**What Is The Procedure for Tire Rotation?: A Complete Guide**

Tire rotation, the practice of periodically changing the position of your vehicle’s tires, is vital for tire maintenance and safety, maximizing tire tread life and ensuring even wear. Proper tire maintenance services can significantly improve vehicle handling and safety. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by CARDIAGTECH.NET, explores the best tire rotation procedures to keep you rolling smoothly.
1. What Does Tire Rotation Mean?
Tire rotation is the process of periodically changing the position of each tire on your vehicle. According to recommendations, it should be done every 5,000 miles or as advised by the vehicle manufacturer. Regular tire maintenance not only extends the life of your tires but also provides an opportunity to inspect them for damage, check air pressure, and ensure they are properly balanced.
Rotating your tires regularly provides an excellent chance to visually inspect them for any signs of damage, ensure they are inflated to the correct pressure, rebalance them if you notice any vibrations, and assess their tread depth. Studies by the Tire and Rim Association, Inc., indicate that consistent tire rotation can extend tire life by as much as 25%. This is because each position on a vehicle places different demands on a tire, leading to uneven wear.
2. What Are The Benefits of Tire Rotation?
Rotating your tires offers several key advantages, including extending tread life, maintaining consistent tread depth, and reducing stress on drivetrain components. Consistent tire maintenance leads to better vehicle performance and safety.
2.1. Maximizing Tread Life
Regular tire rotation ensures that wear is evenly distributed across all four tires, maximizing their tread life. According to a 2022 study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), even tread wear improves overall tire performance and safety. Each position on a vehicle subjects tires to different stresses. For instance, tires on the front of a front-wheel-drive vehicle handle a larger proportion of the torque and friction needed for turning, accelerating, and braking, which can lead to uneven wear. Rotating tires every 5,000 miles can prevent this, especially for new tires with deep tread that are more susceptible to uneven wear.
2.2. Maintaining Consistent Tread Depth
Even tread wear maintains uniform tread depth across all tires, which helps keep traction and handling consistent. This uniformity improves cornering and braking performance, making your vehicle safer. Research from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute found that vehicles with evenly worn tires exhibit superior handling and stability, particularly in adverse weather conditions.
2.3. Reducing Drivetrain Stress
For vehicles with all-wheel-drive, evenly worn tires reduce stress on the drivetrain, which can extend the life of expensive drive components. Uneven tire wear can cause the all-wheel-drive system to work harder, leading to premature wear and potential failure. Regular tire rotation helps prevent these issues, ensuring the drivetrain operates smoothly and efficiently.
3. What Tire Rotation Pattern Should You Use?
The best tire rotation pattern for your vehicle depends on several factors, including the type of tires, the vehicle’s drive type (front, rear, all, or four-wheel), whether the tires are directional or non-directional, and whether you have a full-size spare. Consulting the Tire and Rim Association, Inc., guidelines is recommended for determining the appropriate pattern.
3.1. Tire Rotation Patterns for Uniform, Non-Directional Tires
For tires of uniform size and non-directional tread, several rotation patterns are suitable, including the rearward cross, X-pattern, and forward cross. These patterns ensure that each tire spends time in different positions on the vehicle, promoting even wear.
3.1.1. Rearward Cross Pattern
The rearward cross pattern is recommended for rear-wheel-drive vehicles. In this pattern, the rear tires are moved to the front axle on the same side of the vehicle, while the front tires are moved to opposite sides of the rear axle.
3.1.2. X-Pattern
The X-pattern is suitable for four-wheel and all-wheel-drive vehicles, such as lightweight trucks and sedans. All tires are moved diagonally, meaning they are switched from one axle to the opposite and repositioned from one side to the other.
3.1.3. Forward Cross Pattern
The forward cross pattern is the most common for front-wheel-drive vehicles. The front axle tires are moved directly back, while the rear tires are moved up diagonally to the opposite side of the front axle.
3.2. Tire Rotation Patterns with a Full-Size Spare Tire
Rotating a full-size spare tire along with the other four is essential for ensuring even tread wear on all tires, especially in all-wheel or four-wheel-drive vehicles. Even small differences in tread depth can strain the drivetrain.
