What is Mercedes ESP? Understanding Stability Program

The Electronic Stability Program, or ESP as it is commonly known, is a crucial safety system in modern vehicles, especially in Mercedes-Benz automobiles. Discover how ESP functions, its importance, and how it enhances vehicle safety with CARDIAGTECH.NET. By understanding how ESP integrates with other safety systems such as ABS and traction control, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for its role in preventing accidents and ensuring stable driving.
1. Decoding Mercedes ESP: An In-Depth Overview
Mercedes-Benz ESP (Electronic Stability Program) is an active safety system designed to prevent skidding and loss of control, especially during emergency maneuvers or on slippery surfaces. By understanding its components and operation, drivers can better appreciate how this technology enhances vehicle safety.
1.1. ESP System Components and Their Functions
The ESP system relies on several key components working in harmony:
- Sensors: These monitor various parameters such as wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate (the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis), and lateral acceleration.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): This processes the data from the sensors and determines if the vehicle is behaving as the driver intends.
- Hydraulic Unit: This modulates the braking force at individual wheels based on the ECU’s calculations.
- Brake System: The standard braking components are used to apply braking force as directed by the hydraulic unit.
1.2. How ESP Works to Prevent Skidding
ESP continuously compares the driver’s intended direction (based on steering wheel angle) with the vehicle’s actual direction. If a discrepancy is detected—indicating a potential skid—ESP intervenes by:
- Applying Brakes Individually: ESP can brake one or more wheels independently to generate a corrective force that helps steer the vehicle back on its intended path.
- Reducing Engine Torque: In some cases, ESP may also reduce engine power to prevent wheel spin and improve traction.
This intervention happens in milliseconds and is often imperceptible to the driver, making ESP a highly effective tool in preventing accidents.
 Mercedes ESP System Components
Mercedes ESP System Components
1.3. The Role of ESP in Improving Vehicle Safety
ESP significantly enhances vehicle safety by:
- Reducing Accidents: By preventing skids, ESP reduces the likelihood of losing control and colliding with obstacles or other vehicles.
- Enhancing Stability: ESP helps maintain stability during sudden maneuvers such as swerving to avoid an obstacle or braking on uneven surfaces.
- Improving Traction: By managing engine torque and braking force, ESP helps optimize traction on slippery surfaces, improving acceleration and handling.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
2. The Intricate Mechanics of Mercedes-Benz ESP
To fully appreciate the capabilities of Mercedes-Benz ESP, it’s essential to delve into the underlying technology and how it integrates with other vehicle systems. Let’s explore the mechanics, control algorithms, and the crucial sensors that make ESP a game-changer in vehicle safety.
2.1. Sensors That Drive ESP Functionality
ESP relies on a suite of sensors to gather real-time data about the vehicle’s dynamics:
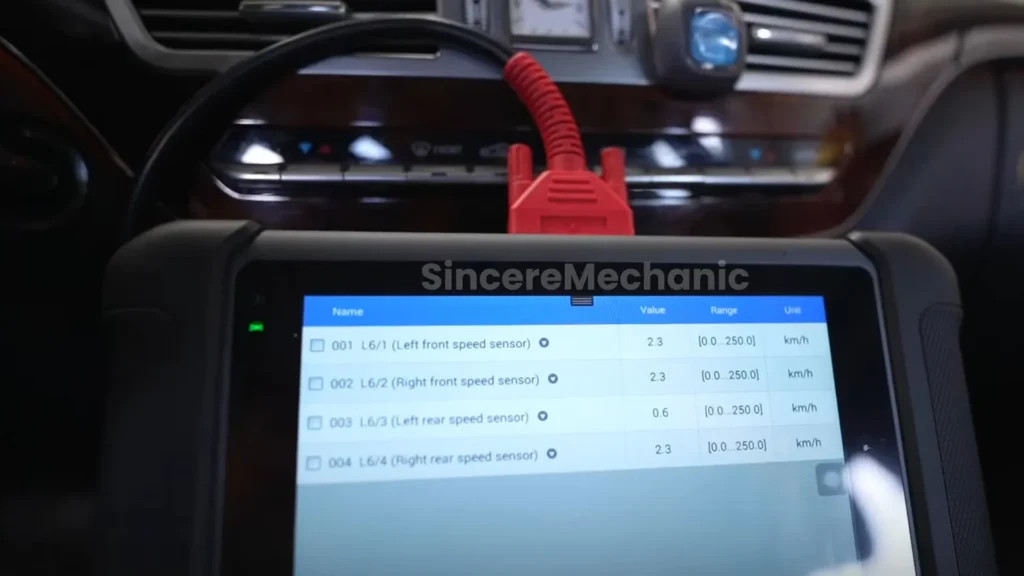
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These measure the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data to detect wheel slip or lockup.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, indicating whether the vehicle is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, indicating how much force is pushing the vehicle to the side.
