ESP Inoperative Mercedes B Class: Diagnosis And Solutions
Is your Mercedes B-Class flashing “ESP inoperative” and “run flat indicator inoperative” messages? CARDIAGTECH.NET offers the diagnostic tools and expertise you need. Explore the causes and solutions for these issues and discover how our equipment can streamline your repair process, enhancing your diagnostic capabilities.
1. Understanding ESP Inoperative in Your Mercedes B-Class
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety feature in your Mercedes B-Class, preventing skidding and maintaining control during challenging driving conditions. When the ESP system malfunctions, a warning message appears on the dashboard, indicating the system is disabled. This deactivation can severely compromise vehicle safety, making it critical to address the issue promptly.
1.1. What is ESP?
ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, actively enhances vehicle control by detecting and mitigating skidding. It uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, the ESP system intervenes by applying braking force to individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course.
1.2. Symptoms of ESP Malfunction
When the ESP system fails, drivers may notice a range of symptoms that affect the handling and safety of their vehicle. Identifying these symptoms early can help prevent accidents and costly repairs.
- Warning Lights: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light may appear as “ESP Inoperative” or a similar message.
- Reduced Traction Control: The vehicle may experience a loss of traction, particularly on slippery surfaces. This can result in wheel spin during acceleration or difficulty maintaining control in turns.
- ABS Issues: The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and ESP are often interconnected. An ESP malfunction can sometimes affect the ABS, leading to longer stopping distances or a pulsating brake pedal.
- Steering Problems: Drivers might notice unusual steering behavior, such as difficulty turning or a feeling of instability, especially at higher speeds.
- Limited Cornering Stability: The vehicle may feel less stable when cornering, with a greater tendency to lean or lose control.
1.3. Common Causes of ESP Failure
Several factors can trigger an ESP malfunction in Mercedes B-Class vehicles. Understanding these potential causes is the first step in diagnosing and resolving the issue.
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide crucial data to the ESP system. If a sensor fails, the ESP may not function correctly.
- Steering Angle Sensor Issues: The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and helps the ESP determine the driver’s intended direction. A faulty sensor can lead to ESP errors.
- Brake Light Switch Problems: The brake light switch signals when the brakes are applied. A malfunctioning switch can disrupt the ESP system, as it relies on this signal to function properly.
- Low Battery Voltage: The ESP system requires stable voltage to operate. A weak or failing battery can cause the ESP to malfunction.
- Hydraulic Pump Failure: The ESP system uses a hydraulic pump to apply braking force to individual wheels. If the pump fails, the ESP will be unable to function.
- Software or Module Issues: Sometimes, the ESP system’s software can become corrupted or the ESP control module itself may fail, requiring reprogramming or replacement.
- Alignment Issues: Incorrect wheel alignment can cause the ESP system to constantly work to compensate, eventually leading to a malfunction.
2. Step-by-Step Diagnosis of ESP Inoperative Mercedes B-Class
Diagnosing an ESP inoperative issue in a Mercedes B-Class requires a systematic approach. Here’s a detailed guide to help you pinpoint the problem.
2.1. Initial Inspection and Checks
Before diving into complex diagnostics, start with a thorough visual inspection and some basic checks.
- Check the Dashboard: Note all warning lights and messages displayed. This provides initial clues about the problem.
- Inspect the Tires: Ensure tires are properly inflated and in good condition. Uneven tire wear or incorrect pressure can affect ESP performance.
- Review Recent Repairs: Check for any recent work done on the vehicle, particularly on the braking or steering systems, which could be related to the ESP issue.
- Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer. This is a crucial step in identifying the specific problem areas. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic tools that can accurately read and interpret these codes.
2.2. Using Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a range of diagnostic tools that are essential for accurately diagnosing ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools allow you to read error codes, monitor sensor data, and perform advanced system tests.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic scanner into the OBD-II port of your Mercedes B-Class.
- Read and Record DTCs: Turn on the ignition and use the scanner to read any stored DTCs. Record these codes, as they will guide your diagnostic process.
