What Is an ESP Malfunction On a Mercedes?
The ESP malfunction on a Mercedes-Benz can be a concerning issue, but CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide clarity and solutions. It’s essential to address the issue promptly to ensure your safety. The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) malfunction indicates a problem with your vehicle’s stability control system, impacting safety and handling. Explore potential causes, troubleshooting steps, and when to seek expert help. You’ll gain insights into maintaining optimal vehicle performance. This article will cover Mercedes-Benz ESP repairs, Electronic Stability Program diagnostics, and ABS sensor issues.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety feature in modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It’s designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. Understanding how ESP works is the first step in addressing malfunctions.
1.1. What is ESP?
ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is an active safety system that enhances vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction. The Bosch company invented ESP, and Mercedes-Benz was the first to introduce it. It uses sensors to monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and vehicle yaw rate. When ESP detects a deviation from the intended path, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels. This helps steer the vehicle back on course.
ESP integrates with other safety systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and traction control to provide comprehensive stability management. ESP is particularly useful in slippery conditions, such as rain, snow, or ice. It can also help prevent accidents during sudden maneuvers.
1.2. Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several key components that work together to ensure optimal performance:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel to detect variations.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel to determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle.
- ESP Control Unit: Processes data from all sensors and determines the necessary corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Modulator: Applies braking force to individual wheels as needed.
These components communicate in real-time. They allow the ESP system to respond quickly to changing driving conditions. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to prevent ESP malfunctions.
1.3. How ESP Works to Prevent Accidents
ESP enhances vehicle stability by continuously monitoring driving conditions. It intervenes when it detects a potential loss of control. The system uses data from various sensors to determine if the vehicle is moving in the driver’s intended direction. If a discrepancy is detected, ESP activates to correct the vehicle’s path.
For example, if the driver steers to avoid an obstacle, but the vehicle begins to skid, ESP will apply brakes to individual wheels. This creates a counteracting force. It helps the driver maintain control. ESP can reduce engine power to further stabilize the vehicle. This proactive intervention helps prevent accidents and ensures a safer driving experience.
An illustration of a Mercedes-Benz ESP warning light, indicating the system’s status and potential malfunctions.
2. Identifying an ESP Malfunction
Recognizing the signs of an ESP malfunction is critical for maintaining vehicle safety. Early detection allows for timely repairs. It prevents more serious issues.
2.1. Common Symptoms of an ESP Malfunction
Several symptoms can indicate an ESP malfunction in your Mercedes-Benz:
- ESP Warning Light: The ESP warning light on the dashboard illuminates. It indicates an issue with the system. The light may be solid or flashing. It depends on the nature of the problem.
- Reduced Traction: Noticeable loss of traction, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Difficulty Steering: Stiff or unresponsive steering, making it hard to control the vehicle.
- ABS Issues: Problems with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), as ESP and ABS are often integrated.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding or clicking noises when braking or turning.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage. It ensures your safety on the road. CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with the right tools and expertise for diagnostics.
2.2. Interpreting the ESP Warning Light
The ESP warning light on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard is a key indicator of the system’s status. When the light illuminates, it signals a potential problem. Understanding the different states of the light can help you diagnose the issue:
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP light indicates that the system is actively working to maintain stability. This usually occurs when driving on slippery surfaces.
- Solid Light: A solid ESP light suggests that the system is disabled or malfunctioning. This could be due to a sensor failure, a wiring issue, or a problem with the ESP control unit.
- Light Stays On: If the ESP light remains on after starting the vehicle, it signifies a persistent issue that needs attention.
Consult your vehicle’s manual for specific details on the ESP warning light. Schedule a diagnostic check at a trusted service center.
2.3. Distinguishing ESP Malfunctions from Other Vehicle Issues
It’s important to differentiate ESP malfunctions from other common vehicle problems. This ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate repairs. ESP issues often manifest as stability and traction control problems. It can be similar to issues caused by faulty tires or worn suspension components.
