ESP Not Functioning Mercedes Benz: Expert Solutions Guide

ESP not functioning Mercedes Benz? At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand how crucial a functioning Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is for your safety and vehicle performance. This comprehensive guide dives deep into diagnosing and resolving ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to tackle these problems effectively. We will cover common causes, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions, empowering you to get back on the road with confidence.
1. Understanding the ESP System in Mercedes-Benz
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a critical safety system in your Mercedes-Benz, designed to prevent skidding and maintain control in challenging driving conditions. It integrates with other systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and traction control to enhance stability.
1.1. Core Functionality of ESP
ESP actively monitors several factors, including wheel speed, steering angle, and vehicle yaw rate. When the system detects a potential loss of control, such as during oversteer or understeer, it selectively applies braking force to individual wheels to steer the vehicle back on its intended path. This is done in a split second, which is usually faster than the driver can react, helping prevent accidents. ESP is designed to:
- Prevent skidding
- Enhance vehicle stability
- Improve handling in adverse conditions
- Reduce the risk of accidents
1.2. Integration with Other Systems
ESP works in harmony with other systems to provide comprehensive safety. These include:
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): Prevents wheel lock-up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Limits wheel spin during acceleration, ensuring optimal traction.
- Brake Assist: Provides additional braking force in emergency situations.
- Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD): Optimizes brake force distribution between the front and rear wheels, improving braking performance and stability.
 ESP malfunction Mercedes Benz
ESP malfunction Mercedes Benz
1.3. Importance of ESP for Safety
ESP is more than just a feature; it’s a life-saving technology. Studies have shown that ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions and emergency maneuvers.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. This makes it one of the most important safety features in modern vehicles. For Mercedes-Benz owners, ensuring your ESP system is functioning correctly is crucial for your safety and the safety of others on the road.
2. Identifying Symptoms of ESP Malfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of an ESP malfunction is the first step in addressing the issue. Several tell-tale signs can indicate problems with your Mercedes-Benz’s ESP system.
2.1. Warning Lights and Messages
The most obvious sign of an ESP issue is the illumination of the ESP warning light on your dashboard. This light, usually an icon of a car skidding, indicates that the system has detected a problem. In some Mercedes-Benz models, you may also receive a specific message on the central display, such as “ESP Inoperative” or “ESP Malfunction.”
2.2. Unusual Handling and Stability Issues
If the ESP system is not functioning correctly, you may notice unusual handling characteristics. This can include:
- Difficulty maintaining control: The vehicle feels unstable, especially during turns or sudden maneuvers.
- Increased skidding: The car is more prone to skidding in wet or slippery conditions.
- Delayed or erratic response: The ESP system doesn’t engage or engages inconsistently when needed.
- Reduced traction: Experiencing wheel spin more frequently when accelerating, especially on loose surfaces.
2.3. ABS and Traction Control Problems
Since ESP integrates with ABS and traction control, problems with these systems can also indicate an ESP malfunction. Symptoms to watch for include:
- ABS light illumination: The ABS warning light turns on, indicating a potential issue with the anti-lock braking system.
- Traction control light: The traction control light flickers or remains on, suggesting a problem with the traction control system.
- Reduced braking performance: Noticeably longer stopping distances or a pulsating sensation when braking.
