ESP Light in Mercedes: Understanding & Solutions
The ESP light in Mercedes vehicles is a crucial indicator of your car’s stability system. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we help you understand this warning and ensure your Mercedes stays safe on the road. Explore the causes, solutions, and importance of maintaining your Electronic Stability Program (ESP), stability control, and anti-skid system.
1. Decoding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is a sophisticated system designed to enhance driving safety and control. Understanding its function is vital for any Mercedes owner.
1.1. What is ESP and Why is it Important?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It is a computerized technology that helps to prevent skidding and loss of control in challenging driving conditions. ESP works by monitoring the vehicle’s direction and comparing it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, indicating a potential skid, ESP intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power to help the driver maintain control. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP systems can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
1.2. Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several key components that work together to ensure optimal performance:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data to the ESP control unit to detect wheel slip or lockup.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, providing information about the vehicle’s actual direction of travel.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, helping to detect skidding or loss of control.
- ESP Control Unit: This is the brain of the system, processing data from all sensors and making decisions on how to intervene to maintain stability.
- Hydraulic Modulator: This component controls the application of brakes to individual wheels, as directed by the ESP control unit.
1.3. How ESP Enhances Driving Safety
ESP enhances driving safety in several ways:
- Prevents Skidding: By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP can prevent skidding and loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces or during sudden maneuvers.
- Maintains Stability: ESP helps to maintain stability by ensuring that the vehicle follows the driver’s intended path, even in challenging driving conditions.
- Reduces Accidents: Studies have shown that ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, particularly single-vehicle crashes.
Mercedes-Benz ESP system components
2. Interpreting the ESP Light: What It Means When It Illuminates
Understanding what the ESP light is telling you is the first step in addressing any potential issues with your Mercedes-Benz’s stability system.
2.1. ESP Light On vs. ESP Light Flashing
The ESP light can illuminate in different ways, each indicating a specific condition:
- ESP Light On (Solid): A solid ESP light typically indicates that the ESP system is disabled or that there is a malfunction within the system. When the light is continuously on, the ESP is not actively assisting in maintaining vehicle stability.
- ESP Light Flashing: A flashing ESP light indicates that the ESP system is actively engaged and working to maintain vehicle stability. This usually occurs when the system detects a loss of traction or a potential skid and is intervening by applying brakes and adjusting engine power.
2.2. Common Reasons for the ESP Light to Illuminate
Several factors can cause the ESP light to illuminate:
- System Malfunction: A malfunction within the ESP system itself can trigger the light. This could be due to a faulty sensor, a problem with the control unit, or an issue with the hydraulic modulator.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: Faulty or damaged wheel speed sensors can cause the ESP light to come on. These sensors are crucial for monitoring wheel rotation and detecting slip.
- Steering Angle Sensor Problems: Issues with the steering angle sensor can also trigger the ESP light. If the sensor is not accurately measuring the steering wheel angle, the ESP system may not function correctly.
- Low Tire Pressure: In some cases, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance and cause the light to illuminate.
- ESP System Disabled: The ESP system can be manually disabled in some vehicles. If the system is turned off, the ESP light will remain on.
2.3. Immediate Actions to Take When the ESP Light Appears
When the ESP light appears, it’s essential to take appropriate actions to ensure safety:
- Stay Calm: Avoid sudden movements or panic. Maintain a steady grip on the steering wheel and remain vigilant.
- Reduce Speed: Gradually reduce your speed and avoid abrupt braking or acceleration.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure that your tires are properly inflated. Low tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Avoid Sharp Turns: Steer smoothly and avoid sharp turns that could cause a loss of control.
- Consult a Professional: If the ESP light remains on or if you notice any unusual behavior, consult a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center for diagnosis and repair.
 ESP light flashing in a Mercedes-Benz
ESP light flashing in a Mercedes-Benz
3. Diagnosing ESP Problems: Pinpointing the Root Cause
Identifying the underlying cause of ESP issues requires a systematic approach and, often, specialized diagnostic tools.
