ESP on a Mercedes: Understanding and Troubleshooting
The Mercedes-Benz ESP® warning light is an important indicator of your vehicle’s stability system. Understanding what this light means, the potential causes, and how to address them is crucial for safe driving. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive solutions for diagnosing and resolving ESP issues, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz maintains optimal performance. Learn about the intricacies of your ESP system, discover effective troubleshooting techniques, and explore how CARDIAGTECH.NET can assist you in keeping your vehicle stable and secure.
1. What is ESP® on a Mercedes-Benz?
Electronic Stability Program (ESP®) is a sophisticated safety system designed to enhance driving confidence by preventing skidding and maintaining control during critical situations. It works by monitoring various parameters, such as wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, to detect potential loss of control. According to Mercedes-Benz official documentation, ESP® utilizes sensors and actuators to automatically intervene by applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine torque to help the driver maintain directional control. ESP ensures your vehicle remains stable, reducing the risk of accidents.
1.1. How Does ESP® Work?
ESP® integrates several systems to prevent skidding and wheel spin, ensuring maximum stability. The anti-lock braking system (ABS) prevents wheel lockup during braking, while the Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) optimizes braking force between the front and rear wheels. ESP® uses these systems, along with sensors that monitor wheel speed and steering angle, to detect and correct potential loss of control. CARDIAGTECH.NET emphasizes that regular maintenance and proper tire condition are essential for ESP® to function effectively.
1.2. Components of the ESP® System
The ESP® system consists of several key components that work together to ensure vehicle stability:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel to detect discrepancies that could indicate a skid.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel to determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration.
- Hydraulic Unit: Modulates brake pressure to individual wheels as needed.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Processes data from the sensors and controls the hydraulic unit and engine management system.
These components ensure your Mercedes-Benz ESP® system responds effectively to changing driving conditions, helping you maintain control.
2. Deciphering the ESP® Warning Light
The ESP® warning light on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard serves as a crucial indicator of the system’s status. Understanding the different ways this light can illuminate will help you quickly identify potential issues and take appropriate action.
2.1. ESP® Light Flashing
A flashing ESP® light indicates that the system is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. This typically occurs when driving on slippery surfaces, during emergency braking, or when the system detects a loss of traction. When the ESP® light flashes, it’s a signal to drive cautiously, as the vehicle is operating near its stability limits.
2.2. ESP® Light On (Solid)
If the ESP® light remains on continuously, it indicates that the system has been disabled. This could be due to a manual deactivation via the “ESP® Off” button or a malfunction within the ESP® system itself. Driving with the ESP® light on is not recommended, as it means the vehicle’s stability control is compromised.
2.3. BAS ESP® Light
Some Mercedes-Benz models feature a BAS ESP® light, which combines the functions of both the Brake Assist System (BAS) and ESP®. If this light illuminates, it could indicate issues with either system. BAS assists in emergency braking situations by providing maximum braking force. If the BAS ESP® light is on, it’s important to have the system diagnosed promptly.
3. Potential Causes of an Illuminated ESP® Light
The ESP® light can illuminate for various reasons, ranging from simple issues to more complex malfunctions. Identifying the cause is the first step in resolving the problem.
3.1. Manual Deactivation
The most straightforward reason for the ESP® light to be on is manual deactivation. Most Mercedes-Benz vehicles have an “ESP® Off” button, which, when pressed, disables the system. If you accidentally pressed this button, simply press it again to re-engage ESP®.
3.2. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are critical for the ESP® system to function correctly. These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide data to the ECU. If a wheel speed sensor fails, the ESP® system may not receive accurate information, causing the ESP® light to illuminate. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), faulty wheel speed sensors are a common cause of ESP® malfunctions.
3.3. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP® system. If the steering angle sensor is faulty, the ESP® system may not be able to accurately determine the driver’s intended direction, leading to an illuminated ESP® light.
3.4. Yaw Rate Sensor Problems
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. This information is crucial for the ESP® system to detect and correct skidding. If the yaw rate sensor is not working correctly, the ESP® system may not be able to accurately assess the vehicle’s stability, triggering the ESP® light.
