What Is ESP On Mercedes Benz: A Comprehensive Guide
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) on Mercedes-Benz vehicles is a critical safety system. This system enhances vehicle control and prevents skidding, working in tandem with other safety features to provide a secure driving experience. Learn how ESP functions, its benefits, and why it’s an essential feature for Mercedes-Benz owners, ensuring you stay safe on the road with advanced vehicle dynamics technology.
1. Understanding Electronic Stability Program (ESP) on Mercedes-Benz
Electronic Stability Program (ESP), also known as electronic stability control (ESC), is a cornerstone of modern automotive safety, particularly in vehicles like the Mercedes-Benz. It’s designed to prevent skidding and loss of control, especially in adverse driving conditions. ESP achieves this by continuously monitoring the vehicle’s direction and comparing it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, such as the vehicle beginning to skid, ESP intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This action creates a corrective force that helps steer the vehicle back onto its intended course. ESP integrates with other safety systems, like anti-lock braking system (ABS) and traction control system (TCS), ensuring a comprehensive approach to vehicle safety. This synergy enhances stability and control, providing drivers with added confidence and safety on the road. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESC systems like ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
1.1 The Genesis of ESP: A Mercedes-Benz Innovation
Mercedes-Benz, in collaboration with Bosch, pioneered the development of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), introducing it in 1995. This innovation marked a significant leap in automotive safety technology. The core idea behind ESP was to create a system that could automatically intervene to prevent skidding and loss of control, thereby enhancing overall vehicle safety. By continuously monitoring the vehicle’s dynamics and comparing them to the driver’s intended path, ESP could detect the onset of a skid and take corrective action. The introduction of ESP by Mercedes-Benz set a new standard in the automotive industry. Its effectiveness in preventing accidents led to its widespread adoption across various vehicle manufacturers. ESP is now recognized as a vital safety feature in modern cars.
1.2 Essential Components of the ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) on a Mercedes-Benz is a complex system composed of several key components that work together to maintain vehicle stability. These components include:
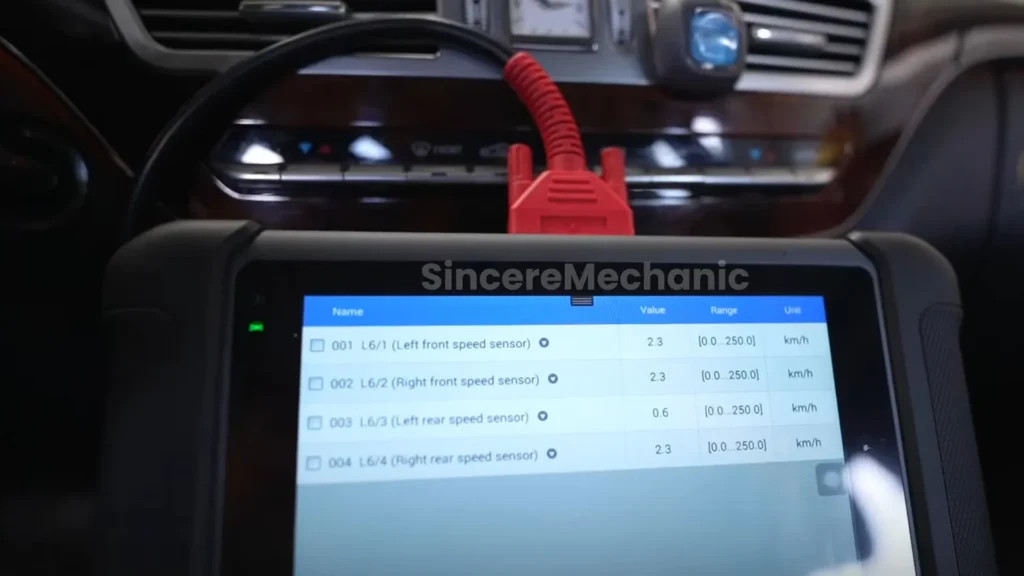
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel individually. This data helps the ESP system determine if one or more wheels are losing traction.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel. It provides information about the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. It detects if the vehicle is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the sideways acceleration of the vehicle. It helps the ESP system understand the vehicle’s movement in relation to its intended path.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU is the brain of the ESP system. It receives data from all the sensors, analyzes it, and then determines if corrective action is needed.
- Hydraulic Modulator: This component applies the brakes to individual wheels as directed by the ECU. It allows the ESP system to selectively brake wheels to correct a skid.
1.3 How ESP Intervenes: A Step-by-Step Process
When the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) detects a potential loss of control, it follows a specific process to intervene and stabilize the vehicle. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Detection of Instability: The ESP system uses its array of sensors to continuously monitor the vehicle’s behavior. If the sensors detect a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual movement, such as a skid or slide, the ESP system is activated.
- Data Analysis by the ECU: Once a potential loss of control is detected, the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) analyzes the data from the sensors. The ECU determines the severity of the situation and the appropriate course of action.
- Selective Braking: Based on the analysis, the ESP system selectively applies the brakes to individual wheels. For example, if the vehicle is oversteering (rear end sliding out), the ESP might apply the brake to the outer front wheel to create a counteracting force.
- Torque Adjustment: In addition to braking, the ESP system can also adjust engine torque to further stabilize the vehicle. This might involve reducing engine power to help regain traction and control.
- Restoring Control: Through a combination of selective braking and torque adjustment, the ESP system helps steer the vehicle back onto its intended path. It prevents the vehicle from skidding or spinning out of control.
- Continuous Monitoring: The ESP system continues to monitor the vehicle’s behavior and make adjustments as needed until the vehicle is back under control.
1.4 Identifying ESP Malfunctions: Warning Signs to Watch For
Recognizing the signs of an ESP malfunction is crucial for maintaining your Mercedes-Benz’s safety. The most common indicator is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light typically resembles a car skidding and serves as a general alert for stability control issues. Other potential symptoms include reduced engine power, erratic braking, or the ESP system engaging unnecessarily, even under normal driving conditions. Unusual noises during turns or when braking could also indicate a problem with the ESP system. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician at CARDIAGTECH.NET as soon as possible. Addressing ESP malfunctions promptly ensures your safety and maintains the integrity of your vehicle’s safety systems. For reliable diagnostic tools and expert advice, contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
2. Key Benefits of Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) offers several significant advantages, enhancing safety, improving handling, and providing greater driver confidence. ESP is designed to mitigate skidding, thereby preventing accidents, especially in challenging driving conditions. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP helps maintain vehicle stability, particularly when cornering, making the car feel more secure on the road. ESP reduces both understeer and oversteer, two common types of skidding, by intervening to keep the vehicle under control. These benefits make ESP an indispensable safety feature in modern vehicles, providing drivers with enhanced control and stability in various driving scenarios. With ESP, drivers can navigate challenging conditions with greater assurance.
2.1 Preventing Skidding: A Primary Safety Advantage
The primary safety advantage of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is its ability to prevent skidding. Skidding can occur when a vehicle loses traction, often due to slippery surfaces, sudden maneuvers, or adverse weather conditions. ESP mitigates this risk by continuously monitoring the vehicle’s direction and comparing it to the driver’s intended path. If ESP detects that the vehicle is starting to skid, it intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This action helps the vehicle regain traction and return to the intended path. By preventing skidding, ESP significantly reduces the risk of accidents, especially in challenging driving conditions. This proactive intervention can be life-saving, making ESP an essential safety feature in modern vehicles.
2.2 Enhanced Vehicle Stability: Cornering and Beyond
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) enhances vehicle stability in various driving situations, most notably when cornering. When a vehicle enters a corner, there is a shift in weight distribution, which can cause the vehicle to become unstable. ESP actively counteracts this instability by monitoring the vehicle’s dynamics and intervening as needed. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP helps maintain traction and control. This ensures that the vehicle remains stable and follows the driver’s intended path. The enhanced stability provided by ESP inspires greater driver confidence, especially when navigating winding roads or making quick maneuvers.
2.3 Reducing Understeer and Oversteer: Maintaining Control
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) effectively reduces understeer and oversteer, two common types of skidding. Understeer occurs when the front wheels lose traction, causing the vehicle to go straight ahead instead of turning. Oversteer happens when the rear wheels lose traction, leading the vehicle to spin out. ESP addresses these issues by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This helps to correct the vehicle’s path and maintain control.
- Understeer: ESP applies the brake to the inside rear wheel. This action helps to pull the front of the car back into the turn.
- Oversteer: ESP applies the brake to the outside front wheel. This counteracts the spin and helps the driver regain control.
3. Mercedes-Benz Models Equipped with ESP
Since the early 2000s, the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) has been a standard feature on most Mercedes-Benz models, reflecting the brand’s commitment to safety. This includes a wide range of vehicles, from sedans to SUVs, ensuring that drivers across the lineup benefit from this crucial safety technology. Popular models equipped with ESP include the C-Class, E-Class, S-Class, GLC, GLE, and many others. ESP is integrated into these vehicles to provide enhanced stability and control, helping to prevent accidents in various driving conditions. Mercedes-Benz continues to prioritize safety by including ESP as a standard feature, ensuring that drivers can navigate the roads with confidence.
3.1 Sedans with Enhanced Stability: The ESP Advantage
Mercedes-Benz sedans are known for their luxury, performance, and advanced safety features, including the Electronic Stability Program (ESP). Models like the C-Class, E-Class, and S-Class come standard with ESP. This enhances stability and control. The ESP system in these sedans works seamlessly with other safety technologies, such as anti-lock brakes and traction control, to provide a comprehensive safety net for drivers and passengers. Whether navigating city streets or cruising on the highway, ESP helps maintain vehicle stability, especially in challenging conditions. This ensures a smooth and secure driving experience in every Mercedes-Benz sedan.
3.2 SUVs Designed for Safety: ESP as Standard
Mercedes-Benz SUVs prioritize safety and performance, with the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) as a standard feature across the lineup. Models such as the GLC, GLE, and GLS are equipped with ESP to enhance stability and control, especially in diverse driving conditions. The ESP system in these SUVs works in conjunction with other advanced safety technologies, such as adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist, to provide a comprehensive safety net for drivers and passengers. Whether navigating urban environments or tackling off-road adventures, ESP helps maintain vehicle stability. It ensures a secure and confident driving experience in every Mercedes-Benz SUV.
3.3 Coupes and Convertibles: Performance with Added Security
Mercedes-Benz coupes and convertibles combine performance with advanced safety features, including the Electronic Stability Program (ESP). Models like the C-Class Coupe, E-Class Coupe, and SL Roadster come standard with ESP. This enhances stability and control, even during dynamic driving maneuvers. The ESP system in these vehicles works in tandem with other safety technologies, such as brake assist and collision prevention assist, to provide a comprehensive safety net for drivers. Whether enjoying a spirited drive on winding roads or cruising with the top down, ESP helps maintain vehicle stability. It ensures a secure and exhilarating driving experience in every Mercedes-Benz coupe and convertible.
4. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Maintaining your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is crucial for ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. Regular inspections and timely maintenance are essential to keep the system functioning optimally. Addressing warning signs promptly can prevent potential issues and maintain the effectiveness of the ESP system. By following these maintenance tips, you can ensure your Mercedes-Benz ESP system continues to provide the stability and control you need for a safe driving experience. For expert diagnostics and maintenance tools, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
4.1 Regular Inspections: Catching Issues Early
Regular inspections are essential for maintaining the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz. These inspections help catch potential issues early, preventing them from escalating into more significant problems. During a routine check, a qualified technician will assess the ESP system’s components. This includes sensors, control units, and hydraulic modulators, to ensure they are functioning correctly. The technician will also check for any error codes or warning signs that could indicate a problem with the ESP system. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent ESP malfunctions. This ensures your vehicle maintains optimal stability and control.
4.2 Addressing Warning Signs: Prompt Action for Safety
Addressing warning signs promptly is crucial for maintaining the safety and effectiveness of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. The ESP warning light on the dashboard is the primary indicator of a potential issue. If this light illuminates, it signals that the ESP system has detected a problem and may not be functioning correctly. Other warning signs may include unusual noises during turns, erratic braking, or a noticeable decrease in vehicle stability. When any of these symptoms occur, it’s essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible. Ignoring these warning signs can compromise the ESP system’s ability to prevent skidding. This increases the risk of accidents, particularly in challenging driving conditions.
4.3 Professional Maintenance: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Professional maintenance is key to ensuring the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz performs optimally. Qualified technicians have the expertise and equipment to diagnose and address any issues with the ESP system accurately. During a professional maintenance service, technicians will conduct thorough inspections, perform necessary repairs, and ensure that all components of the ESP system are functioning correctly. They can also update the ESP system’s software to the latest version, ensuring it operates with maximum efficiency and effectiveness. By entrusting your Mercedes-Benz ESP system to professional maintenance, you can have peace of mind knowing that your vehicle is equipped with a reliable and well-maintained safety feature. For top-quality diagnostic tools and professional assistance, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
5. The Future of ESP: Technological Advancements
The future of Electronic Stability Program (ESP) technology is poised for significant advancements. These improvements will enhance vehicle safety and driving dynamics even further. One key area of development is the integration of more sophisticated sensors. These sensors will provide more detailed and accurate data about the vehicle’s surroundings. This data enables the ESP system to react more quickly and effectively to changing road conditions. Another advancement is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies allow the ESP system to learn from past driving experiences and adapt its responses accordingly. This results in a more personalized and optimized driving experience. Additionally, ESP systems are becoming more integrated with other vehicle systems. This includes adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and autonomous emergency braking. This integration creates a comprehensive safety net for drivers, providing enhanced protection in a wide range of driving scenarios.
5.1 Enhanced Sensors: Precision in Monitoring
Enhanced sensors are a key component in the future of Electronic Stability Program (ESP) technology. These advanced sensors provide more precise and detailed information about the vehicle’s surroundings. This enables the ESP system to react more quickly and effectively to changing road conditions. Some of the specific enhancements in sensor technology include:
- Higher Resolution: Sensors with higher resolution provide more detailed data about the road surface, tire grip, and vehicle dynamics. This allows the ESP system to make more accurate decisions.
- Wider Field of View: Sensors with a wider field of view can monitor a larger area around the vehicle. This helps the ESP system anticipate potential hazards and react proactively.
- Improved Accuracy: Advanced sensors are more accurate and reliable, reducing the risk of false positives and ensuring that the ESP system only intervenes when necessary.
- Integration with Other Sensors: ESP systems are increasingly integrated with other sensors in the vehicle. This includes radar, lidar, and cameras. This integration provides a more comprehensive view of the vehicle’s surroundings.
5.2 AI and Machine Learning: Adaptive Control Systems
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing Electronic Stability Program (ESP) technology. These technologies enable ESP systems to learn from past driving experiences. They also adapt their responses to provide a more personalized and optimized driving experience. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and predict potential hazards. This allows the ESP system to react proactively, preventing skidding and loss of control before they occur. Machine learning algorithms can also optimize the ESP system’s parameters based on individual driving styles. This ensures that the system is tailored to the specific needs of each driver. The integration of AI and machine learning represents a significant step forward in ESP technology. This makes driving safer and more enjoyable.
5.3 Integration with Other Safety Systems: A Holistic Approach
Integration with other safety systems represents a holistic approach to enhancing vehicle safety. By combining ESP with technologies like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and autonomous emergency braking, a comprehensive safety net is created. This integration allows these systems to work together seamlessly, providing enhanced protection in a wide range of driving scenarios. For example, if the adaptive cruise control system detects a sudden slowdown in traffic, it can communicate with the ESP system to ensure that the vehicle remains stable during emergency braking. Similarly, the lane-keeping assist system can work with the ESP system to prevent the vehicle from drifting out of its lane. This collaboration helps to prevent accidents. It also minimizes the severity of collisions when they do occur. The integration of ESP with other safety systems represents a significant advancement in automotive safety technology. This makes driving safer and more secure.
6. The Importance of ESP in Adverse Weather Conditions
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is particularly important in adverse weather conditions. These include rain, snow, ice, and strong winds. These conditions can significantly reduce traction and make it more difficult to control a vehicle. ESP helps to mitigate these risks by monitoring the vehicle’s dynamics and intervening as needed to prevent skidding and loss of control. In rainy conditions, ESP can help maintain traction on slippery surfaces. It selectively applies brakes to individual wheels. In snowy or icy conditions, ESP can prevent wheel spin and help the vehicle maintain its intended path. In windy conditions, ESP can counteract the effects of crosswinds. This helps to keep the vehicle stable and prevent it from drifting out of its lane. The ability of ESP to enhance stability and control in adverse weather conditions makes it an essential safety feature for drivers.
6.1 ESP in Rainy Conditions: Maintaining Traction
In rainy conditions, the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) plays a crucial role in maintaining traction and preventing skidding. Rainwater reduces the friction between the tires and the road surface. This makes it easier for the vehicle to lose traction. ESP helps mitigate this risk by continuously monitoring the vehicle’s dynamics and intervening as needed. If the ESP system detects that the wheels are losing traction, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels. This helps to redistribute the vehicle’s weight and maintain grip. Additionally, ESP can reduce engine power to prevent wheel spin. This helps the vehicle maintain its intended path. By enhancing traction and preventing skidding, ESP significantly improves safety in rainy conditions.
6.2 ESP in Snowy and Icy Conditions: Preventing Wheel Spin
In snowy and icy conditions, the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is essential for preventing wheel spin and maintaining control. Snow and ice reduce traction. This makes it easy for the wheels to lose grip. ESP helps mitigate this risk by continuously monitoring the wheel speeds and intervening as needed. If the ESP system detects that one or more wheels are spinning without providing forward motion, it selectively applies brakes to those wheels. This helps to transfer power to the wheels with better traction. Additionally, ESP can reduce engine power to prevent excessive wheel spin. This helps the vehicle maintain its intended path. By preventing wheel spin and enhancing traction, ESP significantly improves safety in snowy and icy conditions.
6.3 ESP in Windy Conditions: Counteracting Crosswinds
In windy conditions, the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) helps to counteract the effects of crosswinds and maintain vehicle stability. Crosswinds can exert a sideways force on the vehicle. This makes it difficult to stay in the intended lane. ESP helps mitigate this risk by monitoring the vehicle’s direction and intervening as needed. If the ESP system detects that the vehicle is drifting due to crosswinds, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels. This creates a counteracting force that helps to keep the vehicle on course. Additionally, ESP can adjust the steering assist to make it easier for the driver to maintain control. By counteracting the effects of crosswinds, ESP significantly improves safety and stability in windy conditions.
7. ESP and Safe Driving Practices: A Combined Approach
While the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a valuable safety feature, it is not a substitute for safe driving practices. ESP is designed to assist drivers in maintaining control of their vehicles. It cannot overcome the laws of physics or compensate for reckless behavior. To maximize safety on the road, it is essential to combine the benefits of ESP with responsible driving habits. This includes:
- Maintaining a Safe Following Distance: This provides ample time to react to unexpected situations.
- Avoiding Sudden Maneuvers: Smooth and controlled movements reduce the risk of losing control.
- Adjusting Speed to Road Conditions: Slower speeds are necessary in adverse weather or when visibility is reduced.
- Staying Focused on the Road: Distractions can lead to errors and increase the risk of accidents.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Ensuring all safety systems, including ESP, are functioning correctly.
By adopting these safe driving practices, drivers can complement the benefits of ESP and significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
7.1 The Limits of ESP: Understanding Its Capabilities
Understanding the limits of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is crucial for responsible driving. While ESP enhances vehicle stability and control, it is not a substitute for safe driving practices. ESP can help prevent skidding and loss of control in many situations, it has limitations:
- ESP Cannot Overcome Physics: ESP relies on the laws of physics to function. If a vehicle is traveling too fast or making extreme maneuvers, ESP may not be able to prevent an accident.
- ESP is Not a Substitute for Good Tires: ESP relies on having adequate traction to function properly. Worn or improperly inflated tires can reduce traction. This limits the effectiveness of ESP.
- ESP Cannot Prevent All Accidents: ESP is designed to assist drivers in maintaining control of their vehicles. It cannot prevent all accidents. Driver error, road conditions, and other factors can still contribute to collisions.
- ESP Requires Driver Input: ESP relies on the driver to provide steering input and braking force. If the driver does not react appropriately, ESP may not be able to prevent a loss of control.
7.2 Promoting Safe Driving Habits: Complementing ESP
Promoting safe driving habits is essential for complementing the benefits of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP). While ESP can enhance vehicle stability and control, it is most effective when paired with responsible driving practices. Safe driving habits include:
- Maintaining a Safe Following Distance: This provides ample time to react to unexpected situations.
- Avoiding Sudden Maneuvers: Smooth and controlled movements reduce the risk of losing control.
- Adjusting Speed to Road Conditions: Slower speeds are necessary in adverse weather or when visibility is reduced.
- Staying Focused on the Road: Distractions can lead to errors and increase the risk of accidents.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Ensuring all safety systems, including ESP, are functioning correctly.
- Wearing Seatbelts: Seatbelts are essential for protecting drivers and passengers in the event of a collision.
- Avoiding Impaired Driving: Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs significantly increases the risk of accidents.
7.3 The Driver’s Role: Responsibility and Awareness
The driver’s role is paramount in ensuring safety on the road. While advanced safety systems like ESP can assist in maintaining control, ultimate responsibility lies with the driver. This includes being aware of the vehicle’s capabilities and limitations. This also means practicing safe driving habits. Drivers should:
- Stay Focused: Avoid distractions such as cell phones and other electronic devices.
- Be Alert: Pay attention to the road and surrounding traffic.
- Drive Defensively: Anticipate potential hazards and react accordingly.
- Obey Traffic Laws: Follow speed limits and other regulations.
- Maintain Their Vehicle: Ensure all safety systems are functioning correctly.
- Drive Sober: Avoid driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be Well-Rested: Avoid driving when fatigued.
8. Common Misconceptions About ESP
There are several common misconceptions about the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) that can lead to misunderstandings about its capabilities and limitations. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for promoting responsible driving and ensuring that drivers understand how to use ESP effectively. Some of the most common misconceptions include:
- ESP Makes a Vehicle Impossible to Skid: ESP can help prevent skidding. It cannot overcome the laws of physics. Extreme maneuvers or excessive speed can still lead to a loss of control.
- ESP Eliminates the Need for Winter Tires: ESP can enhance traction in snowy or icy conditions. It is not a substitute for winter tires. Winter tires provide superior grip and braking performance in cold weather.
- ESP Allows Drivers to Drive Recklessly: ESP is designed to assist drivers in maintaining control of their vehicles. It is not an invitation to drive recklessly.
- ESP is Always On and Cannot Be Turned Off: While ESP is typically enabled by default, some vehicles allow drivers to disable the system. In certain situations, such as driving in deep snow, disabling ESP may be beneficial.
- ESP is a Substitute for Driver Skill: ESP can help less experienced drivers maintain control. It does not replace the need for proper training and skill development.
8.1 ESP as a Substitute for Safe Driving: Debunking the Myth
One of the most common misconceptions about the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is that it is a substitute for safe driving practices. This is simply not true. While ESP can enhance vehicle stability and control, it is not a replacement for responsible driving habits. ESP is designed to assist drivers in maintaining control of their vehicles. It cannot compensate for reckless behavior. Drivers should continue to practice safe driving habits. This includes maintaining a safe following distance, avoiding sudden maneuvers, and adjusting speed to road conditions. ESP is a valuable safety feature. It is most effective when used in conjunction with safe driving practices.
8.2 ESP and Tire Conditions: The Importance of Proper Traction
Another common misconception about the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is that it eliminates the need for proper tire maintenance. ESP relies on having adequate traction to function properly. Worn or improperly inflated tires can reduce traction and limit the effectiveness of ESP. It is essential to maintain proper tire pressure and replace worn tires promptly. Winter tires provide superior grip and braking performance in cold weather. Using winter tires in snowy or icy conditions can significantly enhance the effectiveness of ESP. ESP and proper tire maintenance are complementary safety measures. They work together to provide optimal vehicle stability and control.
8.3 Overreliance on Technology: Maintaining Driver Awareness
Overreliance on technology is a growing concern in modern driving. Some drivers may become overly confident in advanced safety systems like ESP. This can lead to a decrease in driver awareness and an increased risk of accidents. It is important to remember that ESP is a tool to assist drivers. It is not a substitute for vigilance and attentiveness. Drivers should remain focused on the road and be prepared to react to unexpected situations. Maintaining driver awareness is crucial for safe driving. It is essential to avoid overreliance on technology.
9. Diagnosing ESP Issues: Common Problems and Solutions
Diagnosing ESP issues requires a systematic approach. It involves identifying common problems and implementing effective solutions. When the ESP system malfunctions, it can compromise vehicle stability and control. Common problems include sensor failures, hydraulic modulator issues, and electronic control unit (ECU) malfunctions. Solutions range from replacing faulty sensors to repairing or replacing the hydraulic modulator or ECU. For expert diagnostics and reliable repair solutions, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
9.1 Identifying Common ESP Problems: A Diagnostic Checklist
Identifying common ESP problems involves a thorough diagnostic checklist. This helps pinpoint the source of the malfunction. Begin by checking the ESP warning light on the dashboard. If it’s illuminated, there’s an issue. Use a diagnostic scan tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET to read error codes. This will provide valuable information about the specific problem. Common issues include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor malfunctions, or issues with the yaw rate sensor. Inspect the wiring and connections to these sensors. Look for damage or corrosion. Check the hydraulic modulator for leaks or damage. Also, verify the functionality of the ECU. By systematically checking these components, you can effectively identify the source of the ESP malfunction.
9.2 Troubleshooting Sensor Issues: Step-by-Step Guide
Troubleshooting sensor issues in the ESP system requires a step-by-step approach. First, use a diagnostic scan tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET to identify which sensor is causing the problem. Once you’ve identified the faulty sensor, inspect its wiring and connections. Look for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. If the wiring appears to be in good condition, test the sensor’s functionality using a multimeter. Compare the sensor’s readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the sensor is not functioning within the specified range, replace it with a new one. After replacing the sensor, clear the error codes using the diagnostic scan tool. Then, perform a test drive to ensure that the ESP system is functioning properly.
9.3 Resolving Hydraulic Modulator Problems: Expert Solutions
Resolving hydraulic modulator problems in the ESP system often requires expert solutions. The hydraulic modulator is a complex component. It controls the braking force applied to individual wheels. If it malfunctions, it can significantly compromise the ESP system’s effectiveness. Common problems with the hydraulic modulator include leaks, internal damage, or electrical issues. If you suspect a problem with the hydraulic modulator, it’s best to consult with a qualified technician. They can perform a thorough inspection and recommend the appropriate course of action. In some cases, the hydraulic modulator can be repaired. In other cases, it may need to be replaced. Ensure that any repairs or replacements are performed by a qualified technician using high-quality parts. For expert diagnostic tools and support, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
10. Purchasing Diagnostic Tools for ESP Maintenance
Purchasing diagnostic tools for ESP maintenance is a smart investment for vehicle owners and technicians. Diagnostic tools enable you to identify and address ESP issues quickly and accurately. This can save time and money on repairs. When selecting diagnostic tools, consider factors such as compatibility, functionality, and ease of use. High-quality diagnostic tools can provide valuable insights into the ESP system’s performance. This helps ensure that your vehicle remains safe and reliable. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic tools for ESP maintenance.
10.1 Selecting the Right Diagnostic Tool: Key Features to Consider
Selecting the right diagnostic tool for ESP maintenance requires careful consideration of several key features. Compatibility is paramount. Ensure that the tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Functionality is also important. Look for a tool that can perform a wide range of diagnostic tests. This includes reading error codes, accessing live data, and performing actuator tests. Ease of use is another key factor. Choose a tool that has an intuitive interface and is easy to navigate. Additional features to consider include software updates, customer support, and warranty. By carefully evaluating these key features, you can select the right diagnostic tool for your ESP maintenance needs. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a variety of diagnostic tools designed to meet these requirements.
10.2 Top Diagnostic Tools Available at CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of top-quality diagnostic tools for ESP maintenance. These tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable results. They help you diagnose and resolve ESP issues efficiently. Some of the top diagnostic tools available at CARDIAGTECH.NET include:
- Launch X431 V+: This advanced diagnostic tool offers comprehensive coverage for a wide range of vehicle makes and models. It features advanced diagnostic functions, including error code reading, live data streaming, and actuator testing.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: This versatile diagnostic tool provides advanced diagnostic capabilities. It also features wireless connectivity and a user-friendly interface. It supports a wide range of vehicle systems.
- Bosch ADS 625: This professional-grade diagnostic tool is designed for automotive technicians. It offers advanced diagnostic functions, including ECU programming and coding.
10.3 Investing in Quality: Long-Term Benefits and Savings
Investing in quality diagnostic tools for ESP maintenance offers significant long-term benefits and savings. High-quality tools provide accurate and reliable results. This helps you diagnose and resolve ESP issues quickly and efficiently. By identifying problems early, you can prevent them from escalating into more costly repairs. Quality diagnostic tools are also more durable and reliable. This means they will last longer and require less maintenance. Additionally, investing in quality tools can enhance your reputation as a skilled and knowledgeable technician. This can lead to increased business and customer satisfaction. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic tools. These help you achieve long-term benefits and savings in ESP maintenance. For more information, contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
FAQ: Electronic Stability Program (ESP) on Mercedes-Benz
Q1: What exactly is ESP on a Mercedes-Benz?
A1: ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is a safety system designed to prevent skidding and loss of control by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine torque.
Q2: How does ESP work in a Mercedes-Benz?
A2: ESP monitors the vehicle’s speed, steering angle, and yaw rate. If it detects a skid, it automatically applies brakes to individual wheels to help the vehicle regain control.
Q3: What are the key benefits of having ESP in my Mercedes-Benz?
A3: ESP helps prevent skidding, improves vehicle stability, reduces understeer and oversteer, and enhances overall safety in challenging driving conditions.
Q4: Is ESP a standard feature on all Mercedes-Benz models?
A4: Since the early 2000s, ESP has been a standard feature on most Mercedes-Benz models, including sedans, SUVs, coupes, and convertibles.
Q5: How can I tell if the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz is malfunctioning?
A5: The most common sign is the ESP warning light on the dashboard. Other symptoms include reduced engine power, erratic braking, or the ESP system engaging unnecessarily.
Q6: Can I turn off ESP in my Mercedes-Benz?
A6: While ESP is typically enabled by default, some Mercedes-Benz models allow drivers to disable the system for specific situations like driving in deep snow.
Q7: Does ESP replace the need for winter tires in snowy conditions?
A7: No, ESP enhances traction but does not replace winter tires, which provide superior grip and braking performance in cold weather.
Q8: How often should I have the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz inspected?
A8: Regular inspections are recommended, especially if you notice any warning signs. A qualified technician should inspect the system during routine maintenance.
Q9: What diagnostic tools can I use to check the ESP system in my Mercedes-Benz?
A9: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools, such as the Launch X431 V+ and Autel MaxiSys MS906BT, for comprehensive ESP system checks.
Q10: Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools and maintenance support for my Mercedes-Benz ESP system?
A10: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality diagnostic tools and expert assistance for ESP maintenance. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information and support.
Take Action Now
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Ensure your Mercedes-Benz’s ESP system is functioning optimally with the right diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET. Contact us today via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our range of diagnostic solutions. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in selecting the perfect tools for your needs