How Much Does It Cost to Fix a Car Alternator? Expert Guide
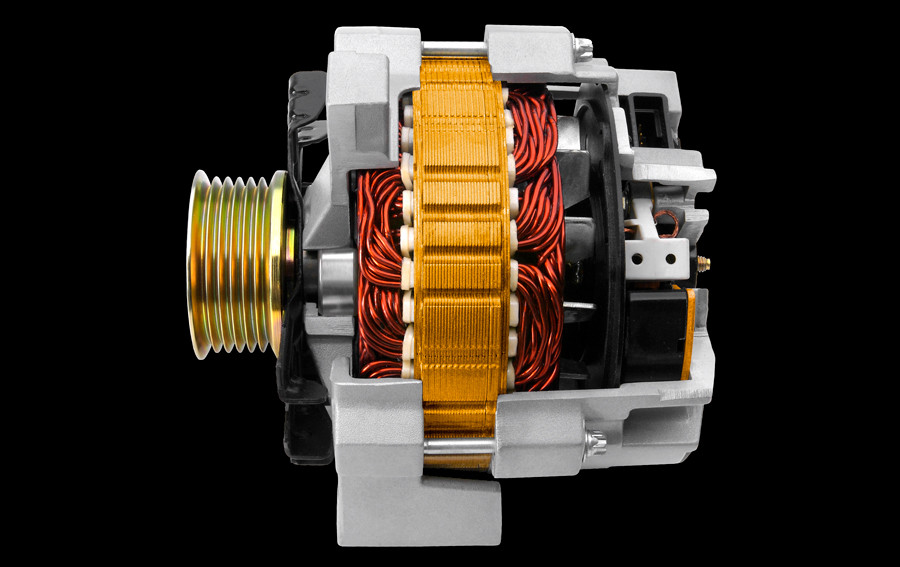
Are you wondering, “How much does it cost to fix a car alternator?” The cost to fix a car alternator typically ranges from $300 to $800, encompassing both parts and labor. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you understand all the factors influencing this cost, so you can make an informed decision and potentially save money. Knowing the signs of a failing alternator, understanding the replacement process, and choosing the right tools can extend its lifespan and keep your car running smoothly with our auto repair solutions. BMW Diagnostic Price
1. What Factors Influence the Cost of Alternator Repair?
How much does it cost to fix a car alternator? Several factors influence the final bill, including the car’s make and model, the quality of the replacement part, and the labor costs in your area. Different car models have different alternators, and some are more expensive than others.
- Vehicle Make and Model: High-end or luxury vehicles often have more expensive alternators. According to a 2022 report by RepairPal, the average cost for an alternator replacement on a Toyota Camry is about $500, while for a BMW 3 Series, it can be closer to $700.
- Alternator Type (New vs. Remanufactured): A new alternator will typically cost more than a remanufactured one. Remanufactured alternators can be a cost-effective option, but they may not last as long as new ones.
- Labor Costs: Labor rates vary widely by region. According to data from AAA, the average labor cost for auto repairs in 2023 ranged from $80 to $200 per hour, depending on the shop’s location and expertise.
- Additional Repairs: Sometimes, other components like the serpentine belt or battery cables may need replacement, adding to the overall cost.
 Car Alternator Replacement Cost Factors
Car Alternator Replacement Cost Factors
2. What is the Average Cost to Replace a Car Alternator?
What are the typical costs associated with replacing a car alternator? The average cost to replace a car alternator can range from $300 to $800, including both parts and labor. However, this figure can vary significantly based on several factors.
- Parts Cost: The alternator itself can range from $150 to $500, depending on the make and model of the vehicle and whether you choose a new or remanufactured unit.
- Labor Cost: Labor costs typically range from $150 to $300, depending on the complexity of the job and the hourly rate of the mechanic.
- Additional Costs: There may be additional costs for diagnosing the problem, replacing the serpentine belt (if necessary), or addressing any related issues.
A study by AutoMD found that the average alternator replacement cost in the United States in 2023 was $488. The study also noted that costs can be higher in urban areas and for luxury vehicles.
3. New vs. Remanufactured Alternators: Which is Best for Your Budget?
Is it better to choose a new or remanufactured alternator when fixing your car? New alternators offer reliability and a longer lifespan, while remanufactured options provide a budget-friendly alternative without sacrificing too much on quality.
