Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program: Comprehensive Guide

Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety system designed to keep you in control. CARDIAGTECH.NET explains how it works, its benefits, and how it enhances vehicle stability. Explore stability control systems, vehicle dynamics, and automotive safety technologies for a safer driving experience.
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program, widely recognized as ESP, is an advanced safety technology designed to prevent skidding and loss of control. This system enhances vehicle stability by automatically intervening when it detects a potential skid.
1.1. The Core Function of ESP
The primary role of ESP is to maintain directional control of the vehicle, especially during emergency maneuvers or adverse road conditions. ESP monitors several factors, including steering angle, wheel speed, and lateral acceleration, to determine if the vehicle is traveling in the intended direction. When a discrepancy is detected, the ESP system selectively applies braking force to individual wheels to counteract oversteer or understeer, helping the driver maintain control.
1.2. Components of the ESP System
ESP consists of several key components that work together seamlessly:
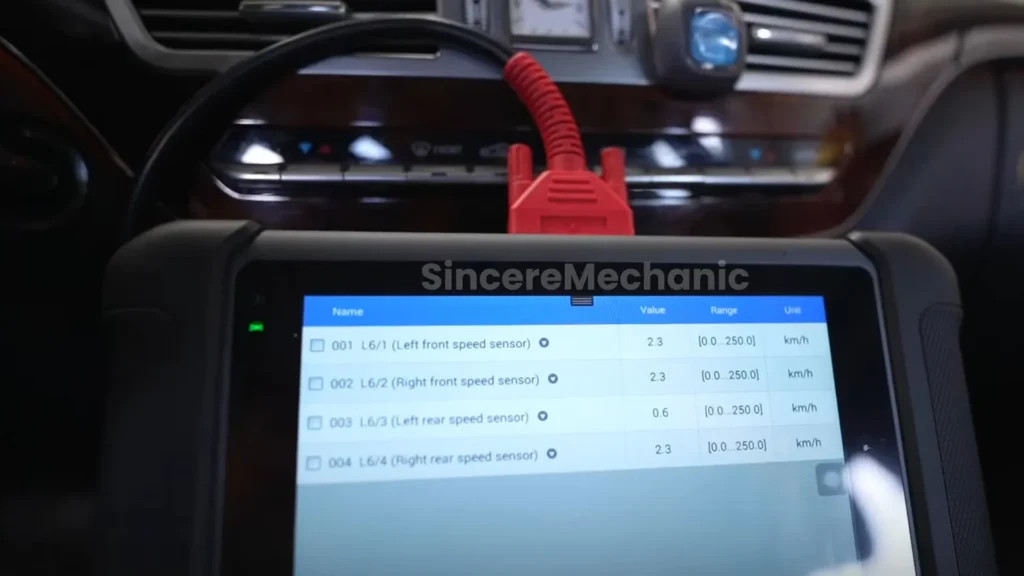
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data to the ESP system about potential wheel slip or lock-up.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, helping the ESP system detect oversteer or understeer.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle, providing additional information about its stability.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU is the brain of the ESP system, processing data from all the sensors and determining the appropriate corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Modulator: The hydraulic modulator controls the braking force applied to each wheel, as directed by the ECU.
1.3. How ESP Works in Real-Time
In real-time, the ESP system continuously monitors the data from its various sensors. If the system detects a deviation from the driver’s intended path, it instantly intervenes by applying braking force to one or more wheels. This targeted braking action creates a corrective torque that helps steer the vehicle back on course. For instance, if the system detects oversteer (where the rear of the car is sliding out), it may apply braking to the outer front wheel to pull the car back into line. Conversely, if understeer is detected (where the front of the car is plowing straight ahead despite steering input), the system may brake the inner rear wheel to help the car turn.
2. The Benefits of ESP in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
ESP offers numerous advantages, significantly improving safety and driving confidence.
2.1. Enhanced Safety
ESP significantly reduces the risk of accidents by preventing skidding and loss of control. By automatically intervening in critical situations, ESP helps drivers maintain control of their vehicles, especially on slippery surfaces or during sudden maneuvers. According to studies, ESP can reduce single-vehicle accidents by up to 30%.
2.2. Improved Stability
ESP enhances vehicle stability by continuously monitoring and adjusting to changing road conditions. Whether driving on a wet, icy, or gravel road, ESP helps maintain optimal traction and control, providing a more stable and predictable driving experience.