However, ESP malfunctions typically trigger the ESP warning light. It may also affect ABS performance. In contrast, tire or suspension issues may cause vibrations, uneven wear, or handling problems without activating the ESP light. Accurate diagnosis requires professional equipment. Technicians at CARDIAGTECH.NET can provide this equipment.
| Symptom | ESP Malfunction | Other Vehicle Issues |
|---|---|---|
| ESP Warning Light | Solid or flashing | Off |
| Traction Control | Reduced or absent | Normal, but may be affected by tire condition |
| ABS Performance | Affected, may not function properly | Normal |
| Steering | Stiff or unresponsive | Normal, unless suspension is compromised |
| Unusual Noises | Grinding or clicking during braking or turning | May vary depending on the issue |
| Diagnostic Trouble Codes | Related to ESP system | Related to other systems |
3. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions
Understanding the common causes of ESP malfunctions can help you prevent issues. It can also inform the diagnostic process.
3.1. Sensor Failures
Sensor failures are a frequent cause of ESP malfunctions. The ESP system relies on input from various sensors. It monitors wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration. If one or more of these sensors fail, the ESP system may not function correctly.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors can become contaminated with debris. This leads to inaccurate readings.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor can drift out of calibration or become damaged due to wear and tear.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor is susceptible to damage from impacts or electrical issues.
Regular inspection and replacement of faulty sensors are essential. This ensures the ESP system operates as intended. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools to identify sensor failures accurately.
3.2. Wiring and Electrical Issues
Wiring and electrical problems can disrupt the communication between ESP components. It leads to malfunctions. Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can cause intermittent or complete ESP failure.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can corrode wiring connectors. It disrupts electrical signals.
- Damage: Physical damage to wiring harnesses can occur due to accidents or maintenance work.
- Loose Connections: Vibrations and normal wear can loosen electrical connections. It leads to signal loss.
Thorough inspection of wiring harnesses and connectors is crucial. Repairing or replacing damaged wiring can restore ESP functionality. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality electrical repair tools and components. This helps you address these issues effectively.
3.3. Hydraulic Unit Problems
The hydraulic unit is a critical component of the ESP system. It applies braking force to individual wheels as needed. Problems with the hydraulic unit can significantly impair ESP performance.
- Pump Failure: The hydraulic pump can fail due to wear and tear. It prevents the system from generating sufficient pressure.
- Valve Issues: Valves within the hydraulic unit can become clogged or damaged. It disrupts the flow of brake fluid.
- Fluid Leaks: Leaks in the hydraulic unit can reduce system pressure. It compromises its effectiveness.
Regular maintenance, including fluid flushes and inspections, can help prevent hydraulic unit problems. If issues arise, professional repair or replacement of the hydraulic unit may be necessary. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers diagnostic tools and replacement parts. This helps you address hydraulic unit problems efficiently.
3.4. Control Module Malfunctions
The ESP control module processes data from sensors and determines the necessary corrective actions. Malfunctions in the control module can disrupt the entire ESP system.
- Software Glitches: Software errors or corruption can cause the control module to malfunction.
- Hardware Failures: Internal components within the control module can fail due to age or electrical stress.
- Communication Issues: The control module may lose communication with other vehicle systems. It leads to ESP failure.
Software updates or reprogramming can sometimes resolve control module issues. In other cases, replacement of the control module may be necessary. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides access to advanced diagnostic tools and programming equipment. This helps you address control module malfunctions effectively.
A visual representation of a Mercedes-Benz dashboard featuring the ESP system, used to maintain control in emergency situations.
4. Diagnosing ESP Malfunctions
Accurate diagnosis is essential for resolving ESP malfunctions efficiently. A systematic approach helps identify the root cause of the problem.
4.1. Using Diagnostic Scan Tools
Diagnostic scan tools are invaluable for diagnosing ESP malfunctions. These tools can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. The DTCs provide information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Reading DTCs: Connect the scan tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and retrieve any stored DTCs related to the ESP system.
