range of driving conditions.
- Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB): ABS is a key component of autonomous emergency braking systems, which can automatically apply the brakes to avoid or mitigate collisions.
6.2. What are Some Emerging Technologies Related to ABS?
Emerging technologies related to ABS include:
- Brake-by-Wire Systems: These systems replace traditional hydraulic brake lines with electronic controls, allowing for faster and more precise braking.
- Regenerative Braking: Used in electric and hybrid vehicles, regenerative braking captures energy during deceleration and uses it to recharge the battery, enhancing efficiency.
- Torque Vectoring: This technology uses ABS to selectively apply brakes to individual wheels, improving handling and stability during cornering.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Some manufacturers are offering over-the-air software updates for ABS systems, allowing for continuous improvement and feature enhancements.
6.3. How Will These Advancements Impact Vehicle Safety?
These advancements are expected to have a significant impact on vehicle safety by:
- Reducing Accident Rates: Enhanced ABS and related technologies will further reduce accident rates by preventing collisions and mitigating their severity.
- Improving Driver Assistance: Advanced braking systems will provide drivers with greater assistance in emergency situations, reducing the risk of human error.
- Enabling Autonomous Driving: ABS is a critical component of autonomous driving systems, providing the foundation for safe and reliable self-driving vehicles.
- Enhancing Overall Vehicle Performance: Improved braking systems will enhance overall vehicle performance, providing drivers with greater control, stability, and confidence.
6.4. What Role Will ABS Play in Autonomous Vehicles?
ABS will play a crucial role in autonomous vehicles by:
- Ensuring Safe Braking: ABS will ensure safe braking performance in a variety of driving conditions, even without human intervention.
- Supporting Emergency Maneuvers: ABS will support emergency maneuvers, such as collision avoidance and lane keeping, by providing precise and reliable braking control.
- Integrating with Other Safety Systems: ABS will integrate with other safety systems, such as adaptive cruise control and lane departure warning, to provide a comprehensive safety net.
- Enabling Remote Control: ABS will enable remote control of braking functions, allowing for autonomous vehicles to be safely operated and monitored from a distance.
6.5. How Can Drivers Stay Informed About the Latest ABS Innovations?
Drivers can stay informed about the latest ABS innovations by:
- Reading Automotive Publications: Subscribe to reputable automotive magazines and websites to stay up-to-date on the latest technology.
- Attending Auto Shows: Visit auto shows to see the latest vehicles and learn about new ABS features and innovations.
- Consulting with Mechanics: Talk to your mechanic about ABS maintenance and repair and ask about the latest advancements.
- Following Industry Experts: Follow industry experts and thought leaders on social media to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies.
- Checking Manufacturer Websites: Regularly check the websites of vehicle manufacturers and ABS suppliers for information about new products and features.
7. ABS and Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
7.1. Why is Proper ABS Diagnostics Crucial?
Proper ABS diagnostics is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety and performance. A malfunctioning ABS system can lead to longer stopping distances, loss of steering control, and an increased risk of accidents. Accurate diagnostics can identify issues early, preventing more costly repairs and ensuring the system functions as intended. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), vehicles with properly functioning ABS systems have a significantly lower risk of being involved in collisions.
7.2. What Types of ABS Diagnostic Tools Does CARDIAGTECH.NET Offer?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of ABS diagnostic tools to meet the needs of both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts. Our selection includes:
- OBD2 Scanners: These versatile tools can read and clear ABS trouble codes, providing valuable insights into system issues.
- Advanced Diagnostic Scanners: These advanced scanners offer more in-depth diagnostics, including live data streaming, component testing, and bi-directional control.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Testers: These specialized tools can test the functionality of wheel speed sensors, ensuring they are providing accurate data to the ABS controller.
- Hydraulic System Testers: These testers can evaluate the performance of the hydraulic system, identifying leaks, blockages, or other issues that may affect ABS operation.
- ABS Module Programmers: These programmers allow you to reprogram or replace the ABS module, ensuring proper functionality and compatibility.
7.3. How Can These Tools Help Mechanics and Car Owners?
Our ABS diagnostic tools can help mechanics and car owners by:
- Accurate Diagnostics: Providing accurate and reliable diagnostic information, allowing for quick and effective troubleshooting.
