ESP Mercedes E320: Understanding and Troubleshooting Guide
The ESP Mercedes E320 system is a crucial safety feature, and at CARDIAGTECH.NET, we aim to help you understand and maintain it effectively. This comprehensive guide explores the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz E320, its functions, common issues, and how to address them, ensuring a safe and smooth driving experience. Explore expert tips and solutions for your ESP system.
1. Decoding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz E320 is an advanced safety system designed to prevent skidding and loss of control. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP works by monitoring the vehicle’s direction and wheel speed, intervening when it detects a deviation from the intended path. It selectively applies braking force to individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course. Understanding how ESP functions is crucial for recognizing and addressing potential issues. ESP, stability control, and vehicle dynamics are key terms to remember.
1.1. The Mechanics of ESP
ESP integrates several subsystems to maintain vehicle stability:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Limits wheel spin during acceleration, enhancing grip on slippery surfaces.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting oversteer or understeer.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Determines the driver’s intended direction, allowing the ESP to compare it with the vehicle’s actual movement.
1.2. ESP Benefits
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents caused by skidding or loss of control, especially in adverse weather conditions.
- Improved Handling: Provides better stability and responsiveness during cornering and emergency maneuvers.
- Increased Driver Confidence: Instills a sense of security, knowing that the vehicle can assist in challenging driving situations.
Alt Text: Mercedes-Benz ESP Warning Light illuminated on the dashboard, indicating a potential issue with the Electronic Stability Program.
2. Recognizing ESP Warning Signs in Your E320
Being vigilant about the warning signs your Mercedes-Benz E320 displays is critical for maintaining optimal performance and safety. The ESP warning light is a key indicator that demands immediate attention. Here’s what you need to know:
2.1. Interpreting the ESP Warning Light
The ESP warning light on your Mercedes-Benz E320 dashboard serves as a vital communication tool, signaling potential issues within the Electronic Stability Program.
- Solid Illumination: A continuously lit ESP warning light typically indicates that the ESP system has been deactivated, either manually by the driver or due to a malfunction. When the light remains on, the ESP system is not actively assisting with vehicle stability, which can reduce safety in challenging driving conditions.
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP warning light means the ESP system is currently engaged and actively working to stabilize the vehicle. This often occurs when driving on slippery surfaces, during sudden maneuvers, or when the system detects a loss of traction. The flashing indicates that ESP is intervening to help maintain control.
2.2. Common Symptoms
Beyond the warning light, be aware of these symptoms:
- Reduced Traction: Noticeable loss of grip, especially on wet or icy roads.
- Difficulty Steering: Increased effort required to maintain direction during turns.
- Unstable Handling: Feeling of instability or swaying, particularly at higher speeds.
- ABS Issues: Problems with the anti-lock braking system, as it’s integrated with ESP.
2.3. Diagnostic Steps
When the ESP warning light appears, take these initial steps:
- Check ESP Button: Ensure the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally deactivated via the ESP button, usually located on the dashboard.
- Restart Vehicle: Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve the issue temporarily.
- Observe Driving Conditions: Note if the light appears only under specific conditions, such as wet roads or sharp turns.
2.4. Professional Inspection
If the warning light persists or you notice significant handling issues, seek professional assistance:
- Certified Technician: Consult a certified Mercedes-Benz technician for accurate diagnosis.
- Diagnostic Tools: Utilize advanced diagnostic tools to pinpoint the underlying cause of the ESP malfunction.
- System Scan: Perform a comprehensive system scan to identify any stored error codes related to ESP.
By understanding the ESP warning signals and taking proactive steps, you can ensure your Mercedes-Benz E320 remains safe and reliable. Early detection and proper maintenance of the ESP system contribute to a confident driving experience, especially under challenging road conditions. Consider CARDIAGTECH.NET for your diagnostic tool needs.
3. Pinpointing the Causes of ESP Malfunctions
Understanding the potential causes of ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz E320 is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. These malfunctions can stem from various issues, each requiring specific attention and repair strategies.
3.1. Sensor Failures
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Accurate wheel speed data is critical for ESP to function correctly. Damaged or faulty sensors can disrupt this data flow, leading to ESP errors.
