What Is The ESP Button On A Mercedes? A Comprehensive Guide
The ESP button on a Mercedes is a crucial component of its safety system. Wondering what it does and how it benefits you? At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we delve into the details of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes vehicles, offering you a clear understanding of its function, benefits, and how it enhances your driving experience. Discover how ESP, stability control, and traction control work together to keep you safe, especially when considering purchasing diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz.
1. Understanding the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is an essential safety feature in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, designed to prevent skidding and maintain control in adverse driving conditions. It is also commonly known as Electronic Stability Control (ESC) or Dynamic Stability Control. This system integrates with other safety systems like the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and the traction control system (TCS) to provide comprehensive stability management.
1.1. History and Development of ESP
Mercedes-Benz, in collaboration with Bosch, pioneered ESP technology, introducing it in 1995. This innovation marked a significant advancement in automotive safety. Initially available on select models, ESP has since become a standard feature in most Mercedes-Benz vehicles, underscoring its importance in preventing accidents and enhancing vehicle stability.
1.2. Core Functionality of ESP
ESP’s primary function is to monitor and correct deviations from the driver’s intended path. Using a network of sensors, the system continuously analyzes the vehicle’s speed, steering angle, and yaw rate. If ESP detects a potential skid or loss of control, it intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This targeted braking action helps to counteract oversteer or understeer, bringing the vehicle back onto its intended course.
1.3. ESP Components and Sensors
The ESP system relies on several key sensors to gather real-time data about the vehicle’s dynamics. These sensors include:
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting any deviation from the intended path.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel, detecting differences that could indicate a skid.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle, helping to detect skidding or instability.
1.4. How ESP Interacts with Other Safety Systems
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems to provide a comprehensive safety net. The anti-lock braking system (ABS) prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. The traction control system (TCS) prevents wheel spin during acceleration, ensuring optimal grip. By integrating these systems, ESP enhances overall vehicle stability and control.
1.5. The ESP Button: What Does It Do?
The ESP button in a Mercedes-Benz allows the driver to partially or fully disable the ESP system. In some situations, such as driving in deep snow or sand, disabling ESP can allow the wheels to spin, providing better traction. However, it is generally recommended to keep ESP enabled for optimal safety, especially in normal driving conditions.
2. Key Benefits of Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) offers numerous benefits that enhance the safety and driving experience of Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Here are some of the primary advantages:
2.1. Preventing Skidding
ESP is highly effective at preventing skidding, particularly in slippery or challenging driving conditions such as wet, icy, or snow-covered roads. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP helps the driver maintain control and avoid potentially dangerous situations. This capability is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the safety of both the driver and passengers.
2.2. Improving Vehicle Stability
ESP significantly improves the overall stability of the vehicle, especially when cornering or making sudden maneuvers. By monitoring the vehicle’s dynamics and intervening when necessary, ESP helps to keep the vehicle planted on the road, providing the driver with increased confidence and control. This is particularly beneficial in emergency situations where quick reactions are required.
2.3. Reducing Understeer and Oversteer
ESP is designed to mitigate both understeer and oversteer, two common types of skidding that can lead to loss of control. Understeer occurs when the front wheels lose traction, causing the vehicle to go straight ahead instead of turning. Oversteer occurs when the rear wheels lose traction, causing the vehicle to spin out. ESP can correct these conditions by applying brakes to the appropriate wheels, helping the driver maintain control and prevent accidents.
2.4. Enhancing Traction and Grip
In addition to preventing skidding, ESP also enhances traction and grip, particularly in challenging driving conditions. By monitoring wheel speed and applying brakes as needed, ESP helps to prevent wheel spin and ensure that the vehicle maintains optimal contact with the road surface. This is especially beneficial when accelerating on slippery surfaces or climbing steep inclines.