- Time Savings: Reducing diagnostic time by quickly identifying the root cause of ABS problems.
- Cost Savings: Preventing unnecessary repairs by pinpointing the exact components that need to be replaced.
- Improved Safety: Ensuring the ABS system is functioning properly, enhancing vehicle safety and reducing the risk of accidents.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Allowing mechanics to provide accurate and reliable service, improving customer satisfaction.
7.4. What are the Key Features of CARDIAGTECH.NET’s Diagnostic Tools?
Key features of CARDIAGTECH.NET’s diagnostic tools include:
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use interface that makes diagnostics quick and efficient.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Support for a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Advanced Functionality: Advanced features such as live data streaming, component testing, and bi-directional control.
- Regular Updates: Regular software updates to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
- Technical Support: Access to expert technical support to assist with any diagnostic challenges.
7.5. How Do CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools Ensure Accurate ABS Readings?
CARDIAGTECH.NET tools ensure accurate ABS readings through:
- High-Quality Components: Use of high-quality sensors and electronic components.
- Precise Calibration: Precise calibration to ensure accurate data acquisition.
- Advanced Algorithms: Sophisticated algorithms that compensate for environmental factors and sensor variations.
- Regular Testing: Rigorous testing and validation to ensure reliable performance.
- Compliance with Standards: Compliance with industry standards for diagnostic accuracy and reliability.
8. Step-by-Step Guide: Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools for ABS Diagnosis
8.1. What Preparations Are Needed Before Starting the Diagnosis?
Before starting the diagnosis, make sure to:
- Gather Information: Collect information about the vehicle, including make, model, year, and VIN.
- Review Symptoms: Document the symptoms of the ABS problem, such as warning lights, unusual noises, or brake pedal issues.
- Consult Manuals: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual and the diagnostic tool’s user manual for specific instructions and procedures.
- Safety Precautions: Follow all safety precautions, including wearing safety glasses and gloves.
- Tool Setup: Ensure the diagnostic tool is properly connected to the vehicle and powered on.
8.2. How to Connect the Diagnostic Tool to the Vehicle?
To connect the diagnostic tool to the vehicle:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port, which is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the OBD2 port, ensuring a secure connection.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn on the vehicle’s ignition, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Tool: Power on the diagnostic tool and wait for it to establish communication with the vehicle.
- Verify Connection: Verify that the tool is successfully connected to the vehicle by checking the display for confirmation messages.
8.3. What Steps Should Be Taken to Read ABS Trouble Codes?
To read ABS trouble codes:
- Select ABS System: Navigate to the ABS system menu on the diagnostic tool.
- Read Codes: Select the “Read Codes” or “Retrieve Codes” option.
- View Codes: View the trouble codes displayed on the screen, noting the code numbers and descriptions.
- Record Codes: Record the trouble codes for further analysis and troubleshooting.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If desired, select the “Clear Codes” option to erase the codes from the ABS controller. Note that clearing codes may not resolve the underlying issue.
8.4. How to Interpret the Trouble Codes and Identify the Faulty Components?
To interpret the trouble codes and identify the faulty components:
- Consult Resources: Refer to the diagnostic tool’s user manual, the vehicle’s service manual, and online resources to understand the meaning of each trouble code.
- Analyze Symptoms: Consider the symptoms of the ABS problem in conjunction with the trouble codes to narrow down the possible causes.
- Component Testing: Use the diagnostic tool to perform component testing, such as testing wheel speed sensors, valves, and the pump.
- Wiring Diagrams: Consult wiring diagrams to check for wiring issues, such as shorts, opens, or corrosion.
- Expert Advice: Seek advice from experienced mechanics or online forums if needed.
8.5. What Maintenance Steps Should Be Taken After the Diagnosis?
After the diagnosis, take these maintenance steps:
- Repair or Replace Faulty Components: Repair or replace any faulty components identified during the diagnosis.
- Clear Trouble Codes: Clear the trouble codes from the ABS controller after the repairs are completed.
- Test the System: Test the ABS system to ensure it is functioning properly.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to verify that the ABS system is working correctly under various driving conditions.