- Impact: Reduced ESP effectiveness, potentially causing instability during maneuvers.
- Troubleshooting: Use diagnostic tools to check sensor readings and replace faulty units.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing essential input for ESP calculations.
- Impact: Inaccurate steering input can lead to ESP miscalculations and incorrect interventions.
- Troubleshooting: Calibrate or replace the steering angle sensor as needed.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation, helping ESP detect oversteer or understeer.
- Impact: Inability to detect vehicle rotation accurately, compromising stability control.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect and replace the yaw rate sensor if it shows erratic readings.
3.2. ABS System Issues
Since ESP relies on the ABS system, any problems with ABS can affect ESP functionality.
- Faulty ABS Pump: An improperly functioning ABS pump can prevent ESP from applying brakes to individual wheels.
- Impact: Loss of selective braking capability, impairing ESP’s ability to stabilize the vehicle.
- Troubleshooting: Test and repair or replace the ABS pump.
- ABS Module Problems: Electrical or software issues within the ABS module can disrupt communication with the ESP system.
- Impact: Complete ESP failure, as the system cannot receive or process critical ABS data.
- Troubleshooting: Scan for error codes and reprogram or replace the ABS module.
3.3. Wiring and Electrical Issues
Electrical problems can cause intermittent or complete ESP failure.
- Damaged Wiring: Wires that are corroded, frayed, or disconnected can interrupt sensor signals and power supply to ESP components.
- Impact: Intermittent ESP failures or complete system shutdown.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect and repair or replace damaged wiring and connectors.
- Grounding Problems: Poor grounding can lead to signal interference and unreliable ESP operation.
- Impact: Erratic ESP behavior, leading to unpredictable responses during driving.
- Troubleshooting: Ensure all grounding points are clean and properly connected.
3.4. Low Brake Fluid
Insufficient brake fluid can affect the entire braking system, including ESP.
- Impact: Reduced braking performance, hindering ESP’s ability to apply brakes effectively.
- Troubleshooting: Check brake fluid levels and replenish as needed. Inspect for leaks in the braking system.
3.5. ESP Control Module Failure
The ESP control module is the brain of the system.
- Impact: Complete ESP failure, as the system cannot process data or control components.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose the ESP control module and replace if necessary.
3.6. Wheel Alignment Issues
Incorrect wheel alignment can lead to ESP intervention even when it’s not needed.
- Impact: Premature wear and tear on tires, unstable handling, and unnecessary ESP activation.
- Troubleshooting: Perform a wheel alignment and adjust to factory specifications.
3.7. Tire Pressure Problems
Improper tire pressure can affect the accuracy of the wheel speed sensors.
- Impact: Inaccurate ESP readings and compromised stability control.
- Troubleshooting: Check and adjust tire pressures to the recommended levels.
Understanding these potential causes can aid in diagnosing and resolving ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz E320. Regular inspection and maintenance, combined with professional diagnostics, can keep your ESP system functioning optimally, ensuring a safe and confident driving experience. Consider using diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
Alt Text: Close-up of the BAS ESP warning light on a Mercedes-Benz dashboard, indicating issues with the Brake Assist System and Electronic Stability Program.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Issues
Diagnosing ESP (Electronic Stability Program) issues in your Mercedes-Benz E320 requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the root cause of the problem. Follow these steps for effective diagnosis:
4.1. Initial Assessment
- Observe Warning Lights:
- Note whether the ESP warning light is solid or flashing.
- Check for any other warning lights, such as ABS or brake system alerts.
- Gather Symptoms:
- Document any unusual driving behavior, such as loss of traction, difficulty steering, or unstable handling.
- Note when the issues occur (e.g., during acceleration, braking, or turning).
- Review Recent Maintenance:
- Consider any recent repairs or maintenance work that might be related, such as brake work or wheel alignment.
4.2. Preliminary Checks
- ESP Button:
- Ensure the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally turned off by pressing the ESP button on the dashboard.
- Try toggling the ESP button to see if the warning light clears.
- Brake Fluid Level:
- Check the brake fluid reservoir to ensure it’s at the proper level.
- Low brake fluid can trigger ESP and ABS warnings.