3.2.1. Rearward Cross with Spare (Rear-Wheel or 4-Wheel Drive)
In this pattern, both rear axle tires move directly forward to the front axle, and the spare tire moves to the right side of the rear axle. The right front tire moves diagonally back to the left side of the rear axle, and the left front tire becomes the new spare tire.
3.2.2. Forward Cross with Spare (Front-Wheel Drive)
Here, the rear tires are moved diagonally to opposite sides on the front axle, and the right front tire becomes the new spare tire. The spare tire is positioned on the right side of the rear axle, while the left tire on the front axle is moved directly back into the left rear position.
3.3. Tire Rotation Patterns for High-Performance and Directional Tires
High-performance and directional tires require specific rotation patterns to maintain optimal performance and safety. These patterns differ based on whether the tires are of different sizes or are directional.
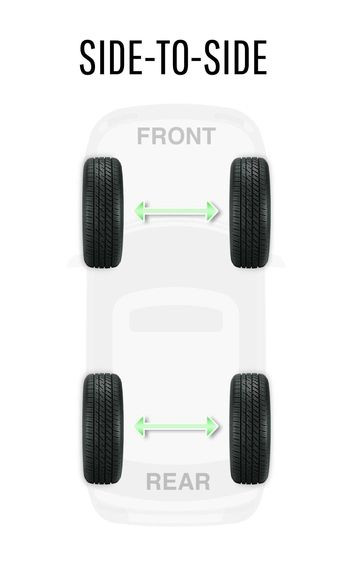
3.3.1. Side-to-Side Rotation
For differently-sized performance tires on the front and rear axles, a side-to-side rotation is used. All tires are switched with their same-sized partner and remain on the same axle. The two rear tires switch to the opposite side, and the two front tires do the same.
3.3.2. Front-to-Back Rotation
For directional tires, all tires are moved from one axle to the other but remain on the same side of the vehicle. For example, the front left tire is moved to the left side of the rear axle, and the rear left tire is repositioned on the left side of the front axle.
 X-Pattern
X-Pattern
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Tire Rotation
Rotating tires can be done at home with the right tools and knowledge. Here’s a detailed guide:
4.1. Gather Your Tools
Before starting, gather the necessary tools: a lug wrench, a jack, jack stands, and a torque wrench. Safety is paramount, so ensure you have gloves and safety glasses.
4.2. Prepare Your Vehicle
Park your vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Loosen the lug nuts on all tires, but don’t remove them completely at this stage.
4.3. Lift Your Vehicle
Use the jack to lift your vehicle. Place jack stands securely under the frame to support the vehicle. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
4.4. Remove the Tires
Completely remove the lug nuts and take off the tires. Keep the lug nuts in a safe place to avoid losing them.
4.5. Rotate the Tires
Follow the appropriate tire rotation pattern for your vehicle, as discussed earlier. This might involve moving the rear tires to the front, crossing them over, or simply swapping sides.
4.6. Reinstall the Tires
Mount the tires back onto the wheel studs. Hand-tighten the lug nuts in a star pattern to ensure even pressure.
4.7. Lower Your Vehicle
Carefully lower the vehicle using the jack, and remove the jack stands.
4.8. Tighten the Lug Nuts
Use a torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque. This is crucial for safety and to prevent wheel damage. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) highlights the importance of using a calibrated torque wrench to ensure accurate tightening.
4.9. Check Tire Pressure
After rotating your tires, check and adjust the tire pressure to the recommended levels, which can be found on the sticker inside your driver’s side door or in your vehicle’s manual.
5. The Role of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS)
Modern vehicles often come equipped with Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS), which alert drivers when tire pressure is significantly low. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining tire health and safety.
5.1. Understanding TPMS
TPMS sensors monitor the air pressure inside your tires and transmit this information to the vehicle’s computer. When the pressure drops below a certain threshold, the TPMS warning light illuminates on the dashboard.
5.2. Benefits of TPMS
TPMS helps drivers maintain optimal tire pressure, which improves fuel efficiency, extends tire life, and enhances safety. According to the EPA, maintaining proper tire pressure can improve fuel economy by up to 3.3%.