- Interpreting Codes: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable database to interpret the DTCs. Each code corresponds to a specific issue.
- Clearing Codes: After addressing the problem, use the scan tool to clear the DTCs and reset the ESP system.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic scan tools. This ensures you have the right equipment for accurate ESP diagnostics.
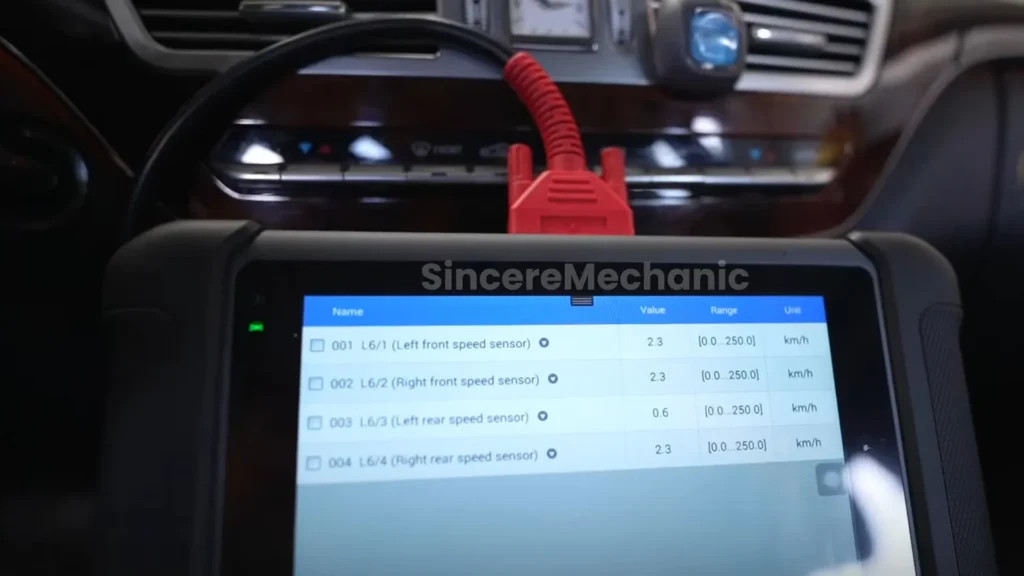
4.2. Checking Sensor Data
Analyzing sensor data is a critical step in diagnosing ESP malfunctions. Live data streams from the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor can reveal anomalies.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Compare the readings from each wheel speed sensor. Look for discrepancies that indicate a faulty sensor.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Verify that the steering angle sensor is providing accurate readings. Check the steering wheel position.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Ensure that the yaw rate sensor is detecting the vehicle’s rotation correctly. Compare with other sensors.
Using a diagnostic scan tool to monitor sensor data in real-time can help identify subtle issues. This may not trigger a DTC. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced scan tools with data streaming capabilities. This simplifies the diagnostic process.
4.3. Testing Wiring and Connections
Thoroughly testing wiring and connections is essential for identifying electrical issues that can cause ESP malfunctions. Use a multimeter to check for continuity, voltage, and resistance in the ESP system’s wiring.
- Continuity Testing: Ensure that there are no breaks in the wiring.
- Voltage Testing: Verify that the correct voltage is reaching each component.
- Resistance Testing: Check for excessive resistance in the wiring. This indicates corrosion or damage.
Inspect connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Clean or replace any faulty wiring or connectors. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of electrical testing tools and components. This helps you perform comprehensive wiring checks.
4.4. Verifying Hydraulic Unit Functionality
Verifying the functionality of the hydraulic unit is crucial for diagnosing ESP malfunctions related to braking performance. Use a diagnostic scan tool to activate the hydraulic unit’s components. It monitors their response.
- Pump Activation: Activate the hydraulic pump and check for proper pressure buildup.
- Valve Testing: Test the individual valves to ensure they are opening and closing correctly.
- Leak Inspection: Inspect the hydraulic unit for any signs of fluid leaks.
