Understanding the ESP Sprinter Mercedes System
ESP Sprinter Mercedes is an essential safety system designed to enhance vehicle stability and control. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the critical role ESP plays in ensuring a safe driving experience. Let’s explore what ESP is, how it works, common issues, and why maintaining it is crucial. Discover the diagnostic tools and repair solutions available to keep your Sprinter Mercedes operating at its best, ensuring safety and performance.
1. What is ESP in a Sprinter Mercedes?
Electronic Stability Program (ESP), crucial for Sprinter Mercedes, elevates driving confidence. This advanced technology actively monitors driving dynamics, counteracting skidding and loss of control, especially in challenging conditions. By precisely intervening with braking and engine power, ESP ensures the vehicle remains stable and follows the driver’s intended path. This is particularly vital for commercial vans like the Sprinter, often carrying heavy loads or navigating diverse terrains.
1.1. Defining ESP
ESP is an automated system that enhances a vehicle’s stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction (skidding). It operates by applying individual brakes to specific wheels to help steer the vehicle back onto its intended course. ESP links several subsystems to maximize its effectiveness:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during braking.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Limits wheel spin during acceleration.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures sideways force on the vehicle.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Detects the driver’s intended direction.
By integrating these inputs, ESP enhances safety and control in various driving conditions, especially crucial for larger vehicles such as the Mercedes Sprinter.
1.2. The Purpose of ESP in Sprinter Mercedes
The primary purpose of ESP in a Sprinter Mercedes is to improve vehicle stability and prevent skidding, especially critical due to the vehicle’s size and weight. ESP is designed to:
- Prevent Oversteer: Corrects when the rear of the vehicle slides out.
- Prevent Understeer: Corrects when the front of the vehicle doesn’t turn as much as intended.
- Enhance Traction: Optimizes grip on slippery surfaces.
- Improve Stability: Maintains control during sudden maneuvers.
ESP is especially beneficial for commercial vans like the Sprinter, which often operate under diverse and demanding conditions.
1.3. Significance of ESP for Vehicle Safety
ESP drastically improves vehicle safety by preventing accidents caused by loss of control. Studies reveal that ESP can reduce single-vehicle accidents by up to 40%. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP is one of the most effective safety technologies available. ESP’s impact includes:
- Reduced Accident Rates: Prevents skidding and rollovers.
- Improved Handling: Makes the vehicle more predictable and controllable.
- Enhanced Safety in Adverse Conditions: Provides better stability on wet, icy, or uneven roads.
- Supports Driver Control: Helps drivers maintain control during emergency situations.
ESP is a vital component for ensuring driver and passenger safety, especially in commercial vehicles like the Sprinter Mercedes.
2. How ESP Sprinter Mercedes Works
ESP in a Sprinter Mercedes utilizes a complex network of sensors and controllers to monitor and adjust vehicle dynamics. Understanding its operation can help diagnose issues and appreciate its importance. The system’s ability to apply precise brake force to individual wheels ensures maximum stability and control.