5.3. TPMS and Tire Rotation
When rotating tires, it’s essential to ensure that the TPMS sensors are functioning correctly. In some cases, the sensors may need to be reset or recalibrated to accurately reflect the new tire positions. Consult your vehicle’s manual or a professional tire service for assistance with TPMS calibration.
6. How Often Should You Rotate Your Tires?
The frequency of tire rotation depends on your vehicle and driving conditions. However, a general guideline is to rotate your tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, or about every six months.
6.1. Factors Influencing Rotation Frequency
Several factors can influence how often you should rotate your tires:
- Driving Habits: Aggressive driving, such as frequent hard braking and acceleration, can accelerate tire wear.
- Road Conditions: Driving on rough or uneven roads can also increase tire wear.
- Vehicle Type: Some vehicles, particularly those with all-wheel-drive, may require more frequent tire rotations.
6.2. Recommendations from Experts
Most tire manufacturers and automotive experts recommend rotating tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles. Checking your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations is always a good idea.
7. The Impact of Wheel Alignment on Tire Wear
Wheel alignment plays a significant role in tire wear. Proper alignment ensures that your tires make optimal contact with the road, reducing uneven wear and improving handling.
7.1. Understanding Wheel Alignment
Wheel alignment refers to the angles of your vehicle’s wheels relative to each other and to the vehicle body. The primary alignment angles are:
- Camber: The angle of the wheel relative to the vertical axis.
- Caster: The angle of the steering axis relative to the vertical axis.
- Toe: The angle of the wheels relative to each other when viewed from above.
7.2. Symptoms of Misalignment
Common symptoms of wheel misalignment include:
- Uneven tire wear
- Pulling to one side while driving
- A crooked steering wheel
- Squealing tires
7.3. How Alignment Affects Tire Wear
Misalignment can cause tires to wear unevenly, reducing their lifespan and compromising safety. For example, excessive camber can cause the inside or outside edge of the tire to wear prematurely.
 Side-to-Side
Side-to-Side
8. Balancing Tires for a Smooth Ride
Tire balancing is another essential aspect of tire maintenance. Balanced tires ensure a smooth and comfortable ride, reduce vibration, and prevent uneven wear.
8.1. Understanding Tire Balancing
Tire balancing involves distributing the weight of the tire and wheel assembly evenly around the axle. Even slight imbalances can cause noticeable vibrations while driving.
8.2. Symptoms of Imbalanced Tires
Common symptoms of imbalanced tires include:
- Vibration in the steering wheel
- Vibration in the seat
- Uneven tire wear
8.3. The Balancing Process
Tire balancing is typically done using a balancing machine, which spins the tire and wheel assembly to detect imbalances. The machine then indicates where weights should be added to correct the imbalance.
9. Seasonal Tire Maintenance Tips
Different seasons bring different challenges for tires. Adjusting your tire maintenance routine to account for these seasonal changes can help extend tire life and improve safety.
9.1. Summer Tire Care
During the summer months, high temperatures can increase tire pressure, leading to overinflation. Check tire pressure regularly and adjust as needed. Also, be mindful of driving on hot asphalt, which can accelerate tire wear.
9.2. Winter Tire Care
In winter, cold temperatures can cause tire pressure to drop, leading to underinflation. Check tire pressure frequently and add air as needed. Consider using winter tires, which provide better traction in snow and ice.
9.3. Spring and Fall Tire Care
Spring and fall are good times to inspect your tires for any signs of damage, such as cuts, bulges, or punctures. Also, check the tread depth to ensure your tires have adequate traction.
10. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Tool Needs
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges faced by automotive technicians and garage owners. Our mission is to provide high-quality tools that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety.
10.1. Addressing Customer Challenges
We recognize that automotive work demands physical strength and involves constant exposure to grease and chemicals. That’s why we offer tools designed for durability and ease of use. We also understand the need to stay updated with the latest automotive technology.
10.2. Services Offered
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of services to help you:
- Enhance work efficiency and reduce repair time.
- Increase accuracy and safety.
- Save on repair and maintenance costs.
- Boost revenue and garage profitability.
- Improve garage reputation and service quality.
10.3. Call to Action
Ready to take your automotive service to the next level? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and top-quality tools.
