Mercedes ESP Malfunction Car Won’t Start: Expert Solutions
Mercedes ESP malfunction car won’t start issues can be incredibly frustrating, but CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide expert solutions. Addressing the root cause of an Electronic Stability Program (ESP) malfunction in your Mercedes is critical to getting your car back on the road quickly and safely. Let’s dive deep into diagnosing and resolving these issues, ensuring a smooth driving experience. We’ll explore common causes, diagnostic steps, and effective solutions to tackle this problem head-on.
1. Understanding the Mercedes ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz vehicles is a sophisticated system designed to enhance vehicle stability and prevent skidding. This system integrates various sensors and modules to monitor the vehicle’s direction and compare it with the driver’s intended path. When a discrepancy is detected, the ESP system intervenes by applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power to help the driver maintain control.
1.1 Key Components of the ESP System
The ESP system consists of several crucial components that work together to ensure optimal vehicle stability. These include:
-
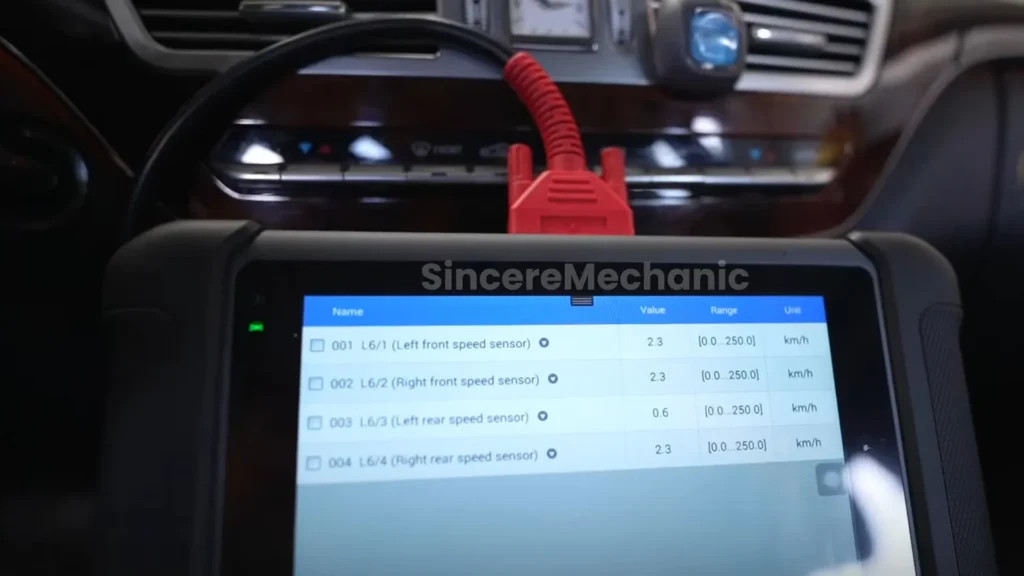
Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data to the ESP control unit to detect differences in wheel speeds that could indicate a skid.
-
Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing the ESP control unit with information about the driver’s intended direction.
-
Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, providing data to the ESP control unit to detect if the car is starting to spin or drift.
-
Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, providing data to the ESP control unit to detect if the car is sliding or drifting.
-
ESP Control Unit: This is the brain of the ESP system, processing data from all the sensors and initiating corrective actions when necessary.
-
Hydraulic Unit: This unit modulates the brake pressure to individual wheels as directed by the ESP control unit.
1.2 How ESP Works to Prevent Skidding
When the ESP system detects a potential skid, it uses a combination of braking and engine power adjustments to help the driver maintain control. Here’s how it works:
-
Detection: The sensors continuously monitor wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration. If these values deviate from expected parameters, the ESP control unit recognizes a potential skid.
-
Intervention: The ESP control unit calculates the necessary corrective actions and sends signals to the hydraulic unit and engine control unit.
-
Braking: The hydraulic unit applies brakes to individual wheels to create a counteracting force that helps steer the vehicle back on its intended path. For example, if the car is oversteering (rear wheels sliding out), the ESP might apply the brake to the outer front wheel to pull the car back into line.