- Tire Pressure:
- Verify that all tires are inflated to the correct pressure, as uneven tire pressure can affect ESP performance.
4.3. Diagnostic Scan
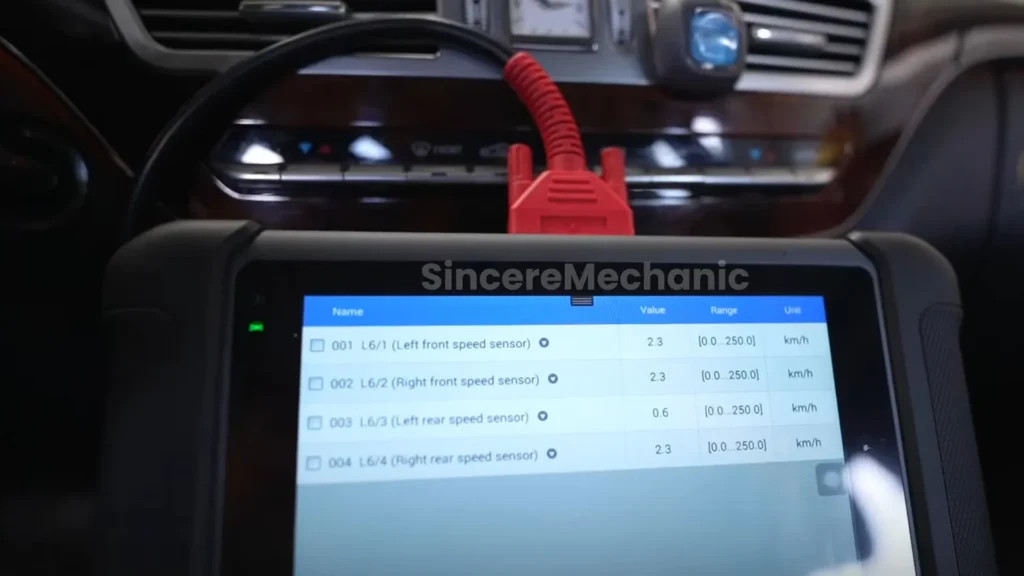
- Connect Diagnostic Tool:
- Use an OBD-II diagnostic scanner compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of suitable diagnostic tools.
- Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Read Error Codes:
- Turn on the ignition (but don’t start the engine).
- Navigate the scanner to read and record any stored error codes related to the ESP, ABS, and brake systems.
- Note the specific codes and their descriptions.
- Clear Codes (Optional):
- If desired, clear the codes and take the vehicle for a short test drive to see if the same codes reappear. This can help confirm if the issue is persistent.
4.4. Component Testing
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Use the diagnostic tool to monitor the real-time data from each wheel speed sensor while driving slowly.
- Check for any erratic readings or complete signal loss from any sensor.
- Inspect the sensors and wiring for physical damage.
- Steering Angle Sensor:
- Use the diagnostic tool to monitor the steering angle sensor readings while turning the steering wheel.
- Ensure the readings are accurate and consistent with the actual steering wheel position.
- Calibrate the steering angle sensor if necessary.
- Yaw Rate Sensor:
- Locate the yaw rate sensor (typically under the seat or center console).
- Check for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Use the diagnostic tool to monitor the yaw rate sensor readings while driving. Look for any erratic or inconsistent data.
4.5. Advanced Troubleshooting
- ABS Module Testing:
- If ABS codes are present, test the ABS module using the diagnostic tool.
- Check for proper communication with the ESP system and other vehicle modules.
- Inspect the ABS pump and solenoids for proper operation.
- Wiring Inspection:
- Carefully inspect all wiring and connectors related to the ESP, ABS, and wheel speed sensors.
- Look for corrosion, frayed wires, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at various points in the system.
- Grounding Points:
- Ensure all grounding points for the ESP and ABS systems are clean and securely connected.
- Poor grounding can cause intermittent issues and false error codes.
4.6. Professional Consultation
If you are unable to pinpoint the cause of the ESP issue or are uncomfortable performing advanced diagnostic procedures:
- Certified Technician: Consult a certified Mercedes-Benz technician for further diagnosis.
