Understanding The ESP Button on Your Mercedes-Benz
The ESP button on a Mercedes-Benz activates a crucial safety feature, and understanding its function is essential for every driver. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the insights you need about this system, offering solutions for maintaining optimal vehicle performance. Learn about stability control systems and electronic stability programs to enhance your driving experience.
1. Decoding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
1.1. What is ESP and Why Is It Important?
Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a vital safety system in your Mercedes-Benz. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP helps to stabilize the vehicle during critical driving situations, reducing the risk of skidding and loss of control. ESP monitors various factors such as wheel speed, steering angle, and lateral acceleration, intervening when it detects a potential loss of control. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power, ESP helps keep the vehicle on its intended path.
For example, if you’re driving on a wet road and start to skid, ESP can detect the loss of traction and automatically apply the brakes to the appropriate wheels, helping you regain control. This technology enhances vehicle safety and reduces the likelihood of accidents, making it a crucial feature for drivers, particularly in adverse weather conditions. Data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) shows that ESP systems can significantly reduce the risk of single-vehicle crashes, highlighting their importance in modern vehicles.
1.2. The Role of ESP in Preventing Accidents
ESP plays a pivotal role in preventing accidents by enhancing vehicle stability and control. ESP helps maintain directional stability by preventing oversteer (where the rear of the car slides out) and understeer (where the front of the car plows straight ahead). ESP uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. When a discrepancy is detected, ESP intervenes to correct the vehicle’s trajectory.
Consider a scenario where you need to make a sudden evasive maneuver to avoid an obstacle. Without ESP, the vehicle might lose traction and skid, making it difficult to steer. With ESP, the system quickly identifies the situation and applies the necessary corrections, allowing you to maintain control and avoid the obstacle. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ESP has been proven to reduce fatal crash rates by a significant margin, underscoring its life-saving potential.
1.3. ESP Components and How They Work Together
The ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz comprises several key components that work in harmony to ensure vehicle stability. These components include:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data on whether a wheel is losing traction.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting if the car is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the force acting on the vehicle from side to side, indicating the severity of a turn or skid.
- Hydraulic Control Unit: This unit controls the brake pressure to each wheel, allowing ESP to selectively apply brakes as needed.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The brain of the ESP system, the ECU processes data from all the sensors and determines the appropriate response to maintain stability.
When the ECU detects a potential loss of control, it activates the hydraulic control unit to apply brakes to one or more wheels. It may also adjust engine power to further stabilize the vehicle. This coordinated effort ensures that the vehicle remains stable and controllable, enhancing safety for the driver and passengers.
2. The ESP Button: Functionality and Usage
2.1. Locating the ESP Button in Your Mercedes-Benz
The ESP button in your Mercedes-Benz is typically located on the center console or dashboard, easily accessible to the driver. The button is usually marked with the ESP symbol, which shows a car with skid marks behind it. Its placement is designed for quick access, allowing you to toggle the system on or off as needed.
The exact location of the ESP button can vary slightly depending on the model year and trim level of your Mercedes-Benz. Consulting your vehicle’s owner’s manual is always a good idea to pinpoint its exact location. Being familiar with the ESP button’s location ensures that you can quickly adjust the system when necessary, enhancing your control over the vehicle in various driving conditions.
2.2. When and Why to Use the ESP Button
Under normal driving conditions, the ESP system should always be enabled to provide maximum stability and safety. However, there are specific situations where temporarily disabling ESP might be beneficial.
- Driving in Deep Snow or Mud: When driving in deep snow or mud, the wheels might need to spin to gain traction. ESP can sometimes interfere with this process by reducing engine power or applying brakes, which can prevent the vehicle from moving forward. Disabling ESP in these conditions allows the wheels to spin freely, helping you to get unstuck.
- Rocking the Vehicle: If your vehicle is stuck in snow or sand, you can use a rocking technique to free it. This involves repeatedly alternating between forward and reverse gears. ESP can sometimes hinder this process by attempting to stabilize the vehicle. Disabling ESP allows you to rock the vehicle more effectively.