-
Engine Power Adjustment: Simultaneously, the engine control unit reduces engine power to decrease acceleration and help regain control.
1.3 Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Enhanced Safety: By preventing skids and maintaining vehicle stability, ESP significantly reduces the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions or emergency maneuvers.
-
Improved Handling: ESP makes the vehicle more predictable and easier to control, particularly during sudden changes in direction or on slippery surfaces.
-
Increased Driver Confidence: Knowing that ESP is there to assist can boost driver confidence and reduce stress, especially for less experienced drivers.
-
Reduced Wear and Tear: By preventing loss of control situations, ESP can also reduce wear and tear on tires and other vehicle components.
2. Common Symptoms of an ESP Malfunction
When the ESP system malfunctions in a Mercedes-Benz, it can manifest in several noticeable symptoms. Recognizing these signs early can help you address the issue promptly and prevent further complications. Here are some common symptoms of an ESP malfunction:
2.1 ESP Warning Light On
The most obvious sign of an ESP malfunction is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light, often depicted as a car with squiggly lines underneath, indicates that the ESP system has detected a problem. The light may turn on intermittently or remain on continuously, depending on the nature and severity of the issue.
2.2 Reduced Engine Power
In some cases, an ESP malfunction can trigger the vehicle’s limp mode, which significantly reduces engine power. This is a safety mechanism designed to prevent further damage to the vehicle. If you experience a sudden loss of power and notice the ESP warning light, it could indicate a problem with the ESP system.
2.3 Difficulty Starting the Car
An ESP malfunction can sometimes interfere with the vehicle’s starting system, making it difficult or impossible to start the car. This can occur if the ESP system is sending incorrect signals to the engine control unit, preventing it from initiating the starting sequence.
2.4 Erratic Revving
Another symptom of an ESP malfunction is erratic engine revving. This can manifest as the engine revving up and down unpredictably, even when the vehicle is stationary. This issue can be caused by faulty sensor data or communication problems within the ESP system.
2.5 ABS Light Illumination
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and ESP are often interconnected, so an ESP malfunction can sometimes trigger the ABS warning light as well. If you see both the ESP and ABS lights illuminated simultaneously, it suggests a problem that affects both systems.
2.6 Steering Issues
In some cases, an ESP malfunction can affect the vehicle’s steering. This can manifest as stiff or unresponsive steering, making it difficult to turn the car. This issue is often related to problems with the steering angle sensor or the ESP control unit.
2.7 Brake Problems
An ESP malfunction can also cause issues with the vehicle’s braking system. This can include uneven braking, where the brakes apply more force to one side of the car than the other, or a general reduction in braking performance. These issues can be dangerous and should be addressed immediately.
Understanding these symptoms can help you quickly identify an ESP malfunction and seek appropriate solutions. Early detection and repair can prevent more serious damage and ensure your safety on the road.
3. Possible Causes of Mercedes ESP Malfunction Car Won’t Start
Identifying the root cause of a Mercedes ESP malfunction can be challenging, as various factors can trigger this issue. Here are some of the most common causes:
3.1 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are crucial for monitoring the rotational speed of each wheel. If one or more of these sensors fail, the ESP system may receive incorrect data, leading to a malfunction. These sensors can fail due to physical damage, corrosion, or electrical issues.
3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing essential data to the ESP control unit. If this sensor is faulty or miscalibrated, it can cause the ESP system to malfunction. Common issues include sensor failure, wiring problems, or incorrect calibration.
3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Problems
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. If this sensor fails, the ESP system may not be able to accurately detect if the car is starting to spin or drift, leading to a malfunction. Sensor failure or wiring issues are common causes.
3.4 Lateral Acceleration Sensor Failure
The lateral acceleration sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration. If this sensor fails, the ESP system may not be able to accurately detect if the car is sliding or drifting, causing a malfunction. Sensor failure or wiring problems are typical causes.
3.5 ESP Control Unit Malfunction
The ESP control unit is the brain of the ESP system. If this unit fails, it can disrupt the entire system, leading to a malfunction. Control unit failures can be caused by electrical issues, software problems, or physical damage.