2.3. Increased Driver Confidence
ESP gives drivers increased confidence behind the wheel, knowing they have an added layer of safety. This confidence can be particularly valuable for new drivers or those who frequently drive in challenging conditions. The system’s ability to automatically correct skids and maintain stability allows drivers to feel more secure and in control, regardless of the situation.
2.4. Reduced Risk of Rollover
In SUVs and other high-center-of-gravity vehicles, ESP plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of rollover accidents. By preventing skidding and maintaining stability, ESP helps keep the vehicle upright, even during aggressive turns or sudden avoidance maneuvers. This is particularly important because rollovers are among the most dangerous types of accidents, often resulting in severe injuries.
2.5. Optimized Braking Performance
ESP works in conjunction with the anti-lock braking system (ABS) to optimize braking performance. By preventing wheel lock-up and maintaining directional control, ESP ensures that the vehicle can stop safely and effectively in emergency situations. The integration of ESP and ABS allows for shorter stopping distances and better overall braking performance, further enhancing safety.
 Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Mercedes-Benz ESP System
3. Situations Where ESP is Most Effective
ESP is particularly effective in various challenging driving scenarios.
3.1. Driving on Slippery Surfaces
ESP is invaluable when driving on slippery surfaces such as wet roads, snow, or ice. These conditions can significantly reduce traction, making it easy to lose control. ESP detects wheel slip and automatically adjusts the braking force to maintain grip, helping the driver stay on course.
3.2. Emergency Maneuvers
In emergency situations requiring sudden swerving or braking, ESP can be a lifesaver. The system helps prevent skidding and maintains directional control, allowing the driver to avoid obstacles and reduce the risk of a collision. Without ESP, sudden maneuvers can easily lead to loss of control, especially at higher speeds.
3.3. Cornering
ESP enhances stability when cornering, especially at higher speeds. The system helps prevent oversteer or understeer, ensuring the vehicle follows the driver’s intended path. By selectively applying braking force to individual wheels, ESP minimizes the risk of losing control and maintains optimal grip.
3.4. Uneven Road Surfaces
ESP is also effective on uneven road surfaces where one or more wheels may lose traction. The system adjusts the braking force to maintain stability and prevent the vehicle from veering off course. This is particularly useful on gravel roads, potholes, or other irregular surfaces where maintaining control can be challenging.
3.5. High Winds
In windy conditions, ESP helps counteract the effects of strong gusts that can push the vehicle off course. By monitoring the vehicle’s stability and making subtle adjustments to the braking force, ESP helps maintain directional control and reduces the risk of being blown into another lane or off the road.
4. How to Know if Your ESP is Active
Knowing when your ESP system is active and functioning correctly is essential for safe driving.
4.1. Indicator Lights
Most Mercedes-Benz vehicles are equipped with an ESP indicator light on the dashboard. This light typically illuminates briefly when the ignition is turned on, indicating that the system is functioning correctly. If the light remains on or flashes while driving, it indicates that the ESP system is actively intervening to maintain stability.
4.2. System Intervention
Drivers may also feel the ESP system working through subtle changes in the vehicle’s behavior. For instance, they may feel a slight pulsation in the brake pedal or hear a whirring sound as the system applies braking force to individual wheels. These are normal indications that the ESP system is actively working to maintain stability.
4.3. Regular Checks
It is advisable to check the ESP system periodically to ensure it is functioning correctly. This can be done by performing a quick test in a safe environment, such as an empty parking lot. Accelerate gently and then make a sharp turn. If the ESP system is working, you should feel it intervene to prevent skidding or loss of control.
4.4. Professional Inspection
During routine maintenance, have a professional mechanic inspect the ESP system to ensure all components are in good working order. This includes checking the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and other critical components. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address potential issues before they become serious problems.
4.5. Diagnostic Tools
Modern diagnostic tools can provide valuable insights into the performance of the ESP system. These tools can read data from the ECU and identify any error codes or malfunctions. Using diagnostic tools, technicians can quickly diagnose and repair issues, ensuring the ESP system functions optimally. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools to help technicians maintain and repair ESP systems effectively. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
5. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any complex system, ESP can experience issues over time. Understanding common problems and how to troubleshoot them can help keep your ESP system functioning correctly.
5.1. Sensor Malfunctions
One of the most common issues with ESP is sensor malfunctions. Wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or yaw rate sensors can fail due to wear and tear, damage, or electrical issues. A malfunctioning sensor can cause the ESP system to behave erratically or stop working altogether.
