Esp Inoperative Mercedes: Causes, Solutions, and Prevention

Are you encountering an “ESP Inoperative Mercedes” warning and seeking a solution? Look no further. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the frustration this can cause. This comprehensive guide will delve into the potential causes of the ESP malfunction, provide step-by-step troubleshooting, and equip you with the knowledge to prevent future occurrences. We’ll also highlight how our top-notch auto repair tools can help you diagnose and resolve this issue efficiently, getting you back on the road with confidence. Explore Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, electronic stability program solutions and vehicle safety systems troubleshooting.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP), a cornerstone of modern vehicle safety, is designed to prevent skidding and maintain directional control during challenging driving conditions. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP uses sensors to monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, allowing it to detect and correct potential loss of control. When the “ESP Inoperative” warning illuminates, it signifies a disruption within this critical system.
1.1. What is ESP and Why Is It Important?
ESP, which stands for Electronic Stability Program, is an active safety system designed to prevent skidding and loss of control. It monitors various parameters, such as wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, and intervenes by applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power to keep the vehicle on its intended path. ESP is crucial for maintaining stability, especially in adverse weather conditions or during emergency maneuvers. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 32%.
1.2. How Does ESP Work in a Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP system in a Mercedes-Benz utilizes a network of sensors to continuously monitor the vehicle’s dynamics. These sensors include:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Determines the angle of the steering wheel.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Detects the sideways acceleration of the vehicle.
When the ESP system detects a discrepancy between the driver’s intended path and the vehicle’s actual movement, it intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine torque. This helps to counteract oversteer (when the rear of the car slides out) or understeer (when the front of the car plows straight ahead).
1.3. Identifying the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
The “ESP Inoperative” warning typically appears on the instrument cluster of your Mercedes-Benz as a message or an illuminated symbol. The symbol often depicts a car with skid marks behind it. It’s important to note that the exact appearance of the warning may vary depending on the specific model and year of your vehicle.
 Mercedes ESP Inoperative warning light on the dashboard
Mercedes ESP Inoperative warning light on the dashboard
2. Common Causes of the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
Several factors can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning in your Mercedes-Benz. Pinpointing the exact cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair. Here are some of the most common culprits:
2.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are vital for the ESP system to function correctly. These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel and transmit this data to the ESP control unit. If one or more wheel speed sensors fail, the ESP system may become disabled, triggering the warning light. According to a study by Bosch, a leading automotive supplier, faulty wheel speed sensors are a common cause of ESP malfunctions.
2.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP system. This data is essential for determining the driver’s intended direction. If the steering angle sensor is misaligned, damaged, or faulty, it can disrupt the ESP system and cause the “ESP Inoperative” warning to appear.
2.3. Low Battery Voltage or a Failing Alternator
The ESP system relies on a stable and consistent power supply to operate correctly. Low battery voltage or a failing alternator can cause voltage fluctuations that interfere with the ESP control unit and trigger the warning light. A weak battery can also lead to other electrical issues in your Mercedes-Benz.
2.4. Faulty Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch activates the brake lights when you press the brake pedal. It also sends a signal to the ESP system, indicating that you are braking. If the brake light switch is faulty, it may send incorrect signals to the ESP system, leading to the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
2.5. Issues with the ESP Control Unit
The ESP control unit is the brain of the ESP system. It processes data from various sensors and controls the braking and engine power adjustments. In rare cases, the ESP control unit itself may fail, causing the “ESP Inoperative” warning to appear.
2.6. Corroded or Damaged Wiring
The ESP system relies on a network of wires to transmit signals between the sensors, control unit, and other components. Corroded or damaged wiring can disrupt these signals, leading to ESP malfunctions and the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
| Cause | Description | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor | Inaccurate wheel speed readings disrupt ESP function. | Replace the faulty sensor. |
| Steering Angle Sensor Issue | Misalignment or malfunction hinders ESP’s ability to determine steering direction. | Calibrate or replace the steering angle sensor. |
| Low Battery Voltage | Insufficient power affects ESP system operation. | Charge or replace the battery; inspect the alternator. |
| Faulty Brake Light Switch | Incorrect signals disrupt ESP’s braking input recognition. | Replace the brake light switch. |
| ESP Control Unit Failure | Malfunction within the control unit disables the ESP system. | Replace the ESP control unit (requires programming). |
| Damaged Wiring | Interrupted signals between components cause system errors. | Repair or replace damaged wiring and connectors. |
3. Diagnosing the “ESP Inoperative” Warning: A Step-by-Step Guide
When the “ESP Inoperative” warning appears on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard, it’s crucial to diagnose the underlying cause before attempting any repairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you pinpoint the problem:
3.1. Initial Inspection
Before diving into complex diagnostics, start with a visual inspection of the following:
- Tires: Check tire pressure and look for any signs of damage or wear. Uneven tire wear can affect wheel speed readings and trigger the ESP warning.