- New Alternators: These are brand new units directly from the manufacturer. They offer the best performance and reliability, but come at a higher price.
- Pros: Longer lifespan, higher reliability, and often better warranty coverage.
- Cons: Higher upfront cost.
- Remanufactured Alternators: These are used alternators that have been rebuilt with new components. They are tested to ensure they meet original performance specifications.
- Pros: Lower cost, environmentally friendly (reusing parts), and often come with a warranty.
- Cons: May not last as long as new alternators, potential for hidden issues.
According to a report by the Motor Information Systems, remanufactured parts can save consumers an average of 30% compared to new parts. However, the report also notes that the lifespan of remanufactured parts can vary.
4. DIY vs. Professional Alternator Replacement: Which Should You Choose?
Should you tackle alternator replacement yourself or hire a professional mechanic? DIY alternator replacement can save on labor costs but requires mechanical knowledge and the right tools. Professional installation ensures expertise and reduces the risk of mistakes.
- DIY Replacement: If you have experience with car repairs and own the necessary tools, you can save on labor costs by replacing the alternator yourself.
- Pros: Cost savings on labor, convenience of doing it on your own schedule.
- Cons: Requires mechanical knowledge, risk of improper installation, voiding warranty.
- Professional Replacement: Hiring a professional mechanic ensures the job is done correctly and often comes with a warranty on parts and labor.
- Pros: Expertise, warranty coverage, and reduced risk of errors.
- Cons: Higher cost due to labor fees.
A survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that DIY repairs have a higher rate of errors compared to professional repairs, which can lead to additional costs in the long run.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Car Alternator
Can you walk me through the steps of replacing a car alternator? Replacing a car alternator involves disconnecting the battery, removing the old alternator, installing the new one, and reconnecting everything. Here’s a detailed guide to help you through the process.
Step 1: Gather Your Tools and Supplies
- New or remanufactured alternator
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- Screwdrivers
- Multimeter
- Battery terminal cleaner
- Gloves
- Safety glasses
Step 2: Disconnect the Battery
- Locate the battery in your vehicle.
- Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (-) terminal.
- Remove the negative cable and tuck it away from the battery.
- Repeat for the positive (+) terminal.
Step 3: Locate the Alternator
- Consult your vehicle’s repair manual to find the location of the alternator.
- It is typically located at the front of the engine and is driven by the serpentine belt.
Step 4: Disconnect Electrical Connections
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the alternator.
- There may be one or more connectors, depending on the vehicle.
- Remove any wiring harnesses or clips that are attached to the alternator.
Step 5: Remove the Serpentine Belt
- Locate the tensioner pulley on the serpentine belt.
- Use a wrench or socket to relieve the tension on the belt.
- Remove the belt from the alternator pulley.
Step 6: Remove the Alternator Mounting Bolts
- Use a socket or wrench to remove the mounting bolts that secure the alternator to the engine.
- There may be two or more bolts, depending on the vehicle.
Step 7: Remove the Old Alternator
- Carefully remove the old alternator from the vehicle.
- Note the orientation of the alternator for reinstallation.
Step 8: Install the New Alternator
- Install the new alternator in the same orientation as the old one.
- Tighten the mounting bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
Step 9: Reconnect the Serpentine Belt
- Route the serpentine belt around the alternator pulley and other pulleys.
- Relieve the tension on the tensioner pulley and secure the belt.
Step 10: Reconnect Electrical Connections
- Reconnect the electrical connectors to the alternator.
- Ensure that all connectors are securely attached.
Step 11: Reconnect the Battery
- Reconnect the positive (+) battery cable to the positive terminal.
- Tighten the nut securely.
- Reconnect the negative (-) battery cable to the negative terminal.
- Tighten the nut securely.
Step 12: Start the Vehicle and Test the Alternator
- Start the vehicle and let it run for a few minutes.
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the battery terminals.
- The voltage should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging properly.
6. Common Symptoms of a Failing Alternator
What are the telltale signs that your alternator is about to fail? Recognizing the symptoms of a failing alternator early can save you from unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Here are some common indicators:
- Dim or Flickering Lights: One of the first signs of a failing alternator is dim or flickering headlights, dashboard lights, or interior lights.
- Battery Light On: The battery light on your dashboard may illuminate, indicating a charging system problem.