Contact Information:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
11. FAQs About Tire Rotation
11.1. What is the main purpose of tire rotation?
The main purpose of tire rotation is to distribute wear evenly across all tires, extending their lifespan and maintaining consistent handling and traction.
11.2. How often should I rotate my tires?
It is generally recommended to rotate your tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, or about every six months.
11.3. What happens if I don’t rotate my tires?
If you don’t rotate your tires, they will wear unevenly, reducing their lifespan and potentially compromising safety due to decreased traction and handling.
11.4. Can I rotate tires myself, or should I go to a professional?
You can rotate tires yourself if you have the right tools and knowledge. However, if you are not comfortable doing it yourself, it is best to go to a professional.
11.5. What tools do I need to rotate tires?
To rotate tires, you will need a lug wrench, a jack, jack stands, and a torque wrench.
11.6. Is tire rotation necessary for all-wheel-drive vehicles?
Yes, tire rotation is especially important for all-wheel-drive vehicles because uneven tire wear can strain the drivetrain.
11.7. Does tire rotation affect tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS)?
Yes, when rotating tires, it’s essential to ensure that the TPMS sensors are functioning correctly and may need to be reset or recalibrated.
11.8. What is the best tire rotation pattern for front-wheel-drive vehicles?
The forward cross pattern is generally recommended for front-wheel-drive vehicles.
11.9. What is the best tire rotation pattern for rear-wheel-drive vehicles?
The rearward cross pattern is generally recommended for rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
11.10. How does wheel alignment affect tire wear?
Proper wheel alignment ensures that your tires make optimal contact with the road, reducing uneven wear and improving handling.
12. The Future of Tire Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and tire technology is no exception. Innovations such as airless tires, self-inflating tires, and smart tires are on the horizon, promising to further enhance safety, efficiency, and performance. According to a report by McKinsey, the global market for advanced tire technologies is expected to reach $300 billion by 2030.
12.1. Airless Tires
Airless tires, also known as non-pneumatic tires, eliminate the risk of punctures and blowouts. These tires are made from a solid material or a network of flexible spokes that provide support and cushioning.
12.2. Self-Inflating Tires
Self-inflating tires use an internal pump to maintain optimal tire pressure automatically. These tires can help improve fuel efficiency and extend tire life by ensuring that they are always properly inflated.
12.3. Smart Tires
Smart tires are equipped with sensors that monitor various parameters, such as tire pressure, temperature, and tread depth. This data can be transmitted to the vehicle’s computer, providing drivers with real-time information about their tires.
13. How to Choose the Right Tires for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right tires for your vehicle is crucial for safety, performance, and fuel efficiency. Consider the following factors when choosing tires:
13.1. Tire Size
Ensure that you select tires that are the correct size for your vehicle. The tire size is typically listed on the sidewall of the tire and in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
13.2. Tire Type
Choose tires that are appropriate for your driving conditions and the type of vehicle you own. Options include all-season tires, summer tires, winter tires, and performance tires.
13.3. Load Index and Speed Rating
Pay attention to the load index and speed rating of the tires. The load index indicates the maximum weight that the tire can carry, while the speed rating indicates the maximum speed at which the tire can be safely driven.
13.4. Tire Reviews and Ratings
Read reviews and ratings from other drivers to get an idea of the tire’s performance, durability, and comfort.
14. Maintaining Your Tires for Optimal Performance
In addition to tire rotation, several other maintenance practices can help extend tire life and improve performance:
14.1. Regular Inspections
Inspect your tires regularly for any signs of damage, such as cuts, bulges, or punctures.
14.2. Proper Inflation
Maintain proper tire pressure at all times. Check and adjust tire pressure at least once a month.
14.3. Wheel Alignment and Balancing
Ensure that your wheels are properly aligned and balanced. Misalignment and imbalance can cause uneven tire wear and vibration.
14.4. Professional Service
Consult with a professional tire service for regular maintenance and inspections.
By following these guidelines and entrusting your automotive tool needs to CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can ensure that your tires are always in top condition, providing a safe and smooth driving experience. Remember, proper tire maintenance is not just about extending tire life; it’s about ensuring your safety and the safety of others on the road. So, take the necessary steps to keep your tires in optimal condition, and enjoy the ride.