- Wiring: Inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors near the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and ESP control unit. Look for any signs of corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Brake Lights: Ensure that all brake lights are functioning correctly. A faulty brake light can interfere with the ESP system.
3.2. Using a Diagnostic Scan Tool
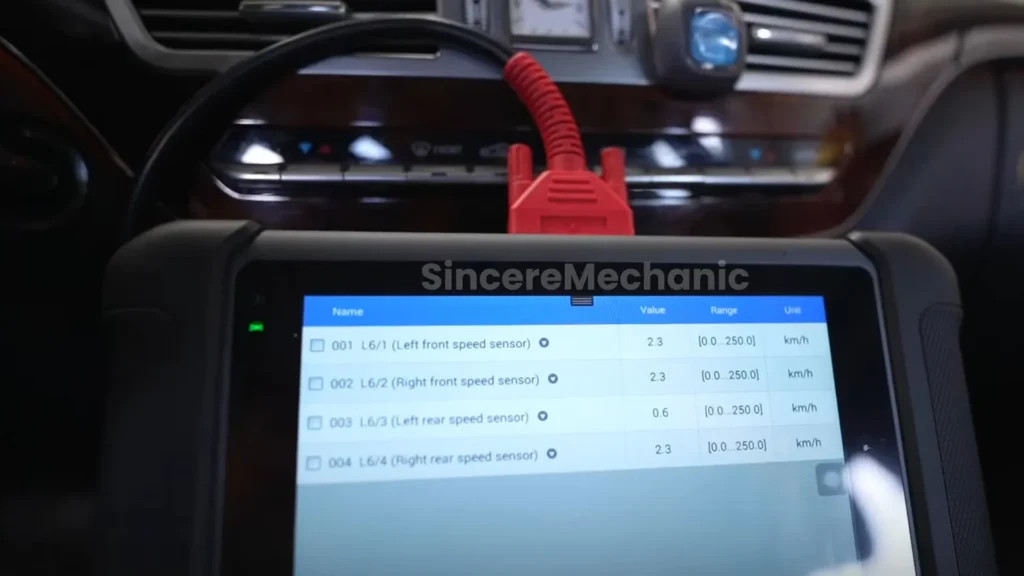
A diagnostic scan tool is an invaluable tool for diagnosing ESP-related issues. Connect the scan tool to your Mercedes-Benz’s OBD-II port (typically located under the dashboard) and retrieve any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the ESP system. These codes can provide valuable clues about the source of the problem.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of professional-grade diagnostic scan tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our tools can read and clear DTCs, perform live data streaming, and even execute advanced functions like sensor calibrations.
3.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Once you’ve retrieved the DTCs, consult a Mercedes-Benz repair manual or online database to interpret their meaning. Here are some common DTCs related to ESP malfunctions:
- C1000: ESP control unit fault
- C1100 – C1103: Wheel speed sensor circuit malfunction
- C1140: Steering angle sensor fault
- C1401: Brake light switch circuit malfunction
The diagnostic trouble codes provide a starting point for troubleshooting the issue.
3.4. Testing Wheel Speed Sensors
If you suspect a faulty wheel speed sensor, you can test its functionality using a multimeter. With the wheel speed sensor disconnected, measure the resistance across its terminals. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications. An open circuit or a reading outside the specified range indicates a faulty sensor.
You can also use a scan tool to monitor the wheel speed sensor readings in real-time while driving. If one or more sensors show erratic or inconsistent readings, it’s likely that they are faulty.
3.5. Checking the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor can be checked using a diagnostic scan tool. The scan tool can display the steering angle in real-time. As you turn the steering wheel, the steering angle reading should change accordingly. If the reading is inaccurate or doesn’t change, the steering angle sensor may need to be calibrated or replaced.
3.6. Evaluating Battery Voltage and Alternator Output
Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off and with the engine running. With the engine off, the battery voltage should be around 12.6 volts. With the engine running, the voltage should be between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. If the voltage is outside of these ranges, the battery or alternator may be faulty.
3.7. Inspecting the Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch can be inspected visually and with a multimeter. Check that the brake lights illuminate when you press the brake pedal. If the brake lights don’t work, the brake light switch may be faulty.