- Brake Pressure Sensor: This measures the pressure in the brake lines, providing information about the driver’s braking input.
2.2. ESP Control Algorithms: How Decisions Are Made
The ECU uses complex control algorithms to process the sensor data and determine when and how to intervene. These algorithms take into account factors such as:
- Vehicle Speed: Adjusts the sensitivity of ESP based on how fast the vehicle is traveling.
- Road Conditions: Detects slippery surfaces based on wheel slip and adjusts ESP intervention accordingly.
- Driver Input: Considers the driver’s steering, acceleration, and braking inputs to determine their intended actions.
Based on this information, the ECU calculates the optimal braking force for each wheel to counteract skidding and maintain stability.
2.3. Integration with ABS, Traction Control, and Other Safety Systems
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems such as:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Prevents wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction on slippery surfaces.
- Brake Assist System (BAS): Detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to reduce stopping distance.
These systems share sensors and work together to provide comprehensive stability and control in various driving conditions.
By integrating these systems, Mercedes-Benz ensures a holistic approach to vehicle safety, providing drivers with the confidence and support they need to handle challenging driving situations.
3. Unraveling Common Mercedes ESP Issues: Symptoms and Causes
While Mercedes-Benz ESP is a robust system, it’s not immune to issues. Recognizing the symptoms of a malfunctioning ESP and understanding the potential causes can help drivers take timely action and prevent more serious problems. If you encounter issues and need assistance, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide expert advice and solutions.
3.1. Common Symptoms of a Faulty ESP System
Several symptoms may indicate an issue with the ESP system:
- ESP Warning Light: The ESP warning light on the dashboard illuminates, indicating that the system has detected a fault or has been deactivated.
- Reduced Stability: The vehicle feels less stable, especially during cornering or on slippery surfaces.
- Erratic Braking: The brakes may apply unevenly or unexpectedly, affecting the vehicle’s handling.
- Loss of Traction: The wheels may spin or lose traction more easily, especially during acceleration.
- ABS Malfunction: Since ESP and ABS are integrated, a fault in one system may affect the other.
3.2. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions
Several factors can cause ESP malfunctions:
- Sensor Issues: Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or yaw rate sensors can provide incorrect data to the ECU, leading to ESP malfunctions.
- ECU Problems: The ECU itself may develop faults due to electrical issues, software glitches, or physical damage.
- Hydraulic Unit Failures: The hydraulic unit may fail due to leaks, pump failures, or clogged valves.
- Brake System Issues: Problems with the brake pads, rotors, or calipers can affect ESP performance.
- Wheel Alignment: Incorrect wheel alignment can cause ESP to work harder and potentially trigger a fault.
- Low Battery Voltage: A weak or failing battery can cause electrical issues that affect the ESP system.
3.3. Diagnosing ESP Problems: A Step-by-Step Approach
Diagnosing ESP problems typically involves the following steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any obvious signs of damage or wear, such as damaged sensors or brake components.
- Diagnostic Scan: Use a diagnostic scanner to read fault codes from the ECU. These codes can provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Sensor Testing: Test the sensors using a multimeter or oscilloscope to verify that they are providing accurate data.
- Hydraulic Unit Testing: Check the hydraulic unit for leaks or other signs of damage.
- Brake System Inspection: Inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear or damage.
- Wheel Alignment Check: Verify that the wheels are properly aligned.
- Battery Voltage Test: Check the battery voltage to ensure it is within the specified range.
By following these steps, technicians can accurately diagnose ESP problems and recommend appropriate repairs.
4. Troubleshooting Your Mercedes ESP: Practical Solutions
Once an ESP issue has been identified, the next step is to implement effective solutions. Here are some practical troubleshooting steps and repairs for common ESP problems. When you need specialized tools or equipment for these tasks, remember that CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality solutions to support your repair needs.
4.1. Addressing Sensor-Related ESP Issues
Sensor problems are a common cause of ESP malfunctions. Here’s how to address them:
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Problem: Faulty wheel speed sensors can cause the ESP warning light to illuminate and affect ABS performance.
- Solution: Replace the faulty sensor. Use a diagnostic scanner to identify which sensor is malfunctioning. Ensure the new sensor is properly installed and calibrated.
- Steering Angle Sensor:
- Problem: A malfunctioning steering angle sensor can cause ESP to activate unnecessarily or fail to activate when needed.