- Slow or Non-Starting Engine: If the alternator is not charging the battery properly, you may experience difficulty starting the engine.
- Electrical Problems: Other electrical components, such as power windows, radio, or air conditioning, may function erratically or stop working altogether.
- Strange Noises: A failing alternator may produce a whining or grinding noise.
- Stalling: In some cases, a failing alternator can cause the engine to stall.
According to a survey by the Car Care Council, electrical system failures are a leading cause of vehicle breakdowns.
7. How to Test Your Car Alternator
How can you check if your car alternator is working correctly? Testing your car alternator can help you determine if it’s functioning correctly. Here’s how to do it using a multimeter:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals while the engine is running. The voltage should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Load Test: Use a load tester to simulate a heavy electrical load on the alternator. The voltage should remain within the specified range under load.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Your Alternator with a Multimeter:
- Gather Your Tools:
- Multimeter
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Prepare the Vehicle:
- Park the vehicle on a level surface.
- Engage the parking brake.
- Open the hood and locate the battery.
- Set Up the Multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting.
- The range should be set to 20 volts or higher.
- Connect the Multimeter:
- Connect the red (positive) lead of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Connect the black (negative) lead of the multimeter to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
- Read the Battery Voltage (Engine Off):
- Read the voltage on the multimeter display.
- A fully charged battery should read approximately 12.6 volts.
- If the voltage is below 12 volts, the battery may be discharged or faulty.
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and let it idle.
- Read the Battery Voltage (Engine Running):
- Read the voltage on the multimeter display again.
- With the engine running, the voltage should increase to between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- This indicates that the alternator is charging the battery.
- Turn on Accessories:
- Turn on the headlights, air conditioning, and other electrical accessories.
- Read the Battery Voltage (Engine Running with Accessories):
- Read the voltage on the multimeter display again.
- The voltage should remain above 13 volts, even with the accessories turned on.
- If the voltage drops below 13 volts, the alternator may not be able to keep up with the electrical load.
- Interpret the Results:
- Voltage between 13.5 and 14.5 volts (engine running): The alternator is functioning properly.
- Voltage below 13.5 volts (engine running): The alternator may be failing or not charging properly.
- Voltage above 14.5 volts (engine running): The alternator may be overcharging the battery, which can damage it.
According to a study by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), regular testing of the charging system can help prevent costly breakdowns.
8. Maintaining Your Alternator to Prolong Its Lifespan
How can you extend the life of your car’s alternator? Proper maintenance can significantly extend the life of your car’s alternator. Here are some tips to keep it in top condition:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the alternator for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
- Proper Battery Maintenance: Ensure your battery is properly maintained and charged. A weak or damaged battery can put extra strain on the alternator.
- Avoid Overloading the Electrical System: Avoid using too many electrical accessories at once, as this can overload the alternator.
- Check the Serpentine Belt: Inspect the serpentine belt regularly and replace it if it shows signs of wear or damage.
- Keep the Engine Clean: Keep the engine compartment clean to prevent dirt and debris from damaging the alternator.
9. What are the Best Tools for Alternator Repair?
What tools are essential for alternator repair, and where can you find them? Having the right tools can make alternator repair easier and more efficient. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality tools for auto repair.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set is essential for removing and installing alternator bolts.
- Wrench Set: Wrenches are needed for various tasks, such as adjusting the serpentine belt tensioner.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used to test the alternator’s voltage output.
- Battery Terminal Cleaner: A battery terminal cleaner helps remove corrosion from the battery terminals.
- Serpentine Belt Tool: A serpentine belt tool makes it easier to remove and install the serpentine belt.
Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Auto Repair Tools?
- High-Quality Tools: We offer a wide selection of high-quality tools from trusted brands.
- Competitive Prices: Our prices are competitive, so you can get the tools you need without breaking the bank.
- Expert Advice: Our team of experts can help you choose the right tools for your specific needs.
- Convenient Online Ordering: You can order tools online from the comfort of your own home.
- Fast Shipping: We offer fast shipping so you can get your tools quickly.
Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and to purchase your auto repair tools today.
10. How Does Location Affect Alternator Repair Costs?
Does your geographic location influence the price of alternator repair? The cost of alternator repair can vary significantly depending on your location. Labor rates, parts availability, and local taxes all play a role.