You can also use a multimeter to check the continuity of the brake light switch. With the brake pedal released, the switch should be open. When you press the brake pedal, the switch should close. If the switch doesn’t function as expected, it should be replaced.
| Diagnostic Step | Procedure | Tools Required | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Inspection | Check tires, wiring, and brake lights for obvious issues. | None | Identify visible problems affecting ESP. |
| Diagnostic Scan Tool | Connect tool to OBD-II port and retrieve DTCs. | Diagnostic scan tool | Obtain specific error codes related to the ESP system. |
| DTC Interpretation | Research DTCs to understand their meaning and implications. | Mercedes-Benz repair manual or online database | Narrow down the potential causes of the ESP issue. |
| Wheel Speed Sensor Testing | Measure resistance across terminals; monitor real-time readings while driving. | Multimeter, diagnostic scan tool | Confirm functionality and consistency of wheel speed sensor readings. |
| Steering Angle Sensor Check | Display steering angle in real-time with a scan tool while turning the wheel. | Diagnostic scan tool | Verify accurate steering angle readings; identify need for calibration or replacement. |
| Battery & Alternator Check | Measure battery voltage with the engine off and running. | Multimeter | Ensure proper voltage ranges for battery and alternator. |
| Brake Light Switch Check | Verify brake light functionality and continuity with a multimeter. | Multimeter | Confirm correct operation of the brake light switch and its signal to the ESP system. |
4. How to Fix the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the “ESP Inoperative” warning, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common solutions:
4.1. Replacing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor is a relatively straightforward repair. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor. It is typically mounted near the wheel hub.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the bolt that secures the sensor to the hub.
- Carefully remove the sensor from the hub.
- Install the new wheel speed sensor in the reverse order of removal.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Clear the DTCs using a diagnostic scan tool.
- Test drive the vehicle to ensure that the ESP warning is gone.
4.2. Calibrating or Replacing the Steering Angle Sensor
If the steering angle sensor is misaligned, it may need to be calibrated. Some diagnostic scan tools can perform this calibration procedure. Follow the instructions provided by the scan tool manufacturer.
If the steering angle sensor is damaged or faulty, it will need to be replaced. The replacement procedure is similar to that of the wheel speed sensor.
4.3. Addressing Battery and Alternator Issues
If the battery voltage is low, try charging the battery using a battery charger. If the battery doesn’t hold a charge, it will need to be replaced.
If the alternator is not producing enough voltage, it will need to be replaced. Replacing the alternator typically involves removing the drive belt, disconnecting the electrical connections, and unbolting the alternator from the engine.
4.4. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
Replacing the brake light switch is a relatively simple repair. The brake light switch is typically located near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the switch from its mounting bracket.
- Install the new switch in the reverse order of removal.
- Adjust the switch so that it is properly aligned.
- Test the brake lights to ensure that they are working correctly.
4.5. Addressing ESP Control Unit Issues
If the ESP control unit is faulty, it will need to be replaced. Replacing the ESP control unit typically requires programming the new unit to match the vehicle’s configuration. This programming can be done by a Mercedes-Benz dealer or a qualified independent repair shop.
4.6. Repairing or Replacing Damaged Wiring
If the wiring is corroded or damaged, it will need to be repaired or replaced. Repairing wiring typically involves splicing in new sections of wire and insulating the connections. Replacing wiring may involve replacing entire wiring harnesses.
| Repair Action | Procedure | Tools Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replace Wheel Speed Sensor | Disconnect battery, remove/replace sensor, reconnect battery, clear DTCs. | Socket set, wrench, diagnostic scan tool. | Ensure correct sensor for the specific wheel. |
| Calibrate Steering Angle Sensor | Use diagnostic tool to perform calibration procedure. | Diagnostic scan tool. | Follow tool manufacturer’s instructions. |
| Replace Steering Angle Sensor | Similar to wheel speed sensor replacement. | Socket set, wrench, diagnostic scan tool. | Requires careful alignment during installation. |
| Address Battery/Alternator Issues | Charge/replace battery; replace alternator if necessary. | Multimeter, socket set, wrench, battery charger. | Ensure proper voltage output after replacement. |
| Replace Brake Light Switch | Disconnect connector, remove/replace switch, adjust alignment, test lights. | Screwdriver, wrench. | Proper alignment is crucial for correct function. |
| Address ESP Control Unit | Requires professional replacement and programming. | Specialized diagnostic equipment, Mercedes-Benz dealer or specialist. | This is a complex repair that should be handled by experienced technicians. |
| Repair/Replace Damaged Wiring | Splice in new sections or replace entire harnesses. | Wire stripper, crimper, soldering iron, electrical tape. | Ensure proper insulation and secure connections. |
5. Preventing Future ESP Problems
While some ESP malfunctions are unavoidable, there are several steps you can take to minimize the risk of future problems:
5.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Adhere to your Mercedes-Benz’s recommended maintenance schedule. This includes regular inspections of the braking system, tires, and electrical components.