- Clear Fault Codes (Optional): After recording the codes, you can clear them to see if they reappear. This can help determine if the issue is intermittent or persistent.
2.3. Interpreting Error Codes
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) provide valuable information about the nature and location of the ESP fault. Here’s how to interpret some common codes:
| Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C1120 | ESP Control Unit Fault | Faulty ESP control module, wiring issues, or poor connection |
| C1140 | Steering Angle Sensor Fault | Defective steering angle sensor, wiring problems, or misalignment |
| C1175 | Wheel Speed Sensor – Implausible Signal | Faulty wheel speed sensor, damaged wiring, or contaminated sensor |
| C1200 | Brake Light Switch Malfunction | Defective brake light switch, wiring issues, or incorrect installation |
| C1401 | Hydraulic Pump Motor Fault | Failing hydraulic pump motor, wiring problems, or low voltage |
| C1000 | Control Unit N47-5 (ESP, SPS, BAS control unit) | Internal fault in the ESP control unit, software corruption, or power supply issues |
| C1025-001 | CAN bus fault | Communication problem on the CAN bus, faulty wiring, or malfunctioning control unit interfering with CAN communication |
| C1121 | Lateral acceleration sensor | The lateral acceleration sensor is faulty, has a wiring problem, or has been installed incorrectly |
| C1132 | Yaw rate sensor | The yaw rate sensor is faulty, has a wiring problem, or the vehicle has sustained damage that affects the sensor’s readings |
| C1141 | BAS function is faulty | Problem with the Brake Assist System (BAS), which could be related to the brake booster, brake pedal sensor, or the BAS control module |
| C1144 | Zero position variation of the steering angle sensor | Steering angle sensor needs to be recalibrated, the steering linkage has been adjusted, or there is a mechanical problem with the steering |
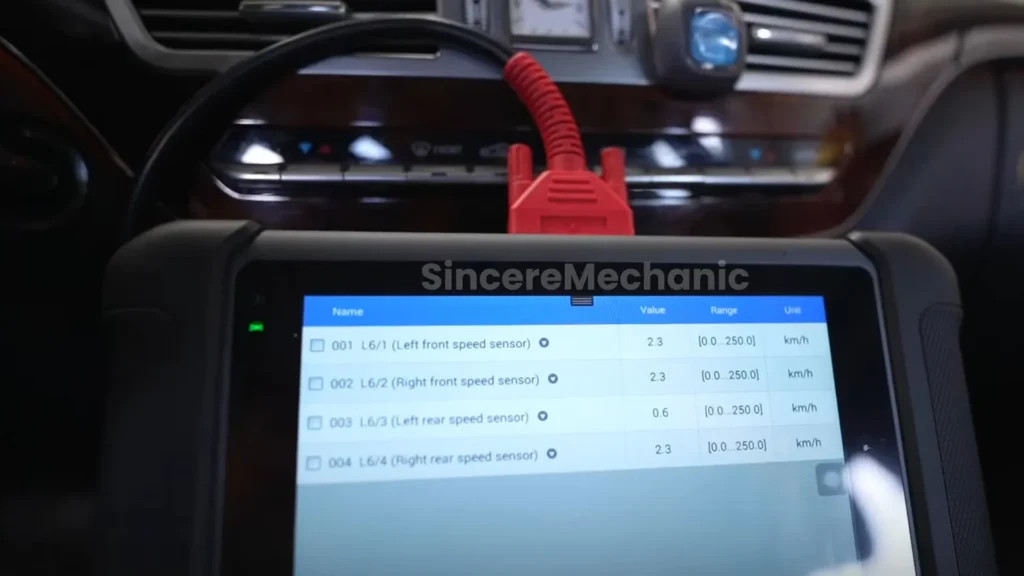
2.4. Checking Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are vital for the ESP system, monitoring each wheel’s speed to detect wheel slip or lock-up.
- Locate the Sensors: Find the wheel speed sensors on each wheel hub.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test the Sensors: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. An inconsistent or out-of-range reading indicates a faulty sensor.