3.5. Low Brake Fluid
Low brake fluid can also cause the ESP® light to illuminate. The ESP® system relies on the hydraulic brake system to apply brakes to individual wheels. If the brake fluid level is low, the system may not be able to function effectively, resulting in the ESP® light turning on.
3.6. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Malfunctions
The ECU is the brain of the ESP® system, processing data from various sensors and controlling the hydraulic unit and engine management system. If the ECU malfunctions, it can disrupt the entire ESP® system, causing the ESP® light to illuminate. ECU issues can be complex and often require professional diagnosis.
3.7. Related System Issues
The ESP® system is interconnected with other vehicle systems, such as the ABS and engine management system. Issues with these related systems can indirectly affect the ESP® system, causing the ESP® light to come on. For example, a faulty ABS sensor can also trigger the ESP® light.
4. Resetting the ESP® Warning Light
In some cases, resetting the ESP® warning light can be a simple process. However, it’s essential to understand when a reset is appropriate and when professional diagnosis is necessary.
4.1. Manual Reset Procedure
If the ESP® light is on due to a simple issue, such as manual deactivation or a temporary glitch, a manual reset may resolve the problem. The procedure typically involves:
- Locating the “ESP® Off” button.
- Pressing and holding the button for a few seconds.
- Starting the vehicle and checking if the light has turned off.
If this procedure doesn’t work, more advanced troubleshooting may be required.
4.2. Steering Wheel Reset
Another method to reset the ESP® light involves turning the steering wheel fully to the left and then fully to the right. This can sometimes recalibrate the steering angle sensor and resolve the issue.
- Start the vehicle.
- Turn the steering wheel completely to the left.
- Turn the steering wheel completely to the right.
- Repeat this process a few times.
- Turn off the vehicle and restart it to check if the light has been reset.
4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If the ESP® light persists after attempting manual reset procedures, it’s essential to seek professional help. This indicates a more complex issue within the ESP® system that requires advanced diagnostic tools and expertise. Attempting to fix the problem without proper knowledge can lead to further damage and safety risks.
5. Diagnosing ESP® Issues
Diagnosing ESP® issues requires a systematic approach and specialized tools. Here are the steps involved in identifying the root cause of an illuminated ESP® light.
5.1. Visual Inspection
The first step in diagnosing ESP® issues is a thorough visual inspection. This involves checking the following:
- Tire Condition: Ensure tires are in good condition and properly inflated.
- Brake Fluid Level: Verify the brake fluid level is within the specified range.
- Wiring and Connectors: Inspect wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Sensors: Visually inspect wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor for any obvious damage.
5.2. Diagnostic Scan
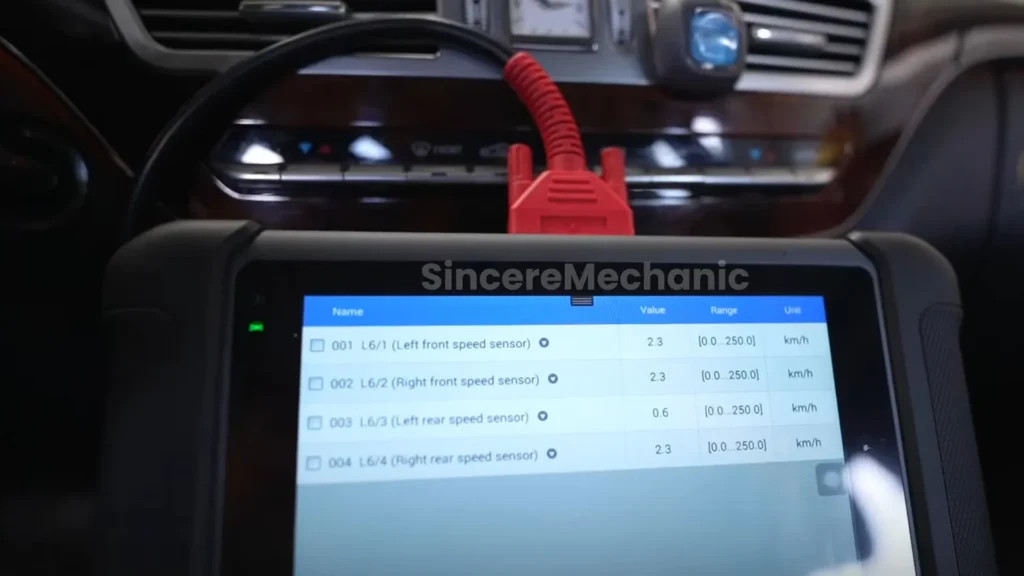
A diagnostic scan is crucial for identifying specific fault codes related to the ESP® system. This involves connecting a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and reading the stored fault codes. These codes provide valuable information about the nature of the problem and the affected components. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that can help you perform this scan effectively.