2.4. Diagnostic Scan Codes
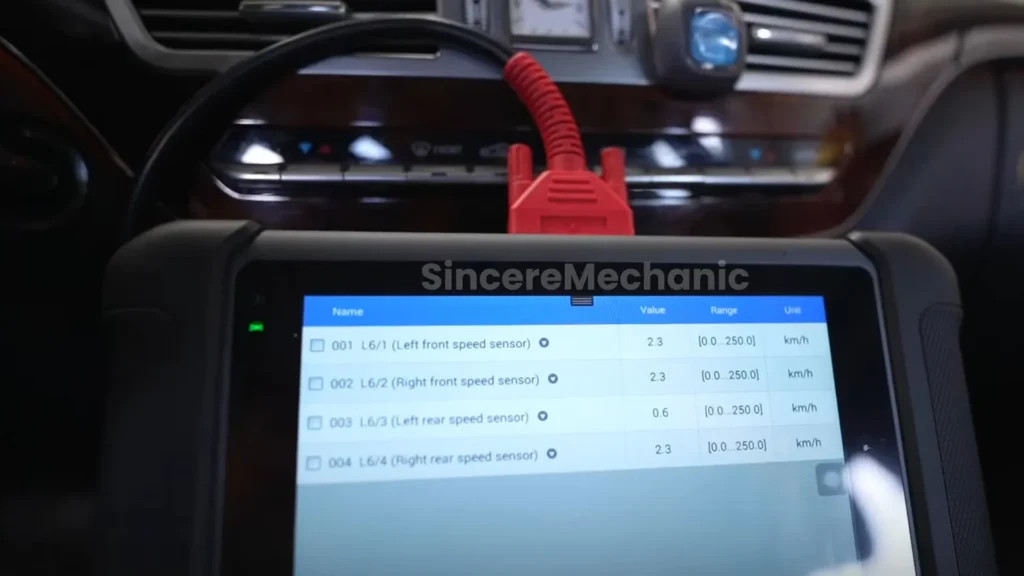
A diagnostic scan using an OBD-II scanner can reveal specific error codes related to the ESP system. Common codes include:
- C1000: Control Unit Fault
- C1100: ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right
- C1200: BAS Function Malfunction
These codes can provide valuable information for diagnosing the root cause of the problem. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your Mercedes-Benz inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
3. Common Causes of ESP Malfunction in Mercedes-Benz
Several factors can contribute to ESP malfunctions in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Understanding these common causes can help you troubleshoot the issue more effectively.
3.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are crucial for the ESP system to function correctly. These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide data to the ESP control unit. If a wheel speed sensor fails or provides inaccurate readings, it can trigger the ESP warning light and disable the system.
Symptoms of Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors:
- ESP warning light illumination
- ABS warning light illumination
- Erratic ABS or ESP engagement
- Loss of traction control
- Diagnostic codes related to wheel speed sensors (e.g., C1100, C1101, C1102, C1103)
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage or debris.
- Check the sensor wiring and connectors for corrosion or damage.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and signal output.
- Replace any faulty wheel speed sensors.
3.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP control unit. This data is essential for the system to determine the driver’s intended direction and make appropriate adjustments.
Symptoms of Steering Angle Sensor Issues:
- ESP warning light illumination
- Difficulty maintaining stability during turns
- Erratic ESP engagement
- Diagnostic codes related to the steering angle sensor
- Stiff Steering
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Check the steering angle sensor calibration.
- Inspect the sensor wiring and connectors for damage.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to read the sensor’s output and identify any errors.
- Replace the steering angle sensor if necessary.
3.3. Brake Light Switch Problems
The brake light switch signals the ESP system when the brakes are applied. A faulty brake light switch can cause the ESP system to engage erratically or not function at all.
Symptoms of Brake Light Switch Problems:
- ESP warning light illumination
- ABS warning light illumination
- Cruise control malfunction
- Brake lights not functioning correctly
- Diagnostic codes related to the brake light switch
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Check the brake light switch for proper operation.
- Inspect the switch wiring and connectors for damage.
- Use a multimeter to test the switch’s continuity.
- Replace the brake light switch if necessary.
3.4. ABS Module Failures
The ABS module controls the anti-lock braking system and works closely with the ESP system. If the ABS module fails, it can affect the operation of the ESP system.
Symptoms of ABS Module Failures:
- ESP warning light illumination
- ABS warning light illumination
- Reduced braking performance
- Pulsating sensation when braking
- Diagnostic codes related to the ABS module (e.g., C1000)
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Check the ABS module for proper operation.
- Inspect the module wiring and connectors for damage.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to read the module’s data and identify any errors.
- Replace or repair the ABS module if necessary.