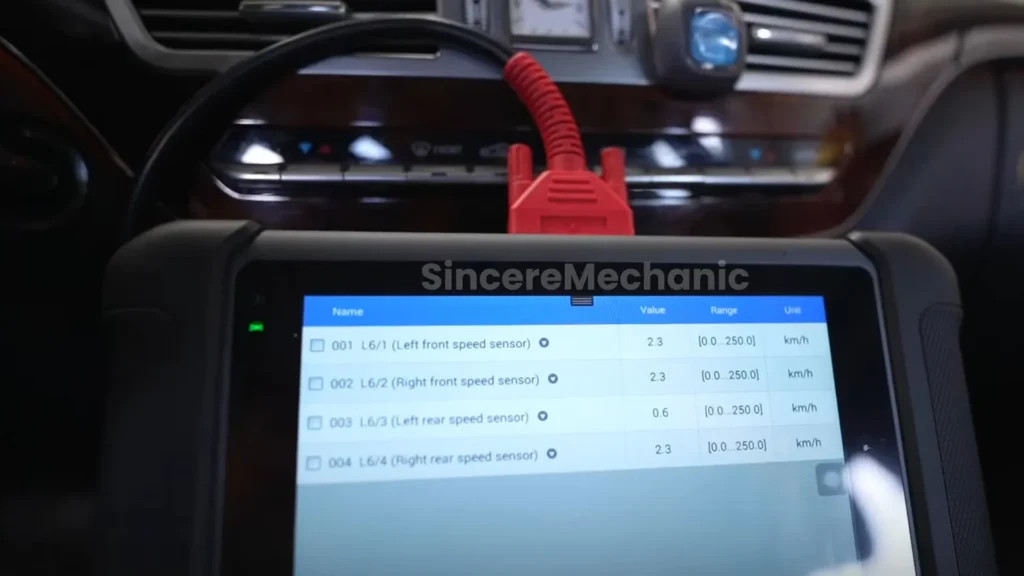
3.1. Using an OBD-II Scanner to Read Error Codes
An OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a valuable tool for diagnosing ESP problems. It can read error codes stored in the vehicle’s computer, providing insights into potential issues:
- Connecting the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Reading Error Codes: Turn on the ignition and use the scanner to read any stored error codes. Common codes related to ESP issues include those associated with wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and the ESP control unit.
- Interpreting the Codes: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource to interpret the meaning of the error codes. This will help you identify the specific component or system that is causing the problem.
3.2. Common Error Codes Associated with ESP Issues
Here are some common error codes associated with ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | ESP Control Unit Fault | Faulty ESP control unit, wiring issues, or software problems. |
| C1101 | Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right – Electrical Fault in Circuit | Damaged or faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the sensor’s connection. |
| C1102 | Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right – Implausible Signal | Incorrect wheel speed sensor signal, sensor misalignment, or issues with the sensor’s reading. |
| C1120 | Steering Angle Sensor – Electrical Fault in Circuit | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the sensor’s connection. |
| C1140 | BAS (Brake Assist System) Component Fault | Faulty BAS component, wiring issues, or problems with the BAS system. |
| C1175 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor – Electrical Fault in Circuit | Faulty lateral acceleration sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the sensor’s connection. |
| C1200 | Stop Light Switch – Implausible Signal | Faulty stop light switch, incorrect signal being sent to the ESP system, or wiring issues. |
| C1401 | N64 (ESP Control Module) is defective | The ESP control module has failed and needs to be replaced or repaired. |
| C1420 | Component A7/7y1 (ESP hydraulic unit control valve) is faulty | The control valve in the ESP hydraulic unit is not functioning correctly. |
| C1440 | Component A7/3b1 (Left front axle V speed sensor) : Signal is faulty | The wheel speed sensor on the front left axle is sending an incorrect signal. |
| C1460 | Control unit N47-5 (Traction system control module) : CAN communication is faulty | The traction system control module is experiencing communication issues with other modules in the vehicle. |
3.3. Inspecting Wheel Speed Sensors and Wiring
Wheel speed sensors are crucial for the ESP system to function correctly. Inspecting these sensors and their wiring can help identify potential issues:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensors for any visible damage, such as cracks, breaks, or corrosion.
- Wiring Inspection: Examine the wiring connected to the sensors for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion.
- Testing the Sensors: Use a multimeter to test the resistance and output voltage of the sensors. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensors are functioning correctly.
3.4. Checking the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor provides data about the driver’s intended direction. Checking this sensor can help diagnose ESP problems:
- Location: The steering angle sensor is typically located near the steering column.
- Testing: Use a diagnostic tool to read the steering angle sensor’s output. Verify that the readings are accurate and consistent with the steering wheel’s position.
- Calibration: In some cases, the steering angle sensor may need to be calibrated to ensure accurate readings.
 Testing a wheel speed sensor
Testing a wheel speed sensor
4. Solutions: Addressing Common ESP Problems
Once you’ve identified the root cause of the ESP issue, you can take steps to address the problem and restore the system’s functionality.
4.1. Resetting the ESP System
In some cases, resetting the ESP system can resolve minor issues and clear the ESP light. Here’s how to do it:
- Turn Off the Vehicle: Turn off the engine and remove the key from the ignition.
- Wait a Few Minutes: Wait for a few minutes to allow the vehicle’s computer to reset.
- Restart the Vehicle: Restart the engine and check if the ESP light has turned off.
- Steering Wheel Reset: If the light is still on, try turning the steering wheel lock-to-lock (from full left to full right) several times. This can help recalibrate the steering angle sensor.
4.2. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a wheel speed sensor is found to be faulty, it will need to be replaced:
- Remove the Wheel: Loosen the lug nuts, lift the vehicle with a jack, and remove the wheel.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Locate the wheel speed sensor and disconnect it from its wiring harness.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location. This may involve removing a bolt or clip.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new wheel speed sensor in the reverse order of removal.
- Reconnect the Wiring: Reconnect the sensor to its wiring harness.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Reinstall the wheel and tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
4.3. Addressing Steering Angle Sensor Issues
If the steering angle sensor is causing the problem, it may need to be replaced or recalibrated:
- Replacement: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for removal and installation.
- Calibration: In some cases, the steering angle sensor may need to be recalibrated using a diagnostic tool. Follow the tool’s instructions for performing the calibration procedure.
4.4. Checking and Replacing the Brake Light Switch
A faulty brake light switch can sometimes cause ESP issues, as the system relies on this switch to detect when the brakes are applied:
- Location: The brake light switch is typically located near the brake pedal.
- Testing: Use a multimeter to test the switch’s continuity. The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is depressed and no continuity when the pedal is released.
- Replacement: If the switch is faulty, replace it with a new one.
4.5. Professional Assistance
For complex ESP issues or if you’re not comfortable performing the repairs yourself, it’s best to seek professional assistance. A qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center can diagnose and repair the problem effectively.
 Replacing a wheel speed sensor
Replacing a wheel speed sensor
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term reliability and performance of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system.
5.1. Regular Inspections and Diagnostics
Schedule regular inspections and diagnostics to catch potential issues early:
- Routine Checkups: Include ESP system checks as part of your routine vehicle maintenance.
- Diagnostic Scans: Periodically scan the vehicle’s computer for error codes, even if the ESP light is not illuminated.
5.2. Keeping Tires Properly Inflated
Maintaining proper tire inflation is crucial for the ESP system to function correctly:
- Check Tire Pressure: Regularly check and adjust tire pressure to the manufacturer’s recommended levels.
- Use a Tire Pressure Gauge: Invest in a reliable tire pressure gauge to ensure accurate readings.
5.3. Ensuring Proper Wheel Alignment
Proper wheel alignment is also important for ESP system performance:
- Wheel Alignment Check: Have the wheel alignment checked periodically, especially if you notice uneven tire wear or handling issues.
- Alignment Adjustment: If necessary, have the wheel alignment adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications.
5.4. Addressing Brake System Issues Promptly
Promptly address any brake system issues, such as worn brake pads or rotors, as these can affect the ESP system’s performance:
- Brake Inspection: Regularly inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear and damage.
- Brake Replacement: Replace worn brake components as needed to maintain optimal braking performance.
5.5. Avoiding Modifications That Could Affect ESP
Avoid modifications to the vehicle that could affect the ESP system, such as aftermarket suspension components or tire sizes that deviate significantly from the manufacturer’s recommendations:
- OEM Parts: Stick to Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts when replacing components.
- Professional Advice: Consult with a qualified mechanic before making any modifications to the vehicle that could affect the ESP system.
6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Maintaining Your ESP System
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the critical role of the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz. We offer a range of tools and services to help you diagnose and maintain your ESP system effectively.
6.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We provide high-quality OBD-II scanners and diagnostic tools that can read error codes and provide valuable insights into potential ESP issues.
6.2. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians can offer expert advice and support to help you diagnose and resolve ESP problems.
6.3. Range of Automotive Repair Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of automotive repair tools, including those necessary for replacing wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and brake components.