- Dyno Testing: When performing dyno testing on your Mercedes-Benz, it is generally recommended to disable ESP. Dyno testing involves running the vehicle’s wheels at high speeds while the car remains stationary, which can confuse the ESP system and lead to inaccurate results.
In most other situations, ESP should remain enabled to provide optimal safety and stability. Always remember to re-enable ESP after navigating the challenging conditions to ensure maximum protection.
2.3. Understanding the ESP Indicator Light
The ESP indicator light on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard provides crucial information about the system’s status. The light typically appears as the same car-with-skid-marks symbol found on the ESP button. Here’s what the different states of the ESP indicator light mean:
- Flashing Light: When the ESP indicator light is flashing, it means that the ESP system is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. This usually occurs when the system detects a loss of traction or a potential skid. If you see the ESP light flashing, it’s a signal to drive more cautiously and allow the system to help maintain control.
- Solid Light: If the ESP indicator light is on and remains illuminated, it means that the ESP system has been manually disabled or that there is a malfunction within the system. If you have intentionally disabled ESP, the light serves as a reminder that the system is not active. If you have not disabled ESP and the light remains on, it indicates a problem that requires attention.
- No Light: Under normal operating conditions, the ESP indicator light should be off. This indicates that the ESP system is enabled and functioning correctly without any issues.
Knowing how to interpret the ESP indicator light helps you understand the status of your vehicle’s stability control system and take appropriate actions to ensure safety.
3. Troubleshooting ESP Issues
3.1. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions
Several factors can cause the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz to malfunction. Understanding these common causes can help you diagnose and address issues more effectively.
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: The wheel speed sensors are critical for monitoring wheel rotation. If one or more of these sensors fail, the ESP system may receive incorrect data, leading to malfunctions.
- Steering Angle Sensor Problems: The steering angle sensor provides data on the driver’s intended direction. If this sensor is faulty, the ESP system may not be able to accurately determine the vehicle’s path, causing it to activate inappropriately or not at all.
- Yaw Rate Sensor Issues: The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation. A malfunctioning yaw rate sensor can provide inaccurate data, leading to ESP errors.
- Brake System Problems: Issues with the brake system, such as a faulty ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module, can affect the ESP system. Since ESP relies on the ABS to apply brakes selectively, any problems with the ABS can impact ESP functionality.
- Low Battery Voltage: Inadequate battery voltage can cause various electronic systems in your vehicle to malfunction, including ESP. Ensure that your battery is in good condition and providing the necessary voltage.
- ECU Problems: Though less common, issues with the ESP system’s electronic control unit (ECU) can also cause malfunctions. The ECU processes data from all the sensors and controls the ESP system, so any problems with the ECU can disrupt the entire system.
Identifying the root cause of an ESP malfunction is the first step toward resolving the issue and restoring your vehicle’s stability control system.
3.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Problems
Diagnosing ESP problems in your Mercedes-Benz involves a systematic approach to identify the underlying issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Check the ESP Indicator Light: Observe the ESP indicator light on your dashboard. Is it flashing, solid, or off? This will provide initial clues about the system’s status.
- Read the Owner’s Manual: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for information on the ESP system and troubleshooting tips. The manual may provide specific guidance related to your vehicle’s model and year.