3.5. Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can cause various electrical issues in your Mercedes-Benz, including problems with the ESP system. The ESP system requires a stable power supply to function correctly.
Symptoms of Low Battery Voltage:
- ESP warning light illumination
- ABS warning light illumination
- Difficulty starting the vehicle
- Dim headlights
- Diagnostic codes related to low voltage
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Check the battery voltage with a multimeter.
- Test the battery’s charging system.
- Replace the battery if it is weak or damaged.
- Ensure the battery terminals are clean and tight.
3.6. Tire Size Mismatch
Using tires of different sizes can cause the ESP system to malfunction. The ESP system relies on accurate wheel speed data, and mismatched tires can lead to incorrect readings.
Symptoms of Tire Size Mismatch:
- ESP warning light illumination
- Difficulty maintaining stability
- Erratic ESP engagement
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Ensure all tires are the same size and have the same load rating.
- Check the tire pressure and adjust as needed.
- Rotate the tires regularly to ensure even wear.
3.7. Corrupted or Outdated Software
The ESP system relies on software to function correctly. If the software is corrupted or outdated, it can cause the system to malfunction.
Symptoms of Software Issues:
- ESP warning light illumination
- Erratic ESP engagement
- Diagnostic codes related to software issues
Troubleshooting and Solutions:
- Check for software updates and install them as needed.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for software errors.
- Re-flash the ESP control unit with the latest software if necessary.
Addressing these common causes can help you resolve ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz and ensure your vehicle’s safety and stability. Remember, if you’re unsure about any of these steps, it’s always best to consult a professional.
4. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify the root cause of the problem.
4.1. Initial Inspection and Visual Checks
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of your vehicle. Check the following:
- Tires: Ensure all tires are the same size, type, and have adequate tread depth.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the sensors for any visible damage, loose connections, or debris.
- Wiring: Look for any damaged, frayed, or corroded wires connected to the ESP system components.
- Brake System: Check the brake pads, rotors, and brake lines for any signs of wear or damage.
- Battery: Ensure the battery terminals are clean and securely connected.
4.2. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing ESP malfunctions. Here’s how to use it:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Record the Codes: Write down all the DTCs, as they will provide valuable information about the nature of the problem.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): If desired, you can clear the codes to see if they reappear after a test drive.
4.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can pinpoint the specific component or system causing the ESP malfunction. Here are some common DTCs and their possible causes:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Unit Fault | Faulty ESP control unit, wiring issues, software problems |
| C1100 | ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right | Faulty wheel speed sensor, damaged wiring, ABS module issue |
| C1200 | BAS Function Malfunction | Brake light switch issue, ABS module problem, sensor malfunction |
| C1400 | Steering Angle Sensor | Faulty steering angle sensor, calibration issue, wiring problem |
| C1500 | Yaw Rate Sensor | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring issue, sensor misalignment |
| C1600 | Low Voltage | Weak battery, alternator problem, wiring issue |
| C1700 | Traction Control Malfunction | Faulty traction control module, ABS module issue, sensor problem |
4.4. Testing Individual Components
After interpreting the DTCs, you may need to test individual components to confirm the diagnosis. Here are some common testing procedures:
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s resistance. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check the sensor’s signal output while rotating the wheel.
- Steering Angle Sensor:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to read the sensor’s output and check for any errors.
- Verify the sensor is correctly calibrated.
- Brake Light Switch:
- Use a multimeter to check the switch’s continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and released.
- Ensure the brake lights are functioning correctly.
- ABS Module:
- Check the module’s power and ground connections.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to perform a module self-test.
- Battery:
- Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Perform a load test to check the battery’s ability to deliver current under load.
4.5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
In some cases, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to pinpoint the cause of the ESP malfunction. These techniques may include:
- Oscilloscope Testing: Using an oscilloscope to analyze the signal waveforms from sensors and actuators.
- Wiring Harness Testing: Checking the wiring harness for shorts, opens, and high resistance connections.