5.2. Electrical Problems
Electrical problems, such as faulty wiring, corroded connectors, or a malfunctioning ECU, can also affect ESP performance. These issues can disrupt the communication between the various components of the system, leading to errors and malfunctions.
5.3. Hydraulic Issues
The hydraulic modulator is a critical component of the ESP system, and issues such as leaks, clogs, or pump failures can impact its performance. These problems can prevent the system from applying braking force to individual wheels, compromising its ability to maintain stability.
5.4. Software Glitches
In some cases, software glitches or programming errors can cause the ESP system to malfunction. These issues may require reprogramming or updating the ECU to restore proper functionality.
5.5. Troubleshooting Steps
When troubleshooting ESP issues, start by checking the indicator light on the dashboard. If the light is on, use a diagnostic tool to read any error codes stored in the ECU. These codes can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. Next, inspect the sensors, wiring, and hydraulic components for any signs of damage or wear. If necessary, replace faulty components and clear the error codes. If the problem persists, seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and effectiveness of your ESP system.
6.1. Regular Inspections
Schedule regular inspections of the ESP system as part of your vehicle’s maintenance routine. Have a qualified mechanic check the sensors, wiring, and hydraulic components for any signs of wear or damage.
6.2. Sensor Cleaning
Keep the wheel speed sensors clean and free from debris. Dirt, grime, and brake dust can accumulate on the sensors, affecting their accuracy and performance. Clean the sensors periodically with a soft brush and a mild cleaning solution.
6.3. Fluid Checks
Check the brake fluid level regularly and top it off as needed. Low brake fluid can affect the performance of the hydraulic modulator and compromise the ESP system’s ability to apply braking force.
6.4. Wiring Maintenance
Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of corrosion or damage. Repair or replace any damaged wiring to ensure proper electrical connections.
6.5. Software Updates
Keep the ECU software up to date by installing the latest updates from Mercedes-Benz. These updates can address known issues and improve the performance of the ESP system.
7. The Future of Electronic Stability Programs
Electronic Stability Programs are continually evolving, with new features and technologies being developed to further enhance safety and performance.
7.1. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Future ESP systems will be increasingly integrated with ADAS features such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. This integration will allow for more comprehensive safety solutions that can prevent accidents before they occur.
7.2. Enhanced Sensor Technology
New sensor technologies, such as advanced radar and lidar systems, will provide more detailed and accurate information about the vehicle’s surroundings. This will enable ESP systems to react more quickly and effectively to changing conditions.
7.3. Predictive Stability Control
Predictive stability control systems use advanced algorithms to anticipate potential skidding or loss of control before it occurs. These systems can proactively adjust the braking force and engine torque to maintain stability, providing an even higher level of safety.
7.4. Over-the-Air Updates
Future ESP systems will be able to receive over-the-air software updates, allowing for continuous improvement and the addition of new features. This will ensure that vehicles are always equipped with the latest safety technologies.
7.5. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI will play an increasingly important role in ESP systems, enabling them to learn from experience and adapt to different driving conditions. AI-powered ESP systems will be able to optimize their performance based on individual driving styles and environmental factors, providing a more personalized and effective safety solution.
8. Disabling ESP: When and Why
While ESP is a valuable safety feature, there may be certain situations where disabling it is appropriate.
8.1. Deep Snow or Sand
In deep snow or sand, the ESP system may interfere with the vehicle’s ability to gain traction. The system may detect wheel slip and reduce engine power, making it difficult to move forward. In these situations, disabling ESP can allow the wheels to spin freely, helping the vehicle to gain momentum and escape from the soft surface.
8.2. Performance Driving
Experienced drivers may choose to disable ESP when participating in performance driving events such as track days or autocross. Disabling ESP allows for more wheel spin and greater control over the vehicle’s dynamics, which can be beneficial for achieving faster lap times.
8.3. Testing Purposes
Technicians may disable ESP for testing purposes, such as diagnosing issues or evaluating the performance of other systems. Disabling ESP allows for more precise control over the vehicle’s behavior, making it easier to identify problems.
8.4. How to Disable ESP
Most Mercedes-Benz vehicles have a button or menu option that allows you to disable ESP. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific instructions on how to disable the system. Keep in mind that disabling ESP reduces the vehicle’s stability and increases the risk of losing control, so it should only be done in controlled environments or when necessary.
8.5. Re-engaging ESP
After disabling ESP, it is essential to re-engage the system as soon as possible. ESP is a critical safety feature that can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, so it should always be active during normal driving conditions. To re-engage ESP, simply press the button or select the menu option again. The ESP indicator light on the dashboard should illuminate, indicating that the system is active.