If the hydraulic unit is not functioning correctly, repair or replacement may be necessary. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides diagnostic tools and replacement parts. This helps you address hydraulic unit problems effectively.
5. Repairing ESP Malfunctions
Repairing ESP malfunctions requires a systematic approach. It addresses the root cause of the problem. Following best practices ensures the ESP system is restored to proper working condition.
5.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
Replacing faulty sensors is a common repair for ESP malfunctions. Use a diagnostic scan tool to identify the specific sensor that is causing the problem.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector and remove the faulty sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor. Ensure it is properly seated and secured.
- Connect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Verify Functionality: Use a diagnostic scan tool to verify that the new sensor is providing accurate readings.
- Clear DTCs: Clear any stored DTCs related to the replaced sensor.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality replacement sensors. This ensures the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.2. Repairing Wiring and Connections
Repairing damaged wiring and connections is essential for resolving electrical issues. These issues can cause ESP malfunctions.
- Inspect Wiring: Thoroughly inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear.
- Repair Damaged Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring by splicing in new sections or replacing the entire wiring harness.
- Clean Connectors: Clean corroded connectors with a wire brush or contact cleaner.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all electrical connections are tight and secure.
- Test Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the repaired wiring.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a variety of electrical repair tools and components. This helps you address wiring and connection issues effectively.
5.3. Servicing the Hydraulic Unit
Servicing the hydraulic unit may involve cleaning, repairing, or replacing components. It depends on the nature of the problem.
- Clean the Unit: Clean the hydraulic unit to remove dirt and debris.
- Replace Components: Replace faulty valves, seals, or the hydraulic pump.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the hydraulic unit for any signs of fluid leaks. Repair as needed.
- Flush the System: Flush the hydraulic system to remove contaminants.
- Test Functionality: Verify that the hydraulic unit is functioning correctly. Use a diagnostic scan tool.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of hydraulic system tools and replacement parts. This helps you maintain and repair the ESP hydraulic unit.
5.4. Reprogramming the Control Module
Reprogramming the control module may be necessary to resolve software glitches or compatibility issues.
- Connect Diagnostic Tool: Connect a diagnostic scan tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access Reprogramming Function: Access the reprogramming function within the scan tool’s software.
- Download Updates: Download the latest software updates or firmware from the vehicle manufacturer’s website.
- Reprogram the Module: Follow the scan tool’s instructions to reprogram the control module.
- Verify Functionality: Verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly after reprogramming.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools and programming equipment. This helps you reprogram ESP control modules effectively.
6. Preventing Future ESP Malfunctions
Preventing future ESP malfunctions involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Following these best practices ensures the ESP system remains in optimal condition.
6.1. Regular Maintenance Checks
Regular maintenance checks are crucial for preventing ESP malfunctions. These checks should include:
- Sensor Inspections: Inspect wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors for damage or contamination.
- Wiring Inspections: Inspect wiring harnesses and connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Hydraulic Unit Inspections: Inspect the hydraulic unit for leaks and proper functionality.
- Fluid Level Checks: Check and maintain proper brake fluid levels.
- Diagnostic Scans: Perform regular diagnostic scans to identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Incorporating these checks into your routine maintenance schedule can help prevent ESP malfunctions.
6.2. Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is essential for ESP system performance. Uneven tire wear or incorrect tire pressures can affect the system’s ability to maintain stability.
- Tire Pressure: Maintain proper tire pressures as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Tire Rotation: Rotate tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Tire Condition: Replace worn or damaged tires promptly.
- Alignment: Ensure proper wheel alignment to prevent uneven tire wear.
Following these tire maintenance practices can help prevent ESP malfunctions. It ensures the system operates effectively.
6.3. Driving Habits to Protect ESP
Driving habits can significantly impact the ESP system’s performance. Avoid aggressive driving maneuvers that can stress the system.
- Smooth Driving: Drive smoothly. Avoid sudden acceleration, braking, and steering inputs.