- Use a Diagnostic Tool: Employ the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to monitor live data from the wheel speed sensors while rotating the wheels. Look for any erratic or missing signals.
2.5. Evaluating the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor provides essential data about the driver’s intended direction.
- Locate the Sensor: The steering angle sensor is usually located near the steering column.
- Check Connections: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Monitor Live Data: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to monitor the steering angle sensor data in real-time. Turn the steering wheel and observe the readings. The values should change smoothly and accurately reflect the steering angle.
- Perform Calibration: If the sensor seems to be functioning but the readings are inaccurate, try calibrating it using the diagnostic tool.
2.6. Testing the Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch signals the ESP system when the brakes are applied.
- Locate the Switch: Find the brake light switch near the brake pedal.
- Inspect the Switch: Check the switch for physical damage or loose connections.
- Test with a Multimeter: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the switch in both the pressed and released positions. The switch should show continuity when pressed and no continuity when released.
- Check Brake Lights: Ensure that the brake lights illuminate when the brake pedal is pressed. If they don’t, the switch is likely faulty.
2.7. Assessing Battery Voltage and Condition
A stable battery voltage is essential for the proper functioning of the ESP system.
- Measure Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Load Test: Perform a load test to check the battery’s ability to hold a charge under load. A significant drop in voltage during the load test indicates a weak or failing battery.
- Check Connections: Inspect the battery terminals and cables for corrosion or loose connections. Clean and tighten as necessary.
2.8. Inspecting Hydraulic Pump and Fluid
The hydraulic pump provides the necessary pressure for the ESP system to apply individual brakes.
- Locate the Pump: Find the ESP hydraulic pump, typically located near the ABS module.
- Listen for Operation: Turn on the ignition and listen for the pump to activate. If the pump does not run, it may be faulty.
- Check Fluid Level: Inspect the brake fluid reservoir. Low fluid levels can affect the pump’s performance.
- Test with Diagnostic Tool: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to activate the pump and monitor its performance. Look for any error messages or unusual readings.
2.9. Checking and Cleaning ABS Module Connections
Poor connections to the ABS module can disrupt the ESP system.
- Locate the ABS Module: Find the ABS module, usually located in the engine compartment.
- Inspect Connections: Check the wiring harness and connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Clean Connections: Use electrical contact cleaner to clean the connectors and ensure a good connection.
- Reseat Connectors: Disconnect and reconnect the connectors to ensure they are properly seated.
2.10. Road Testing the Vehicle
After performing the above checks, a road test can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Drive Carefully: Drive the vehicle in a safe area where you can test the ESP system.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to any warning lights, unusual handling, or ESP intervention.
- Simulate Slippery Conditions: If possible, test the ESP system on a low-traction surface (such as gravel or a wet road) to see if it activates correctly.
3. Solutions for ESP Inoperative Mercedes B-Class
Once you’ve identified the cause of the ESP malfunction, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here’s a breakdown of common solutions:
3.1. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a wheel speed sensor is found to be faulty, replacement is necessary.
- Purchase a Replacement: Obtain a new wheel speed sensor that is compatible with your Mercedes B-Class from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Disconnect the old sensor and carefully remove it from the wheel hub.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is securely in place and properly connected.
- Test the System: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to clear any error codes and verify that the new sensor is functioning correctly.
3.2. Calibrating or Replacing Steering Angle Sensor
If the steering angle sensor is malfunctioning, calibration or replacement may be required.
- Attempt Calibration: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to calibrate the steering angle sensor. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the calibration procedure.
- Replace if Necessary: If calibration fails, replace the steering angle sensor with a new one from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned and connected.
- Calibrate the New Sensor: After installation, calibrate the new sensor using the diagnostic tool.
3.3. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
A faulty brake light switch is a common cause of ESP problems.
- Purchase a Replacement: Obtain a new brake light switch that is compatible with your Mercedes B-Class from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Remove the Old Switch: Disconnect the old switch and carefully remove it from its mounting location.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new switch, ensuring it is properly adjusted and connected.
- Test the System: Verify that the brake lights illuminate when the brake pedal is pressed and use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to clear any error codes.