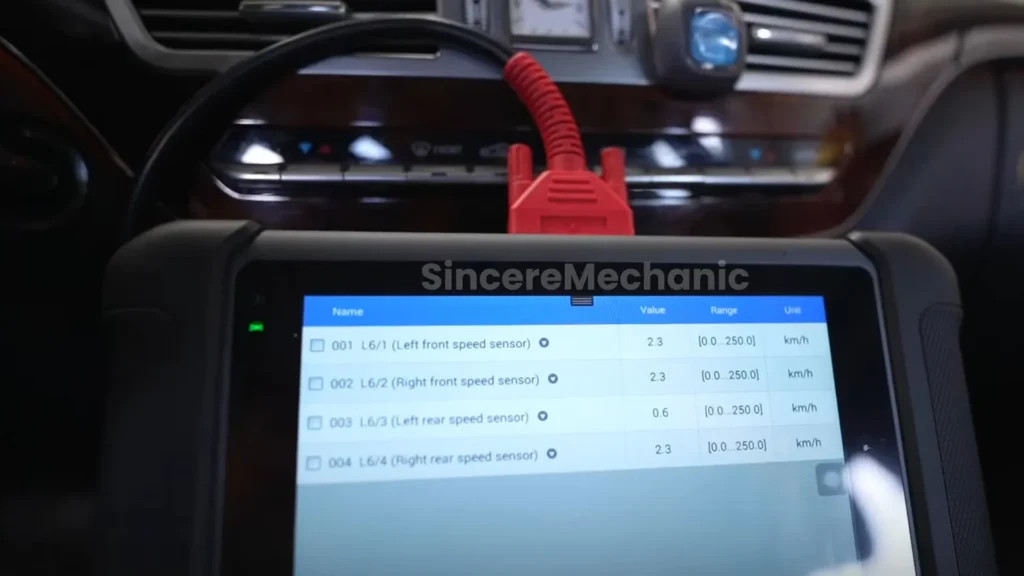
- Use an OBD-II Scanner: Connect an OBD-II scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port. This scanner can read trouble codes stored in the ECU, providing valuable information about potential issues. Common codes related to ESP problems include those indicating issues with wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or yaw rate sensors.
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Check the wheel speed sensors for damage or contamination. Clean the sensors and ensure they are properly connected. If a sensor is faulty, replace it.
- Check Steering Angle Sensor: Use the OBD-II scanner to monitor the steering angle sensor’s readings. Ensure that the sensor is providing accurate data as you turn the steering wheel. If the readings are erratic or incorrect, the sensor may need to be replaced.
- Inspect Yaw Rate Sensor: The yaw rate sensor is typically located under the seat or in the center console. Check the sensor for damage or loose connections. Use the OBD-II scanner to monitor its readings and ensure they are accurate.
- Check Brake System: Inspect the brake system for any issues, such as low brake fluid, worn brake pads, or problems with the ABS module. Address any brake-related issues, as they can affect the ESP system.
- Check Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. Ensure that the battery is providing the correct voltage, as low voltage can cause electronic systems to malfunction.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unable to diagnose the problem using these steps, consult a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center. They have the expertise and equipment to diagnose and repair complex ESP issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with professionals equipped to handle these issues efficiently. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose ESP problems in your Mercedes-Benz and take appropriate action to restore the system’s functionality.
3.3. When to Seek Professional Help
While some ESP issues can be resolved with simple troubleshooting steps, there are situations where seeking professional help is necessary. Here are some scenarios where you should consult a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center:
- Persistent ESP Light: If the ESP indicator light remains on despite your troubleshooting efforts, it indicates a more complex problem that requires professional diagnosis.
- Complex Diagnostic Codes: If the OBD-II scanner reveals complex diagnostic codes that you are unable to interpret or address, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
- ABS Problems: If you suspect issues with the ABS module or other components of the brake system, professional diagnosis and repair are essential.
- ECU Issues: Problems with the ESP system’s electronic control unit (ECU) often require specialized equipment and expertise to resolve.
- Unusual Symptoms: If you experience unusual symptoms such as erratic braking, loss of power, or instability while driving, it’s crucial to have your vehicle inspected by a professional.
- Safety Concerns: If you are concerned about your safety or the safety of others, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. ESP is a critical safety system, and any issues should be addressed promptly.
Seeking professional help ensures that ESP problems are accurately diagnosed and properly repaired, restoring your vehicle’s stability control system and enhancing safety.
4. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
4.1. Regular Maintenance Tips for ESP
Maintaining your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is crucial for ensuring its proper functioning and longevity. Here are some regular maintenance tips to help keep your ESP system in good condition:
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain the correct tire pressure as recommended by Mercedes-Benz. Proper tire pressure is essential for optimal ESP performance. Uneven or incorrect tire pressure can affect the system’s ability to accurately monitor wheel speed and stability.
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Regularly inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage, contamination, or loose connections. Clean the sensors as needed and ensure they are securely mounted.
- Monitor Brake System: Keep the brake system in good condition by regularly checking brake fluid levels, inspecting brake pads, and addressing any issues promptly. A properly functioning brake system is essential for ESP to operate effectively.
- Check Battery Voltage: Ensure that your vehicle’s battery is in good condition and providing the necessary voltage. Low battery voltage can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Address Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights on your dashboard, including the ESP indicator light. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage or malfunctions.
- Regular Servicing: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule for your Mercedes-Benz, including regular servicing by a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center. Regular servicing can help identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help keep your Mercedes-Benz ESP system in good condition and ensure its reliable performance.
4.2. The Importance of Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is critical for the performance and effectiveness of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Tires are the primary point of contact between your vehicle and the road, and their condition directly affects traction and stability. Here’s why tire maintenance is so important:
- Tire Pressure: Maintaining the correct tire pressure ensures that the tires have optimal contact with the road. Underinflated tires can reduce fuel efficiency, increase tire wear, and compromise handling and stability. Overinflated tires can reduce traction and make the ride uncomfortable.
- Tire Tread: Adequate tire tread is essential for maintaining traction, especially in wet or slippery conditions. As tires wear down, their ability to grip the road diminishes, increasing the risk of skidding and loss of control. Regularly inspect your tires for wear and replace them when the tread depth reaches the minimum limit.
- Tire Alignment: Proper tire alignment ensures that all four wheels are pointing in the correct direction. Misalignment can cause uneven tire wear, reduce fuel efficiency, and affect handling and stability. Have your tires aligned regularly to ensure optimal performance.
- Tire Rotation: Rotating your tires regularly helps to distribute wear evenly, extending their lifespan and maintaining consistent performance. Follow the recommended tire rotation pattern for your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Tire Quality: Invest in high-quality tires that are appropriate for your vehicle and driving conditions. High-quality tires provide better traction, handling, and stability, enhancing the overall performance of your ESP system.
By prioritizing proper tire maintenance, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz ESP system operates effectively and provides the maximum level of safety and stability.
4.3. Recognizing Signs of ESP System Wear and Tear
Recognizing the signs of ESP system wear and tear is essential for addressing issues promptly and preventing further damage. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- ESP Indicator Light: The ESP indicator light is the primary indicator of system issues. If the light remains on despite your troubleshooting efforts, it indicates a potential problem that needs attention.
- Erratic Braking: If you experience erratic braking, such as sudden or uneven braking, it could be a sign of ESP system problems.
- Loss of Stability: If you notice a loss of stability or control while driving, especially in slippery conditions, it could indicate that the ESP system is not functioning correctly.
- Unusual Noises: Unusual noises, such as grinding or clicking sounds, during braking or turning could be a sign of ESP system wear and tear.
- Reduced Performance: A noticeable reduction in overall vehicle performance, such as decreased acceleration or handling, could be related to ESP system issues.
- Diagnostic Codes: If you use an OBD-II scanner and find trouble codes related to the ESP system, it’s a clear sign that there is a problem that needs to be addressed.
By recognizing these signs of ESP system wear and tear, you can take prompt action to diagnose and repair any issues, ensuring the continued safety and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
5. Optimizing ESP Performance for Different Driving Conditions
5.1. Adjusting ESP Settings for Various Road Conditions
Your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is designed to provide optimal stability and control in a wide range of driving conditions. However, certain situations may require you to adjust the ESP settings to enhance performance. Here’s how to optimize ESP performance for different road conditions:
- Normal Conditions: Under normal driving conditions, the ESP system should be fully enabled. This provides the maximum level of stability and control, helping to prevent skidding and loss of control.
