What Is The BAS ESP Light Mercedes? Complete Guide
The BAS ESP light Mercedes is more than just an indicator; it’s your Mercedes-Benz communicating vital information about its stability systems. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of keeping your vehicle running smoothly and safely. This comprehensive guide dives into the BAS ESP system, its function, and how to troubleshoot related warning lights, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle any situation. Learn about wheel speed sensors, yaw rate sensors, and lateral acceleration sensors.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP System
The Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP (Brake Assist System Electronic Stability Program) system is a sophisticated safety feature designed to enhance vehicle stability and control. This system integrates two key components: Brake Assist System (BAS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP). Together, they work to prevent skidding and loss of control, particularly in emergency situations. The integration of these systems makes the vehicle more stable and easier to control.
1.1. The Role of Brake Assist System (BAS)
The Brake Assist System (BAS) is designed to recognize emergency braking situations. When the system detects that the driver is attempting to brake suddenly, it automatically increases the braking force to the maximum level, helping to reduce stopping distances. BAS uses sensors to monitor the speed and force with which the driver presses the brake pedal.
According to research, BAS can significantly decrease stopping distances in emergency situations, potentially preventing accidents.
1.2. The Function of Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) monitors the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. If the system detects a discrepancy, such as a skid or loss of traction, it selectively applies the brakes to individual wheels and adjusts engine power to help steer the vehicle back on course. ESP relies on various sensors, including wheel speed sensors, yaw rate sensors, and lateral acceleration sensors.
A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that ESP reduces single-vehicle crashes by 32% and rollover crashes by as much as 77%.
1.3. Key Components of the BAS ESP System
The BAS ESP system relies on several critical components to function effectively. These include:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors measure the speed of each wheel, providing data to the ESP system to detect wheel slippage or locking.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, helping the ESP system determine if the vehicle is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle, providing data to the ESP system to detect skidding or sliding.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Hydraulic Unit: The hydraulic unit controls the braking force applied to each wheel based on the data received from the sensors.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes the data from the sensors and controls the hydraulic unit and engine power to maintain stability.
Understanding the BAS ESP light on your Mercedes-Benz.
2. Interpreting the BAS ESP Warning Light
The BAS ESP warning light on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard is an essential indicator of the system’s status. Understanding what this light means can help you take appropriate action to ensure your safety and the proper functioning of your vehicle.
2.1. Steady Illumination
When the BAS ESP warning light is illuminated steadily, it typically indicates that there is a malfunction within the system. This could be due to a variety of reasons, such as a faulty sensor, a problem with the hydraulic unit, or an issue with the electronic control unit (ECU). In this case, the ESP system may be disabled, reducing the vehicle’s ability to maintain stability in critical situations.
It is crucial to address a steady BAS ESP warning light promptly. Driving with a malfunctioning ESP system can increase the risk of accidents, particularly in adverse weather conditions or during emergency maneuvers. Consulting a qualified technician is recommended to diagnose and resolve the underlying issue.
2.2. Flashing Light
If the BAS ESP warning light is flashing, it indicates that the ESP system is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. This typically occurs when the system detects a loss of traction or a potential skid. The ESP system will selectively apply the brakes to individual wheels and adjust engine power to help steer the vehicle back on course.
When the BAS ESP warning light is flashing, it is essential to drive with caution and avoid sudden maneuvers. Allow the ESP system to work effectively by maintaining a steady speed and steering smoothly. Once the vehicle regains stability, the warning light should stop flashing.
2.3. Intermittent Illumination
In some cases, the BAS ESP warning light may illuminate intermittently, appearing and disappearing at random. This can be caused by a temporary sensor malfunction, an intermittent electrical connection issue, or a software glitch. While the system may function normally most of the time, the intermittent illumination of the warning light indicates that there is an underlying problem that needs to be addressed.
It is advisable to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician to diagnose the cause of the intermittent BAS ESP warning light. Ignoring the issue could lead to a more significant malfunction in the future, compromising the vehicle’s safety and stability.
2.4. No Illumination
If the BAS ESP warning light does not illuminate at all, even when the ignition is turned on, it could indicate a problem with the warning light itself or with the system’s ability to detect malfunctions. This can be due to a blown fuse, a faulty bulb, or a more complex issue within the ESP system.
In this case, it is essential to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician to determine the cause of the non-illuminating BAS ESP warning light. Failure to address this issue could result in driving without the safety benefits of the ESP system, increasing the risk of accidents in critical situations.
Here’s a summary table of the BAS ESP warning light statuses and their meanings:
| Light Status | Meaning | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Steady Illumination | Malfunction within the BAS ESP system; ESP may be disabled. | Consult a qualified technician to diagnose and resolve the issue. Avoid driving in hazardous conditions until the system is repaired. |
| Flashing Light | ESP is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. | Drive with caution, avoid sudden maneuvers, and allow the ESP system to work effectively. |
| Intermittent Illumination | Temporary sensor malfunction, intermittent electrical connection issue, or software glitch. | Have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician to diagnose the cause of the intermittent warning light. |
| No Illumination | Problem with the warning light itself or with the system’s ability to detect malfunctions. | Have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician to determine the cause of the non-illuminating warning light. Do not drive without ESP system. |
3. Common Causes of the BAS ESP Light Mercedes
Several factors can trigger the BAS ESP light in your Mercedes-Benz. Identifying these common causes can help you better understand the potential issues and take appropriate action.
3.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are crucial components of the BAS ESP system, measuring the speed of each wheel to detect slippage or locking. When one or more wheel speed sensors fail, the ESP system may not receive accurate data, triggering the BAS ESP light. Faulty wheel speed sensors can be caused by:
- Physical Damage: Impact from road debris or accidents can damage the sensors.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can corrode the sensors or their connectors.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or disconnected wiring can disrupt the sensor’s signal.
- Sensor Malfunction: The sensor itself may fail due to wear and tear or internal defects.
According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India, faulty wheel speed sensors are a common cause of ESP system malfunctions, accounting for approximately 30% of ESP-related issues.
3.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing data to the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction. If the steering angle sensor malfunctions, the ESP system may not be able to accurately compare the driver’s input with the vehicle’s actual movement, triggering the BAS ESP light. Common causes of steering angle sensor issues include:
- Misalignment: The sensor may become misaligned due to steering system repairs or adjustments.
- Contamination: Dirt or debris can contaminate the sensor, affecting its accuracy.
- Electrical Problems: Wiring issues or a faulty sensor can disrupt the signal.
3.3. Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can affect the performance of various electronic systems in your Mercedes-Benz, including the BAS ESP system. Insufficient voltage can cause the ESP system to malfunction or display false error codes, triggering the BAS ESP light. Low battery voltage can be caused by:
- Old Battery: Batteries degrade over time and may not provide sufficient voltage.
- Charging System Issues: Problems with the alternator or voltage regulator can prevent the battery from charging properly.
- Parasitic Drain: Electrical components drawing power when the vehicle is off can drain the battery.
3.4. Brake Light Switch Failure
The brake light switch activates the brake lights when the brake pedal is pressed. It also sends a signal to the ESP system, indicating that the driver is braking. If the brake light switch fails, the ESP system may not receive the correct signal, triggering the BAS ESP light. Common causes of brake light switch failure include:
- Wear and Tear: The switch can wear out over time due to repeated use.
- Physical Damage: Impact or stress can damage the switch.
- Electrical Problems: Wiring issues or a faulty switch can disrupt the signal.
3.5. ESP System Malfunctions
In some cases, the BAS ESP light may be triggered by a malfunction within the ESP system itself. This can include issues with the hydraulic unit, the electronic control unit (ECU), or other internal components. ESP system malfunctions can be caused by:
- Software Glitches: Software errors can cause the ESP system to behave erratically.
- Component Failure: Internal components may fail due to wear and tear or manufacturing defects.
- Hydraulic Issues: Problems with the hydraulic unit can affect the ESP system’s ability to control braking force.
Here’s a table summarizing the common causes of the BAS ESP light:
| Cause | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors | Inaccurate wheel speed data due to damaged, corroded, or malfunctioning sensors. | Replace the faulty wheel speed sensor. Check and repair wiring connections. |
| Steering Angle Sensor Issues | Misalignment, contamination, or electrical problems affecting the accuracy of the steering angle sensor. | Realignment or replacement of the steering angle sensor. Check and clean the sensor. Repair any wiring issues. |
| Low Battery Voltage | Insufficient voltage affecting the performance of the BAS ESP system. | Replace the battery. Check and repair the charging system. Identify and address any parasitic drain. |
| Brake Light Switch Failure | Failure of the brake light switch to activate brake lights and send a signal to the ESP system. | Replace the faulty brake light switch. Check and repair wiring connections. |
| ESP System Malfunctions | Issues within the ESP system itself, including software glitches, component failure, or hydraulic problems. | Consult a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair. Software updates or component replacements may be necessary. |
The Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP light and its functions.
4. Diagnosing the BAS ESP Light Mercedes
Diagnosing the BAS ESP light on your Mercedes-Benz requires a systematic approach to identify the underlying issue. By following these steps, you can effectively troubleshoot the problem and take appropriate action.
4.1. Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle’s components, focusing on the BAS ESP system-related parts.
- Check Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the wheel speed sensors for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Ensure that the wiring is intact and properly connected.
- Inspect Brake Light Switch: Examine the brake light switch for any signs of damage or loose connections. Verify that the brake lights illuminate properly when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Check Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. Ensure that the voltage is within the specified range (typically 12.6 volts or higher when the engine is off).
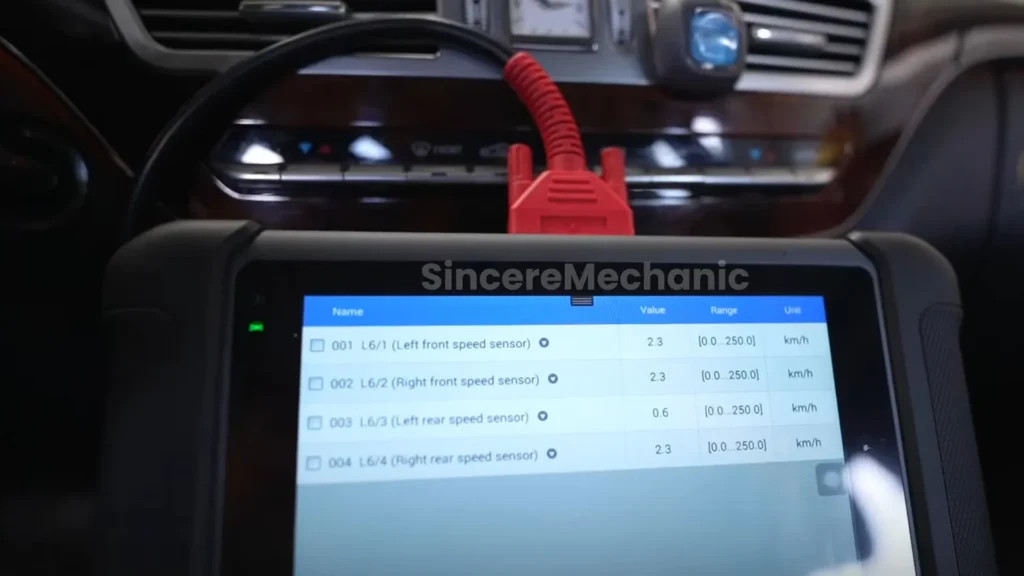
4.2. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can provide valuable diagnostic information about the BAS ESP system.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the vehicle’s diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Turn on the ignition and use the scanner to read any stored DTCs related to the BAS ESP system. Record the codes for further analysis.
- Research the Codes: Use a reliable source, such as a repair manual or online database, to research the meaning of the DTCs. This will help you identify the potential causes of the BAS ESP light.
Some common DTCs related to the BAS ESP system include:
- C1100: Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- C1101: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- C1200: Brake Light Switch Circuit Malfunction
- C1300: Steering Angle Sensor Circuit Malfunction
4.3. Testing Components
Testing individual components of the BAS ESP system can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each wheel speed sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. A significant deviation may indicate a faulty sensor.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Use an advanced diagnostic tool to monitor the steering angle sensor’s output while turning the steering wheel. Verify that the sensor’s readings are accurate and consistent.
- Brake Light Switch: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the brake light switch when the brake pedal is pressed and released. Ensure that the switch is functioning properly.
4.4. Professional Diagnostic Services
If you are unable to diagnose the BAS ESP light using the above methods, it is recommended to seek professional diagnostic services.
- Authorized Mercedes-Benz Service Center: An authorized Mercedes-Benz service center has the specialized tools, equipment, and expertise to diagnose and repair BAS ESP system issues accurately.
- Qualified Independent Mechanic: A qualified independent mechanic with experience in Mercedes-Benz vehicles can also diagnose and repair BAS ESP system problems.
Here’s a table summarizing the diagnostic steps for the BAS ESP light:
| Step | Description | Tools/Equipment Needed |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Visual Inspection | Check wheel speed sensors, brake light switch, and battery voltage for any issues. | None |
| 2. OBD-II Scanner | Read and research Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the BAS ESP system. | OBD-II scanner, repair manual or online database |
| 3. Component Testing | Test wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and brake light switch. | Multimeter, advanced diagnostic tool |
| 4. Professional Diagnostic Services | Seek help from an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center or qualified independent mechanic. | Specialized tools, equipment, and expertise |
5. Repairing the BAS ESP Light Mercedes
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the BAS ESP light, the next step is to repair the issue. Depending on the problem, the repair process may involve replacing faulty components, repairing wiring, or reprogramming the ESP system.
5.1. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a faulty wheel speed sensor is causing the BAS ESP light, the sensor will need to be replaced.
- Gather the Necessary Tools: You will need a wrench or socket set, a new wheel speed sensor, and a torque wrench.
- Disconnect the Old Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the old wheel speed sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a wrench or socket to remove the old wheel speed sensor from the wheel hub.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new wheel speed sensor into the wheel hub and tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new wheel speed sensor.
- Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs and verify that the BAS ESP light is no longer illuminated.
5.2. Addressing Steering Angle Sensor Issues
If the steering angle sensor is causing the BAS ESP light, the sensor may need to be realigned or replaced.
- Gather the Necessary Tools: You will need a wrench or socket set, a new steering angle sensor (if replacement is necessary), and an advanced diagnostic tool.
- Disconnect the Old Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the old steering angle sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a wrench or socket to remove the old steering angle sensor from the steering column.
- Install the New Sensor (If Necessary): Install the new steering angle sensor into the steering column and tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Realign the Sensor: Use an advanced diagnostic tool to realign the steering angle sensor to the correct position.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the steering angle sensor.
- Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs and verify that the BAS ESP light is no longer illuminated.
5.3. Resolving Low Battery Voltage Issues
If low battery voltage is causing the BAS ESP light, the battery may need to be replaced or the charging system repaired.
- Test the Battery: Use a battery tester to assess the condition of the battery. If the battery is weak or unable to hold a charge, it should be replaced.
- Replace the Battery (If Necessary): Disconnect the old battery and install a new battery of the correct type and specifications.
- Check the Charging System: Use a multimeter to check the output voltage of the alternator. Ensure that the alternator is charging the battery properly (typically 13.5 to 14.5 volts with the engine running).
- Repair the Charging System (If Necessary): If the alternator is not charging properly, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs and verify that the BAS ESP light is no longer illuminated.
5.4. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
If a faulty brake light switch is causing the BAS ESP light, the switch will need to be replaced.
- Gather the Necessary Tools: You will need a wrench or socket set, a new brake light switch, and a multimeter.
- Disconnect the Old Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the old brake light switch.
- Remove the Old Switch: Use a wrench or socket to remove the old brake light switch from the brake pedal assembly.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new brake light switch into the brake pedal assembly and tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new brake light switch.
- Test the System: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the brake light switch when the brake pedal is pressed and released. Verify that the brake lights illuminate properly.
- Test the System: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs and verify that the BAS ESP light is no longer illuminated.
5.5. Addressing ESP System Malfunctions
If the BAS ESP light is caused by a malfunction within the ESP system itself, the repair process may be more complex and require specialized tools and expertise.
- Consult a Qualified Technician: Seek help from an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center or a qualified independent mechanic with experience in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Diagnose the Issue: The technician will use specialized diagnostic tools to pinpoint the source of the ESP system malfunction.
- Repair or Replace Components: Depending on the diagnosis, the technician may repair or replace faulty components within the ESP system, such as the hydraulic unit or the electronic control unit (ECU).
- Reprogram the System (If Necessary): In some cases, the ESP system may need to be reprogrammed to function properly.
- Test the System: The technician will test the ESP system to ensure that it is functioning correctly and that the BAS ESP light is no longer illuminated.
Here’s a table summarizing the repair steps for the BAS ESP light:
| Repair | Steps |
|---|---|
| Replace Wheel Speed Sensor | 1. Disconnect the old sensor. 2. Remove the old sensor. 3. Install the new sensor. 4. Reconnect the electrical connector. 5. Test the system. |
| Address Steering Angle Sensor Issues | 1. Disconnect the old sensor. 2. Remove the old sensor. 3. Install the new sensor (if necessary). 4. Realign the sensor. 5. Reconnect the electrical connector. 6. Test the system. |
| Resolve Low Battery Voltage Issues | 1. Test the battery. 2. Replace the battery (if necessary). 3. Check the charging system. 4. Repair the charging system (if necessary). 5. Test the system. |
| Replace Brake Light Switch | 1. Disconnect the old switch. 2. Remove the old switch. 3. Install the new switch. 4. Reconnect the electrical connector. 5. Test the system. |
| Address ESP System Malfunctions | 1. Consult a qualified technician. 2. Diagnose the issue. 3. Repair or replace components. 4. Reprogram the system (if necessary). 5. Test the system. |
6. Preventing BAS ESP Light Issues
Preventing BAS ESP light issues involves proactive maintenance and care of your Mercedes-Benz. By following these tips, you can minimize the risk of BAS ESP system malfunctions and ensure the safety and reliability of your vehicle.
6.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing BAS ESP light issues.
- Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the maintenance schedule outlined in your Mercedes-Benz owner’s manual. This includes regular inspections and servicing of the brake system, wheel speed sensors, and other BAS ESP system components.
- Check and Replace Brake Pads and Rotors: Regularly inspect the brake pads and rotors for wear and tear. Replace them as needed to ensure optimal braking performance.
- Inspect and Maintain Wheel Speed Sensors: Periodically inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean the sensors and connectors as necessary.
6.2. Proper Tire Care
Proper tire care is crucial for maintaining the stability and handling of your Mercedes-Benz.
- Maintain Proper Tire Pressure: Check and maintain the recommended tire pressure as specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or on the tire placard.
- Rotate Tires Regularly: Rotate the tires according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure even wear and prolong tire life.
- Replace Worn Tires: Replace worn tires promptly to maintain optimal traction and handling.
6.3. Careful Driving Habits
Careful driving habits can help prevent BAS ESP light issues.
- Avoid Hard Braking and Acceleration: Avoid sudden and aggressive braking and acceleration, as this can put unnecessary stress on the BAS ESP system.
- Drive Cautiously in Adverse Weather Conditions: Drive cautiously in rain, snow, or ice to minimize the risk of skidding or loss of control.
- Avoid Driving Through Deep Water: Avoid driving through deep water, as this can damage the wheel speed sensors and other BAS ESP system components.
6.4. Promptly Address Warning Lights
Promptly address any warning lights that appear on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard.
- Investigate and Resolve Warning Lights: Do not ignore warning lights, as they indicate a potential issue that needs to be addressed.
- Seek Professional Help When Needed: If you are unable to diagnose or resolve a warning light issue, seek help from an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center or a qualified independent mechanic.
Here’s a table summarizing the preventive measures for BAS ESP light issues:
| Preventive Measure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Maintenance | Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. | Ensures optimal performance and longevity of the BAS ESP system components. |
| Proper Tire Care | Maintain proper tire pressure, rotate tires regularly, and replace worn tires promptly. | Maintains optimal traction and handling, reducing the risk of skidding or loss of control. |
| Careful Driving Habits | Avoid hard braking and acceleration, drive cautiously in adverse weather conditions. | Minimizes stress on the BAS ESP system and reduces the risk of malfunctions. |
| Promptly Address Warning Lights | Investigate and resolve warning lights, seek professional help when needed. | Prevents minor issues from escalating into major problems and ensures the continued safety and reliability of the vehicle. |
7. The Importance of Professional Service
While some BAS ESP light issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting and component replacement, it’s crucial to recognize when professional service is necessary.
7.1. Complex Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing BAS ESP light issues can sometimes involve complex diagnostic procedures that require specialized tools and expertise.
- Advanced Diagnostic Equipment: Authorized Mercedes-Benz service centers and qualified independent mechanics have access to advanced diagnostic equipment, such as scan tools, oscilloscopes, and diagnostic software, that can accurately pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Expertise and Experience: Professional technicians have the expertise and experience to interpret diagnostic data and identify the underlying causes of BAS ESP light issues.
7.2. Specialized Repairs
Some BAS ESP light issues require specialized repairs that should only be performed by trained professionals.
- Hydraulic Unit Repairs: Repairs to the hydraulic unit, which controls the braking force applied to each wheel, require specialized tools and expertise to ensure proper functioning and safety.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Reprogramming: Reprogramming the ECU, which controls the BAS ESP system, requires specialized software and expertise to ensure that the system functions correctly and does not cause other issues.
7.3. Safety Considerations
The BAS ESP system is a critical safety feature that helps prevent skidding and loss of control.
- Proper Functioning is Essential: It is essential to ensure that the BAS ESP system is functioning properly to maintain the safety and stability of the vehicle.
- Professional Service Ensures Safety: Professional service ensures that repairs are performed correctly and that the BAS ESP system is functioning as intended, providing peace of mind and enhancing safety.
7.4. Warranty Implications
Performing repairs on your Mercedes-Benz yourself or using an unqualified mechanic can void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Warranty Coverage: Authorized Mercedes-Benz service centers are trained to perform repairs according to the manufacturer’s specifications and can ensure that warranty coverage is maintained.
- Protect Your Investment: Protecting your investment by using professional service can help avoid costly repairs in the future and maintain the value of your vehicle.
Here’s a table highlighting the importance of professional service for BAS ESP light issues:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Complex Diagnostics | Specialized tools and expertise are required to accurately diagnose BAS ESP light issues. |
| Specialized Repairs | Some BAS ESP light issues require specialized repairs, such as hydraulic unit repairs or ECU reprogramming, that should only be performed by trained professionals. |
| Safety Considerations | The BAS ESP system is a critical safety feature, and professional service ensures that it is functioning properly to maintain the safety and stability of the vehicle. |
| Warranty Implications | Performing repairs yourself or using an unqualified mechanic can void the vehicle’s warranty, while professional service ensures that warranty coverage is maintained. |
8. The Future of Stability Control Systems
Stability control systems like BAS ESP are continuously evolving, with new technologies and features being developed to enhance vehicle safety and performance.
8.1. Integration with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Stability control systems are increasingly being integrated with ADAS to provide a more comprehensive suite of safety features.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Adaptive cruise control uses radar and cameras to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, automatically adjusting speed as needed.
- Lane Keeping Assist: Lane keeping assist uses cameras to monitor the vehicle’s position within its lane and automatically steer the vehicle back into the lane if it begins to drift.
- Automatic Emergency Braking: Automatic emergency braking uses sensors to detect potential collisions and automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact.
8.2. Enhanced Sensor Technology
New sensor technologies are being developed to provide more accurate and detailed information to stability control systems.
- High-Resolution Radar: High-resolution radar can provide more detailed information about the vehicle’s surroundings, improving the accuracy of collision detection and avoidance systems.