3.4. Resolving Battery Issues
A weak or failing battery can cause various electrical problems, including ESP malfunctions.
- Charge the Battery: If the battery is low, charge it fully using a battery charger.
- Replace if Necessary: If the battery fails a load test, replace it with a new one that meets the specifications for your Mercedes B-Class.
- Clean Connections: Clean any corrosion from the battery terminals and ensure they are securely connected.
3.5. Repairing or Replacing Hydraulic Pump
A faulty hydraulic pump will prevent the ESP system from functioning correctly.
- Inspect the Pump: Check the pump for any signs of damage or leaks.
- Test the Pump: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to activate the pump and monitor its performance.
- Repair or Replace: If the pump is faulty, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Bleed the System: After repairing or replacing the pump, bleed the ESP system to remove any air bubbles.
3.6. Addressing ABS Module Problems
Issues with the ABS module can also affect the ESP system.
- Check Connections: Inspect the wiring harness and connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Clean Connections: Clean the connectors with electrical contact cleaner to ensure a good connection.
- Reprogram or Replace: If the ABS module is faulty, it may need to be reprogrammed or replaced.
3.7. Performing a System Reset
After completing any repairs, it’s important to perform a system reset to clear any stored error codes and ensure that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
- Use Diagnostic Tool: Use the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to clear all DTCs related to the ESP system.
- Perform Adaptation: Some systems may require adaptation or relearning procedures after repairs. Follow the instructions in the diagnostic tool to perform these procedures.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly and that no warning lights are illuminated.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Complex ESP Issues
For more complex ESP problems, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary.
4.1. Using Oscilloscopes to Analyze Sensor Signals
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the signals from the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and other components.
- Connect the Oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope to the sensor signal wire.
- Monitor the Signal: Observe the signal waveform while the vehicle is in operation. Look for any irregularities, such as dropouts, noise, or incorrect voltage levels.
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the signal waveform to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any deviations.
4.2. Advanced CAN Bus Diagnostics
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) in the vehicle to communicate with each other. Problems with the CAN bus can cause a variety of issues, including ESP malfunctions.
- Check CAN Bus Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the voltage on the CAN bus wires. The voltage should be within the specified range.
- Use a CAN Bus Analyzer: A CAN bus analyzer can be used to monitor the data traffic on the CAN bus and identify any communication errors.
- Isolate Faulty Modules: Disconnect modules one at a time to see if the CAN bus communication improves. This can help identify a faulty module that is disrupting the network.
4.3. Analyzing Wiring Diagrams
Wiring diagrams provide valuable information about the wiring connections and circuits related to the ESP system.
- Obtain Wiring Diagrams: Obtain the wiring diagrams for your Mercedes B-Class.
- Trace Circuits: Use the wiring diagrams to trace the circuits related to the ESP system and identify any potential problem areas.
- Check for Shorts and Opens: Use a multimeter to check for shorts to ground or open circuits in the wiring.
5. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid ESP Problems
Preventive maintenance can help avoid ESP malfunctions and keep your Mercedes B-Class running smoothly.
5.1. Regular Vehicle Inspections
Regular vehicle inspections can help identify potential problems before they lead to ESP malfunctions.
- Check Tire Condition: Ensure tires are properly inflated and in good condition.
- Inspect Brakes: Check brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels regularly.
- Test Battery: Have the battery tested to ensure it is in good condition.
5.2. Maintaining Proper Wheel Alignment
Proper wheel alignment is essential for the ESP system to function correctly.
- Check Alignment Regularly: Have the wheel alignment checked regularly, especially after hitting potholes or curbs.
- Adjust as Needed: Adjust the wheel alignment as needed to ensure it is within the manufacturer’s specifications.
5.3. Keeping the ABS Module Clean
Keeping the ABS module clean and free of corrosion can help prevent ESP problems.
- Inspect Regularly: Inspect the ABS module and connections regularly for signs of corrosion.
- Clean Connections: Clean the connections with electrical contact cleaner to ensure a good connection.