- Avoid Slippery Surfaces: Be cautious when driving on slippery surfaces. Reduce speed to minimize the risk of skidding.
- Proper Braking: Use proper braking techniques. Avoid locking the wheels during emergency stops.
- Load Management: Avoid overloading the vehicle. This can affect stability and ESP performance.
Adopting these driving habits can help protect the ESP system. It ensures its long-term reliability.
6.4. Importance of Professional Inspections
Professional inspections are essential for maintaining the ESP system. Certified technicians can identify and address potential issues. This may not be apparent during routine maintenance checks.
- Expert Diagnostics: Professional technicians have the expertise and equipment to diagnose ESP malfunctions accurately.
- Comprehensive Checks: They can perform comprehensive checks. This includes sensor testing, wiring inspections, and hydraulic unit evaluations.
- Preventive Maintenance: Technicians can recommend preventive maintenance measures. This ensures the ESP system remains in optimal condition.
Scheduling regular professional inspections can help prevent ESP malfunctions. It ensures your vehicle’s safety systems are functioning correctly.
7. Choosing the Right Tools for ESP Repairs
Selecting the right tools is crucial for effective ESP repairs. High-quality diagnostic and repair tools ensure accurate and efficient service.
7.1. Essential Diagnostic Tools
Essential diagnostic tools for ESP repairs include:
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A high-quality scan tool is essential for reading DTCs, monitoring sensor data, and reprogramming control modules.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is necessary for testing wiring continuity, voltage, and resistance.
- ABS Tester: An ABS tester can help diagnose issues with the Anti-lock Braking System, which is often integrated with ESP.
- Hydraulic Pressure Gauge: A hydraulic pressure gauge can measure the pressure within the ESP hydraulic unit.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope can analyze electrical signals to identify intermittent issues.
Investing in these essential diagnostic tools ensures you can accurately diagnose ESP malfunctions.
7.2. Recommended Repair Equipment
Recommended repair equipment for ESP repairs includes:
- Wiring Repair Kit: A wiring repair kit includes various tools and components for repairing damaged wiring.
- Sensor Socket Set: A sensor socket set includes specialized sockets for removing and installing sensors.
- Hydraulic Line Wrench Set: A hydraulic line wrench set includes wrenches designed for working on hydraulic lines.
- Brake Bleeder Kit: A brake bleeder kit simplifies the process of bleeding the brakes after hydraulic repairs.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is essential for tightening bolts and nuts to the correct specifications.
Having the right repair equipment ensures you can perform ESP repairs safely and efficiently.
7.3. Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts
Sourcing quality replacement parts is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of ESP repairs.
- OEM Parts: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are made by the vehicle manufacturer. They guarantee a perfect fit and optimal performance.
- Aftermarket Parts: Aftermarket parts are made by third-party manufacturers. Choose reputable brands known for quality and reliability.
- Reputable Suppliers: Purchase replacement parts from reputable suppliers. This ensures you are getting genuine and high-quality components.
- Warranty: Look for parts with a warranty. This protects you against defects and premature failure.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality replacement parts for ESP repairs. This ensures your repairs are reliable and long-lasting.
7.4. CARDIAGTECH.NET Solutions for ESP Repairs
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides comprehensive solutions for ESP repairs, including:
- Diagnostic Scan Tools: Access to a wide range of advanced diagnostic scan tools for accurate ESP diagnostics.
- Repair Equipment: High-quality repair equipment for performing ESP repairs safely and efficiently.
- Replacement Parts: Sourcing of quality replacement parts, including OEM and reputable aftermarket brands.
- Technical Support: Expert technical support to assist with diagnostic and repair procedures.
- Training Programs: Training programs to enhance your knowledge and skills in ESP diagnostics and repairs.
With CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can confidently tackle ESP repairs. You’ll also ensure optimal vehicle safety and performance. Contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or call +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information.
8. Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting the ESP System
Resetting the ESP system may be necessary after performing repairs. It clears diagnostic trouble codes. It also restores the system to normal operation.