2.1. Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several key components working in harmony:
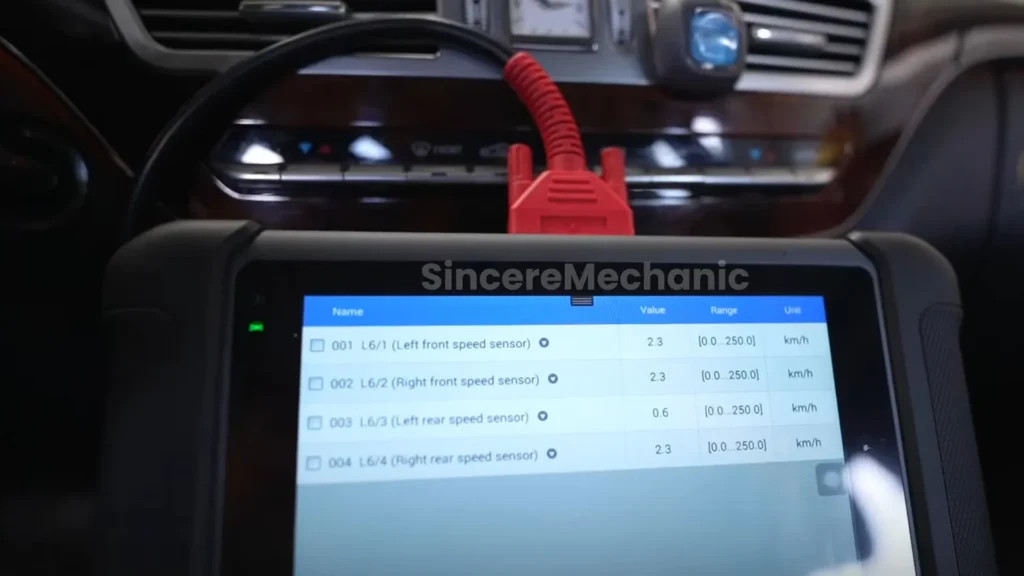
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel to detect variances indicating a skid.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Processes sensor data and determines appropriate corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Modulator: Controls brake pressure to individual wheels as directed by the ECU.
These components work together to ensure ESP functions effectively.
2.2. The Process of Detecting and Correcting Skids
When ESP detects a potential skid, it follows a precise sequence of actions:
- Detection: Sensors identify discrepancies between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual movement.
- Analysis: The ECU analyzes sensor data to determine the severity and type of skid.
- Intervention: The ECU activates the hydraulic modulator to apply braking force to one or more wheels.
- Correction: By selectively braking individual wheels, ESP helps steer the vehicle back on its intended path.
- Stabilization: The system continuously monitors and adjusts brake pressure until stability is regained.
2.3. Interaction with Other Vehicle Systems
ESP integrates with other critical vehicle systems to maximize its effectiveness:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing ESP to maintain control.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Reduces engine power and applies brakes to prevent wheel spin during acceleration.
- Engine Management System (EMS): Adjusts engine output to reduce wheel slip and enhance stability.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Maintains a safe distance from other vehicles and adjusts speed to prevent skids.
This integration ensures a coordinated and effective response to potential skidding situations.
3. Common ESP Sprinter Mercedes Issues
Several issues can affect the performance of ESP in a Sprinter Mercedes. Identifying and addressing these problems promptly is essential for maintaining vehicle safety. Knowing the symptoms and causes can aid in accurate diagnosis and repair.
3.1. Sensor Malfunctions
Sensor malfunctions are common ESP problems:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Failure can result in ABS and ESP deactivation, causing inaccurate speed readings.
- Symptoms: ABS warning light, ESP warning light, erratic speedometer readings.
- Causes: Physical damage, wiring issues, sensor contamination.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Failure can prevent ESP from accurately determining the driver’s intended direction.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, difficulty maintaining lane position, reduced steering responsiveness.
- Causes: Misalignment, electrical faults, sensor wear.
- Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensors: Failure can lead to incorrect assessment of vehicle dynamics.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, unstable handling, unpredictable responses during turns.
- Causes: Physical damage, calibration issues, sensor failure.
3.2. Wiring and Electrical Problems
Wiring and electrical issues can disrupt ESP functionality:
- Damaged Wiring: Corrosion, breaks, or shorts in the wiring harness can interrupt sensor signals and power supply.
- Symptoms: Intermittent ESP warning light, erratic system behavior, complete system failure.
- Causes: Environmental exposure, physical damage, rodent activity.
- Faulty Connections: Loose or corroded connectors can cause signal degradation and system malfunctions.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, system malfunction during specific conditions (e.g., bumps in the road), intermittent issues.
- Causes: Vibration, environmental exposure, improper maintenance.