- Specialized Tools: They have access to specialized diagnostic tools and expertise to accurately diagnose and repair complex ESP issues.
By following these steps, you can systematically diagnose ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz E320 and take appropriate action to restore its proper function. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs can help prevent ESP malfunctions and ensure a safe driving experience. Consider CARDIAGTECH.NET for your diagnostic and repair needs.
Alt Text: ESP warning light illuminated on a Mercedes-Benz dashboard, highlighting the need for immediate attention to the Electronic Stability Program.
5. Repairing ESP Malfunctions: A Practical Guide
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the ESP malfunction in your Mercedes-Benz E320, the next step is to perform the necessary repairs. Here’s a practical guide to help you through the process:
5.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
-
Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Preparation:
- Gather the necessary tools: wrench set, socket set, screwdrivers, and a new wheel speed sensor.
- Safely lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent electrical accidents.
- Removal:
- Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor (identified during diagnosis).
- Disconnect the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Remove any retaining bolts or clips securing the sensor to the wheel hub.
- Carefully extract the sensor from the hub.
- Installation:
- Clean the hub surface to ensure proper sensor contact.
- Insert the new wheel speed sensor into the hub.
- Secure it with the retaining bolts or clips, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Testing:
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Use a diagnostic tool to clear any stored error codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive and monitor the wheel speed sensor readings to ensure proper operation.
- Preparation:
-
Steering Angle Sensor:
- Preparation:
- Gather tools: screwdriver set, socket set, and a new steering angle sensor.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Removal:
- Locate the steering angle sensor (usually behind the steering wheel).
- Remove the steering wheel (refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions).
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove any screws or clips securing the sensor to the steering column.
- Carefully remove the sensor.
- Installation:
- Install the new steering angle sensor onto the steering column.
- Secure it with the screws or clips, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reinstall the steering wheel, ensuring it’s properly aligned.
- Calibration:
- Use a diagnostic tool to calibrate the new steering angle sensor. Follow the tool’s instructions to ensure accurate readings.
- Clear any stored error codes.
- Test drive the vehicle to verify proper operation.
- Preparation:
-
Yaw Rate Sensor:
- Preparation:
- Gather tools: socket set, screwdriver set, and a new yaw rate sensor.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Removal:
- Locate the yaw rate sensor (typically under the seat or center console).
- Remove any trim panels or seats necessary to access the sensor.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove any bolts or screws securing the sensor to the vehicle’s chassis.
- Carefully remove the sensor.
- Installation:
- Install the new yaw rate sensor onto the chassis.
- Secure it with the bolts or screws, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reinstall any trim panels or seats that were removed.
- Testing:
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Use a diagnostic tool to clear any stored error codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive and monitor the yaw rate sensor readings to ensure proper operation.
- Preparation:
5.2. Addressing ABS System Issues
-
Faulty ABS Pump:
- Preparation:
- Gather tools: wrench set, socket set, screwdrivers, brake line wrenches, and a new ABS pump.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Removal:
- Locate the ABS pump (typically in the engine compartment).
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the pump.
- Carefully disconnect the brake lines from the pump using brake line wrenches.
- Remove any bolts or brackets securing the pump to the vehicle.
- Carefully remove the pump.
- Installation:
- Install the new ABS pump, ensuring it’s properly aligned.
- Secure it with the bolts or brackets, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the brake lines to the pump, ensuring they are properly tightened to prevent leaks.
- Reconnect the electrical connectors.
- Bleeding Brakes:
- Bleed the brakes to remove any air from the system. Follow the vehicle’s service manual for the proper bleeding procedure.
- Testing:
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Use a diagnostic tool to clear any stored error codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive and verify proper ABS operation.
- Preparation:
-
ABS Module Problems:
- Preparation:
- Gather tools: socket set, screwdriver set, and a new ABS module.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Removal:
- Locate the ABS module (typically attached to the ABS pump).
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the module.
- Remove any bolts or screws securing the module to the pump.
- Carefully remove the module.
- Installation:
- Install the new ABS module onto the pump.
- Secure it with the bolts or screws, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the electrical connectors.
- Programming:
- Use a diagnostic tool to program the new ABS module. Follow the tool’s instructions to ensure proper configuration.
- Testing:
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Use a diagnostic tool to clear any stored error codes.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive and verify proper ABS operation.
- Preparation:
5.3. Addressing Wiring and Electrical Issues
- Visual Inspection:
- Carefully inspect all wiring and connectors related to the ESP, ABS, and wheel speed sensors.
- Look for corrosion, frayed wires, or loose connections.
- Repair or Replacement:
- Repair any damaged wiring by splicing in new sections of wire and using proper connectors.
- Replace any corroded or damaged connectors.
- Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at various points in the system.
- Ensure proper grounding by cleaning and tightening all grounding points.
5.4. Other Repairs
- Brake Fluid: If low brake fluid was the issue, replenish the fluid and inspect the system for leaks.
- Wheel Alignment: If wheel alignment was off, have a professional perform a wheel alignment and adjust to factory specifications.
- Tire Pressure: Adjust tire pressures to the recommended levels.
- ESP Control Module: Replace the ESP control module if it is faulty.
5.5. Final Testing
After completing the repairs, perform a thorough test of the ESP system:
- Clear Error Codes: Use a diagnostic tool to clear any stored error codes.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive and monitor the ESP system for proper operation.
- Verify Functionality: Perform maneuvers that would typically engage the ESP system, such as sharp turns and sudden braking, to ensure it is functioning correctly.
By following this practical guide, you can effectively repair ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz E320. Always prioritize safety and accuracy, and consider seeking professional assistance if you are unsure about any aspect of the repair process. Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET for the necessary diagnostic tools and equipment.
Alt Text: Mercedes-Benz ESP warning light illuminated on the dashboard, a reminder to address Electronic Stability Program issues promptly.
6. The Importance of Regular Maintenance for ESP
Maintaining the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz E320 is crucial for ensuring its continued reliability and effectiveness. Regular maintenance helps prevent malfunctions, prolongs the lifespan of the system, and ensures your safety on the road.
6.1. Scheduled Inspections
- Frequency:
- Incorporate ESP checks into your regular maintenance schedule, ideally every 12 months or 12,000 miles, whichever comes first.
- Key Components:
- Inspect wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, yaw rate sensor, and ABS components.
- Visual Checks:
- Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear on sensors and wiring.
6.2. Sensor Cleaning
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Regularly clean wheel speed sensors to remove dirt, debris, and brake dust.
- Use a soft brush or cloth and a specialized sensor cleaner.
- Benefits:
- Ensures accurate readings and prevents false triggers of the ESP system.
6.3. Brake System Maintenance
- Brake Fluid:
- Check brake fluid levels regularly and replenish as needed.
- Flush and replace brake fluid every two years to maintain its effectiveness.
- Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Inspect brake pads and rotors for wear and replace as necessary.
- Proper brake system maintenance ensures optimal braking performance, which is essential for ESP functionality.
6.4. Tire Maintenance
- Tire Pressure:
- Maintain proper tire pressure at all times.
- Check tire pressure monthly and adjust as needed.
- Tire Condition:
- Inspect tires for wear and tear, and replace them when necessary.
- Ensure tires are properly balanced and aligned.
6.5. Wheel Alignment
- Frequency:
- Perform a wheel alignment every two years or whenever you notice signs of misalignment, such as uneven tire wear or pulling to one side.
- Benefits:
- Ensures proper vehicle handling and prevents unnecessary ESP activation.
6.6. Diagnostic Scans
- Annual Scans:
- Perform annual diagnostic scans to check for any stored error codes related to the ESP system.
- Proactive Issue Detection:
- Detect and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
6.7. Wiring Inspections
- Regular Checks:
- Inspect wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Protection:
- Protect wiring from environmental factors, such as moisture and heat.
6.8. Professional Maintenance
- Qualified Technicians:
- Entrust ESP maintenance to qualified technicians with expertise in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Specialized Tools:
- Ensure they have access to specialized diagnostic tools and equipment.
6.9. Record Keeping
- Detailed Records:
- Maintain detailed records of all ESP maintenance activities.
- Future Reference:
- Use these records for future reference and to track the performance of the system.