2.5. Minimizing Rollover Risk
ESP plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of rollover accidents, particularly in SUVs and other high-center-of-gravity vehicles. By detecting and correcting instability, ESP helps to prevent the vehicle from tipping over during sudden maneuvers or when driving on uneven surfaces. This is a critical safety feature that can save lives and prevent serious injuries.
2.6. Improving Overall Safety
The combination of these benefits results in a significant improvement in overall safety. ESP helps to prevent accidents, reduce the severity of collisions, and protect both the driver and passengers. It is one of the most important safety features to consider when buying a car, and it has become a standard feature in most modern vehicles.
3. Understanding Understeer and Oversteer
Understeer and oversteer are two common handling characteristics that can occur in vehicles, especially during cornering or when making sudden maneuvers. Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending how ESP works and why it is so important for vehicle safety.
3.1. What is Understeer?
Understeer occurs when the front wheels of a vehicle lose traction, causing the vehicle to turn less sharply than the driver intends. In other words, the vehicle tends to “push” or “plow” straight ahead, even when the steering wheel is turned. This can happen when the front tires are overloaded, or when the road surface is slippery, reducing the available grip.
3.1.1. Causes of Understeer
- Excessive Speed: Entering a corner too quickly can overload the front tires, causing them to lose traction.
- Slippery Road Conditions: Wet, icy, or snow-covered roads can reduce the amount of grip available to the front tires.
- Improper Weight Distribution: If the vehicle’s weight is concentrated towards the rear, the front tires may have less grip.
- Aggressive Acceleration: Accelerating too hard while cornering can transfer weight to the rear, reducing grip at the front.
3.1.2. How ESP Corrects Understeer
ESP can detect understeer by monitoring the vehicle’s steering angle and yaw rate. If the system detects that the vehicle is not turning as sharply as the driver intends, it will apply the brakes to the inside rear wheel. This braking action creates a yaw moment that helps to rotate the vehicle and bring it back onto its intended path.
3.2. What is Oversteer?
Oversteer occurs when the rear wheels of a vehicle lose traction, causing the vehicle to turn more sharply than the driver intends. In other words, the rear of the vehicle tends to “swing” or “slide” out, potentially leading to a spin. This can happen when the rear tires are overloaded, or when the road surface is slippery, reducing the available grip.
3.2.1. Causes of Oversteer
- Excessive Speed: Entering a corner too quickly can overload the rear tires, causing them to lose traction.
- Slippery Road Conditions: Wet, icy, or snow-covered roads can reduce the amount of grip available to the rear tires.
- Improper Weight Distribution: If the vehicle’s weight is concentrated towards the front, the rear tires may have less grip.
- Sudden Throttle Changes: Lifting off the throttle suddenly while cornering can transfer weight to the front, reducing grip at the rear.
3.2.2. How ESP Corrects Oversteer
ESP can detect oversteer by monitoring the vehicle’s steering angle and yaw rate. If the system detects that the vehicle is turning more sharply than the driver intends, it will apply the brakes to the outside front wheel. This braking action creates a yaw moment that helps to stabilize the vehicle and prevent it from spinning out.
3.3. The Importance of ESP in Correcting Understeer and Oversteer
ESP is a valuable tool for correcting both understeer and oversteer, helping drivers maintain control in challenging situations. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP can counteract these handling characteristics and prevent accidents. This is particularly important for inexperienced drivers or those who may not have the skills to correct understeer or oversteer manually.
4. Mercedes-Benz Safety Features Beyond ESP
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are equipped with a comprehensive suite of safety features designed to protect occupants and prevent accidents. While ESP is a critical component, it is just one of many advanced technologies that contribute to the overall safety of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
4.1. Pre-Safe® System
The PRE-SAFE® system is a proactive safety system that prepares the vehicle and its occupants for a potential collision. If the system detects an imminent crash, it can tighten the seatbelts, adjust the seats to a more upright position, and close the windows and sunroof. These actions help to minimize the risk of injury in the event of a collision.