- ECU Malfunctions: Failure of the ECU can prevent proper processing of sensor data and activation of corrective actions.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, ABS warning light, complete system failure, inability to diagnose system issues.
- Causes: Electrical surges, overheating, internal component failure.
3.3. Hydraulic Unit Failures
Hydraulic unit failures can significantly impair ESP performance:
- Pump Motor Failure: Failure of the pump motor can prevent the system from generating adequate hydraulic pressure.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, ABS warning light, reduced braking performance, system inoperability.
- Causes: Wear and tear, electrical issues, contamination.
- Valve Block Issues: Malfunctioning valves can prevent precise control of brake pressure to individual wheels.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, ABS warning light, uneven braking, system inoperability.
- Causes: Contamination, corrosion, mechanical failure.
- Pressure Sensor Problems: Inaccurate pressure sensor readings can lead to incorrect brake force application.
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, ABS warning light, erratic braking, system inoperability.
- Causes: Sensor failure, contamination, electrical issues.
4. Diagnosing ESP Sprinter Mercedes Issues
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effectively addressing ESP problems in a Sprinter Mercedes. Employing the right diagnostic tools and methods ensures that issues are correctly identified and resolved. This approach minimizes downtime and maximizes repair effectiveness.
4.1. Diagnostic Tools
Utilizing appropriate diagnostic tools is critical for identifying ESP issues:
- OBD-II Scanners: Read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the ECU to identify potential problems.
- Function: Retrieves and interprets DTCs, provides live data readings from sensors.
- Benefits: Quick identification of potential issues, aids in pinpointing faulty components.
- Advanced Diagnostic Systems: Provide in-depth analysis of ESP system performance, including sensor data, actuator tests, and system calibrations.
- Function: Performs comprehensive system tests, including component activation and data analysis.
- Benefits: Enhanced diagnostic capabilities, precise identification of complex issues, facilitates system calibration.
- Multimeters: Test electrical circuits for continuity, voltage, and resistance to identify wiring and connection problems.
- Function: Measures electrical parameters to diagnose wiring issues, faulty connections, and sensor malfunctions.
- Benefits: Essential for diagnosing electrical problems, verifies circuit integrity, aids in component-level diagnostics.
4.2. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs provide valuable insights into ESP system problems:
- Procedure: Connect the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve stored DTCs.
- Interpretation: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable DTC database to understand the meaning of each code.
- Common ESP-Related DTCs:
- C0031: Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0034: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0037: Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0040: Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0196: Yaw Rate Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0121: ABS Control Valve Malfunction.
- Action: Use DTCs as a starting point for further investigation, including visual inspections, component testing, and wiring checks.
4.3. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Follow a structured approach to diagnose ESP issues:
- Initial Scan: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve and record all stored DTCs.
- Visual Inspection: Check for obvious signs of damage, such as broken wires, corroded connectors, and damaged sensors.
- Component Testing: Use a multimeter or advanced diagnostic system to test the functionality of individual components, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor.
- Wiring Checks: Inspect wiring harnesses for continuity, shorts, and proper grounding.
- Hydraulic Unit Testing: Verify the operation of the hydraulic pump, valves, and pressure sensors using diagnostic tools.
- Data Analysis: Analyze live sensor data to identify anomalies or inconsistencies that may indicate a problem.
- System Calibration: Perform system calibrations as needed to ensure proper ESP functionality after repairs.
- Final Scan: Clear DTCs and perform a final scan to verify that the issue has been resolved.
5. Repairing ESP Sprinter Mercedes Issues
Effective repairs are essential for resolving ESP issues in a Sprinter Mercedes. Addressing problems promptly and correctly ensures the vehicle’s safety and stability. Proper repair techniques and component replacements are crucial for restoring ESP functionality.
5.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
Replacing faulty sensors involves:
- Identification: Diagnose malfunctioning sensors using diagnostic tools and procedures.
- Removal: Disconnect the sensor and remove it from its mounting location, noting the orientation and any specific installation requirements.