5.4. Using Quality Replacement Parts
When replacing parts related to the ESP system, use only high-quality replacement parts from trusted suppliers like CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Choose OEM Parts: Opt for Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts or high-quality aftermarket parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications.
- Avoid Cheap Parts: Avoid using cheap, low-quality parts, as they may not function correctly and can cause further problems.
6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ESP Issues
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools, equipment, and support to help you resolve ESP inoperative issues in Mercedes B-Class vehicles efficiently and effectively.
6.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools that are essential for accurately diagnosing ESP issues. These tools allow you to read error codes, monitor sensor data, and perform advanced system tests.
6.2. Expert Technical Support
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert technical support to help you troubleshoot ESP problems and use our diagnostic tools effectively.
- Access to Technicians: Our team of experienced technicians is available to answer your questions and provide guidance.
- Online Resources: We offer a library of online resources, including troubleshooting guides, videos, and technical articles.
6.3. Comprehensive Range of Equipment
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of equipment to support your ESP diagnostic and repair needs, including:
- OBD-II Scanners: Advanced scanners for reading and clearing DTCs.
- Multimeters: High-quality multimeters for testing electrical circuits and components.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes for analyzing sensor signals and identifying irregularities.
- CAN Bus Analyzers: Tools for monitoring and analyzing CAN bus communication.
7. Case Studies: Real-World ESP Inoperative Repairs
Here are a couple of case studies illustrating how to diagnose and repair ESP inoperative issues in Mercedes B-Class vehicles.
7.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Problem: A Mercedes B-Class displayed an “ESP Inoperative” message on the dashboard. The OBD-II scanner revealed a C1175 code, indicating an implausible signal from the right front wheel speed sensor.
Diagnosis:
- Visual Inspection: The technician inspected the wheel speed sensor and found that the wiring was damaged.
- Sensor Testing: Using a multimeter, the technician measured the resistance of the sensor and found that it was out of range.
- Live Data Monitoring: The technician used the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to monitor live data from the wheel speed sensor while rotating the wheel. The signal was erratic and inconsistent.
Solution: The technician replaced the faulty wheel speed sensor with a new one from CARDIAGTECH.NET. After clearing the error codes and performing a system reset, the ESP system functioned correctly.
7.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
Problem: A Mercedes B-Class displayed an “ESP Inoperative” message on the dashboard after a steering wheel replacement. The OBD-II scanner revealed a C1140 code, indicating a steering angle sensor fault.
Diagnosis:
- Visual Inspection: The technician inspected the steering angle sensor and found no visible damage.
- Live Data Monitoring: The technician used the CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tool to monitor live data from the steering angle sensor while turning the steering wheel. The readings were inaccurate and did not correspond to the actual steering angle.
- Calibration Attempt: The technician attempted to calibrate the steering angle sensor using the diagnostic tool, but the calibration failed.
Solution: The technician replaced the steering angle sensor with a new one from CARDIAGTECH.NET. After installing the new sensor and performing a calibration, the ESP system functioned correctly.
8. The Financial Impact of Ignoring ESP Issues
Ignoring an ESP inoperative warning in your Mercedes B-Class can lead to significant financial consequences. Addressing the issue promptly not only ensures your safety but also prevents further damage and expenses.
8.1. Potential for Accidents and Increased Insurance Premiums
Driving with a malfunctioning ESP system significantly increases the risk of accidents, particularly in adverse weather conditions or emergency maneuvers. Accidents can result in costly repairs, medical bills, and potential legal liabilities.
- Increased Accident Risk: Without ESP, the vehicle is more prone to skidding and loss of control, leading to accidents.
- Higher Insurance Premiums: An accident will likely increase your insurance premiums, costing you more in the long run.
8.2. Costly Repairs Due to System Neglect
Delaying ESP repairs can lead to more extensive damage to the system and related components.
- Cascading Failures: A small issue in the ESP system can cause other components, such as the ABS or brake system, to fail.
- Expensive Replacements: Neglecting minor repairs can result in the need to replace entire systems, which can be very costly.