5.2. Tire Care and Maintenance
Maintain proper tire pressure and ensure that your tires are in good condition. Replace worn tires promptly and consider using tires that are specifically designed for your vehicle.
5.3. Proper Battery Care
Keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion. If you notice any signs of battery weakness, have it tested by a professional.
5.4. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Don’t ignore minor issues with your vehicle, such as unusual noises or warning lights. Addressing these problems early can prevent them from escalating into more significant ESP malfunctions.
5.5. Professional Inspections
Consider having your Mercedes-Benz inspected by a qualified technician at least once a year. A professional inspection can identify potential problems before they lead to ESP malfunctions.
| Preventive Measure | Action | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Maintenance | Adhere to maintenance schedule for braking, tires, and electrical components. | As recommended in the vehicle’s manual. | Detects and prevents minor issues from escalating. |
| Tire Care | Maintain proper tire pressure, replace worn tires, use recommended tires. | Regularly (e.g., monthly for pressure, as needed for wear). | Ensures accurate wheel speed readings and optimal ESP performance. |
| Battery Care | Keep terminals clean, test battery regularly, replace as needed. | Regularly (e.g., every six months for cleaning, testing as needed). | Provides stable voltage for ESP operation. |
| Prompt Issue Resolution | Address unusual noises or warning lights immediately. | As soon as noticed. | Prevents minor problems from becoming major malfunctions. |
| Professional Inspections | Have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician. | At least annually. | Identifies potential issues before they lead to ESP problems. |
6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in ESP Diagnostics and Repair
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing you with the tools and resources you need to diagnose and repair ESP-related issues in your Mercedes-Benz. Our extensive selection of diagnostic scan tools, along with our team of expert technicians, can help you get to the bottom of the problem quickly and efficiently.
6.1. Our Range of Diagnostic Scan Tools
We offer a wide range of diagnostic scan tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools can read and clear DTCs, perform live data streaming, and execute advanced functions like sensor calibrations.
6.2. Expert Technical Support
Our team of expert technicians is available to provide you with technical support and guidance. We can help you interpret DTCs, troubleshoot ESP malfunctions, and recommend the appropriate repair procedures.
6.3. High-Quality Replacement Parts
We offer a comprehensive selection of high-quality replacement parts for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, brake light switches, and ESP control units. All of our parts are sourced from reputable manufacturers and are backed by a warranty.
6.4. Benefits of Choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Extensive selection of diagnostic tools and replacement parts
- Expert technical support from experienced technicians
- Competitive prices
- Fast and reliable shipping
- Commitment to customer satisfaction
When it comes to diagnosing and repairing ESP-related issues in your Mercedes-Benz, CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner.
Is the “ESP Inoperative Mercedes” warning light causing you stress? Don’t let it compromise your safety and driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert assistance and top-quality diagnostic tools. Our team is ready to help you diagnose and resolve the issue efficiently, so you can get back to enjoying your Mercedes-Benz with complete peace of mind. We are located at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
 Technician using a diagnostic tool on a Mercedes-Benz
Technician using a diagnostic tool on a Mercedes-Benz
7. Real-World Case Studies
To illustrate the diagnostic and repair process, let’s examine a few real-world case studies involving the “ESP Inoperative” warning in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
7.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
A customer reported an “ESP Inoperative” warning in their Mercedes-Benz C-Class. Using a diagnostic scan tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET, the technician retrieved a DTC indicating a malfunction in the right front wheel speed sensor circuit.
The technician then tested the wheel speed sensor using a multimeter and found that it had an open circuit. The wheel speed sensor was replaced, the DTC was cleared, and the ESP warning disappeared.
7.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Misalignment
A customer complained of an “ESP Inoperative” warning in their Mercedes-Benz E-Class. The diagnostic scan tool revealed a DTC related to the steering angle sensor.
The technician used the scan tool to monitor the steering angle in real-time. It was found that the steering angle reading was inaccurate. The technician performed a steering angle sensor calibration using the scan tool, and the ESP warning was resolved.
7.3. Case Study 3: Low Battery Voltage
A customer experienced an intermittent “ESP Inoperative” warning in their Mercedes-Benz S-Class. The technician measured the battery voltage and found that it was below the specified range.
The battery was replaced, and the ESP warning disappeared. The technician also recommended that the customer have the alternator tested to ensure that it was charging the battery properly.