- Installation: Install the new sensor, ensuring proper alignment and secure connections.
- Testing: Verify the functionality of the new sensor using diagnostic tools and perform system calibrations as needed.
5.2. Repairing Wiring and Electrical Connections
Repairing wiring and electrical connections includes:
- Inspection: Identify damaged wiring, corroded connectors, and loose connections.
- Repair: Repair or replace damaged wiring, clean corroded connectors, and secure loose connections.
- Testing: Verify the integrity of the repaired circuits using a multimeter to ensure proper continuity, voltage, and resistance.
5.3. Hydraulic Unit Repairs and Replacements
Hydraulic unit repairs and replacements involve:
- Diagnosis: Determine the cause of hydraulic unit failure, such as pump motor issues, valve block problems, or pressure sensor malfunctions.
- Repair: Repair or replace faulty components within the hydraulic unit, such as the pump motor, valves, or pressure sensors.
- Replacement: Replace the entire hydraulic unit if necessary, following manufacturer’s instructions for installation and calibration.
- Testing: Verify the functionality of the repaired or replaced hydraulic unit using diagnostic tools and perform system calibrations as needed.
6. Maintaining ESP Sprinter Mercedes for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability and effectiveness of ESP in a Sprinter Mercedes. Following a proactive maintenance schedule and addressing issues promptly can prevent major problems and maintain vehicle safety.
6.1. Regular System Checks
Perform regular ESP system checks:
- Frequency: Conduct system checks at least annually or as part of routine maintenance.
- Procedure: Use diagnostic tools to scan for DTCs and verify the functionality of all ESP components.
- Benefits: Early detection of potential issues, proactive maintenance, and prevention of major problems.
6.2. Keeping Sensors Clean and Free of Debris
Maintaining clean sensors is important:
- Procedure: Regularly inspect and clean wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants.
- Tools: Use a soft brush or cloth and a mild cleaning solution to clean sensors without causing damage.
- Benefits: Accurate sensor readings, reliable ESP performance, and prevention of sensor malfunctions.
6.3. Ensuring Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for ESP functionality:
- Tire Pressure: Maintain proper tire pressure according to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Benefits: Optimal traction, even wear, and accurate wheel speed sensor readings.
- Tire Condition: Regularly inspect tires for wear, damage, and proper tread depth.
- Benefits: Enhanced grip, reduced risk of skidding, and reliable ESP performance.
- Tire Alignment: Ensure proper wheel alignment to prevent uneven tire wear and maintain optimal handling.
- Benefits: Balanced handling, reduced tire wear, and accurate steering angle sensor readings.
7. The Importance of Professional Service
While some ESP maintenance and minor repairs can be performed by vehicle owners, professional service is essential for accurate diagnosis and complex repairs. Certified technicians have the expertise, tools, and training to ensure ESP systems are properly maintained and repaired.
7.1. Expertise and Training
Certified technicians have specialized knowledge and training in ESP systems:
- Knowledge: In-depth understanding of ESP system components, operation, and diagnostic procedures.
- Training: Completion of specialized training programs and certifications in automotive electronics and safety systems.
- Benefits: Accurate diagnosis, effective repairs, and assurance of proper system functionality.
7.2. Specialized Tools and Equipment
Professional service centers have access to specialized tools and equipment:
- Advanced Diagnostic Systems: Comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for accurate problem identification.
- Hydraulic Unit Testers: Tools for testing hydraulic unit performance and diagnosing malfunctions.
- System Calibration Equipment: Equipment for performing system calibrations and ensuring proper ESP functionality after repairs.
- Benefits: Precise diagnostics, efficient repairs, and assurance of system performance.
7.3. Ensuring System Integrity and Safety
Professional service ensures system integrity and safety:
- Proper Repairs: Correct identification and resolution of ESP issues to maintain system functionality.
- System Calibration: Accurate system calibrations to ensure proper integration with other vehicle systems.