3.6 Blown Fuses
Blown fuses can interrupt the power supply to the ESP system, causing it to malfunction. Checking the fuses related to the ESP system is a simple but important step in diagnosing the issue.
3.7 Wiring Problems
Wiring problems, such as damaged or corroded wires, can disrupt the communication between the various components of the ESP system. These issues can lead to intermittent or complete ESP malfunctions.
3.8 Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can cause various electrical issues in modern vehicles, including ESP malfunctions. Ensuring that the battery is in good condition and properly charged is essential for maintaining the proper functioning of the ESP system.
3.9 Faulty Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch signals the ESP system when the brakes are applied. If this switch is faulty, it can send incorrect signals, leading to an ESP malfunction. Replacing the brake light switch may resolve the issue.
3.10 Communication Issues with Other Modules
The ESP system communicates with other modules in the vehicle, such as the engine control unit (ECU) and the ABS system. If there are communication problems between these modules, it can cause the ESP system to malfunction.
3.11 Crank Position Sensor Failure
The crank position sensor is essential for engine timing and function. If it fails, the engine won’t start, and it can sometimes trigger ESP-related errors.
Understanding these potential causes can help you narrow down the source of the ESP malfunction and take appropriate steps to resolve the issue. If you’re unsure about the cause, it’s always best to consult with a qualified mechanic.
4. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing a Mercedes ESP malfunction requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you troubleshoot the issue:
4.1 Initial Inspection
-
Check the ESP Warning Light: Verify that the ESP warning light is illuminated on the dashboard. Note whether it is on continuously or intermittent.
-
Observe Other Symptoms: Pay attention to any other symptoms, such as reduced engine power, difficulty starting the car, erratic revving, or ABS light illumination.
-
Check the Fuses: Locate the fuse box and check the fuses related to the ESP system. Replace any blown fuses with new ones of the same amperage.
-
Inspect the Battery: Ensure the battery is in good condition and properly charged. Low battery voltage can cause various electrical issues, including ESP malfunctions.
4.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner
-
Connect the Scanner: Plug an OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port of your Mercedes-Benz.
-
Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Turn on the ignition and use the scanner to read any stored DTCs related to the ESP system. Common codes include:
- C1000 – Control unit N47-5 (Electronic Stability Program control unit)
- C1100 – Wheel speed sensor, front right : Plausibility
- C1120 – Steering angle sensor : Not initialized
-
Record the Codes: Write down all the DTCs for further analysis.
-
Clear the Codes: After recording the codes, clear them and see if they reappear after a test drive.
4.3 Checking Wheel Speed Sensors
-
Visual Inspection: Inspect each wheel speed sensor for physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each wheel speed sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Signal Test: Use an oscilloscope to check the signal output of each wheel speed sensor while the wheels are rotating. Look for any irregularities or dropouts in the signal.
4.4 Evaluating the Steering Angle Sensor
-
Visual Inspection: Check the steering angle sensor for any visible damage or loose connections.
-
Calibration Check: Use an OBD-II scanner to check the calibration of the steering angle sensor. If it is not properly calibrated, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to recalibrate it.
-
Signal Test: Use an oscilloscope to check the signal output of the steering angle sensor while turning the steering wheel. Look for any irregularities or dropouts in the signal.
4.5 Testing Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensors
-
Visual Inspection: Check the yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensors for any visible damage or loose connections.
-
Signal Test: Use an oscilloscope to check the signal output of these sensors while driving the car. Look for any irregularities or dropouts in the signal.
4.6 Inspecting Wiring and Connections
-
Visual Inspection: Inspect all the wiring and connections related to the ESP system for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring. Look for any breaks or shorts in the wiring.
4.7 Checking the Brake Light Switch
-
Functionality Test: Verify that the brake lights illuminate when the brake pedal is pressed. If they do not, the brake light switch may be faulty.
-
Signal Test: Use a multimeter to check the signal output of the brake light switch when the brake pedal is pressed. Look for any irregularities or dropouts in the signal.
4.8 ESP Control Unit Diagnosis
-
Visual Inspection: Check the ESP control unit for any visible damage or corrosion.