6.10. Benefits of Regular Maintenance
- Enhanced Safety:
- Ensures the ESP system is always ready to assist in challenging driving situations.
- Prolonged Lifespan:
- Extends the lifespan of the ESP system and its components.
- Reduced Repair Costs:
- Prevents major malfunctions and reduces the likelihood of costly repairs.
- Optimal Performance:
- Maintains optimal vehicle handling and stability.
By following these guidelines for regular ESP maintenance, you can ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of your Mercedes-Benz E320. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the life of the ESP system but also provides peace of mind, knowing that your vehicle is equipped to handle challenging driving conditions. Consider CARDIAGTECH.NET for all your diagnostic and maintenance tool needs.
7. Cost of ESP Repairs for a Mercedes-Benz E320
When the ESP (Electronic Stability Program) system in your Mercedes-Benz E320 malfunctions, understanding the potential repair costs is essential for budgeting and making informed decisions. The cost of ESP repairs can vary widely depending on the underlying issue, the components involved, and whether you choose to visit a dealership or an independent repair shop. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the factors influencing ESP repair costs:
7.1. Diagnostic Fees
- Initial Inspection:
- Before any repairs can be performed, a diagnostic test is necessary to identify the root cause of the ESP malfunction.
- Cost Range:
- Diagnostic fees typically range from $75 to $200.
- Factors Influencing Cost:
- Dealerships often charge higher diagnostic fees compared to independent repair shops.
- Advanced diagnostic procedures may incur additional costs.
7.2. Sensor Replacement Costs
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Replacement of a faulty wheel speed sensor can range from $150 to $400 per sensor.
- Steering Angle Sensor:
- Replacing the steering angle sensor may cost between $200 and $500.
- Yaw Rate Sensor:
- The cost to replace the yaw rate sensor typically falls between $250 and $600.
- Factors Influencing Cost:
- The cost of the sensor itself can vary depending on the brand and quality.
- Labor costs will depend on the complexity of the sensor replacement.
7.3. ABS System Repair Costs
- ABS Pump Replacement:
- Replacing a faulty ABS pump can be a significant expense, ranging from $800 to $2,000.
- ABS Module Replacement:
- The cost to replace the ABS module typically falls between $500 and $1,500.
- Factors Influencing Cost:
- ABS components are often expensive, especially for luxury vehicles like Mercedes-Benz.
- Labor costs can be substantial due to the complexity of ABS system repairs.
7.4. Wiring and Electrical Repairs
- Cost Range:
- Wiring and electrical repairs can vary widely, from $100 to $500 or more, depending on the extent of the damage.
- Factors Influencing Cost:
- Simple repairs, such as replacing a damaged connector, will be relatively inexpensive.
- Extensive wiring repairs or replacements can be more costly due to the labor involved.
7.5. ESP Control Module Replacement
- Cost Range:
- Replacing the ESP control module can cost between $500 and $1,500 or more.
- Factors Influencing Cost:
- The ESP control module is a critical component, and its replacement often requires programming and calibration.
7.6. Labor Costs
- Hourly Rate:
- Labor rates vary depending on the location and type of repair shop.
- Dealerships typically charge higher hourly rates compared to independent shops.
- Average Range:
- Labor rates can range from $80 to $150 per hour or more.
7.7. Additional Costs
- Wheel Alignment:
- If the ESP malfunction is related to wheel alignment issues, a wheel alignment service may be necessary, costing between $75 and $200.
- Tire Replacement:
- If tire wear is uneven due to ESP issues, replacing the tires may be necessary, adding to the overall cost.
7.8. Cost-Saving Tips
- Obtain Multiple Estimates:
- Get estimates from multiple repair shops to compare prices and services.
- Consider Independent Shops:
- Independent repair shops often offer competitive pricing compared to dealerships.
- DIY Repairs:
- If you have the skills and experience, consider performing some of the repairs yourself to save on labor costs. However, be cautious and ensure you have the necessary tools and knowledge.
- Warranty Coverage:
- Check if your vehicle is still under warranty, as some ESP repairs may be covered.