These case studies highlight the importance of proper diagnosis and the use of appropriate diagnostic tools in resolving ESP-related issues.
| Case Study | Vehicle Model | Problem | Diagnostic Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C-Class | Faulty wheel speed sensor | DTC retrieval, multimeter testing of sensor. | Wheel speed sensor replacement. |
| 2 | E-Class | Steering angle sensor misalignment | DTC retrieval, real-time monitoring of steering angle with tool. | Steering angle sensor calibration. |
| 3 | S-Class | Low battery voltage | Battery voltage measurement. | Battery replacement. |
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions about the “ESP Inoperative” warning in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
8.1. Can I drive my car with the “ESP Inoperative” warning on?
While it is technically possible to drive your car with the “ESP Inoperative” warning illuminated, it is not recommended. The ESP system is a critical safety feature, and driving without it can increase the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions or during emergency maneuvers.
8.2. How much does it cost to fix the “ESP Inoperative” warning?
The cost to fix the “ESP Inoperative” warning can vary depending on the underlying cause of the problem. Replacing a wheel speed sensor may cost a few hundred dollars, while replacing the ESP control unit can cost several thousand dollars.
8.3. Can I reset the ESP system myself?
In some cases, you may be able to reset the ESP system by turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left to full right) several times. However, this may not work for all ESP malfunctions. It is always recommended to have the system diagnosed by a qualified technician.
8.4. Is the “ESP Inoperative” warning covered under warranty?
Whether the “ESP Inoperative” warning is covered under warranty depends on the age and mileage of your vehicle, as well as the terms of your warranty. Consult your warranty booklet or contact your Mercedes-Benz dealer for more information.
8.5. Can low tire pressure cause the “ESP Inoperative” warning?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect wheel speed readings and trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning. Make sure that your tires are properly inflated.
8.6. What does the ESP button do in my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP button allows you to temporarily disable the ESP system. This may be useful in certain situations, such as when driving in deep snow or mud. However, it is generally recommended to keep the ESP system enabled.
8.7. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
It is recommended to have your ESP system checked at least once a year, or whenever you notice any unusual symptoms.
8.8. Can a faulty ABS system cause the “ESP Inoperative” warning?
Yes, a faulty ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) can cause the “ESP Inoperative” warning to appear, as the two systems are interconnected and share some components.
8.9. Where can I find a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician to diagnose my ESP system?
You can find a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician by contacting your local Mercedes-Benz dealer or searching for independent repair shops that specialize in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
8.10. What should I do if the “ESP Inoperative” warning comes on while I’m driving?
If the “ESP Inoperative” warning comes on while you’re driving, pull over to a safe location as soon as possible and turn off the engine. Restart the engine and see if the warning disappears. If the warning persists, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Drive with ESP Inoperative warning? | Not recommended; ESP is a critical safety feature. |
| Cost to fix? | Varies; wheel speed sensor replacement may cost a few hundred dollars, while ESP control unit replacement can cost thousands. |
| Reset ESP system myself? | Sometimes turning the steering wheel lock to lock may work, but professional diagnosis is recommended. |
| Covered under warranty? | Depends on vehicle age, mileage, and warranty terms; consult warranty booklet or dealer. |
| Low tire pressure cause warning? | Yes, it can affect wheel speed readings. |
| What does ESP button do? | Temporarily disables the ESP system; generally recommended to keep it enabled. |
| How often check ESP system? | At least annually, or whenever you notice unusual symptoms. |
| Faulty ABS cause ESP warning? | Yes, the systems are interconnected. |
| Find qualified technician? | Contact local Mercedes-Benz dealer or independent repair shops specializing in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. |
| ESP Inoperative warning while driving? | Pull over safely, turn off the engine, and restart. If the warning persists, have the vehicle inspected. |
9. Conclusion: Ensuring Your Mercedes-Benz’s Safety and Performance
The “ESP Inoperative” warning in your Mercedes-Benz should not be ignored. By understanding the ESP system, diagnosing the cause of the warning, and performing the necessary repairs, you can ensure your vehicle’s safety and performance.
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner in ESP diagnostics and repair. We offer a wide range of diagnostic scan tools, expert technical support, and high-quality replacement parts. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely.
Don’t compromise on safety. Act now and ensure your Mercedes-Benz’s ESP system is functioning perfectly. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert assistance and premium tools that will empower you to resolve any ESP issue with confidence. Our location is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you drive safely and securely.
Remember, a well-maintained ESP system is crucial for your safety and the safety of others on the road.