-
Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the voltage supply to the ESP control unit. Ensure that it is receiving the correct voltage.
-
Module Communication Test: Use a specialized diagnostic tool to perform a module communication test. This test can help identify any communication problems between the ESP control unit and other modules in the vehicle.
By following this step-by-step diagnostic process, you can systematically identify the cause of the ESP malfunction and take appropriate steps to resolve the issue. Remember to consult with a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any of the diagnostic steps.
5. Solutions to Fix Mercedes ESP Malfunction Car Won’t Start
Once you have identified the cause of the Mercedes ESP malfunction, you can take steps to fix the issue. Here are some common solutions:
5.1 Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a wheel speed sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced. Here’s how:
-
Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the faulty wheel speed sensor.
-
Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from the wheel hub. This may require removing a retaining bolt or clip.
-
Install the New Sensor: Install the new wheel speed sensor into the wheel hub and secure it with the retaining bolt or clip.
-
Connect the Sensor: Connect the electrical connector to the new wheel speed sensor.
-
Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.2 Recalibrating or Replacing the Steering Angle Sensor
If the steering angle sensor is miscalibrated or faulty, it may need to be recalibrated or replaced. Here’s how:
-
Recalibration: Use an OBD-II scanner to recalibrate the steering angle sensor. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the recalibration procedure.
-
Replacement: If recalibration does not resolve the issue, replace the steering angle sensor. Disconnect the electrical connector and remove the sensor from the steering column. Install the new sensor and connect the electrical connector.
-
Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.3 Replacing Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensors
If the yaw rate or lateral acceleration sensor is faulty, it should be replaced. Here’s how:
-
Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the faulty sensor.
-
Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location.
-
Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor into its mounting location and secure it with the retaining bolts or clips.
-
Connect the Sensor: Connect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
-
Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.4 Repairing or Replacing Damaged Wiring
If damaged or corroded wiring is causing the ESP malfunction, it should be repaired or replaced. Here’s how:
-
Identify the Damaged Wiring: Locate the damaged or corroded wiring.
-
Repair the Wiring: Repair the wiring by splicing in new sections of wire or using heat-shrink tubing to insulate damaged sections.
-
Replace the Wiring: If the wiring is too damaged to repair, replace it with new wiring of the same gauge and type.
-
Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.5 Replacing the Brake Light Switch
If the brake light switch is faulty, it should be replaced. Here’s how:
-
Disconnect the Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the faulty brake light switch.
-
Remove the Switch: Remove the switch from its mounting location. This may require twisting or unscrewing the switch.
-
Install the New Switch: Install the new brake light switch into its mounting location and secure it.
-
Connect the Switch: Connect the electrical connector to the new brake light switch.
-
Test the System: Verify that the brake lights illuminate when the brake pedal is pressed. Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.6 Replacing the ESP Control Unit
If the ESP control unit is faulty, it may need to be replaced. This is a more complex repair that may require specialized tools and knowledge. Here’s a general overview:
-
Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical damage.
-
Remove the Old Unit: Locate the ESP control unit and disconnect the electrical connectors. Remove the unit from its mounting location.
-
Install the New Unit: Install the new ESP control unit into its mounting location and connect the electrical connectors.
-
Program the Unit: The new ESP control unit may need to be programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications. This typically requires specialized diagnostic equipment and software.
-
Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5.7 Addressing Communication Issues
If there are communication issues between the ESP system and other modules in the vehicle, these issues need to be addressed. This may involve:
-
Checking Connections: Verify that all the connections between the ESP system and other modules are secure and free of corrosion.
-
Updating Software: Update the software of the ESP control unit and other modules to the latest versions.
-
Replacing Faulty Modules: If a module is found to be faulty, it may need to be replaced.
-
Testing the System: Use a specialized diagnostic tool to perform a module communication test and verify that the communication issues have been resolved.
By following these solutions, you can effectively fix a Mercedes ESP malfunction and restore the proper functioning of the system. If you are unsure about any of the repair steps, it is always best to consult with a qualified mechanic.