8.1. When to Reset the ESP System
You may need to reset the ESP system in the following situations:
- After Replacing Sensors: When you replace faulty sensors, resetting the ESP system ensures the new sensors are properly recognized.
- After Repairing Wiring: Repairing damaged wiring requires a reset. This clears any stored DTCs.
- After Servicing the Hydraulic Unit: Servicing the hydraulic unit, a reset ensures the system operates correctly.
- After Reprogramming the Control Module: Reprogramming the control module, a reset is necessary to activate the new software.
- False Alarms: Sometimes, the ESP system may trigger false alarms due to temporary issues. A reset can clear these alarms.
Resetting the ESP system should be part of your routine maintenance. It should also be done after repairs.
8.2. Step-by-Step Reset Procedure
Follow these steps to reset the ESP system:
- Turn Off the Ignition: Turn off the vehicle’s ignition and remove the key.
- Locate the ESP Button: Locate the ESP button on the dashboard or center console.
- Press and Hold the ESP Button: Press and hold the ESP button for approximately five to ten seconds.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition on without starting the engine.
- Wait for the ESP Light: Wait for the ESP warning light to illuminate and then turn off.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and check if the ESP warning light remains off.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly.
If the ESP warning light remains on after the reset procedure, there may be an underlying issue. Further diagnostics and repairs may be necessary.
8.3. Using Diagnostic Tools for Resetting
Using diagnostic tools for resetting the ESP system provides a more precise and reliable method.
- Connect the Scan Tool: Connect a diagnostic scan tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access the ESP System: Access the ESP system within the scan tool’s software.
- Select Reset Function: Select the reset or clear codes function.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the scan tool’s instructions to reset the ESP system.
- Verify the Reset: Verify that the ESP system has been successfully reset by checking for any stored DTCs.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly.
Using a diagnostic scan tool ensures a complete and accurate reset.
8.4. Common Issues During Reset and Troubleshooting
Common issues during the ESP system reset process include:
- Incomplete Reset: The ESP warning light may remain on after the reset procedure. This indicates that the reset was incomplete.
- DTCs Reappearing: Diagnostic trouble codes may reappear after the reset. This suggests that the underlying issue has not been resolved.
- Scan Tool Compatibility: Some scan tools may not be compatible with certain vehicle models or ESP systems.
- Software Glitches: Software glitches in the scan tool can cause errors during the reset procedure.
To troubleshoot these issues:
- Verify Connections: Ensure that all connections are secure. This applies to both the scan tool and the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Update Scan Tool Software: Update the scan tool’s software to the latest version. This ensures compatibility and resolves known issues.
- Check for Underlying Issues: Address any underlying issues. This causes the ESP malfunction before attempting to reset the system.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unable to resolve the issues, consult a professional technician for assistance.
9. The Role of ABS in ESP Malfunctions
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) plays a significant role in ESP malfunctions. The two systems are often integrated. Problems with ABS can affect ESP performance.
9.1. How ABS and ESP Interact
ABS and ESP are closely related safety systems. They work together to enhance vehicle stability and control. ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking. ESP uses ABS to apply braking force to individual wheels. This helps steer the vehicle back on course.
When ABS detects that one or more wheels are about to lock up, it modulates the braking pressure. It allows the wheels to maintain traction. ESP uses this same technology to selectively apply brakes to individual wheels. This creates a counteracting force. It helps the driver maintain control.
9.2. Common ABS Issues Affecting ESP
Common ABS issues that can affect ESP performance include:
- Sensor Failures: Faulty wheel speed sensors can disrupt both ABS and ESP. They provide inaccurate data to the control units.
- Hydraulic Unit Problems: Problems with the ABS hydraulic unit can impair its ability to modulate braking pressure. This affects ESP’s ability to control individual wheel braking.
- Wiring Issues: Electrical issues, such as damaged or corroded wiring, can disrupt communication between the ABS and ESP systems.
- Control Module Malfunctions: Malfunctions in the ABS control module can affect its ability to communicate with the ESP control module.