7.9. Summary of Estimated Costs
| Repair Type | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Diagnostic Fee | $75 – $200 |
| Wheel Speed Sensor | $150 – $400 |
| Steering Angle Sensor | $200 – $500 |
| Yaw Rate Sensor | $250 – $600 |
| ABS Pump Replacement | $800 – $2,000 |
| ABS Module Replacement | $500 – $1,500 |
| Wiring/Electrical Repairs | $100 – $500+ |
| ESP Control Module | $500 – $1,500+ |
| Wheel Alignment | $75 – $200 |
Understanding the potential costs associated with ESP repairs in your Mercedes-Benz E320 can help you budget effectively and make informed decisions. Always prioritize safety and seek professional assistance when needed to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly. Consider CARDIAGTECH.NET for diagnostic tools and equipment that can help you identify and address ESP issues.
8. Enhancing ESP Performance Through Aftermarket Upgrades
While the ESP (Electronic Stability Program) system in your Mercedes-Benz E320 is designed to provide optimal stability and safety, there are aftermarket upgrades available that can further enhance its performance. These upgrades can improve handling, responsiveness, and overall driving experience, particularly for enthusiasts seeking more from their vehicle. Here’s a look at some popular aftermarket upgrades for ESP performance:
8.1. Performance Tires
- Improved Grip:
- Upgrading to high-performance tires can significantly improve traction and grip, which is essential for ESP to function effectively.
- Enhanced Handling:
- Performance tires offer better handling and responsiveness, allowing the ESP system to react more quickly and accurately to changing driving conditions.
- Considerations:
- Choose tires that are specifically designed for performance driving and are compatible with your vehicle’s specifications.
8.2. Upgraded Suspension Components
- Coilover Systems:
- Installing a coilover suspension system can improve vehicle stability and handling by reducing body roll and enhancing cornering performance.
- Performance Springs and Dampers:
- Upgrading to performance springs and dampers can provide a firmer and more controlled ride, enhancing the ESP system’s effectiveness.
- Sway Bars:
- Installing stiffer sway bars can reduce body roll and improve vehicle stability, allowing the ESP system to intervene more precisely.
- Considerations:
- Ensure that any suspension upgrades are properly installed and aligned to avoid adverse effects on the ESP system.
8.3. Performance Brake Upgrades
- Big Brake Kits:
- Upgrading to a big brake kit can improve braking performance, allowing the ESP system to apply brakes more effectively when needed.
- High-Performance Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Installing high-performance brake pads and rotors can provide better stopping power and reduce brake fade, enhancing the ESP system’s responsiveness.
- Considerations:
- Ensure that any brake upgrades are compatible with the ESP system and are properly installed and maintained.
8.4. ECU Tuning and Software Upgrades
- ESP Calibration:
- Some aftermarket tuners offer ECU tuning and software upgrades that can recalibrate the ESP system for improved performance.
- Enhanced Responsiveness:
- These upgrades can enhance the ESP system’s responsiveness and allow it to intervene more effectively in challenging driving situations.
- Considerations:
- Choose a reputable tuner with experience in Mercedes-Benz vehicles and ensure that any software upgrades are compatible with your vehicle’s ESP system.
8.5. Aftermarket ESP Modules
- Advanced Control:
- Some aftermarket companies offer advanced ESP modules that provide more control over the system’s parameters.
- Customization:
- These modules allow you to customize the ESP system’s intervention thresholds and response characteristics to suit your driving style.
- Considerations:
- Ensure that any aftermarket ESP modules are compatible with your vehicle and are properly installed and calibrated.
8.6. Lightweight Wheels
- Reduced Rotational Mass:
- Upgrading to lightweight wheels can reduce rotational mass, improving acceleration, braking, and handling.
- Enhanced Agility:
- Lightweight wheels can make the vehicle feel more agile and responsive, enhancing the ESP system’s effectiveness.
- Considerations:
- Choose wheels that are compatible with your vehicle’s specifications and are properly balanced and aligned.
8.7. Performance Alignment
- Optimized Handling:
- Having a performance alignment performed can optimize vehicle handling and stability, allowing the ESP system to function more effectively.
- Custom Settings:
- A performance alignment can be tailored to your driving style and preferences, enhancing the ESP system