- Solution: Recalibrate the steering angle sensor using a diagnostic scanner. If recalibration doesn’t resolve the issue, replace the sensor.
- Yaw Rate Sensor:
- Problem: A faulty yaw rate sensor can cause ESP to misinterpret the vehicle’s rotation, leading to incorrect interventions.
- Solution: Replace the yaw rate sensor. Ensure the new sensor is properly mounted and calibrated.
4.2. Repairing Hydraulic Unit Problems
The hydraulic unit is a critical component of the ESP system. Here’s how to address common issues:
- Leaks:
- Problem: Leaks in the hydraulic unit can reduce its effectiveness and cause the ESP warning light to illuminate.
- Solution: Repair or replace the hydraulic unit. Check all fittings and connections for tightness.
- Pump Failures:
- Problem: A failing pump can prevent the hydraulic unit from generating sufficient pressure, affecting ESP performance.
- Solution: Replace the hydraulic unit. Ensure the new unit is properly bled to remove any air from the system.
- Clogged Valves:
- Problem: Clogged valves can restrict the flow of brake fluid, affecting ESP’s ability to control individual wheels.
- Solution: Clean or replace the hydraulic unit. Use a brake fluid flush to remove any contaminants from the system.
4.3. Fixing Brake System Issues Affecting ESP
The brake system plays a crucial role in ESP performance. Here’s how to address common issues:
- Worn Brake Pads:
- Problem: Worn brake pads can reduce braking performance and affect ESP’s ability to control individual wheels.
- Solution: Replace the brake pads. Ensure the new pads are properly bedded in.
- Damaged Rotors:
- Problem: Damaged rotors can cause uneven braking and affect ESP performance.
- Solution: Replace the rotors. Ensure the new rotors are properly installed and torqued.
- Sticking Calipers:
- Problem: Sticking calipers can cause uneven braking and affect ESP’s ability to control individual wheels.
- Solution: Rebuild or replace the calipers. Ensure the new calipers are properly lubricated and functioning smoothly.
4.4. Recalibrating ESP After Repairs
After performing repairs on the ESP system, it’s essential to recalibrate the system to ensure proper operation. This typically involves using a diagnostic scanner to:
- Clear Fault Codes: Clear any fault codes that may have been stored in the ECU.
- Recalibrate Sensors: Recalibrate the steering angle sensor, yaw rate sensor, and other sensors as needed.
- Perform Road Test: Perform a road test to verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
By following these troubleshooting steps and repairs, you can effectively address common ESP problems and restore your Mercedes-Benz to optimal performance.
5. The Significance of ESP Warning Lights in Mercedes Vehicles
The ESP warning light is a critical indicator of your vehicle’s stability system status. Understanding what this light means and how to respond can help prevent accidents and ensure your safety on the road.
5.1. Interpreting Different ESP Warning Light Signals
The ESP warning light can illuminate in different ways, each indicating a specific situation:
- Solid Light: A solid ESP warning light typically indicates that the ESP system has detected a fault and is not functioning correctly. This could be due to a sensor problem, ECU issue, or hydraulic unit failure.
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP warning light indicates that the ESP system is actively intervening to prevent a skid. This is normal during emergency maneuvers or on slippery surfaces.
- ESP and ABS Lights Together: If both the ESP and ABS warning lights are illuminated, this typically indicates a more serious problem affecting both systems.
5.2. Immediate Actions to Take When the ESP Light Appears
When the ESP warning light appears, take the following actions:
- Stay Calm: Avoid sudden movements or braking.
- Reduce Speed: Slow down gradually and avoid abrupt changes in direction.
- Find a Safe Place to Stop: Pull over to a safe location as soon as possible.
- Turn Off and Restart the Vehicle: Sometimes, a simple restart can reset the ESP system and clear the warning light.
- Consult a Professional: If the warning light persists, consult a qualified technician to diagnose and repair the problem.
5.3. When to Seek Professional Assistance
It’s essential to seek professional assistance in the following situations:
- The ESP warning light remains on after restarting the vehicle.
- The ESP warning light is accompanied by other warning lights, such as the ABS light.
- You notice a significant decrease in vehicle stability or handling.
- You are unsure about the cause of the ESP warning light or how to address it.
6. Maximizing ESP Performance: Maintenance and Best Practices
To ensure that your Mercedes-Benz ESP system performs optimally, regular maintenance and adherence to best practices are essential.
6.1. Regular Maintenance Tips for ESP Systems
Follow these maintenance tips to keep your ESP system in top condition:
- Check Tire Pressure Regularly: Maintain proper tire pressure to ensure optimal traction and handling.
- Inspect Brake Components: Regularly inspect brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear or damage.