- Module Programming: Re-flashing or reprogramming the ESP control unit with the latest software.
- Data Logging: Recording data from various sensors and systems during a test drive to identify intermittent problems.
By following these step-by-step diagnostic procedures, you can effectively troubleshoot ESP malfunctions in your Mercedes-Benz and take the appropriate steps to resolve the issue. If you encounter difficulties or are unsure about any of these steps, consult with a qualified technician.
5. Solutions for Common ESP Problems
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the ESP malfunction, you can proceed with the appropriate solutions. Here are some common fixes for common ESP problems.
5.1. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a wheel speed sensor is identified as the cause of the ESP malfunction, replacement is usually necessary. Here’s how to do it:
- Gather Tools and Parts: You’ll need a new wheel speed sensor, socket set, wrench, and possibly a torque wrench.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor and disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the bolt or screws securing the sensor to the wheel hub.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new wheel speed sensor and tighten the mounting hardware to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect the Sensor: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any DTCs and verify the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.2. Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
If the steering angle sensor is misaligned or needs calibration, follow these steps:
- Use a Diagnostic Scanner: Connect a diagnostic scanner to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access Calibration Function: Navigate to the steering angle sensor calibration function in the scanner’s menu.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the scanner’s on-screen instructions to calibrate the sensor. This usually involves turning the steering wheel from lock to lock.
- Verify Calibration: After calibration, verify the sensor’s output is within the specified range.
5.3. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
If the brake light switch is faulty, replacement is a straightforward process:
- Locate the Switch: The brake light switch is usually located near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the Switch: Remove the switch from its mounting bracket.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new brake light switch and secure it in place.
- Reconnect the Switch: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new switch.
- Test the System: Verify the brake lights are functioning correctly and the ESP warning light is off.
5.4. Repairing or Replacing the ABS Module
Repairing or replacing the ABS module can be more complex and may require professional assistance. Here are the general steps:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Remove the ABS Module: Locate the ABS module and disconnect the electrical connectors and brake lines.
- Install the New or Repaired Module: Install the new or repaired ABS module and reconnect the brake lines and electrical connectors.
- Bleed the Brakes: Bleed the brake system to remove any air.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to verify the ABS and ESP systems are functioning correctly.
5.5. Ensuring Proper Battery Voltage
Maintaining proper battery voltage is crucial for the ESP system’s operation. Here are some tips:
- Check Battery Voltage: Regularly check the battery voltage with a multimeter.
- Clean Battery Terminals: Clean any corrosion from the battery terminals.
- Replace Weak Battery: Replace the battery if it is weak or not holding a charge.
- Check Charging System: Have the charging system tested to ensure it is functioning correctly.
5.6. Matching Tire Sizes
Ensuring all tires are the same size is essential for the ESP system to function correctly. If you have mismatched tires:
- Replace Mismatched Tires: Replace any mismatched tires with tires that match the original equipment specifications.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Test the System: After replacing the tires, test the ESP system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
5.7. Updating or Re-flashing Software
If the ESP malfunction is caused by corrupted or outdated software, updating or re-flashing the software may be necessary. This usually requires specialized equipment and software, so it’s best to consult a professional.
- Consult a Professional: Take your vehicle to a qualified technician with the necessary equipment and software.
- Update or Re-flash Software: Follow the technician’s instructions to update or re-flash the ESP control unit.
- Test the System: After updating or re-flashing the software, test the ESP system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
By following these solutions, you can address common ESP problems in your Mercedes-Benz and ensure your vehicle’s safety and stability. If you are unsure about any of these steps, it is always best to consult a professional.
6. Preventive Maintenance for ESP Systems
Preventive maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Regular maintenance can help you avoid costly repairs and maintain optimal vehicle safety.
6.1. Regular Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of your vehicle’s ESP system components. Check the following:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the sensors for any visible damage, loose connections, or debris.
- Wiring: Look for any damaged, frayed, or corroded wires connected to the ESP system components.
- Tires: Ensure all tires are the same size, type, and have adequate tread depth.