4.2. Attention Assist®
ATTENTION ASSIST® is a driver drowsiness detection system that monitors the driver’s behavior and alerts them if they show signs of fatigue. The system analyzes factors such as steering inputs, eye movements, and driving time to determine the driver’s level of alertness. If drowsiness is detected, the system will issue a visual and audible warning, advising the driver to take a break.
4.3. Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive Cruise Control is a cruise control system that automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. The system uses radar sensors to monitor the distance to the preceding vehicle and can accelerate or brake as needed to maintain the set gap. This feature can help to reduce driver fatigue and prevent accidents in stop-and-go traffic.
4.4. Blind Spot Assist
Blind Spot Assist is a safety feature that alerts the driver to the presence of vehicles in their blind spots. The system uses radar sensors to monitor the areas alongside and behind the vehicle. If a vehicle is detected in the blind spot, a warning light will illuminate in the corresponding side mirror. If the driver attempts to change lanes while a vehicle is in the blind spot, the system may also issue an audible warning.
4.5. Lane Keeping Assist
Lane Keeping Assist is a safety feature that helps to prevent unintentional lane departures. The system uses cameras to monitor the vehicle’s position within its lane. If the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane without the turn signal being activated, the system will issue a warning and may also provide steering assistance to help keep the vehicle in its lane.
4.6. Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
The Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. ABS works by modulating the brake pressure to each wheel, preventing them from locking up and skidding. This is particularly important in emergency braking situations or when driving on slippery surfaces.
4.7. Brake Assist
Brake Assist is a safety feature that detects emergency braking situations and provides additional braking force to help the driver stop more quickly. The system monitors the speed and force with which the driver applies the brake pedal. If it detects that the driver is attempting an emergency stop, it will automatically apply maximum braking force, even if the driver does not fully depress the brake pedal.
4.8. Electronic Brake-Force Distribution (EBD)
Electronic Brake-Force Distribution (EBD) is a safety feature that optimizes the distribution of braking force between the front and rear wheels. EBD works in conjunction with ABS to ensure that each wheel receives the appropriate amount of braking force, based on factors such as vehicle load, road conditions, and braking force.
5. Disabling and Resetting the ESP System
While ESP is generally beneficial, there are certain situations where disabling it may be advantageous. Understanding how to disable and reset the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz is important for optimizing vehicle performance in specific driving conditions.
5.1. When to Consider Disabling ESP
- Driving in Deep Snow or Sand: In deep snow or sand, disabling ESP can allow the wheels to spin, providing better traction and helping the vehicle to move forward. When ESP is enabled, it may reduce engine power or apply the brakes to prevent wheel spin, which can hinder progress in these conditions.
- Rocking the Vehicle: If the vehicle is stuck in mud, snow, or sand, disabling ESP can allow the driver to rock the vehicle back and forth to gain momentum and free it from the obstruction.
- Performance Driving: In certain performance driving situations, such as drifting or track driving, disabling ESP can give the driver more control over the vehicle’s handling. However, this should only be done by experienced drivers in a controlled environment.
5.2. How to Disable ESP
The procedure for disabling ESP may vary depending on the specific Mercedes-Benz model. However, in most cases, it involves pressing the ESP button located on the center console. Pressing the button once may partially disable the system, while pressing and holding it for several seconds may fully disable it. The instrument cluster will typically display a warning light to indicate that ESP has been disabled.
5.3. How to Reset ESP
To reset ESP and re-enable the system, simply press the ESP button again. The warning light in the instrument cluster should turn off, indicating that ESP is now active. In some cases, it may be necessary to restart the vehicle to fully reset the system.
5.4. Potential Issues and Troubleshooting
If the ESP system is not functioning properly, the instrument cluster may display a warning light. This could indicate a problem with one of the ESP sensors, the ESP control unit, or another component of the system. In this case, it is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
5.5. Considerations for Diagnostic Tools
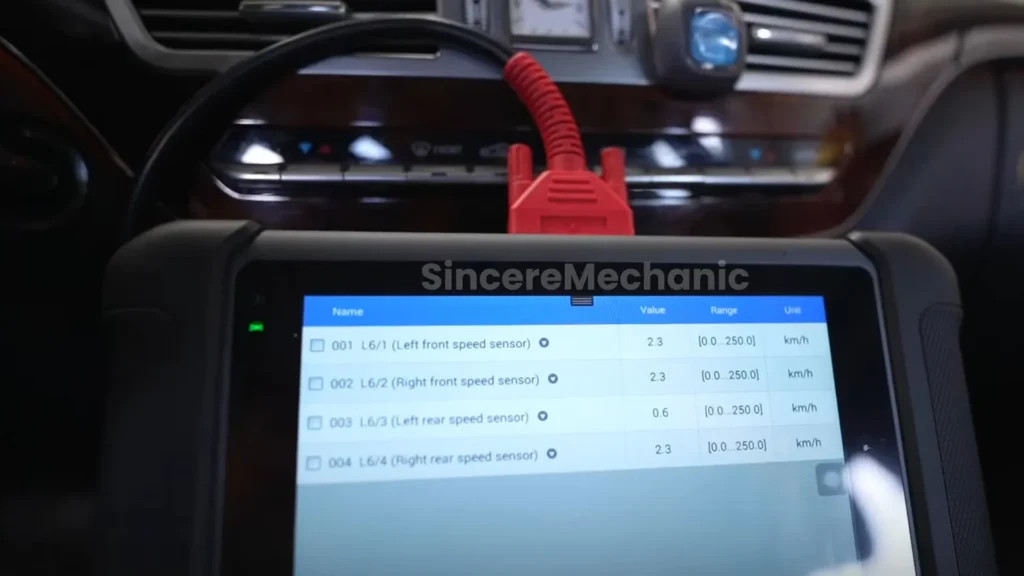
For those who prefer to perform their own maintenance and repairs, diagnostic tools can be invaluable for troubleshooting ESP issues. These tools can read fault codes, monitor sensor data, and perform system tests to help identify the source of the problem. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, allowing you to diagnose and resolve ESP issues quickly and efficiently.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Proper maintenance of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is essential for ensuring its continued performance and reliability. Regular inspections and timely repairs can help to prevent issues and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
6.1. Regular Inspections
- Check for Warning Lights: Regularly check the instrument cluster for any ESP warning lights. If a warning light illuminates, it indicates that there may be a problem with the system.
- Inspect Sensors: Periodically inspect the ESP sensors for damage or contamination. Clean any dirt or debris from the sensors to ensure accurate readings.
- Check Brake System: Ensure that the brake system is in good condition, as ESP relies on the brakes to function properly. Check the brake pads, rotors, and fluid level regularly.
6.2. Addressing Warning Lights
If an ESP warning light illuminates, it is important to address the issue promptly. Use a diagnostic tool to read the fault codes and identify the source of the problem. Consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician for diagnosis and repair.
6.3. Professional Servicing
Schedule regular servicing appointments with a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician. During these appointments, the technician can inspect the ESP system and perform any necessary maintenance or repairs.
6.4. Importance of Quality Parts
When replacing ESP components, use only high-quality parts that are specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Using aftermarket or low-quality parts can compromise the performance and reliability of the ESP system.
6.5. Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools and equipment that can help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. Our tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable data, allowing you to diagnose and resolve issues quickly and efficiently. With our tools, you can perform your own maintenance and repairs, saving time and money.
7. ESP Button on a Mercedes: Common Misconceptions
Despite being a crucial safety feature, the ESP button and the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) itself are often misunderstood. Clearing up these misconceptions can help drivers use the system more effectively and safely.
7.1. ESP is Only for Winter Driving
One common misconception is that ESP is only useful in winter driving conditions such as snow and ice. While ESP is certainly beneficial in these situations, it is also effective in a wide range of other driving conditions, including wet roads, gravel roads, and even dry pavement. ESP can help to prevent skidding and maintain control in any situation where the vehicle’s stability is compromised.
7.2. ESP Makes the Car Unstoppable
Another misconception is that ESP makes the car unstoppable. While ESP can significantly improve vehicle stability and control, it is not a substitute for safe driving habits. Drivers should still exercise caution and adjust their driving to the conditions, even when ESP is enabled. ESP can help to prevent accidents, but it cannot overcome the laws of physics.
7.3. Disabling ESP Improves Performance
Some drivers believe that disabling ESP improves performance, particularly in sports cars or high-performance vehicles. While disabling ESP can allow for more wheel spin and greater driver control, it also reduces the vehicle’s stability and increases the risk of skidding or loss of control. Disabling ESP should only be done by experienced drivers in a controlled environment, such as a racetrack.
7.4. ESP is the Same as Traction Control
ESP and traction control are related but distinct systems. Traction control prevents wheel spin during acceleration, while ESP prevents skidding and maintains stability during cornering or braking. Both systems work together to enhance vehicle safety, but they address different aspects of vehicle dynamics.
7.5. All ESP Systems are the Same
Not all ESP systems are created equal. The sophistication and effectiveness of ESP systems can vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer and model. Some ESP systems may offer more advanced features, such as torque vectoring or brake-based limited-slip differentials, which can further enhance vehicle stability and control.
8. The Future of ESP Technology
ESP technology continues to evolve, with new advancements and features being developed to further enhance vehicle safety and performance. Here are some of the trends and developments that are shaping the future of ESP technology:
8.1. Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
As autonomous driving technology becomes more prevalent, ESP systems are being integrated with these systems to provide an additional layer of safety. ESP can help to maintain stability and control in situations where the autonomous driving system may be unable to react quickly enough.
8.2. Advanced Sensor Technology
New sensor technologies, such as lidar and radar, are being integrated into ESP systems to provide more accurate and comprehensive data about the vehicle’s surroundings. This allows the ESP system to react more quickly and effectively to potential hazards.
8.3. Over-the-Air Updates
Some manufacturers are now offering over-the-air updates for ESP systems, allowing them to improve the system’s performance and add new features without requiring a visit to the dealership. This ensures that the ESP system remains up-to-date with the latest advancements in technology.
8.4. Enhanced Customization
Future ESP systems may offer more customization options, allowing drivers to adjust the system’s sensitivity and intervention levels to suit their driving style and preferences. This would allow drivers to tailor the ESP system to their individual needs, providing a more personalized driving experience.
8.5. Predictive ESP Systems
Predictive ESP systems use advanced algorithms and data analysis to anticipate potential hazards and intervene proactively. These systems can analyze factors such as road conditions, traffic patterns, and driver behavior to predict when a loss of control is likely to occur. This allows the ESP system to take preventative action, such as applying the brakes or reducing engine power, before the driver even realizes there is a problem.
9. Real-World Examples of ESP in Action
To better understand the benefits of ESP, let’s examine some real-world examples of how the system can help to prevent accidents and enhance vehicle safety.
9.1. Avoiding a Skid on a Wet Road
Imagine you are driving on a wet road and suddenly encounter a patch of standing water. The tires lose traction, and the vehicle begins to skid. With ESP enabled, the system detects the skid and selectively applies the brakes to individual wheels, helping to regain traction and prevent the vehicle from spinning out of control.
9.2. Maintaining Control in a Sudden Swerve
Suppose you are driving on the highway and a vehicle suddenly cuts in front of you, forcing you to swerve to avoid a collision. Without ESP, the sudden swerve could cause the vehicle to become unstable and potentially roll over. However, with ESP enabled, the system detects the instability and intervenes by applying the brakes and adjusting engine power, helping to maintain control and prevent a rollover.
9.3. Navigating a Sharp Corner
Consider driving on a winding mountain road and approaching a sharp corner. If you enter the corner too quickly, the tires may lose traction, causing the vehicle to understeer or oversteer. With ESP enabled, the system detects the loss of traction and selectively applies the brakes to individual wheels, helping to maintain control and prevent the vehicle from running off the road.
9.4. Recovering from a Loss of Control
Imagine you are driving on an icy road and suddenly lose control of the vehicle. The vehicle begins to spin, and you are unable to steer. With ESP enabled, the system detects the loss of control and intervenes by applying the brakes and adjusting engine power, helping to regain control and prevent a collision.
9.5. Preventing a Rollover in an SUV
SUVs and other high-center-of-gravity vehicles are more prone to rollovers than passenger cars. ESP can help to prevent rollovers by detecting instability and intervening to maintain control. For example, if you are driving an SUV on a gravel road and suddenly encounter a sharp turn, ESP can help to prevent the vehicle from tipping over by applying the brakes to the appropriate wheels.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the ESP Button on a Mercedes
Here are some frequently asked questions about the ESP button on a Mercedes, along with detailed answers to help you better understand this important safety feature.
10.1. What does the ESP button do on a Mercedes?
The ESP button allows the driver to partially or fully disable the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system. ESP is a safety feature that helps prevent skidding and maintain control in adverse driving conditions.
10.2. When should I disable ESP on my Mercedes?
Disabling ESP may be beneficial in specific situations, such as driving in deep snow or sand, where wheel spin can provide better traction. However, it is generally recommended to keep ESP enabled for optimal safety in normal driving conditions.
10.3. How do I know if ESP is enabled or disabled?
When ESP is disabled, a warning light will illuminate in the instrument cluster. The warning light typically consists of a car with skid marks behind it.
10.4. Can I permanently disable ESP on my Mercedes?
In most Mercedes-Benz models, ESP cannot be permanently disabled. The system will automatically re-enable itself each time the vehicle is started.
10.5. What happens if I drive with ESP disabled?
Driving with ESP disabled reduces the vehicle’s stability and increases the risk of skidding or loss of control. This is particularly dangerous in adverse driving conditions such as wet, icy, or snow-covered roads.
10.6. Does ESP affect braking performance?
ESP can affect braking performance in certain situations. When ESP intervenes to prevent skidding, it may apply the brakes to individual wheels, which can alter the vehicle’s braking distance.
10.7. Is ESP the same as traction control?
No, ESP and traction control are related but distinct systems. Traction control prevents wheel spin during acceleration, while ESP prevents skidding and maintains stability during cornering or braking.
10.8. How do I reset the ESP system on my Mercedes?
To reset ESP and re-enable the system, simply press the ESP button again. The warning light in the instrument cluster should turn off, indicating that ESP is now active. In some cases, it may be necessary to restart the vehicle to fully reset the system.
10.9. What should I do if the ESP warning light stays on?
If the ESP warning light remains illuminated, it indicates that there may be a problem with the system. It is recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician to diagnose and repair the issue.
10.10. Can diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP issues?
Yes, CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools can read fault codes, monitor sensor data, and perform system tests to help identify and resolve ESP issues quickly and efficiently. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
Conclusion: Maximizing Safety with Mercedes-Benz ESP
The ESP button on a Mercedes controls a sophisticated system designed to enhance your safety on the road. By understanding how ESP works, its benefits, and when to use the ESP button, you can maximize the safety and performance of your vehicle. Remember, regular maintenance and the use of quality diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET can help keep your ESP system in optimal condition.
Are you looking to ensure your Mercedes-Benz’s ESP system is functioning perfectly? Do you want to diagnose and resolve any potential issues quickly and efficiently? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and top-quality diagnostic tools. We’re here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely. Don’t compromise on safety – invest in the best diagnostic solutions available. Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET now to explore our range of products and services. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.