- Flush Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two years to remove contaminants and ensure proper hydraulic function.
- Inspect Sensors: Check wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors for damage or corrosion.
- Keep Wheels Aligned: Ensure that the wheels are properly aligned to prevent ESP from working harder than necessary.
6.2. Safe Driving Habits to Complement ESP
While ESP is a valuable safety feature, it’s not a substitute for safe driving habits. Follow these practices to complement ESP and enhance your safety on the road:
- Drive at Safe Speeds: Reduce your speed in adverse weather conditions or on unfamiliar roads.
- Avoid Distractions: Stay focused on the road and avoid distractions such as cell phones or eating.
- Maintain a Safe Following Distance: Allow plenty of space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you.
- Brake Smoothly: Avoid sudden braking, which can overwhelm the ESP system.
- Steer Gently: Avoid abrupt steering movements, which can cause the vehicle to lose control.
6.3. Seasonal Considerations for ESP Performance
ESP performance can be affected by seasonal changes in weather and road conditions. Here are some considerations for each season:
- Winter:
- Use winter tires for optimal traction on snow and ice.
- Reduce speed and increase following distance in snowy or icy conditions.
- Be extra cautious when driving on bridges or overpasses, which tend to freeze more quickly.
- Spring:
- Be aware of increased rainfall and potential hydroplaning.
- Check tire tread depth to ensure adequate traction.
- Adjust driving habits to account for slippery road surfaces.
- Summer:
- Monitor tire pressure, as it can increase in hot weather.
- Avoid driving aggressively, which can overheat the brakes.
- Be aware of potential hazards such as construction zones and increased traffic.
- Fall:
- Be aware of fallen leaves, which can create slippery road surfaces.
- Check tire pressure, as it can decrease in cooler weather.
- Adjust driving habits to account for changing weather conditions.
7. Mercedes ESP and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles often come equipped with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) that work in conjunction with ESP to provide even greater levels of safety and convenience.
7.1. How ESP Integrates with ADAS Features
ESP integrates with ADAS features such as:
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle in front.
- Lane Keeping Assist: Helps keep the vehicle centered in its lane by providing steering assistance.
- Blind Spot Monitoring: Alerts the driver to the presence of vehicles in their blind spots.
- Automatic Emergency Braking: Automatically applies the brakes to avoid or mitigate a collision.
These systems use sensors such as cameras, radar, and lidar to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and provide additional layers of safety.
7.2. The Synergistic Effect of ESP and ADAS
The combination of ESP and ADAS creates a synergistic effect, providing drivers with enhanced safety and convenience in a wide range of driving situations. For example, ESP can help prevent skidding during emergency maneuvers, while ADAS features can help avoid the need for such maneuvers in the first place.
7.3. Future Trends in ESP and ADAS Technology
The future of ESP and ADAS technology is likely to include:
- Increased Automation: More advanced systems that can handle a wider range of driving situations with minimal driver input.
- Improved Sensor Technology: Higher-resolution cameras, more accurate radar systems, and the integration of lidar technology.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Systems that can communicate with other vehicles and infrastructure to provide real-time information about road conditions and potential hazards.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered systems that can learn from experience and adapt to changing driving conditions.
8. Real-World Impact: Studies and Statistics on ESP Effectiveness
Numerous studies and statistics demonstrate the effectiveness of ESP in preventing accidents and saving lives.
8.1. Key Studies on ESP’s Role in Accident Prevention
Several key studies have highlighted the role of ESP in accident prevention:
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA): A study by NHTSA found that ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
- European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP): Euro NCAP has consistently recognized the safety benefits of ESP and has made it a requirement for achieving top safety ratings.
- Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS): IIHS studies have shown that ESP can significantly reduce the risk of rollovers and other types of accidents.
8.2. Statistical Evidence of ESP’s Impact on Road Safety
Statistical evidence supports the findings of these studies:
- Reduced Accident Rates: Vehicles equipped with ESP have lower accident rates compared to those without ESP.
- Fewer Fatalities: ESP has been shown to reduce the risk of fatal accidents, especially in single-vehicle crashes.
- Lower Insurance Claims: Vehicles with ESP tend to have lower insurance claims due to reduced accident rates.
8.3. ESP as a Standard Safety Feature: A Global Perspective
ESP has become a standard safety feature in many countries around the world. In the United States, ESP has been required on all new vehicles since 2012. In Europe, ESP has been mandatory since 2014. Many other countries have also adopted similar regulations.
9. Purchasing Considerations: ESP in Used Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
When purchasing a used Mercedes-Benz vehicle, it’s essential to consider the presence and condition of the ESP system.