- Brake System: Check the brake pads, rotors, and brake lines for any signs of wear or damage.
- Battery: Ensure the battery terminals are clean and securely connected.
6.2. Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is essential for the ESP system to function correctly. Follow these tips:
- Maintain Correct Tire Pressure: Check the tire pressure regularly and inflate the tires to the recommended pressure.
- Rotate Tires Regularly: Rotate the tires every 5,000 to 7,000 miles to ensure even wear.
- Replace Tires When Needed: Replace tires when they reach the end of their service life or show signs of damage.
6.3. Brake System Service
The brake system is closely linked to the ESP system, so regular brake service is crucial. Follow these guidelines:
- Inspect Brake Pads and Rotors: Check the brake pads and rotors for wear and replace them when necessary.
- Flush Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two years to remove moisture and contaminants.
- Inspect Brake Lines: Inspect the brake lines for leaks or damage.
6.4. Battery Maintenance
A healthy battery is essential for the proper operation of the ESP system. Follow these tips:
- Check Battery Voltage: Regularly check the battery voltage with a multimeter.
- Clean Battery Terminals: Clean any corrosion from the battery terminals.
- Test Battery Regularly: Have the battery tested regularly to ensure it is holding a charge.
6.5. Software Updates
Keep the ESP system software up to date. Check for software updates and install them as needed. This can help ensure the system is functioning correctly and has the latest features and improvements.
6.6. Professional Check-ups
Schedule regular check-ups with a qualified technician. A professional can perform a comprehensive inspection of the ESP system and identify any potential problems before they become major issues.
By following these preventive maintenance tips, you can help ensure the longevity and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system and maintain optimal vehicle safety.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Maintaining Your ESP System
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we’re committed to providing high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Our range of products is designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
7.1. Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide selection of OBD-II scanners and diagnostic tools that can help you identify ESP malfunctions and troubleshoot problems effectively. Our tools are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information.
7.2. Wheel Speed Sensors and Components
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality wheel speed sensors, ABS modules, and other components necessary for maintaining your ESP system. Our parts are sourced from trusted manufacturers and are designed to meet or exceed OEM specifications.
7.3. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support. Whether you have questions about diagnosing an ESP malfunction or need help selecting the right tools and parts, we’re here to assist you.
7.4. Training and Resources
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers training programs and resources to help you improve your diagnostic skills and stay up-to-date on the latest automotive technologies. Our training materials cover a wide range of topics, including ESP system diagnostics and repair.
7.5. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET?
- Quality Products: We offer high-quality diagnostic tools and parts from trusted manufacturers.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support.
- Competitive Prices: We offer competitive prices on all our products.
- Fast Shipping: We offer fast shipping to get you the tools and parts you need quickly.
- Customer Satisfaction: We are committed to providing excellent customer service and ensuring your satisfaction.
8. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Specific ESP Features
Mercedes-Benz vehicles often incorporate advanced ESP features tailored to enhance safety and performance. Recognizing these specific features can help you better understand and maintain your ESP system.
8.1. Adaptive ESP
Adaptive ESP is an advanced version of the standard ESP system that adjusts its intervention based on driving conditions and vehicle load. It considers factors such as vehicle speed, steering angle, and load distribution to optimize stability control. This system is designed to:
- Provide enhanced stability in various driving conditions
- Adjust intervention based on vehicle load
- Optimize braking performance
8.2. Curve Dynamic Assist
Curve Dynamic Assist is a feature that enhances stability when cornering. It applies targeted braking to the inside wheels to reduce understeer and improve handling. This system is particularly useful in maintaining control during high-speed turns. Key benefits include:
- Reduced understeer during cornering
- Improved handling and stability
- Enhanced driving confidence
8.3. Crosswind Assist
Crosswind Assist helps stabilize the vehicle when driving in strong crosswinds. It uses the ESP system to apply targeted braking to one side of the vehicle, counteracting the effects of the wind. This feature is especially useful on highways and bridges where crosswinds can be strong. Advantages include:
- Enhanced stability in strong crosswinds
- Reduced driver fatigue
- Improved safety on highways and bridges
8.4. Load Adaptive Control
Load Adaptive Control adjusts the ESP system’s parameters based on the vehicle’s load. It optimizes stability control for different load conditions, ensuring consistent performance whether the vehicle is empty or fully loaded. The system is designed to:
- Optimize stability control for different load conditions
- Ensure consistent performance
- Enhance safety
8.5. Trailer Stability Assist
Trailer Stability Assist helps stabilize the vehicle when towing a trailer. It detects trailer sway and applies targeted braking to the vehicle’s wheels to counteract the sway. This feature is crucial for maintaining control when towing heavy loads. Key features include:
- Detection of trailer sway
- Targeted braking to counteract sway
- Enhanced stability when towing
8.6. ESP with ASR (Acceleration Skid Control)
ESP with ASR combines the benefits of ESP with Acceleration Skid Control (ASR). ASR prevents wheel spin during acceleration, ensuring optimal traction and stability. This system is particularly useful on slippery surfaces. Advantages include:
- Prevention of wheel spin during acceleration
- Optimal traction and stability
- Enhanced safety on slippery surfaces
Understanding these Mercedes-Benz specific ESP features can help you appreciate the sophistication of your vehicle’s safety systems and maintain them effectively. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential for ensuring these features function correctly.
9. The Impact of Aftermarket Modifications on ESP Systems
Aftermarket modifications can significantly impact the performance and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for making informed decisions about vehicle modifications.
9.1. Suspension Modifications
Lowering or modifying the suspension can alter the vehicle’s center of gravity and handling characteristics. This can affect the ESP system’s ability to accurately detect and correct instability. Potential issues include:
- Inaccurate sensor readings
- Delayed or erratic ESP engagement
- Reduced stability control
9.2. Wheel and Tire Upgrades
Upgrading to larger or wider wheels and tires can change the vehicle’s rolling circumference and affect the accuracy of the wheel speed sensors. This can lead to ESP malfunctions. Key considerations include:
- Ensuring correct tire size and rolling circumference
- Calibrating the ESP system for new wheel and tire specifications
- Avoiding mismatched tire sizes
9.3. Engine Tuning and Performance Enhancements
Engine tuning and performance enhancements can increase the vehicle’s power output, which can overwhelm the ESP system’s ability to maintain control. This can lead to increased skidding and reduced stability. Potential risks include:
- Overloading the ESP system
- Increased risk of skidding
- Reduced stability control
9.4. Brake System Upgrades
Upgrading the brake system with aftermarket components can affect the ESP system’s ability to distribute braking force effectively. This can lead to uneven braking and reduced stability. Key considerations include:
- Ensuring compatibility with the ESP system
- Calibrating the ESP system for new brake components
- Avoiding mismatched brake components
9.5. Exhaust System Modifications
While exhaust system modifications typically do not directly affect the ESP system, they can impact the vehicle’s overall performance and handling, which can indirectly affect the ESP system’s operation. Considerations include:
- Ensuring proper exhaust flow
- Avoiding modifications that negatively impact vehicle performance
- Monitoring the ESP system for any signs of malfunction
9.6. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Tuning
ECU tuning can alter the parameters of the ESP system, potentially leading to unintended consequences. It’s crucial to ensure that any ECU tuning is performed by a qualified professional who understands the ESP system. Risks include:
- Altering the ESP system’s parameters
- Potentially leading to unintended consequences
- Compromising vehicle safety
Before making any aftermarket modifications, it’s essential to research the potential impact on the ESP system and consult with a qualified technician. Ensuring compatibility and proper calibration can help minimize the risk of ESP malfunctions.
10. Troubleshooting ESP Issues in Specific Mercedes-Benz Models
ESP issues can manifest differently across various Mercedes-Benz models. Understanding model-specific nuances can aid in more accurate diagnosis and resolution.