5.3. Interpreting Fault Codes
Interpreting fault codes requires technical knowledge and understanding of the ESP® system. Each fault code corresponds to a specific issue, and the diagnostic tool provides a description of the code. Common ESP® fault codes include:
- C1000: Control Unit Fault
- C1100: Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
- C1200: Steering Angle Sensor Fault
- C1300: Yaw Rate Sensor Fault
Based on the fault codes, you can narrow down the possible causes of the ESP® light and proceed with further testing.
5.4. Testing Components
Once you have identified potential problem areas based on the fault codes, the next step is to test the individual components. This may involve using a multimeter to check the resistance and voltage of sensors, or using a diagnostic tool to monitor sensor data in real-time. Testing components helps you confirm whether they are functioning correctly and identify any faulty parts.
6. Repairing ESP® System
Repairing ESP® system issues requires expertise and precision. Depending on the nature of the problem, the repair may involve replacing faulty sensors, repairing wiring, or recalibrating the system.
6.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
If a sensor is identified as faulty, it needs to be replaced. This involves disconnecting the old sensor, installing the new sensor, and ensuring it is properly connected. It’s important to use high-quality replacement sensors that meet the vehicle’s specifications. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality sensors for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
6.2. Wiring and Connector Repairs
Damaged or corroded wiring and connectors can disrupt the ESP® system’s communication and cause the ESP® light to illuminate. Repairing wiring involves identifying the damaged sections, cutting them out, and splicing in new wiring. Connectors may need to be cleaned or replaced if they are corroded.
6.3. System Recalibration
After replacing sensors or performing other repairs, the ESP® system may need to be recalibrated. This involves using a diagnostic tool to reset the system and teach it the new sensor data. Recalibration ensures the ESP® system functions correctly with the new components.
7. Maintaining Your ESP® System
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability of your ESP® system. Regular inspections and preventative measures can help prevent issues and keep your ESP® system functioning optimally.
7.1. Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect your tires, brakes, and sensors to identify any potential issues early on. Check tire pressure and condition, brake fluid level, and sensor wiring. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems.
7.2. Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for the ESP® system to function effectively. Ensure tires are properly inflated, and rotate them regularly to promote even wear. Replace tires when they reach the end of their lifespan to maintain optimal traction.
7.3. Brake System Maintenance
Maintain your brake system by regularly checking brake fluid level and inspecting brake pads and rotors. Replace brake components as needed to ensure the ESP® system can function effectively during braking.
7.4. Professional Servicing
Schedule regular servicing with a qualified technician who can inspect and maintain your ESP® system. Professional servicing includes diagnostic scans, component testing, and system recalibration to ensure your ESP® system is functioning correctly.
8. Common ESP® Problems and Solutions
Here are some common ESP® problems and their solutions to help you troubleshoot your Mercedes-Benz ESP® system:
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| ESP® light stays on | Manual deactivation | Press the “ESP® Off” button to re-engage ESP® |
| ESP® light stays on | Faulty wheel speed sensor | Replace the faulty wheel speed sensor |
| ESP® light stays on | Steering angle sensor issue | Recalibrate or replace the steering angle sensor |
| ESP® light stays on | Low brake fluid | Add brake fluid to the specified level |
| ESP® light flashing frequently | Slippery road conditions | Drive cautiously and reduce speed |
| ESP® light and ABS light on | Faulty ABS sensor | Replace the faulty ABS sensor |
| ESP® system not functioning | ECU malfunction | Seek professional diagnosis and repair of the ECU |
| BAS ESP® light illuminated | Brake Assist System issue | Have the BAS system diagnosed and repaired |
| ESP® light after battery change | System requires reset | Perform steering wheel reset procedure |
| ESP® light with no fault codes | Intermittent issue | Inspect wiring and connectors, and monitor the system for recurring issues |
9. Benefits of Maintaining a Functional ESP® System
Maintaining a functional ESP® system offers numerous benefits, including enhanced safety, improved vehicle control, and reduced risk of accidents.