- Document Repairs: Document the repairs performed, including the trouble codes, components replaced, and test results.
9. Real-World Examples of ABS in Action
9.1. Case Study 1: Preventing a Collision on a Wet Road
A driver is traveling on a wet road when a car suddenly cuts in front. The driver slams on the brakes, and the ABS system activates immediately. The system prevents wheel lock-up, allowing the driver to maintain steering control and steer around the car, avoiding a collision.
9.2. Case Study 2: Maintaining Control on an Icy Surface
A driver is driving on an icy surface when they encounter a patch of black ice. The vehicle begins to skid, but the ABS system kicks in, modulating brake pressure to each wheel. The driver is able to maintain control of the vehicle and steer it safely to the side of the road.
9.3. Case Study 3: Reducing Stopping Distance in an Emergency
A driver is traveling on a highway when traffic suddenly stops ahead. The driver applies the brakes forcefully, and the ABS system activates. The system reduces stopping distance, allowing the driver to stop the vehicle safely before colliding with the car in front.
9.4. Case Study 4: Improving Stability During Hard Braking
A driver is driving on a winding road when they encounter a sharp turn. The driver applies the brakes hard, and the ABS system helps maintain vehicle stability. The system prevents wheel lock-up and reduces the risk of skidding or spinning out, allowing the driver to safely navigate the turn.
9.5. Case Study 5: Enhancing Safety for Teen Drivers
A teenage driver is learning to drive in a vehicle equipped with ABS. During a practice session, the teenager panics and slams on the brakes. The ABS system prevents wheel lock-up, allowing the teenager to maintain control of the vehicle and avoid a collision. The ABS system enhances safety for teen drivers by providing them with greater control and stability in emergency situations.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ABS
10.1. What does the ABS warning light mean?
The ABS warning light indicates a problem with the anti-lock braking system. It could be a minor issue like a faulty sensor or a more serious problem with the ABS module.
10.2. Can I drive my car if the ABS light is on?
Yes, you can drive your car if the ABS light is on, but it’s important to get it checked as soon as possible. Your regular brakes will still work, but the ABS system may not function in an emergency.
10.3. How often should I have my ABS system checked?
It is recommended to have your ABS system checked at least once a year or whenever you notice any issues with your brakes.
10.4. Does ABS work on all types of vehicles?
ABS is available on most modern vehicles, including cars, trucks, and SUVs. However, the specific features and performance of ABS systems may vary depending on the vehicle make and model.
10.5. Can I upgrade my car to have ABS if it doesn’t already have it?
Retrofitting a car with ABS can be complex and expensive, as it involves installing new sensors, valves, and a control module. It is generally not recommended unless you are a skilled mechanic with the necessary tools and expertise.
10.6. Does ABS affect my car insurance rates?
Having ABS in your car can potentially lower your insurance rates, as it is considered a safety feature that reduces the risk of accidents. However, the actual impact on your rates may vary depending on your insurance provider and other factors.
10.7. How does ABS interact with other safety systems like ESC and traction control?
ABS often works in conjunction with other safety systems like Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and traction control to provide comprehensive vehicle stability and control. ABS prevents wheel lock-up, while ESC helps prevent skidding and traction control limits wheel spin during acceleration.
10.8. What should I do if my ABS activates unexpectedly?
If your ABS activates unexpectedly, maintain steady pressure on the brake pedal and steer the vehicle in the desired direction. Avoid pumping the brakes, as this can interfere with ABS operation.
10.9. Are there different types of ABS systems?
Yes, there are different types of ABS systems, including:
- One-Channel ABS: Controls both rear wheels together.
- Three-Channel ABS: Controls each front wheel individually and both rear wheels together.
- Four-Channel ABS: Controls each wheel individually.
10.10. How much does it cost to repair or replace an ABS module?
The cost to repair or replace an ABS module can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, the complexity of the repair, and the labor rates in your area. It can range from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars.
Don’t let ABS issues compromise your safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and top-quality diagnostic tools. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET today and drive with confidence. Our team is ready to help you find the perfect tools to diagnose and resolve any ABS problem, ensuring your vehicle is safe and reliable.