10.1. C-Class (W204, W205)
Common ESP issues in C-Class models include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor malfunctions, and brake light switch problems. Specific troubleshooting steps include:
- Checking wheel speed sensor readings using a diagnostic scanner
- Calibrating the steering angle sensor
- Verifying brake light switch operation
10.2. E-Class (W212, W213)
E-Class models may experience ESP issues related to the ABS module, low battery voltage, and tire size mismatch. Key troubleshooting steps include:
- Testing the ABS module for proper operation
- Checking battery voltage and charging system
- Ensuring all tires are the same size and type
10.3. S-Class (W221, W222)
S-Class models often have advanced ESP features, such as Adaptive ESP and Curve Dynamic Assist. Common issues include sensor malfunctions, software problems, and suspension-related issues. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Using a diagnostic scanner to read sensor data
- Checking for software updates
- Inspecting the suspension system for damage or wear
10.4. GLC (X253)
GLC models may experience ESP issues related to the 4MATIC all-wheel-drive system, including sensor problems and software glitches. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Checking 4MATIC system components for proper operation
- Using a diagnostic scanner to read sensor data
- Ensuring the transfer case is functioning correctly
10.5. GLE (W166)
GLE models may encounter ESP issues related to the air suspension system, Adaptive Damping System (ADS), and sensor malfunctions. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Inspecting the air suspension system for leaks or damage
- Checking ADS components for proper operation
- Using a diagnostic scanner to read sensor data
10.6. Sprinter Van (W906)
Sprinter vans often experience ESP issues due to heavy loads and commercial use, including wheel speed sensor problems, steering angle sensor malfunctions, and ABS module failures. Troubleshooting steps include:
- Checking wheel speed sensor readings using a diagnostic scanner
- Calibrating the steering angle sensor
- Testing the ABS module for proper operation
By understanding these model-specific nuances, you can more effectively diagnose and resolve ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz. Remember to consult a qualified technician if you encounter difficulties or are unsure about any troubleshooting steps.
FAQ: Addressing Your ESP Concerns
1. What does the ESP warning light mean in my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP warning light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program has detected a malfunction or is actively engaged to prevent skidding.
2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP warning light on?
It is generally safe to drive with the ESP warning light on, but you should have the system inspected and repaired as soon as possible. The ESP system may not function correctly, which can reduce stability control.
3. How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz?
You can try resetting the ESP system by turning off the engine, waiting a few minutes, and then restarting the vehicle. If the warning light remains on, a diagnostic scan is necessary.
4. What are the common causes of ESP malfunction in Mercedes-Benz?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, brake light switch problems, ABS module failures, low battery voltage, tire size mismatch, and software issues.
5. How can I diagnose ESP problems in my Mercedes-Benz?
You can use an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and test individual components, such as wheel speed sensors and the steering angle sensor.
6. Can aftermarket modifications affect the ESP system?
Yes, aftermarket modifications, such as suspension modifications, wheel and tire upgrades, and engine tuning, can affect the ESP system.
7. How often should I have the ESP system inspected?
You should have the ESP system inspected during regular maintenance check-ups, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles.
8. What should I do if the ESP warning light comes on while driving?
If the ESP warning light comes on while driving, reduce your speed, avoid sudden maneuvers, and have the system inspected as soon as possible.
9. Can I disable the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz?
Some Mercedes-Benz models allow you to disable the ESP system, but it is generally not recommended for normal driving conditions.
10. How does CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP system maintenance?
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality diagnostic tools, wheel speed sensors, ABS modules, and expert advice to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz ESP system.
Take Action: Ensure Your ESP System is Functioning Optimally
Don’t compromise on safety. Ensure your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is functioning correctly with the right tools and expertise from CARDIAGTECH.NET. We understand the challenges you face as automotive technicians and garage owners, from the physical demands of the job to the constant need for updated knowledge. Let us help you enhance your work efficiency, reduce repair times, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Contact us today for expert advice and support. Invest in your success with CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re here to help you stay ahead in the automotive industry.