9.1. Enhanced Safety
A functional ESP® system enhances safety by preventing skidding and maintaining vehicle control during critical situations. This is particularly important in adverse weather conditions or during emergency maneuvers.
9.2. Improved Vehicle Control
ESP® improves vehicle control by automatically intervening to correct loss of traction. This helps the driver maintain directional control and avoid accidents.
9.3. Reduced Risk of Accidents
By preventing skidding and improving vehicle control, ESP® reduces the risk of accidents. This can save lives and prevent costly vehicle damage.
9.4. Increased Confidence
Knowing that your vehicle is equipped with a functional ESP® system can increase your confidence behind the wheel, especially in challenging driving conditions.
9.5. Lower Insurance Costs
Some insurance companies offer discounts for vehicles equipped with advanced safety systems like ESP®. Maintaining a functional ESP® system can potentially lower your insurance costs.
10. CARDIAGTECH.NET Solutions for ESP® Issues
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of solutions to help you diagnose, repair, and maintain your Mercedes-Benz ESP® system. Our products and services include:
10.1. Diagnostic Tools
We offer a variety of diagnostic tools that can help you scan your vehicle for ESP® fault codes and diagnose issues. Our diagnostic tools are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and provide accurate and reliable results.
10.2. High-Quality Sensors
We offer a wide range of high-quality sensors for Mercedes-Benz ESP® systems, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors. Our sensors are designed to meet or exceed OEM specifications and provide reliable performance.
10.3. Repair Parts
We offer a variety of repair parts for ESP® systems, including wiring, connectors, and hydraulic units. Our repair parts are designed to help you fix ESP® issues quickly and effectively.
10.4. Expert Support
Our team of expert technicians is available to provide you with support and guidance on diagnosing and repairing ESP® issues. We can help you interpret fault codes, test components, and perform system recalibrations.
10.5. Training Resources
We offer a variety of training resources to help you learn more about ESP® systems and how to diagnose and repair them. Our training resources include articles, videos, and online courses.
FAQ: ESP® on a Mercedes-Benz
-
What does the ESP® light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP® light indicates the status of the Electronic Stability Program. If it’s flashing, ESP® is actively working. If it’s on continuously, ESP® is disabled.
-
Can I drive with the ESP® light on?
It’s not recommended. A solid ESP® light means the system is disabled, reducing your vehicle’s stability.
-
How do I reset the ESP® light on my Mercedes-Benz?
Try pressing the “ESP® Off” button or performing the steering wheel reset procedure. If the light persists, seek professional help.
-
What causes the ESP® light to come on?
Common causes include manual deactivation, faulty sensors, low brake fluid, and ECU malfunctions.
-
How do I diagnose ESP® issues?
Perform a visual inspection, use a diagnostic tool to scan for fault codes, and test individual components.
-
Where can I get high-quality ESP® sensors and parts?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality sensors and parts for Mercedes-Benz ESP® systems.
-
What is BAS ESP®?
BAS ESP® combines the functions of the Brake Assist System and ESP®. If this light is on, it indicates issues with either system.
-
Can low tire pressure affect the ESP® system?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP® system by reducing traction and stability.
-
How often should I have my ESP® system serviced?
Schedule regular servicing with a qualified technician who can inspect and maintain your ESP® system.
-
Is it safe to disable ESP®?
Generally, no. ESP® enhances safety and vehicle control. Only disable it in specific situations, like when stuck in deep snow, and only if recommended by your vehicle’s manual.
Don’t wait until it’s too late! Ensure your Mercedes-Benz’s ESP system is functioning perfectly with CARDIAGTECH.NET. Contact us now for expert advice and the best tools for diagnostics and repairs. Our team is ready to assist you with any questions and guide you to the best solutions. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit CARDIAGTECH.NET today. Drive with confidence and stay safe on the road.
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.