8.3. Depreciation of Vehicle Value
A vehicle with a known ESP issue will have a lower resale value compared to one with a fully functional safety system.
- Reduced Resale Value: Potential buyers may be hesitant to purchase a vehicle with an ESP malfunction, leading to a lower selling price.
- Increased Repair Costs for Buyers: If you sell the vehicle with an ESP issue, the buyer may demand a lower price to cover the cost of repairs.
9. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs
CARDIAGTECH.NET stands out as a premier provider of automotive diagnostic tools and solutions, offering numerous advantages for both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts. Here’s why you should choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for your automotive needs.
9.1. Wide Selection of High-Quality Products
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of high-quality diagnostic tools, equipment, and replacement parts.
- Diagnostic Tools: Advanced OBD-II scanners, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and CAN bus analyzers.
- Replacement Parts: OEM and high-quality aftermarket wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, brake light switches, and more.
9.2. Competitive Pricing and Special Offers
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides competitive pricing on all products, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
- Affordable Options: We offer a range of products to fit different budgets.
- Regular Discounts: Take advantage of our regular discounts and special offers to save even more.
9.3. Fast and Reliable Shipping
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers fast and reliable shipping, ensuring you receive your products quickly and efficiently.
- Quick Processing: Orders are processed quickly to minimize downtime.
- Tracking Information: You’ll receive tracking information to monitor the progress of your shipment.
9.4. Customer Satisfaction Guarantee
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to customer satisfaction.
- Easy Returns: If you’re not satisfied with your purchase, we offer easy returns and exchanges.
- Responsive Support: Our customer support team is available to assist you with any questions or concerns.
10. FAQs About ESP Inoperative Mercedes B-Class
Here are some frequently asked questions about ESP inoperative issues in Mercedes B-Class vehicles:
-
What does “ESP inoperative” mean in a Mercedes B-Class?
- “ESP inoperative” indicates that the Electronic Stability Program, a crucial safety system, is not functioning. This can compromise vehicle stability and safety, especially in challenging driving conditions.
-
Can I drive my Mercedes B-Class with the ESP light on?
- While it’s technically possible, it’s not recommended. Driving with the ESP light on means the system is disabled, increasing the risk of losing control, especially on slippery surfaces or during sudden maneuvers.
-
How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes B-Class?
- You can try resetting the system by turning off the ignition, waiting a few minutes, and then restarting the car. If the light persists, a diagnostic tool like those from CARDIAGTECH.NET is needed to clear the error codes.
-
What are the common causes of ESP failure in a Mercedes B-Class?
- Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, a malfunctioning brake light switch, low battery voltage, or problems with the ESP control module.
-
How much does it cost to fix an ESP inoperative issue?
- The cost can vary widely depending on the cause. Simple fixes like replacing a brake light switch might cost around $100-$200, while more complex issues like replacing the ESP control module could cost upwards of $1000.
-
Is it possible to diagnose ESP problems myself?
- Yes, with the right tools and knowledge. Using a diagnostic scanner from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can read error codes and perform basic troubleshooting. However, complex issues may require professional expertise.
-
Where is the ESP control module located in a Mercedes B-Class?
- The ESP control module is typically located in the engine compartment, often near the ABS module. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for the exact location.
-
Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system?
- Yes, low or uneven tire pressure can affect the ESP system, as it relies on accurate wheel speed data. Ensure your tires are properly inflated and in good condition.
-
Does a wheel alignment affect the ESP system?
- Yes, improper wheel alignment can cause the ESP system to constantly work to compensate, eventually leading to a malfunction. Regular wheel alignments are recommended.
-
What tools do I need to diagnose ESP problems in my Mercedes B-Class?
- Essential tools include an OBD-II scanner, a multimeter, and potentially an oscilloscope for advanced diagnostics. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic tools to suit your needs.
Don’t let an ESP inoperative warning compromise your safety and driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET today to explore our range of diagnostic tools and equipment. Our expert team is ready to assist you in diagnosing and resolving any ESP issues in your Mercedes B-Class, ensuring a safe and smooth ride.