- Safety Verification: Thorough testing and verification to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly and safely.
- Benefits: Reliable ESP performance, enhanced vehicle safety, and peace of mind.
8. ESP Sprinter Mercedes Warning Lights and What They Mean
Understanding ESP warning lights on a Sprinter Mercedes is essential for proactive vehicle maintenance. Different signals indicate various conditions, from active system engagement to critical malfunctions. Reacting appropriately to these warnings can prevent severe damage and ensure vehicle safety.
8.1. Types of ESP Warning Lights
Several ESP-related warning lights may appear on the dashboard:
- ESP Active Light: Flashes when ESP is actively engaged, indicating the system is working to stabilize the vehicle.
- ESP Inactive Light: Stays illuminated, indicating that ESP has been manually deactivated or a system fault has been detected.
- ABS Warning Light: May illuminate in conjunction with the ESP warning light, indicating a problem with the ABS system that affects ESP functionality.
- Brake Warning Light: May illuminate if there is a problem with the braking system that affects ESP performance.
8.2. Interpreting Different Light Signals
Understanding what each light signal means is essential:
- Flashing ESP Active Light:
- Meaning: ESP is actively working to stabilize the vehicle during a skid or loss of traction.
- Action: Reduce speed, avoid sudden maneuvers, and drive cautiously until the light stops flashing.
- Solid ESP Inactive Light:
- Meaning: ESP has been manually deactivated or a system fault has been detected.
- Action: Check if ESP has been manually turned off. If not, have the system diagnosed by a professional technician.
- ABS Warning Light with ESP Light:
- Meaning: There is a problem with the ABS system that is affecting ESP functionality.
- Action: Have the ABS system diagnosed and repaired by a professional technician.
- Brake Warning Light with ESP Light:
- Meaning: There is a problem with the braking system that is affecting ESP performance.
- Action: Have the braking system diagnosed and repaired by a professional technician.
8.3. Immediate Actions to Take When a Warning Light Appears
When an ESP warning light appears:
- Assess the Situation: Evaluate the driving conditions and vehicle behavior to determine if ESP is actively engaged or if there is a system fault.
- Check ESP Button: Verify that ESP has not been manually deactivated by checking the ESP button or menu settings.
- Reduce Speed and Drive Cautiously: If the ESP light is flashing, reduce speed, avoid sudden maneuvers, and drive cautiously until the light stops flashing.
- Seek Professional Service: If the ESP light remains illuminated or if there are other warning lights, have the system diagnosed and repaired by a professional technician.
9. Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system in a Sprinter Mercedes offers numerous benefits, enhancing safety, stability, and overall driving experience. Ensuring the system is well-maintained and promptly repaired is crucial for realizing these advantages.
9.1. Enhanced Safety
ESP significantly enhances vehicle safety:
- Skid Prevention: Prevents skidding and loss of control, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Rollover Prevention: Helps prevent rollovers, especially in high-center-of-gravity vehicles like the Sprinter.
- Improved Handling: Enhances vehicle handling and stability, making it easier to control in challenging conditions.
- Reduced Accident Risk: Reduces the overall risk of accidents, protecting drivers and passengers.
9.2. Improved Vehicle Stability
ESP improves vehicle stability:
- Better Control: Provides better control during emergency maneuvers, such as sudden braking or swerving.
- Enhanced Traction: Enhances traction on slippery surfaces, improving grip and stability.
- Predictable Handling: Makes vehicle handling more predictable and consistent, reducing the risk of unexpected behavior.
- Stable Cornering: Provides stable cornering and reduces the risk of oversteer or understeer.
9.3. Increased Driver Confidence
ESP increases driver confidence:
- Peace of Mind: Provides peace of mind, knowing that the vehicle is equipped with advanced safety technology.
- Reduced Stress: Reduces stress and fatigue, making driving more comfortable and enjoyable.