9.1. Verifying ESP Presence and Functionality
Here’s how to verify ESP presence and functionality:
- Check the Vehicle’s Specifications: Review the vehicle’s specifications to confirm that it is equipped with ESP.
- Look for the ESP Button: Check for an ESP button on the dashboard, which allows the driver to disable or enable the system.
- Inspect the Dashboard Warning Lights: Turn on the ignition and observe the dashboard warning lights. The ESP light should illuminate briefly and then turn off.
- Perform a Test Drive: During a test drive, try to provoke ESP intervention by making sudden maneuvers or driving on a slippery surface.
9.2. Assessing the Condition of ESP Components
When assessing the condition of ESP components:
- Check for Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for any fault codes related to the ESP system.
- Inspect Sensors: Check wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors for damage or corrosion.
- Inspect Hydraulic Unit: Check the hydraulic unit for leaks or other signs of damage.
- Inspect Brake Components: Check brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear or damage.
9.3. Questions to Ask When Buying a Used Mercedes with ESP
Ask the seller the following questions when buying a used Mercedes with ESP:
- Has the ESP system ever been serviced or repaired?
- Are there any known issues with the ESP system?
- When was the brake fluid last flushed?
- Have the wheel speed sensors ever been replaced?
- Is the steering angle sensor properly calibrated?
10. Expert Insights on Mercedes ESP from CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of ESP in ensuring vehicle safety and performance. Here are some expert insights on Mercedes ESP:
10.1. Common Pitfalls to Avoid with ESP Systems
Avoid these common pitfalls with ESP systems:
- Ignoring Warning Lights: Don’t ignore ESP warning lights, as they indicate a potential problem.
- Neglecting Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to ESP malfunctions.
- Using Incorrect Parts: Using incorrect parts during repairs can compromise ESP performance.
- Failing to Recalibrate: Failing to recalibrate the ESP system after repairs can lead to incorrect operation.
10.2. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for ESP Issues
Advanced diagnostic techniques for ESP issues include:
- Using Oscilloscopes: Use oscilloscopes to analyze sensor signals and identify subtle problems.
- Performing Component-Level Testing: Perform component-level testing to isolate faults in the ECU or hydraulic unit.
- Using Factory Scan Tools: Use factory scan tools to access advanced diagnostic functions and recalibration procedures.
10.3. Tips for Maintaining Optimal ESP Performance
Follow these tips for maintaining optimal ESP performance:
- Use High-Quality Brake Fluid: Use high-quality brake fluid that meets Mercedes-Benz specifications.
- Replace Worn Components Promptly: Replace worn brake pads, rotors, and sensors promptly.
- Keep Tires Properly Inflated: Maintain proper tire pressure to ensure optimal traction and handling.
- Have the System Professionally Serviced: Have the ESP system professionally serviced at regular intervals.
By following these expert insights, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz ESP system provides reliable and effective protection in a wide range of driving situations. If you’re facing challenges in maintaining or diagnosing your ESP system, CARDIAGTECH.NET offers the tools and expertise you need. Contact us today to discover how we can assist you with your automotive diagnostic and repair needs.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Mercedes ESP
-
What does ESP stand for in Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
- ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program.
-
How does ESP work in a Mercedes-Benz?
- ESP uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s direction and intervenes by applying brakes to individual wheels to prevent skidding.
-
What are the main components of the ESP system in a Mercedes-Benz?
- The main components include wheel speed sensors, a steering angle sensor, a yaw rate sensor, an electronic control unit (ECU), and a hydraulic unit.
-
What does it mean when the ESP warning light comes on in my Mercedes?
- It indicates that the ESP system has detected a fault or has been deactivated.
-
Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz if the ESP warning light is on?
- It is generally safe to drive, but you should have the system checked by a professional as soon as possible.
-
How often should I have the ESP system checked in my Mercedes-Benz?
- It should be checked during routine maintenance, typically every 12 months or 10,000 miles.
-
What are some common issues that can cause the ESP light to come on in a Mercedes-Benz?
- Common issues include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor problems, or issues with the hydraulic unit.
-
Is ESP the same as traction control in a Mercedes-Benz?
- No, but they work together. ESP helps prevent skidding, while traction control prevents wheel spin during acceleration.
-
How does ESP contribute to overall vehicle safety in a Mercedes-Benz?
- ESP enhances vehicle safety by preventing skidding, improving stability, and optimizing traction, reducing the risk of accidents.
-
Can I disable the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz?
- Yes, but it is generally recommended to keep it enabled for maximum safety. It should only be disabled in specific situations, such as when trying to free a stuck vehicle.
Remember, for all your diagnostic and repair tool needs, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely with our top-quality equipment.