Addressing these ABS issues is essential for restoring proper ESP functionality.
9.3. Diagnosing ABS-Related ESP Problems
Diagnosing ABS-related ESP problems involves:
- Reading DTCs: Use a diagnostic scan tool to read DTCs from both the ABS and ESP systems.
- Checking Sensor Data: Monitor live data from the wheel speed sensors to ensure they are providing accurate readings.
- Testing Hydraulic Unit: Test the ABS hydraulic unit. This ensures it is functioning correctly.
- Inspecting Wiring: Inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Consulting Service Manuals: Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and troubleshooting tips.
Accurate diagnosis is essential. It is necessary to address ABS-related ESP problems. This ensures the safety systems are working as intended.
9.4. Repairing ABS to Restore ESP Functionality
Repairing ABS to restore ESP functionality involves:
- Replacing Faulty Sensors: Replace any faulty wheel speed sensors to ensure accurate data.
- Repairing Wiring: Repair damaged or corroded wiring to restore communication.
- Servicing Hydraulic Unit: Service the ABS hydraulic unit to ensure proper pressure modulation.
- Reprogramming Control Module: Reprogram the ABS control module if necessary.
- Clearing DTCs: Clear any stored DTCs related to the ABS and ESP systems after repairs.
Addressing ABS issues promptly can help prevent ESP malfunctions. It ensures the vehicle’s safety systems are functioning correctly.
10. ESP Malfunction and Vehicle Safety
ESP malfunction can significantly impact vehicle safety. Understanding the risks and taking appropriate action is essential.
10.1. Risks of Driving with an ESP Malfunction
Driving with an ESP malfunction can increase the risk of accidents. This is especially true in challenging driving conditions.
- Loss of Stability: The vehicle may become less stable, especially on slippery surfaces. This makes it harder to control.
- Reduced Traction: Traction control may be reduced or absent. It increases the risk of skidding.
- Difficulty Steering: Steering may become stiff or unresponsive. This makes it difficult to avoid obstacles.
- Increased Stopping Distance: Stopping distances may increase due to impaired braking performance.
It’s important to address ESP malfunctions. It is necessary to ensure your safety on the road.
10.2. How ESP Enhances Safety in Various Conditions
ESP enhances safety in various driving conditions:
- Slippery Surfaces: On snow, ice, or rain, ESP helps maintain traction. It prevents skidding.
- Emergency Maneuvers: During sudden steering or braking, ESP helps stabilize the vehicle. It avoids loss of control.
- Cornering: When cornering, ESP helps maintain stability. It prevents oversteering or understeering.
- Uneven Road Surfaces: On uneven surfaces, ESP helps maintain contact with the road. It improves stability.
ESP’s ability to enhance stability and control makes it a crucial safety feature.
10.3. Real-Life Examples of ESP Preventing Accidents
Real-life examples of ESP preventing accidents include:
- Avoiding Skidding on Ice: ESP detects a loss of traction. It applies brakes to individual wheels. This prevents the vehicle from skidding on icy roads.
- Correcting Oversteering: When a vehicle begins to oversteer, ESP applies brakes to the outer wheels. This helps steer the vehicle back on course.
- Maintaining Control During Emergency Braking: ESP prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking. It allows the driver to maintain steering control.
- Stabilizing During Sudden Lane Changes: ESP detects a sudden lane change. It applies brakes to individual wheels. This helps stabilize the vehicle and prevent a rollover.
These examples illustrate the effectiveness of ESP. It helps prevent accidents.
10.4. Seeking Professional Help for ESP Issues
Seeking professional help for ESP issues is essential. This ensures accurate diagnosis and effective repairs.
- Expert Diagnostics: Certified technicians have the expertise and equipment to diagnose ESP malfunctions accurately.
- Proper Repairs: They can perform proper repairs. This restores the ESP system to optimal working condition.
- Safety Assurance: Professional repairs ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly. This enhances your safety on the road.