- Greater Control: Gives drivers a greater sense of control over the vehicle, enhancing confidence in challenging situations.
- Safer Driving Experience: Contributes to a safer and more secure driving experience for both drivers and passengers.
10. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your ESP Sprinter Mercedes Needs
For all your ESP Sprinter Mercedes needs, trust CARDIAGTECH.NET to provide expert solutions and support. Whether you need diagnostic tools, replacement components, or professional advice, we are here to help you maintain the safety and performance of your vehicle.
10.1. Expert Advice and Support
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert advice and support:
- Experienced Technicians: Access to experienced technicians with in-depth knowledge of ESP systems.
- Diagnostic Assistance: Assistance with diagnosing ESP issues and identifying appropriate solutions.
- Technical Support: Technical support for installation, calibration, and troubleshooting.
- Customer Service: Dedicated customer service to answer questions and provide assistance.
10.2. Wide Range of Diagnostic Tools and Components
We provide a wide range of diagnostic tools and components:
- OBD-II Scanners: High-quality OBD-II scanners for reading and interpreting DTCs.
- Advanced Diagnostic Systems: Comprehensive diagnostic systems for in-depth analysis of ESP performance.
- Replacement Sensors: High-quality replacement sensors, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors.
- Hydraulic Units: Replacement hydraulic units and components for repairing or replacing faulty units.
10.3. Contact Information
Contact us today for assistance:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
FAQ About ESP Sprinter Mercedes
1. What does ESP do in a Sprinter Mercedes?
ESP (Electronic Stability Program) enhances vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction (skidding). It applies individual brakes to specific wheels to help steer the vehicle back onto its intended course, preventing oversteer and understeer.
2. How do I know if my Sprinter Mercedes ESP is working?
When ESP is actively working, the ESP warning light on the dashboard will flash. If the light stays on without flashing, it indicates that ESP has been manually deactivated or a system fault has been detected.
3. Can I drive my Sprinter Mercedes if the ESP light is on?
If the ESP light is flashing, it is generally safe to drive cautiously. However, if the ESP light stays illuminated, it indicates a potential system fault, and you should have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional technician as soon as possible.
4. What are the common causes of ESP problems in a Sprinter Mercedes?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor malfunctions, wiring problems, hydraulic unit failures, and ECU malfunctions.
5. How do I reset the ESP light on my Sprinter Mercedes?
To reset the ESP light, try turning the steering wheel lock-to-lock (full left to full right) while parked. If the light remains on, there may be a system fault, and you should seek professional diagnostic services.
6. Is it safe to drive with ESP turned off in my Sprinter Mercedes?
It is generally not recommended to drive with ESP turned off, as it reduces vehicle stability and increases the risk of skidding and accidents, especially in adverse driving conditions.
7. How often should I have my Sprinter Mercedes ESP system checked?
You should have your ESP system checked at least annually or as part of routine maintenance to ensure all components are functioning correctly and to identify any potential issues early on.
8. Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system in my Sprinter Mercedes?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system by causing inaccurate wheel speed sensor readings, leading to reduced system performance. Maintaining proper tire pressure is crucial for optimal ESP functionality.
9. What tools are needed to diagnose ESP problems in a Sprinter Mercedes?
Diagnostic tools include OBD-II scanners for reading DTCs, advanced diagnostic systems for in-depth analysis, and multimeters for testing electrical circuits.
10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with my Sprinter Mercedes ESP issues?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert advice, diagnostic assistance, technical support, and a wide range of diagnostic tools and replacement components to help you maintain and repair your Sprinter Mercedes ESP system effectively. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information.
Don’t wait until it’s too late! Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to ensure your Sprinter Mercedes ESP system is functioning perfectly. Our expert team is ready to assist you with all your diagnostic and repair needs. Call us now at +1 (641) 206-8880 for a consultation, or visit CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our range of diagnostic tools and components. Trust CARDIAGTECH.NET to keep you safe on the road.