6. Preventing Future ESP Malfunctions
Preventing future ESP malfunctions involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Here are some tips to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz ESP system in optimal condition:
6.1 Regular Vehicle Maintenance
-
Follow the Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your Mercedes-Benz. This includes regular inspections and servicing of the braking system, electrical system, and other critical components.
-
Check Tire Condition: Ensure that your tires are in good condition and properly inflated. Uneven tire wear or low tire pressure can affect the performance of the ESP system.
-
Inspect Brake Components: Regularly inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear and damage. Replace any worn or damaged components promptly.
6.2 Battery Maintenance
-
Keep the Battery Charged: Ensure that your battery is properly charged and in good condition. Low battery voltage can cause various electrical issues, including ESP malfunctions.
-
Clean Battery Terminals: Clean the battery terminals regularly to remove any corrosion. Corrosion can interfere with the flow of electricity and cause electrical problems.
-
Test the Battery: Have the battery tested periodically to ensure that it is functioning properly. Replace the battery if it is weak or failing.
6.3 Proper Wiring Care
-
Inspect Wiring: Regularly inspect the wiring related to the ESP system for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Protect Wiring: Protect the wiring from damage by using wire looms or other protective coverings.
-
Repair Damage Promptly: Repair any damaged wiring promptly to prevent further electrical issues.
6.4 Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions
-
Drive Carefully: Avoid harsh driving conditions, such as excessive speeding, sudden braking, and aggressive turning. These conditions can put extra stress on the ESP system and increase the risk of malfunctions.
-
Adjust to Weather Conditions: Adjust your driving to the weather conditions. Drive slower and more cautiously in wet or icy conditions.
-
Avoid Potholes and Road Debris: Avoid driving through potholes and over road debris, as these can damage the wheel speed sensors and other components of the ESP system.
6.5 Regular Diagnostic Checks
-
Use an OBD-II Scanner: Use an OBD-II scanner to regularly check for any stored DTCs related to the ESP system. This can help you identify potential problems early on.
-
Professional Inspections: Have your Mercedes-Benz inspected by a qualified mechanic on a regular basis. They can perform a thorough inspection of the ESP system and identify any potential issues.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of ESP malfunctions and keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely. Regular maintenance and proactive care are essential for maintaining the proper functioning of the ESP system and ensuring your safety on the road.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ESP Issues
CARDIAGTECH.NET plays a vital role in helping you solve Mercedes ESP malfunction issues. We offer a range of high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment to help you accurately identify and address ESP problems. Our products are designed to meet the needs of both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
7.1 High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of having reliable diagnostic tools. That’s why we offer a wide selection of OBD-II scanners, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and other essential tools for diagnosing ESP malfunctions. Our tools are sourced from trusted manufacturers and are designed to provide accurate and reliable results.
7.2 Expert Technical Support
We don’t just sell tools; we also provide expert technical support to help you get the most out of our products. Our team of experienced technicians can answer your questions, provide troubleshooting assistance, and guide you through the diagnostic process. We are committed to helping you resolve your ESP issues quickly and efficiently.
7.3 Wide Range of Spare Parts
In addition to diagnostic tools, CARDIAGTECH.NET also offers a wide range of spare parts for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, and ESP control units. We source our spare parts from reputable suppliers and ensure that they meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
7.4 Comprehensive Training Resources
We believe that knowledge is power. That’s why we provide comprehensive training resources to help you learn more about the ESP system and how to diagnose and repair ESP malfunctions. Our training resources include articles, videos, and online courses that cover a wide range of topics related to ESP diagnostics and repair.
7.5 Customer-Focused Approach
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing excellent customer service. We strive to make your shopping experience as smooth and hassle-free as possible. We offer fast shipping, easy returns, and a dedicated customer support team to assist you with any questions or concerns.
By choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can be confident that you are getting the best tools, support, and resources to solve your Mercedes ESP malfunction issues. We are your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.
8. Case Studies: Resolving Mercedes ESP Malfunctions
To illustrate the diagnostic and repair processes, let’s examine a few case studies involving Mercedes ESP malfunctions:
8.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
-
Vehicle: 2010 Mercedes-Benz C300
-
Symptoms: ESP warning light on, ABS light on, reduced engine power
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Used an OBD-II scanner to read DTCs. The scanner revealed code C1100, indicating a problem with the front right wheel speed sensor.
- Inspected the front right wheel speed sensor for physical damage and loose connections.
- Used a multimeter to measure the resistance of the sensor. The reading was out of the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Solution: Replaced the front right wheel speed sensor. Cleared the DTCs and test-drove the vehicle. The ESP and ABS lights turned off, and the engine power was restored.
8.2 Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
-
Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz E350
-
Symptoms: ESP warning light on, stiff steering
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Used an OBD-II scanner to read DTCs. The scanner revealed code C1120, indicating a problem with the steering angle sensor.
- Checked the calibration of the steering angle sensor using the scanner. The sensor was miscalibrated.
-
Solution: Recalibrated the steering angle sensor using the OBD-II scanner, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Cleared the DTCs and test-drove the vehicle. The ESP warning light turned off, and the steering returned to normal.
8.3 Case Study 3: Damaged Wiring
-
Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz S550
-
Symptoms: Intermittent ESP warning light, erratic revving
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Used an OBD-II scanner to read DTCs. The scanner revealed multiple codes related to the ESP system.
- Inspected the wiring related to the ESP system for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Found a section of damaged wiring near the ESP control unit.
-
Solution: Repaired the damaged wiring by splicing in new sections of wire and using heat-shrink tubing to insulate the connections. Cleared the DTCs and test-drove the vehicle. The ESP warning light remained off, and the engine revving returned to normal.
8.4 Case Study 4: Faulty Brake Light Switch
-
Vehicle: 2008 Mercedes-Benz CLK350
-
Symptoms: ESP warning light on, difficulty starting the car
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Used an OBD-II scanner to read DTCs. The scanner revealed a code related to the brake light switch.
- Verified that the brake lights were not illuminating when the brake pedal was pressed.
- Tested the brake light switch with a multimeter. The switch was not functioning properly.
-
Solution: Replaced the brake light switch. Verified that the brake lights were now illuminating when the brake pedal was pressed. Cleared the DTCs and started the vehicle. The ESP warning light turned off, and the car started without issue.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of a systematic diagnostic approach and the use of reliable diagnostic tools in resolving Mercedes ESP malfunctions. With the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively diagnose and repair these issues and keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
9. Cost Considerations for ESP Repairs
When dealing with a Mercedes ESP malfunction, it’s important to consider the potential costs associated with diagnosis and repair. Here’s a breakdown of typical expenses:
9.1 Diagnostic Costs
- OBD-II Scan: $75 – $150 (Professional diagnostic scan to identify trouble codes)
- Sensor Testing: $50 – $100 per sensor (Testing individual sensors like wheel speed, steering angle, etc.)
- Wiring Inspection: $100 – $200 (Checking and diagnosing wiring issues)
9.2 Component Replacement Costs
| Component | Estimated Cost (Parts & Labor) |
|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensor | $150 – $300 |
| Steering Angle Sensor | $200 – $400 |
| Yaw Rate Sensor | $250 – $450 |
| Lateral Acceleration Sensor | $200 – $400 |
| Brake Light Switch | $100 – $200 |
| ESP Control Unit | $800 – $1500+ |
| Wiring Repair | $150 – $500+ |
9.3 Additional Costs
- Software Updates: $50 – $150 (Required for certain sensor or module replacements)
- Recalibration: $75 – $150 (Steering angle sensor, etc.)
- Towing: $100 – $300 (If the car is not drivable)
9.4 Factors Affecting Costs
- Vehicle Model and Year: Older or more complex models may have higher parts costs.
- Labor Rates: Vary by location and shop expertise.
- Extent of Damage: Complex electrical issues can significantly increase labor time.
- DIY vs. Professional Repair: DIY can save on labor but requires the right tools and knowledge.
Note: Prices are estimates and can vary. Always get a detailed quote from a trusted mechanic.
10. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs?
When it comes to solving Mercedes ESP malfunctions and maintaining your vehicle, choosing the right partner is crucial. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a unique combination of high-quality products, expert support, and comprehensive resources to meet all your automotive needs. Here’s why you should choose us:
10.1 Superior Quality Products
We are committed to providing only the highest quality diagnostic tools, spare parts, and equipment. Our products are sourced from trusted manufacturers and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet our strict standards of performance, reliability, and durability.
10.2 Expert Technical Assistance
Our team of experienced technicians is always ready to assist you with any questions or concerns. Whether you need help diagnosing an ESP malfunction, selecting the right tool, or troubleshooting a repair, we are here to provide expert guidance and support.
10.3 Comprehensive Solutions
We offer a comprehensive range of solutions to address all your automotive needs. From diagnostic tools and spare parts to training resources and technical support, we have everything you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
10.4 Competitive Pricing
We understand the importance of value for money. That’s why we offer competitive pricing on all our products and services. We strive to provide the best possible value without compromising on quality or performance.
10.5 Customer Satisfaction Guarantee
We are committed to ensuring your complete satisfaction. If you are not satisfied with our products or services for any reason, please contact us, and we will do everything we can to make it right.
10.6 Convenient Online Shopping Experience
Our user-friendly website makes it easy to find the products and resources you need. With detailed product descriptions, customer reviews, and secure online ordering, you can shop with confidence from the comfort of your own home.
10.7 Fast and Reliable Shipping
We offer fast and reliable shipping to ensure that you receive your order as quickly as possible. We partner with trusted shipping carriers to deliver your products safely and efficiently.
10.8 Commitment to Excellence
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are dedicated to excellence in everything we do. We are constantly striving to improve our products, services, and customer support to better meet your needs.
Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for your automotive needs and experience the difference that quality, expertise, and customer service can make. We are your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.
Is your Mercedes showing signs of ESP malfunction? Don’t wait until it leaves you stranded. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, and let our experts guide you to the best diagnostic tools and solutions. Visit our website, CARDIAGTECH.NET, for immediate assistance and take the first step towards ensuring your vehicle’s safety and reliability.
FAQ: Mercedes ESP Malfunction Car Won’t Start
1. What does ESP stand for in a Mercedes-Benz?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It’s a safety feature that helps prevent skidding and maintains vehicle stability.
2. What are the common symptoms of an ESP malfunction?
Common symptoms include the ESP warning light on the dashboard, reduced engine power, difficulty starting the car, erratic revving, and ABS light illumination.
3. Can a faulty wheel speed sensor cause an ESP malfunction?
Yes, faulty wheel speed sensors are a common cause of ESP malfunctions. They provide crucial data to the ESP system, and if they fail, the system may not function correctly.
4. How can I diagnose an ESP malfunction?
You can diagnose an ESP malfunction by using an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), inspecting wheel speed sensors, checking the steering angle sensor, and inspecting wiring and connections.
5. Can low battery voltage cause an ESP malfunction?
Yes, low battery voltage can cause various electrical issues in modern vehicles, including ESP malfunctions.
6. What tools do I need to diagnose and repair an ESP malfunction?
You will need an OBD-II scanner, multimeter, oscilloscope, and basic hand tools.
7. Can I fix an ESP malfunction myself, or do I need a professional mechanic?
Some simple issues, like replacing a blown fuse or recalibrating a sensor, can be done yourself. However, more complex repairs, such as replacing the ESP control unit, should be done by a professional mechanic.
8. How much does it cost to repair an ESP malfunction?
The cost of repair can vary depending on the cause and the parts needed. It can range from $100 for a simple fix like replacing a brake light switch to over $1500 for replacing the ESP control unit.
9. How can I prevent future ESP malfunctions?
You can prevent future ESP malfunctions by following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, ensuring the battery is in good condition, inspecting wiring regularly, and avoiding harsh driving conditions.
10. Why does my Mercedes ESP malfunction, and the car won’t start?
The ESP malfunction could be due to several reasons such as a faulty crank position sensor, steering angle sensor, or issues with the ESP module. These problems can sometimes prevent the car from starting as the engine management system relies on these sensors for proper operation. For accurate diagnosis and repair, it is recommended to consult with a qualified mechanic.