- Wet Conditions: In wet conditions, the ESP system can help maintain traction and stability by preventing wheel spin and skidding. Ensure that the ESP system is enabled and drive cautiously, allowing extra time for braking and maneuvering.
- Snowy Conditions: In snowy conditions, you may need to adjust the ESP settings to optimize performance. In some cases, disabling ESP can allow the wheels to spin more freely, providing better traction in deep snow. However, remember to re-enable ESP once you are out of the snowy conditions.
- Icy Conditions: Icy conditions can be extremely challenging to navigate. Ensure that the ESP system is enabled and drive very cautiously, as even small inputs can cause the vehicle to lose control. Consider using winter tires for added traction.
- Off-Road Conditions: When driving off-road, you may need to disable ESP to allow the wheels to spin and maintain momentum. However, be aware that disabling ESP reduces stability control, so drive with caution and be prepared to react to changing conditions.
By adjusting the ESP settings for various road conditions, you can optimize the system’s performance and enhance your driving experience.
5.2. Driving Techniques to Complement ESP
While ESP is a valuable safety feature, it is not a substitute for good driving techniques. Here are some driving techniques that can complement ESP and enhance your safety on the road:
- Smooth Steering: Use smooth and deliberate steering inputs to avoid sudden movements that can upset the vehicle’s balance.
- Controlled Braking: Practice controlled braking techniques to maintain traction and stability. Avoid slamming on the brakes, as this can cause the wheels to lock up and reduce control.
- Proper Acceleration: Accelerate smoothly and gradually to avoid wheel spin, especially in slippery conditions.
- Maintain Safe Distance: Maintain a safe following distance to allow ample time to react to changing conditions and avoid sudden maneuvers.
- Anticipate Hazards: Scan the road ahead and anticipate potential hazards, such as pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles. Be prepared to react quickly and safely.
- Stay Focused: Avoid distractions while driving, such as using your phone or adjusting the radio. Stay focused on the road and be aware of your surroundings.
By combining these driving techniques with the benefits of ESP, you can enhance your safety and confidence on the road.
5.3. The Role of Winter Tires in Enhancing ESP Effectiveness
Winter tires play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system in cold and snowy conditions. Winter tires are designed with a special rubber compound that remains flexible in low temperatures, providing superior grip on ice and snow. Here’s how winter tires enhance ESP effectiveness:
- Improved Traction: Winter tires provide significantly better traction on ice and snow compared to all-season or summer tires. This improved traction allows the ESP system to operate more effectively, as it has more grip to work with.
- Enhanced Braking: Winter tires can significantly reduce braking distances on ice and snow, allowing you to stop more quickly and safely. This enhanced braking performance complements the ESP system’s ability to prevent wheel lockup.
- Better Handling: Winter tires provide better handling and stability in cold and snowy conditions, allowing you to maintain control of your vehicle more easily. This improved handling enhances the ESP system’s ability to prevent skidding and loss of control.
- Increased Safety: By providing superior grip, braking, and handling in winter conditions, winter tires significantly increase safety for you and other drivers on the road.
Investing in a set of winter tires for your Mercedes-Benz is a wise decision if you live in an area with cold and snowy winters. Winter tires can enhance the effectiveness of your ESP system and provide you with the confidence to drive safely in challenging conditions. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of tools to help you maintain your tires, ensuring they’re always ready for winter. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information.
6. Advanced ESP Features in Modern Mercedes-Benz Models
6.1. Overview of Adaptive ESP Systems
Modern Mercedes-Benz models often feature advanced adaptive ESP systems that provide even greater levels of stability and control. These systems use sophisticated sensors and algorithms to continuously monitor driving conditions and adjust ESP parameters accordingly. Here are some key features of adaptive ESP systems:
- Automatic Adaptation: Adaptive ESP systems automatically adjust to changing road conditions, such as wet, snowy, or icy surfaces. The system continuously monitors wheel speed, steering angle, and other factors to optimize ESP performance in real-time.
- Curve Dynamic Assist: Curve Dynamic Assist helps to reduce understeer when cornering by applying brakes to the inside rear wheel. This enhances stability and allows the vehicle to maintain its intended path.
- Crosswind Assist: Crosswind Assist helps to compensate for the effects of strong crosswinds by selectively applying brakes to one side of the vehicle. This enhances stability and reduces the risk of being blown off course.
- Load Adaptive Control: Load Adaptive Control adjusts the ESP parameters based on the vehicle’s load. This helps to maintain stability when carrying heavy loads or towing a trailer.
Adaptive ESP systems provide a more refined and effective level of stability control compared to traditional ESP systems, enhancing safety and confidence for drivers in a wide range of conditions.
6.2. How Torque Vectoring Works with ESP
Torque vectoring is an advanced technology that works in conjunction with ESP to enhance handling and stability. Torque vectoring systems distribute torque between the rear wheels to improve cornering performance. Here’s how torque vectoring works with ESP:
- Enhanced Cornering: Torque vectoring enhances cornering performance by sending more torque to the outside rear wheel during turns. This helps to reduce understeer and allows the vehicle to turn more sharply.
- Improved Traction: Torque vectoring can improve traction by sending torque to the wheel with the most grip. This is particularly beneficial in slippery conditions, where one wheel may lose traction.
- Seamless Integration: Torque vectoring systems are seamlessly integrated with ESP, working together to provide optimal stability and control. The ESP system monitors the vehicle’s dynamics and adjusts torque distribution as needed to maintain stability.
- Increased Agility: By enhancing cornering performance and improving traction, torque vectoring increases the vehicle’s agility and responsiveness. This makes the vehicle more enjoyable to drive and enhances safety in emergency situations.
Torque vectoring is a valuable addition to ESP, providing an extra layer of control and stability for drivers.
6.3. Integration with Other Safety Systems
The ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz is often integrated with other safety systems to provide a comprehensive suite of safety features. Here are some of the safety systems that are commonly integrated with ESP:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, allowing you to maintain steering control. ESP works with ABS to selectively apply brakes to individual wheels, enhancing stability and control.
- Traction Control System (TCS): TCS prevents wheel spin during acceleration, helping to maintain traction and stability. ESP works with TCS to reduce engine power and apply brakes as needed to prevent wheel spin.
- Brake Assist System (BAS): BAS detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to help you stop more quickly. ESP works with BAS to enhance stability during emergency braking maneuvers.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC maintains a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead and can automatically adjust speed to avoid collisions. ESP works with ACC to enhance stability during automated braking and acceleration.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): LKA helps to prevent unintentional lane departures by providing steering assistance or warnings. ESP works with LKA to enhance stability when making lane changes or corrections.
By integrating with these and other safety systems, ESP provides a comprehensive safety net that helps to protect you and your passengers in a wide range of driving situations.
7. DIY ESP Button Fixes and When to Avoid Them
7.1. Simple Solutions for Common ESP Button Issues
Sometimes, the ESP button on your Mercedes-Benz might seem unresponsive or cause issues. Before heading to a mechanic, there are a few simple solutions you can try at home. These fixes are easy and can potentially save you time and money.
- Check the Button: Ensure the ESP button is not physically stuck or damaged. Gently press the button to see if it moves freely. Clean around the button with a soft cloth to remove any dirt or debris that might be causing it to stick.
- Restart Your Car: A simple restart can sometimes reset the system. Turn off your car, wait a few minutes, and then start it again. This can resolve temporary software glitches that might affect the ESP button’s functionality.
- Check the Fuse: Locate the fuse box in your Mercedes-Benz and check the fuse associated with the ESP system. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new one of the same amperage. Refer to your car’s manual for the location of the fuse box and the specific fuse for the ESP system.
- Reset the ESP System: Some Mercedes-Benz models allow you to reset the ESP system by turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left to full right) and then driving the car a short distance. Consult your owner’s manual for specific instructions on how to reset the ESP system in your vehicle.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure that all your tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can sometimes trigger the ESP system to malfunction. Adjust the tire pressure to the recommended levels specified in your car’s manual.
If these simple solutions don’t resolve the issue, it might be time to seek professional help.
7.2. When DIY Repairs Can Do More Harm Than Good
While DIY repairs can be tempting, especially to save money, there are situations where attempting to fix the ESP button or system yourself can lead to more harm than good. Here are scenarios where you should avoid DIY repairs:
- Complex Electrical Issues: If the ESP button issue involves complex electrical problems, such as wiring issues or faulty sensors, it’s best to leave it to a professional. Incorrectly handling electrical components can damage your car’s electrical system and create safety hazards.
- Internal System Malfunctions: If the ESP system malfunctions due to internal issues, such as a faulty control module or hydraulic unit, DIY repairs are not recommended. These components require specialized tools and expertise to diagnose and repair.
- Lack of Diagnostic Tools: Diagnosing ESP issues often requires advanced diagnostic tools, such as OBD-II scanners, that can read trouble codes and monitor system parameters. If you don’t have access to these tools, you won’t be able to accurately identify the problem.
- Warranty Concerns: Attempting DIY repairs on a car that’s still under warranty can void the warranty. It’s best to take your car to an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center to ensure that repairs are done correctly and don’t affect your warranty coverage.
- Safety-Critical Systems: The ESP system is a safety-critical system that plays a vital role in preventing accidents. Incorrectly repairing the ESP system can compromise its functionality and put you and others at risk.
In these situations, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center. They have the expertise, tools, and experience to diagnose and repair ESP issues safely and effectively.
7.3. The Importance of Using the Right Tools and Parts
When performing DIY repairs on your Mercedes-Benz, it’s crucial to use the right tools and parts. Using the wrong tools or parts can damage your car and create safety hazards. Here’s why using the right tools and parts is so important:
- Proper Fit: The right tools and parts are designed to fit your car’s specific make and model. Using generic or incorrect tools and parts can damage components and prevent them from functioning properly.
- Safety: Using the right tools and parts ensures that repairs are done safely and correctly. Incorrectly installed parts or improperly used tools can create safety hazards and put you and others at risk.
- Performance: Using the right parts ensures that your car performs as intended. Genuine Mercedes-Benz parts are designed to meet the highest standards of quality and performance, ensuring that your car operates safely and efficiently.
- Durability: Using high-quality tools and parts ensures that repairs are durable and long-lasting. Cheap or low-quality tools and parts can fail prematurely, leading to additional repairs and expenses.
- Warranty Compliance: Using genuine Mercedes-Benz parts is often required to maintain your car’s warranty coverage. Using aftermarket parts can void your warranty and leave you responsible for any repairs.
Investing in the right tools and parts is essential for performing DIY repairs safely and effectively. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools and diagnostic equipment to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and assistance.
8. ESP Button and System: Legal and Safety Standards
8.1. Legal Requirements for ESP Systems
In many countries, including the United States and Europe, Electronic Stability Program (ESP) systems are mandated on all new vehicles. These legal requirements underscore the importance of ESP in enhancing vehicle safety and reducing accidents. Here are some key aspects of the legal requirements for ESP systems:
- Mandatory Installation: Many countries require all new passenger vehicles to be equipped with ESP systems. This ensures that all drivers have access to this life-saving technology.
- Performance Standards: ESP systems must meet certain performance standards to be compliant with legal requirements. These standards specify the minimum level of stability control that the system must provide.
- Testing and Certification: ESP systems are typically tested and certified by regulatory agencies to ensure that they meet the required performance standards.
- Recall Requirements: If an ESP system is found to be defective or non-compliant with legal requirements, the manufacturer may be required to issue a recall to repair or replace the system.
These legal requirements reflect the widespread recognition of ESP as a critical safety feature and the importance of ensuring that all vehicles are equipped with this technology.
8.2. Safety Standards and Ratings for ESP
In addition to legal requirements, ESP systems are also subject to various safety standards and ratings. These standards and ratings provide consumers with valuable information about the effectiveness and reliability of ESP systems. Here are some key aspects of safety standards and ratings for ESP:
- Euro NCAP: The European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) is an independent organization that assesses the safety of new vehicles. Euro NCAP tests ESP systems as part of its overall safety assessment and awards ratings based on their performance.
- IIHS: The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) is an independent organization that conducts research and testing on vehicle safety. The IIHS has conducted numerous studies on the effectiveness of ESP systems and has found that they significantly reduce the risk of single-vehicle crashes.
- NHTSA: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is a U.S. government agency responsible for setting and enforcing vehicle safety standards. NHTSA conducts research and testing on ESP systems and provides consumers with information about their effectiveness.
These safety standards and ratings provide consumers with valuable information about the safety performance of vehicles and the effectiveness of their ESP systems.
8.3. The Role of Regular Inspections in Maintaining Safety Compliance
Regular inspections play a crucial role in maintaining the safety compliance of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems and ensure that your ESP system is functioning correctly. Here are some key aspects of regular inspections for ESP systems:
- Visual Inspection: A visual inspection can help identify any obvious damage or issues with the ESP system, such as damaged sensors, loose connections, or worn components.
- Diagnostic Testing: Diagnostic testing using an OBD-II scanner can help identify any trouble codes stored in the ECU, providing valuable information about potential issues with the ESP system.
- Performance Testing: Performance testing can help verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly and meeting the required performance standards. This may involve testing the system’s ability to prevent wheel spin, maintain stability during braking, and correct for oversteer or understeer.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance and repairs can help keep your ESP system in good condition and ensure that it continues to function safely and effectively.
By performing regular inspections and addressing any issues promptly, you can help maintain the safety compliance of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system and ensure that it continues to protect you and your passengers on the road.
9. Purchasing Guide: Finding the Right ESP Tools and Equipment
9.1. Essential Tools for ESP Diagnostics and Repair
Having the right tools is crucial for diagnosing and repairing ESP issues on your Mercedes-Benz. Here are some essential tools that every DIY mechanic or professional technician should have:
- OBD-II Scanner: An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading trouble codes stored in the ECU. This tool can help you identify the specific problem affecting your ESP system.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is useful for testing electrical components, such as wheel speed sensors and wiring connections. This tool can help you identify faulty components and diagnose electrical issues.
- Scan Tool with ABS/ESP Capabilities: A scan tool with ABS/ESP capabilities allows you to access and monitor the ESP system in real-time. This tool can help you diagnose complex ESP issues and verify that repairs are done correctly.
- Hydraulic Brake Bleeding Kit: A hydraulic brake bleeding kit is essential for bleeding the brake system after performing repairs. This ensures that the brake system is functioning correctly and that the ESP system can operate effectively.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is necessary for tightening bolts and fasteners to the correct torque specifications. This prevents damage to components and ensures that repairs are secure.
Investing in these essential tools will enable you to diagnose and repair ESP issues on your Mercedes-Benz effectively.
9.2. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Equipment
Choosing the right diagnostic equipment is crucial for accurately diagnosing ESP issues. Here are some factors to consider when selecting diagnostic equipment:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the diagnostic equipment is compatible with your Mercedes-Benz model. Some diagnostic tools are designed to work with specific makes and models of vehicles, so it’s essential to choose one that’s compatible with your car.
- Features: Look for diagnostic equipment with advanced features, such as ABS/ESP capabilities, live data streaming, and bidirectional control. These features can help you diagnose complex ESP issues and verify that repairs are done correctly.
- Ease of Use: Choose diagnostic equipment that’s easy to use and navigate. Look