- Advanced Camera Systems: Advanced camera systems can provide a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings, enhancing situational awareness and improving the performance of lane keeping assist and other ADAS features.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR uses laser beams to create a 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings, providing highly accurate and detailed information for autonomous driving systems.
8.3. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to remotely update the software in vehicle systems, including stability control systems.
- Improved Performance: OTA updates can improve the performance of stability control systems by fixing bugs, adding new features, and optimizing algorithms.
- Enhanced Security: OTA updates can enhance the security of vehicle systems by patching vulnerabilities and protecting against cyberattacks.
8.4. Predictive Stability Control
Predictive stability control systems use advanced algorithms and sensor data to anticipate potential skidding or loss of control before it occurs.
- Proactive Interventions: Predictive stability control systems can proactively intervene to prevent skidding or loss of control, improving vehicle safety and stability.
- Enhanced Performance: Predictive stability control systems can enhance vehicle performance by optimizing the stability control system for different driving conditions and styles.
Here’s a table summarizing the future trends in stability control systems:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Integration with ADAS | Stability control systems are increasingly being integrated with ADAS to provide a more comprehensive suite of safety features. |
| Enhanced Sensor Technology | New sensor technologies, such as high-resolution radar and advanced camera systems, are being developed to provide more accurate and detailed information to stability control systems. |
| Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates | Over-the-air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to remotely update the software in vehicle systems, including stability control systems. |
| Predictive Stability Control Systems | Predictive stability control systems use advanced algorithms and sensor data to anticipate potential skidding or loss of control before it occurs. |
Navigating the complexities of your Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP system doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With the right tools and knowledge, you can keep your vehicle running safely and efficiently. Remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you with top-quality diagnostic tools and expert advice. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for all your automotive diagnostic needs. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
Are you experiencing BAS ESP light issues or any other car diagnostic challenges? Don’t wait! Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET now to get the expert assistance you need. Our team is ready to provide you with the best tools and support to keep your Mercedes-Benz in top condition.
FAQ: BAS ESP Light Mercedes
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about the BAS ESP light on Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- What does the BAS ESP light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
- The BAS ESP light indicates an issue with the Brake Assist System (BAS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP). It could mean a malfunction in the system, a faulty sensor, or low battery voltage.
- Is it safe to drive with the BAS ESP light on?
- It’s generally not recommended. The BAS ESP system helps maintain stability, and driving with a malfunctioning system can increase the risk of accidents, especially in adverse conditions.
- How can I reset the BAS ESP light on my Mercedes-Benz?
- Sometimes, turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left to full right) can reset the system. However, if the light persists, there’s likely an underlying issue that needs professional attention.
- What are common causes of the BAS ESP light illuminating?
- Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, low battery voltage, a bad brake light switch, or internal ESP system malfunctions.
- Can low tire pressure trigger the BAS ESP light?
- While low tire pressure itself may not directly trigger the BAS ESP light, it can affect the overall stability of the vehicle and potentially interact with the ESP system, leading to the light turning on.
- Do I need a special tool to diagnose the BAS ESP light issue?
- Yes, an OBD-II scanner is needed to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and pinpoint the source of the problem. More complex issues may require advanced diagnostic tools.
- Can I replace a faulty wheel speed sensor myself?
- If you have mechanical experience, you can replace a wheel speed sensor. However, it’s important to follow the correct procedures and use the appropriate tools.
- How much does it cost to repair a BAS ESP light issue on a Mercedes-Benz?
- The cost varies depending on the cause. A simple fix like replacing a brake light switch might be a few hundred dollars, while more complex repairs like replacing the ESP hydraulic unit could cost over a thousand dollars.
- Can a software update fix the BAS ESP light issue?
- In some cases, yes. If the issue is due to a software glitch, a software update from an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center can resolve the problem.
- When should I seek professional help for the BAS ESP light?
- If you are unable to diagnose the issue, or if the light persists after basic troubleshooting, it’s best to seek professional help from a qualified technician or an authorized Mercedes-Benz service center.