- Warranty Protection: Professional repairs may come with a warranty. This protects you against defects and premature failure.
Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or call +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. We can connect you with the tools and expertise. This helps you address ESP malfunctions effectively.
11. Advanced ESP Technologies in Modern Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles feature advanced ESP technologies. These technologies enhance safety and driving performance.
11.1. Adaptive ESP Systems
Adaptive ESP systems adjust their parameters based on driving conditions. They provide optimal stability control.
- Speed-Sensitive ESP: Adjusts its intervention based on vehicle speed.
- Load-Adaptive ESP: Adjusts its parameters based on the vehicle’s load.
- Road Surface Detection: Detects the type of road surface. It optimizes ESP performance accordingly.
Adaptive ESP systems provide enhanced stability. They improve control in various driving scenarios.
11.2. Integration with Driver Assistance Systems
ESP integrates with other driver assistance systems. This includes adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assist, and blind-spot monitoring.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: ESP works with adaptive cruise control. This maintains a safe following distance.
- Lane Keeping Assist: ESP helps keep the vehicle within its lane. It reduces the risk of unintentional lane departures.
- Blind-Spot Monitoring: ESP can intervene. It prevents lane changes. This occurs if a vehicle is detected in the blind spot.
This integration enhances overall safety. It provides a more seamless driving experience.
11.3. Predictive ESP Functions
Predictive ESP functions anticipate potential loss of control. They take proactive measures to prevent accidents.
- Pre-Safe Brake: Detects an impending collision. It pre-charges the brakes for maximum stopping power.
- Evasive Steering Assist: Provides steering support during emergency maneuvers. This helps the driver avoid obstacles.
- Crosswind Assist: Detects strong crosswinds. It applies brakes to individual wheels. This helps maintain stability.
Predictive ESP functions provide an extra layer of safety. They reduce the risk of accidents.
11.4. Future Trends in ESP Technology
Future trends in ESP technology include:
- Artificial Intelligence: Using AI to analyze driving patterns and predict potential loss of control.
- Enhanced Sensor Technology: Developing more accurate and reliable sensors. This improves ESP performance.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Providing over-the-air software updates. This improves ESP functionality.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: Enhancing cybersecurity measures. This protects the ESP system.
These advancements will further enhance vehicle safety and driving performance.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ESP Malfunctions
Here are some frequently asked questions about ESP malfunctions:
1. What does an ESP malfunction mean on a Mercedes-Benz?
An ESP malfunction indicates a problem with the Electronic Stability Program. It can affect the vehicle’s stability and traction control.
2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP light on?
It’s not recommended. Driving with the ESP light on means the system is not functioning. This compromises your safety.
3. How do I reset the ESP light on my Mercedes-Benz?
You can try resetting it. Turn off the ignition, then turn it back on. Press and hold the ESP button for a few seconds.
4. What are the common causes of ESP malfunctions?
Common causes include faulty sensors, wiring issues, hydraulic unit problems, and control module malfunctions.
5. How much does it cost to repair an ESP malfunction?
The cost varies. It depends on the cause. Sensor replacements are less expensive than hydraulic unit repairs.
6. Is the ABS system related to the ESP system?
Yes, they’re often integrated. Problems with ABS can affect ESP performance.
7. Can I diagnose ESP malfunctions myself?
You can. Use a diagnostic scan tool. However, professional help ensures accurate diagnosis and repairs.
8. What tools do I need to repair ESP malfunctions?
Essential tools include a diagnostic scan tool, multimeter, wiring repair kit, and sensor socket set.
9. How can I prevent ESP malfunctions?
Regular maintenance checks, proper tire maintenance, and smooth driving habits can help prevent ESP malfunctions.
10. Where can I source quality replacement parts for ESP repairs?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality replacement parts for ESP repairs.
Conclusion
Understanding what an ESP malfunction means on a Mercedes, identifying its causes, and knowing how to address it are crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner. We provide diagnostic tools, repair equipment, and quality replacement parts.
Remember, addressing