9. ESP and Other Safety Systems
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems to provide comprehensive protection for drivers and passengers.
9.1. Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. ESP and ABS work together to optimize braking performance and maintain stability.
9.2. Traction Control System (TCS)
TCS prevents wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction and stability. ESP and TCS work together to maintain optimal grip in a variety of driving conditions.
9.3. Electronic Brake-Force Distribution (EBD)
EBD distributes braking force between the front and rear wheels to optimize braking performance. ESP and EBD work together to ensure that the vehicle stops safely and effectively in emergency situations.
9.4. Brake Assist (BA)
BA detects emergency braking situations and automatically applies maximum braking force to reduce stopping distance. ESP and BA work together to provide enhanced braking performance and prevent accidents.
9.5. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
ACC maintains a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead and automatically adjusts speed to avoid collisions. ESP and ACC work together to provide a more comfortable and safer driving experience.
10. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools for ESP Maintenance
Selecting the appropriate diagnostic tools is crucial for effectively maintaining and repairing ESP systems.
10.1. Understanding Diagnostic Tool Features
When choosing diagnostic tools, consider features such as:
- Error Code Reading: The ability to read and interpret error codes stored in the ECU.
- Live Data Streaming: The ability to monitor real-time data from sensors and other components.
- Component Testing: The ability to perform tests on individual components to verify their functionality.
- Software Updates: The ability to update the ECU software with the latest versions.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface that makes it easy to navigate and use the tool.
10.2. Recommended Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that are ideal for maintaining and repairing ESP systems. Some of our recommended tools include:
- Launch X431 V+: A comprehensive diagnostic tool that supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models, including Mercedes-Benz.
- Autel MaxiSys Elite: A powerful diagnostic tool with advanced features such as ECU programming and coding.
- Bosch ADS 625: A versatile diagnostic tool that is ideal for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
10.3. Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Diagnostic Tools
Using diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET offers numerous benefits:
- Accurate Diagnostics: Our tools provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information, helping you identify and address issues quickly and effectively.
- Time Savings: Our tools can save you time by quickly pinpointing the source of the problem, reducing the need for extensive troubleshooting.
- Cost Savings: By accurately diagnosing and repairing issues, our tools can help you avoid unnecessary repairs and save money.
- Improved Efficiency: Our tools can improve your efficiency by streamlining the diagnostic process and providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions.
Don’t wait for an ESP malfunction to compromise your safety. Invest in the right diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET and ensure your Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program is always in top condition. Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert advice and support. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
FAQ: Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program
1. What is Mercedes-Benz ESP?
Mercedes-Benz ESP (Electronic Stability Program) is a safety system that helps prevent skidding and loss of control by selectively applying braking force to individual wheels.
2. How does ESP work?
ESP monitors wheel speed, steering angle, and other factors to detect potential skidding. When a skid is detected, the system applies braking force to one or more wheels to help the driver maintain control.
3. What are the benefits of ESP?
ESP enhances safety, improves stability, increases driver confidence, reduces the risk of rollover, and optimizes braking performance.
4. When is ESP most effective?
ESP is most effective when driving on slippery surfaces, during emergency maneuvers, when cornering, on uneven road surfaces, and in high winds.
5. How do I know if my ESP is active?
Most Mercedes-Benz vehicles have an ESP indicator light on the dashboard that illuminates when the system is active. You may also feel the system working through subtle changes in the vehicle’s behavior.
6. What are common issues with ESP?
Common issues include sensor malfunctions, electrical problems, hydraulic issues, and software glitches.
7. How can I maintain my ESP system?
Maintain your ESP system by scheduling regular inspections, cleaning the sensors, checking the fluid levels, and keeping the software up to date.
8. When should I disable ESP?
You may disable ESP when driving in deep snow or sand, when participating in performance driving events, or for testing purposes.
9. What diagnostic tools are recommended for ESP maintenance?
Recommended diagnostic tools include Launch X431 V+, Autel MaxiSys Elite, and Bosch ADS 625, available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
10. How does ESP work with other safety systems?
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems such as ABS, TCS, EBD, and BA to provide comprehensive protection for drivers and passengers.
Do you need assistance diagnosing or repairing your Mercedes-Benz ESP system? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and support. Our team of experienced technicians can help you identify and address any issues, ensuring your vehicle is always safe and reliable. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. We’re here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely.