Can You Fix Rust on a Car? Your Ultimate Guide
Can you fix rust on a car? Yes, fixing rust on your car is entirely possible, especially when addressed early. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the detrimental effects of rust and offer comprehensive solutions to tackle it head-on, preserving your vehicle’s integrity and appearance. With the right tools and techniques, rust removal becomes a manageable task, ensuring your car remains in top condition for years to come. Explore our range of automotive repair tools designed to efficiently eliminate rust and protect your vehicle from further corrosion.
1. Understanding Car Rust: Types and Identification
Identifying the type and severity of rust on your car is the first crucial step in determining the best course of action. Rust manifests in various forms, each requiring a specific approach for effective treatment. The three primary types of car rust are surface rust, scale rust, and penetrating rust. Understanding these distinctions helps in choosing the appropriate tools and methods for repair, which CARDIAGTECH.NET can assist you with.
1.1. Surface Rust
Surface rust is the initial stage of corrosion, affecting only the top layer of the metal surface. It commonly occurs due to minor scratches or paint damage that exposes the metal to environmental elements.
- What it looks like: It appears as small, reddish-brown spots on the car’s surface.
- How to address it: Surface rust is typically easy to fix and involves sanding down the affected area, applying a rust converter, and then repainting.
1.2. Scale Rust
When surface rust is left untreated, it progresses to scale rust, penetrating deeper into the metal. This type of rust weakens the metal as it corrodes, causing it to flake off.
- What it looks like: Scale rust presents as flaking and bubbling paint around the affected areas.
- How to address it: Repairing scale rust requires more aggressive methods, such as using a wire brush or grinder to remove the rust, followed by treating the area with a rust inhibitor and applying body filler if necessary.
1.3. Penetrating Rust
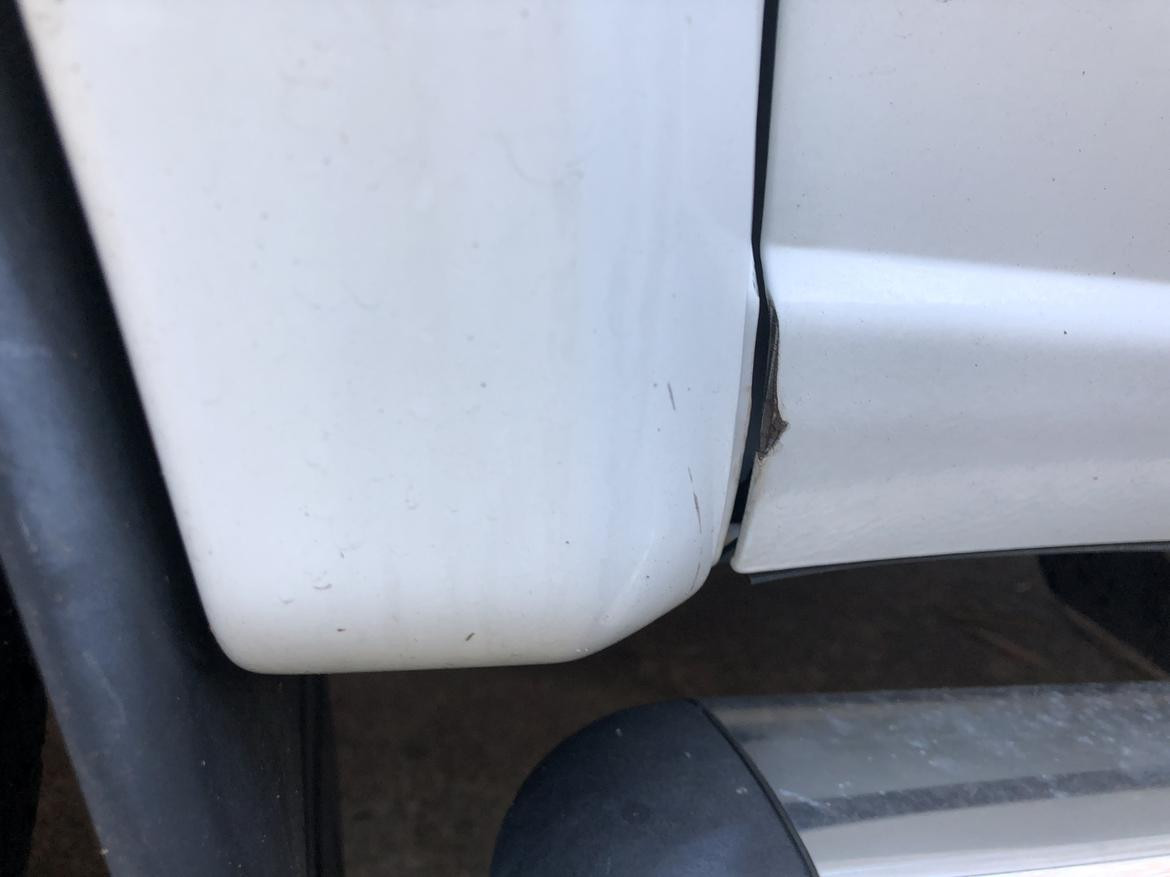
Penetrating rust is the most severe form of corrosion, where rust has eaten completely through the metal, compromising the car’s structural integrity.
- What it looks like: This type of rust is characterized by holes and structural damage in the body panels or other metal parts.
- How to address it: Fixing penetrating rust often involves cutting out the damaged section and welding in a new piece of metal. In some cases, the damage may be too extensive, making the repair uneconomical.
2. The Process of Fixing Rust on a Car: A Step-by-Step Guide
Fixing rust on a car involves a detailed process that, when done correctly, can significantly extend the life of your vehicle. The key is to address the rust promptly and thoroughly. Working in a well-ventilated area is essential to avoid inhaling harmful fumes from primers, paints, and clear coats. Always wear safety gear to protect yourself from dust and chemicals. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to fix rust on a car, with insights on how CARDIAGTECH.NET can equip you with the necessary tools.
2.1. Assessing the Damage
The first step in fixing rust on a car is to accurately assess the extent of the damage. Surface rust can often be remedied with simple treatments, while deeper rust may necessitate more extensive repairs or even panel replacements.
- Surface Rust: If the rust is only on the surface, the repair is usually straightforward.
- Deeper Rust: If the rust has penetrated deeper, more intensive methods will be required.
2.2. Preparing the Area
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful rust repair. Start by washing the area with soap and water to remove any dirt and grime. Dry the area thoroughly to ensure no moisture is trapped during the repair process.
- Cleaning: Use a high-quality car wash soap for best results.
- Protection: Apply painter’s tape and plastic sheeting to cover the surrounding areas, protecting them from dust and overspray.
2.3. Removing the Rust
The next step involves removing the rust using appropriate tools. The method you choose will depend on the severity of the rust.
- Sandpaper: For surface rust, start with coarse-grit sandpaper and gradually move to finer grits.
- Wire Brush or Grinder: For more stubborn rust, a wire brush or grinder may be necessary. Ensure you remove all traces of rust to prevent it from spreading.
- Power Tools: A power sander or grinder can be used for larger areas, but exercise caution to avoid damaging the surrounding metal.
2.4. Applying a Rust Inhibitor
After removing the rust, apply a rust inhibitor, also known as a rust converter. This chemical treatment neutralizes any remaining rust and prevents it from spreading.
- Application: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the best results.
- Drying Time: Allow the rust inhibitor to dry completely before moving on to the next step.
2.5. Priming the Area
Once the rust inhibitor is dry, apply an automotive primer to the bare metal. Primer helps the paint adhere better and provides an additional protective layer.
- Application: Apply the primer in thin, even coats.
- Drying Time: Let the primer dry completely before sanding it lightly with fine-grit sandpaper for a smooth finish.
2.6. Addressing Holes with Body Filler
If removing the rust leaves a hole in the sheet metal, you’ll need to use body filler.
- Primer Application: First, apply primer to the area around the hole and let it dry.
- Body Filler Application: Fill in the hole using body filler according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Shaping: Try to shape the body filler to match the contour of the panel.
- Hardening: Allow the body filler to harden completely before sanding it down for a smooth finish.
2.7. Painting the Area
Apply touch-up paint that matches your car’s paint code. Achieving a seamless finish requires patience and attention to detail.
- Thin Coats: Use thin, even coats to avoid drips and ensure a smooth finish.
- Drying Time: Allow each coat to dry before applying the next one.
- Multiple Coats: Multiple thin coats are better than one thick coat for even coverage.
2.8. Applying the Clear Coat
Once the paint is dry, apply a clear coat to protect the new paint and blend it with the surrounding area.
- Application: Apply the clear coat in thin, even coats.
- Drying Time: Allow the clear coat to dry completely before moving on to the final steps.
2.9. Buffing and Polishing
The final steps involve buffing and polishing the area to blend the new paint with the existing finish.
- Buffing: Use a rubbing compound to buff the area, smoothing out any imperfections.
- Polishing: Follow up with a polishing compound to restore the shine and blend the repair seamlessly with the surrounding paint.
3. Essential Tools and Equipment for Rust Repair
Having the right tools and equipment is crucial for effective rust repair. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality tools designed to make the rust removal process easier and more efficient. Here are some essential tools and equipment you’ll need:
- Sandpaper (various grits): Used for removing surface rust and smoothing the repaired area.
- Wire brush or grinder: Ideal for removing more stubborn rust.
- Rust converter: Chemically neutralizes rust and prevents it from spreading.
- Primer: Helps paint adhere to the metal surface and provides a protective layer.
- Touch-up paint: Matches your car’s paint code for a seamless finish.
- Clear coat: Protects the new paint and blends it with the surrounding area.
- Masking tape and plastic sheeting: Protects surrounding areas from dust and overspray.
- Safety gear (gloves, goggles, mask): Essential for protecting yourself from dust and chemicals.
- Body filler: Used to fill in holes left by severe rust damage.
- Sanding block: Provides a flat surface for sanding, ensuring an even finish.
- Rubbing and polishing compounds: Used for buffing and polishing the repaired area to restore shine.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of these tools, ensuring you have everything you need for a professional-quality rust repair. Our products are selected for their durability and effectiveness, helping you achieve the best possible results.
4. Is Car Rust Permanent? Understanding the Longevity of Repairs
Car rust is not necessarily permanent, but its effects can be long-lasting if not treated properly. The extent to which rust can be removed and the vehicle restored depends on the severity of the rust and how quickly it’s treated. Regular inspections and maintenance can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems, and CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the tools for these inspections.
4.1. Factors Influencing Repair Longevity
Several factors influence how long a rust repair will last:
- Severity of the Rust: Minor surface rust is easier to treat and prevent from recurring compared to penetrating rust.
- Quality of Repair: A thorough and well-executed repair will last longer than a quick fix.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to salt, moisture, and other corrosive elements can accelerate the return of rust.
- Preventative Measures: Regular cleaning, waxing, and rustproofing can significantly extend the life of the repair.
4.2. Professional Assessment
If you’re unsure about the extent of the rust damage or the best course of action, it’s always a good idea to seek a professional assessment. A trusted body shop can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most effective repair solutions.
- Detailed Inspection: Professionals use specialized equipment to thoroughly inspect the vehicle for rust and structural damage.
- Expert Advice: They can advise you on the best repair options based on the severity of the rust and the overall condition of the vehicle.
5. The Safety Implications of Driving a Car with Rust
Driving a car with a rusted frame can pose significant safety hazards, especially if the corrosion is severe. Rust weakens the structural integrity of the vehicle, making it more susceptible to damage in an accident. Regular inspections and timely repairs are crucial for maintaining vehicle safety.
5.1. Frame Integrity
A rusted frame compromises the vehicle’s ability to protect occupants in a collision. The frame provides the primary support and protection, and when it’s weakened by rust, it can fail to perform as intended.
- Structural Weakness: Rust can reduce the frame’s ability to absorb impact energy.
- Increased Risk of Failure: A rusted frame is more likely to break or collapse in an accident.
5.2. Component Safety
Rust can also affect other critical components of the vehicle, such as the suspension, brakes, and fuel lines.
- Suspension Damage: Rusted suspension components can lead to instability and reduced handling.
- Brake Line Corrosion: Rust on brake lines can cause leaks, leading to brake failure.
- Fuel Line Issues: Rusted fuel lines can leak, posing a fire hazard.
5.3. Professional Inspection
If you suspect your car has significant rust damage, it’s essential to have it inspected by a professional. Body shop technicians can thoroughly assess the vehicle and determine whether it’s safe to drive.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Technicians use lifts to inspect the undercarriage and frame from all angles.
- Expert Recommendations: They can advise you on whether welding or other repairs can fix the frame or if it’s better to sell the car for scrap.
6. How Long Will A Rusty Car Last?
The lifespan of a rusty car depends on several factors, including the extent and location of the rust, as well as how quickly it’s treated. Addressing rust promptly can significantly extend the life of your vehicle.
6.1. Early Intervention
If you catch rust early and address it promptly, you can prevent it from spreading and causing more extensive damage. Regular maintenance and inspections are key to identifying rust in its early stages.
6.2. Severity of Rust
Cars with minor surface rust that is treated quickly can last for many years. However, cars with severe frame rust may not be safe to drive and may need to be scrapped.
6.3. Spread of Rust
Rust will spread to other parts of the car if left untreated. What starts as a small problem can quickly develop into a major issue, potentially compromising the vehicle’s structural integrity.
6.4. Cost of Repairs
Consider the cost of repairs when deciding whether to fix a rusty car. Extensive rust damage can be expensive to repair, and in some cases, it may be more cost-effective to replace the vehicle.
6.5. Professional Assessment
Consulting with a professional can provide valuable insights into the condition of the car and the potential for future rust-related issues. A mechanic can assess the extent of the rust damage and provide an estimate for repairs.
7. Determining the Threshold: How Much Rust Is Too Much?
When considering buying a used car, it’s essential to assess the amount of rust present. Several factors come into play when determining whether the rust is manageable or a deal-breaker.
7.1. Age, Mileage, and Price
When evaluating a used car, weigh the age, mileage, and price carefully. A 15-year-old car with 200,000+ miles and significant rust is less desirable than a newer model with less rust.
- Age: Older cars are more likely to have rust due to years of exposure to the elements.
- Mileage: Higher mileage cars may have more wear and tear, including rust damage.
- Price: The price should reflect the condition of the car, including any rust issues.
7.2. Type of Rust
Understanding the different types of rust is crucial for assessing the severity of the problem.
- Surface Rust: This is the easiest and most affordable type of rust to fix.
- Scale Rust: This type of rust is more difficult to repair, as it exposes the bare metal under the paint.
- Penetrating Rust: This is the most severe type of rust, as it transforms the car’s steel into iron oxide, making it brittle and causing holes to form.
7.3. Location of the Rust
The location of the rust is another critical factor to consider.
- Exhaust and Fuel Tank Supports: Corroded supports for the exhaust or fuel tank are significant safety hazards.
- Underframe: Rust on the underframe can negatively impact your ability to drive safely.
- Body Panels: Rusted body panels can endanger you and your passengers in case of an accident.
- Water and Exhaust Leaks: Penetrating rust can allow water or exhaust to enter the vehicle, posing health and safety risks.
7.4. Structural Integrity
Rust that affects the structural integrity of the vehicle is a major concern. Always have the car inspected by a professional to assess the extent of the damage.
- Frame Damage: Rust on the frame can weaken the car’s ability to withstand impacts.
- Component Damage: Rust on critical components like suspension and brakes can compromise their functionality.
8. Preventing Rust on Your Car: Proactive Strategies
Preventing rust is always better than trying to fix it. Taking proactive steps to protect your car from rust can save you time and money in the long run. CARDIAGTECH.NET supports your preventative efforts with a range of protective products.
8.1. Regular Cleaning and Waxing
Washing and waxing your vehicle regularly not only makes it look great but also protects against rust.
- Washing: Wash your car, including the underbody, regularly, especially during winter to remove road salt.
- Waxing: Apply a coat of wax 2-4 times a year to create a protective barrier against moisture and salt.
8.2. Early Rust Detection
Catching rust in its early stages is crucial for preventing more extensive damage.
- Regular Inspections: Check your wheel wells and bumpers for rust spots whenever you rotate your tires.
- Rinse Dirt: Rinse dirt off with a garden hose and inspect the area with a flashlight.
8.3. Mud Flaps
Consider installing mud flaps to protect against water, snow, salt, and gravel, all of which can contribute to rust.
- Protection: Mud flaps provide an additional barrier against road debris.
- Prevention: They help prevent damage to the car’s paint and underbody.
8.4. Paint Protection
Scratches and chips in your car’s paint can leave it vulnerable to rust.
- Scratch Repair: Repair any scratches or chips in the paint as soon as possible.
- Professional Repair: If the scratch exposes bare metal, have it repaired by a professional to prevent rust from forming.
8.5. Gentle Car Care
Treating your car with care can help prevent the nicks and scratches that eventually lead to rust.
- Snow Removal: Use a foam brush without stiff bristles to remove snow.
- Surface Protection: Avoid placing heavy items on the car that could scratch the paint.
9. The Economics of Rust Repair: Is It Worth the Investment?
Deciding whether to repair rust on your car involves considering several economic factors. Evaluate the cost of repairs versus the car’s overall value and condition.
9.1. Repair Costs
The cost of rust repair can vary depending on the extent of the damage and the methods used.
- Surface Rust: Minor surface rust repairs are typically inexpensive.
- Extensive Damage: Major rust repairs, such as welding in new panels, can be costly.
9.2. Vehicle Value
Consider the overall value of your car when deciding whether to invest in rust repair.
- High-Value Cars: For newer or more valuable cars, rust repair is often a worthwhile investment.
- Low-Value Cars: For older, less valuable cars, the cost of rust repair may exceed the car’s value.
9.3. Long-Term Costs
Think about the long-term costs of neglecting rust repair.
- Spreading Rust: Untreated rust will continue to spread, leading to more extensive and costly repairs in the future.
- Safety Issues: Rust can compromise the safety of the vehicle, potentially leading to accidents and injuries.
9.4. Professional Assessment
Obtain a professional assessment from a trusted mechanic to determine the extent of the rust damage and the estimated cost of repairs.
- Detailed Quote: A mechanic can provide a detailed quote outlining the necessary repairs and associated costs.
- Expert Advice: They can advise you on whether the repairs are worth the investment based on the car’s condition and value.
10. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Rust Prevention and Repair
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges car owners face when dealing with rust. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of tools, equipment, and products to help you prevent and repair rust effectively.
10.1. High-Quality Tools
We provide high-quality tools designed to make rust removal easier and more efficient.
- Sanders and Grinders: Our selection of sanders and grinders allows you to remove rust quickly and effectively.
- Wire Brushes: We offer a variety of wire brushes for removing rust from hard-to-reach areas.
10.2. Rust Converters and Inhibitors
Our rust converters and inhibitors help neutralize rust and prevent it from spreading.
- Chemical Treatments: We offer a range of chemical treatments that effectively convert rust into a stable compound.
- Protective Coatings: Our protective coatings provide a barrier against moisture and salt, preventing future rust formation.
10.3. Body Repair Products
We offer a variety of body repair products for filling in holes and repairing damaged panels.
- Body Fillers: Our body fillers are easy to use and provide a durable, long-lasting repair.
- Primers and Paints: We offer a range of primers and paints to match your car’s color and provide a seamless finish.
10.4. Preventative Products
We offer a range of preventative products to help protect your car from rust.
- Waxes and Sealants: Our waxes and sealants provide a protective barrier against moisture and salt.
- Undercoating Sprays: Our undercoating sprays protect the underbody of your car from rust and corrosion.
10.5. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experts is available to provide advice and support on rust prevention and repair.
- Product Recommendations: We can recommend the best products for your specific needs.
- Repair Tips: We offer tips and advice on how to effectively repair rust on your car.
11. Real-World Examples: Success Stories in Rust Repair
Hearing about successful rust repair projects can provide inspiration and confidence. Here are a few real-world examples of how car owners have tackled rust and restored their vehicles to excellent condition.
11.1. Restoring a Classic Car
One classic car enthusiast purchased a vintage vehicle with significant rust damage. By using high-quality tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET and following a meticulous repair process, they were able to restore the car to its former glory.
- Detailed Sanding: They used various grits of sandpaper to remove surface rust and scale rust.
- Panel Replacement: They cut out and replaced severely rusted panels with new metal.
- Protective Coatings: They applied rust converters and protective coatings to prevent future rust formation.
11.2. Saving a Daily Driver
A car owner noticed rust forming on their daily driver and took immediate action to prevent further damage.
- Early Detection: They regularly inspected their car and caught the rust in its early stages.
- DIY Repair: They used rust converters and touch-up paint from CARDIAGTECH.NET to repair the affected areas.
- Preventative Measures: They washed and waxed their car regularly to protect it from future rust formation.
11.3. Overcoming Severe Frame Rust
A truck owner discovered severe rust on their vehicle’s frame and sought professional assistance.
- Professional Inspection: They had the frame inspected by a qualified mechanic.
- Welding Repairs: The mechanic welded in new sections of metal to repair the rusted frame.
- Protective Coatings: They applied protective coatings to the frame to prevent future rust formation.
12. DIY vs. Professional Rust Repair: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to tackle rust repair yourself or hire a professional depends on several factors, including your skill level, the extent of the damage, and your budget.
12.1. DIY Rust Repair
DIY rust repair can be a cost-effective option for minor rust issues.
- Cost Savings: You can save money on labor costs by doing the work yourself.
- Learning Experience: DIY repair can be a rewarding learning experience.
- Tool Investment: You’ll need to invest in the necessary tools and equipment.
12.2. Professional Rust Repair
Professional rust repair is often the best option for more extensive damage or if you lack the necessary skills and tools.
- Expertise: Professionals have the knowledge and experience to properly assess and repair rust damage.
- Quality Results: They can achieve high-quality results that are both durable and aesthetically pleasing.
- Warranty: Professional repairs often come with a warranty, providing peace of mind.
12.3. Assessing Your Skills
Evaluate your skills and comfort level before deciding whether to tackle rust repair yourself.
- Welding: If the rust damage requires welding, it’s best to hire a professional.
- Painting: Achieving a seamless paint finish requires skill and experience.
12.4. Budget Considerations
Consider your budget when deciding whether to DIY or hire a professional.
- DIY Costs: Factor in the cost of tools, materials, and any potential mistakes.
- Professional Costs: Obtain quotes from multiple shops to compare prices and services.
13. Exploring Advanced Rust Repair Techniques
For severe rust damage, advanced repair techniques may be necessary. These techniques require specialized skills and equipment.
13.1. Panel Replacement
Replacing entire panels is often the best option for severely rusted areas.
- Cutting and Welding: This involves cutting out the rusted panel and welding in a new one.
- Precision Fit: The new panel must be precisely fitted to ensure a seamless repair.
13.2. Media Blasting
Media blasting involves using abrasive materials to remove rust and corrosion.
- Effective Removal: This technique can effectively remove rust from hard-to-reach areas.
- Surface Preparation: Media blasting also prepares the surface for painting and protective coatings.
13.3. Rust Encapsulation
Rust encapsulation involves sealing the rusted area to prevent further corrosion.
- Protective Coatings: Specialized coatings are applied to encapsulate the rust and prevent it from spreading.
- Long-Term Protection: This technique provides long-term protection against rust.
13.4. Galvanic Corrosion Treatment
Galvanic corrosion treatment involves using electrical currents to prevent rust formation.
- Electrochemical Process: This technique uses an electrochemical process to inhibit corrosion.
- Advanced Technology: Galvanic corrosion treatment is an advanced technology that requires specialized equipment.
14. The Impact of Climate and Environment on Car Rust
Climate and environmental conditions play a significant role in the formation and spread of car rust. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to protect your vehicle.
14.1. Coastal Regions
Cars in coastal regions are more susceptible to rust due to the high salt content in the air.
- Saltwater Exposure: Saltwater can accelerate the corrosion process.
- Protective Measures: Regular washing and waxing are essential for protecting cars in coastal areas.
14.2. Cold Climates
Cold climates often involve the use of road salt, which can accelerate rust formation.
- Road Salt: Salt used to melt ice and snow can damage the car’s paint and underbody.
- Underbody Washing: Regular underbody washing is crucial for removing road salt.
14.3. Humid Regions
Humid regions provide a favorable environment for rust formation.
- Moisture: Moisture promotes the corrosion process.
- Ventilation: Ensuring proper ventilation can help reduce moisture buildup.
14.4. Industrial Areas
Industrial areas often have high levels of pollutants that can contribute to rust formation.
- Air Pollution: Pollutants can damage the car’s paint and protective coatings.
- Protective Coatings: Applying protective coatings can help shield the car from pollutants.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Car Rust
Addressing common questions about car rust can help you better understand the issue and take appropriate action.
15.1. What Causes Car Rust?
Car rust is caused by the oxidation of iron, which occurs when iron is exposed to oxygen and moisture.
15.2. How Can I Tell If My Car Has Rust?
Look for small, reddish-brown spots or flaking paint on the car’s surface. Inspect the underbody and wheel wells for signs of corrosion.
15.3. Is It Safe to Drive a Car with Rust?
Driving a car with severe rust can be unsafe, as it can compromise the vehicle’s structural integrity.
15.4. Can I Fix Car Rust Myself?
Minor surface rust can often be repaired DIY, but more extensive damage may require professional repair.
15.5. How Much Does It Cost to Fix Car Rust?
The cost of rust repair varies depending on the extent of the damage and the methods used.
15.6. How Can I Prevent Car Rust?
Regular washing, waxing, and protective coatings can help prevent car rust.
15.7. What Are the Best Tools for Repairing Car Rust?
Essential tools include sandpaper, wire brushes, rust converters, and protective coatings. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of high-quality tools for rust repair.
15.8. How Often Should I Inspect My Car for Rust?
Inspect your car for rust at least twice a year, especially before and after winter.
15.9. Does Car Insurance Cover Rust Repair?
Car insurance typically does not cover rust repair, as it is considered a form of normal wear and tear.
15.10. Is Rust a Sign of a Poorly Maintained Car?
Rust is often a sign of neglect, but it can also occur on well-maintained cars in certain climates and environments.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Rust on Your Car
Addressing rust on your car is essential for maintaining its appearance, safety, and value. Whether you choose to tackle rust repair yourself or seek professional assistance, taking proactive steps to prevent and repair rust can significantly extend the life of your vehicle. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing you with the tools, equipment, and knowledge you need to keep your car in top condition.
Ready to take control of rust on your car? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and high-quality rust prevention and repair products. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your car looking and performing its best.
Remember, dealing with rust promptly and effectively can save you time, money, and hassle in the long run. Trust CARDIAGTECH.NET to be your partner in rust prevention and repair.