6.4. Commitment to Customer Satisfaction
We are committed to providing excellent customer service and ensuring your satisfaction with our products and services. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
7. Real-World Scenarios: ESP in Action
Understanding how ESP works in real-world scenarios can help you appreciate its importance and effectiveness.
7.1. Navigating Slippery Road Conditions
On icy or snowy roads, ESP can help prevent skidding and maintain control:
- Scenario: You’re driving on a snow-covered road and begin to lose traction while turning.
- ESP Action: The ESP system detects the loss of traction and selectively applies brakes to individual wheels, helping to steer the vehicle back on course and prevent a skid.
7.2. Emergency Maneuvering
During emergency maneuvers, such as swerving to avoid an obstacle, ESP can help maintain stability:
- Scenario: A pedestrian suddenly steps into the road, and you need to swerve to avoid them.
- ESP Action: The ESP system detects the sudden change in direction and intervenes to prevent the vehicle from rolling over or skidding out of control.
7.3. Cornering at High Speeds
When cornering at high speeds, ESP can help prevent understeer or oversteer:
- Scenario: You’re taking a corner too quickly and begin to experience understeer (the vehicle doesn’t turn as much as you steer) or oversteer (the rear of the vehicle slides out).
- ESP Action: The ESP system detects the loss of control and applies brakes to the appropriate wheels, helping to keep the vehicle stable and on the intended path.
8. Integrating ESP with Other Safety Systems
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems to provide comprehensive protection:
8.1. ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing you to maintain steering control:
- How They Work Together: ESP and ABS work together to provide maximum stability and control during braking and maneuvering.
8.2. Traction Control System (TCS)
TCS limits wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction and preventing loss of control:
- How They Work Together: ESP and TCS work together to optimize traction and stability in various driving conditions.
8.3. Brake Assist System (BAS)
BAS detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to help reduce stopping distances:
- How They Work Together: ESP and BAS work together to provide enhanced braking performance and stability in emergency situations.
9. ESP and Vehicle Performance
While ESP primarily enhances safety, it can also have an impact on vehicle performance:
9.1. Impact on Acceleration and Handling
ESP can slightly reduce acceleration and handling performance in certain situations:
- Intervention: When ESP intervenes, it may reduce engine power or apply brakes, which can affect acceleration and handling.
- Trade-off: However, the trade-off is increased safety and stability, which is generally more important than slight performance reductions.
9.2. Optimizing Performance While Maintaining Safety
You can optimize vehicle performance while maintaining safety by:
- Driving Skill: Improving your driving skills to minimize the need for ESP intervention.
- Proper Maintenance: Ensuring that the ESP system is properly maintained and functioning correctly.
- Quality Tires: Using high-quality tires that provide good traction and stability.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About ESP in Mercedes-Benz
Here are some frequently asked questions about ESP in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
1. What does the ESP light mean in my Mercedes-Benz?
- The ESP light indicates the status of the Electronic Stability Program. A solid light means the system is disabled or malfunctioning, while a flashing light indicates the system is actively engaged.
2. Is it safe to drive with the ESP light on?
- If the ESP light is solid, it’s best to have the vehicle inspected by a professional, as the system may not be functioning correctly. Driving with a malfunctioning ESP system can reduce stability and safety.
3. Can I turn off ESP in my Mercedes-Benz?
- Some Mercedes-Benz models allow you to turn off ESP. However, it’s generally not recommended, as ESP enhances safety and stability.
4. How do I reset the ESP light in my Mercedes-Benz?
- Try turning off the engine, waiting a few minutes, and restarting the vehicle. If the light persists, turn the steering wheel lock-to-lock several times. If these steps don’t work, consult a professional.
5. What are the common causes of ESP problems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
- Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, and problems with the ESP control unit.
6. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
- Include ESP system checks as part of your routine vehicle maintenance.
7. Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system?
- Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance. Ensure that your tires are properly inflated.
8. What tools are needed to diagnose ESP problems?
- An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading error codes. A multimeter can be used to test sensors.
9. Where can I find quality replacement parts for my ESP system?
- CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality replacement parts for ESP systems.
10. What should I do if I’m not comfortable repairing my ESP system myself?
- Seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center.
Addressing ESP issues promptly and maintaining the system properly are essential for ensuring the safety and stability of your Mercedes-Benz.
Don’t wait until it’s too late! Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and the tools you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Let us help you maintain the safety and performance of your vehicle!