- Urban vs. Rural Areas: Labor rates are typically higher in urban areas due to the higher cost of living.
- Regional Differences: Some regions may have higher parts costs due to supply and demand.
- Local Taxes: Sales tax rates can vary widely by state and county, affecting the overall cost of repair.
According to a report by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average hourly wage for automotive technicians in metropolitan areas is higher than in non-metropolitan areas.
11. Insurance Coverage for Alternator Repair: What to Expect
Will your insurance cover the cost of alternator repair or replacement? Most standard auto insurance policies do not cover alternator repair or replacement, as it is considered a maintenance issue. However, if the alternator failure is the result of an accident or covered event, your insurance may provide coverage.
- Maintenance vs. Accident: Auto insurance typically covers damage resulting from accidents, collisions, or other covered events. Regular maintenance items, such as alternator replacement, are usually not covered.
- Warranty Coverage: If your vehicle is still under warranty, the alternator may be covered. Check your warranty documentation for details.
- Extended Warranty: An extended warranty or service contract may cover alternator repair or replacement, depending on the terms of the agreement.
It’s essential to review your insurance policy and warranty documentation to understand what is covered and what is not.
12. What is the Warranty on a New or Remanufactured Alternator?
How long does the warranty typically last on a new or remanufactured alternator? The warranty on a new or remanufactured alternator can vary depending on the manufacturer and vendor. New alternators typically come with a longer warranty period than remanufactured units.
- New Alternators: New alternators often come with a warranty of 1 to 3 years or more.
- Remanufactured Alternators: Remanufactured alternators may have a warranty of 3 months to 1 year.
- Warranty Coverage: The warranty typically covers defects in materials and workmanship. It may not cover damage resulting from improper installation or use.
Be sure to read the warranty documentation carefully to understand the terms and conditions.
13. Can a Bad Alternator Drain My Car Battery?
Can a faulty alternator cause your car battery to drain unexpectedly? Yes, a bad alternator can drain your car battery. When the alternator fails to charge the battery properly, the battery will eventually run out of power.
- Normal Operation: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running.
- Failing Alternator: If the alternator is not producing enough voltage, the battery will not be fully charged, and it may eventually become depleted.
- Parasitic Drain: A failing alternator can also cause a parasitic drain on the battery, where it draws power even when the engine is off.
If you suspect that your alternator is draining your battery, have it tested by a professional mechanic.
14. What Happens If You Don’t Fix a Bad Alternator?
What are the potential consequences of ignoring a failing alternator? Ignoring a bad alternator can lead to several problems, including:
- Dead Battery: The most common consequence of a bad alternator is a dead battery.
- Stalling: A failing alternator can cause the engine to stall.
- Electrical Problems: Other electrical components may function erratically or stop working altogether.
- Damage to Other Components: In some cases, a bad alternator can damage other components, such as the battery or the engine control unit (ECU).
It’s essential to address alternator problems promptly to avoid these issues.
15. How to Find a Reputable Mechanic for Alternator Repair
How can you ensure you’re hiring a trustworthy mechanic for alternator repair? Finding a reputable mechanic for alternator repair can ensure the job is done correctly and at a fair price. Here are some tips:
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or coworkers for recommendations.
- Check Online Reviews: Read online reviews on sites like Yelp, Google, and Angie’s List.
- Look for ASE Certification: Choose a mechanic who is certified by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
- Get a Written Estimate: Get a written estimate before authorizing any repairs.
- Ask Questions: Ask the mechanic questions about their experience, qualifications, and warranty policy.
CARDIAGTECH.NET can also help you find local Preferred Shops in your area that can help you tackle the job.
16. Emergency Alternator Repair: What to Do When It Fails on the Road
What should you do if your alternator fails while you’re driving? If your alternator fails while you’re on the road, here are some steps you can take:
- Pull Over: Pull over to a safe location as soon as possible.
- Turn Off Accessories: Turn off all non-essential accessories, such as the radio, air conditioning, and lights.
- Call for Help: Call for roadside assistance or a tow truck.
- Conserve Power: If you must drive, conserve power by driving slowly and avoiding stop-and-go traffic.
It’s important to have a plan in place for dealing with unexpected breakdowns.
17. Can a Jump Start Damage My Alternator?
Is it safe to jump start your car, or could it harm the alternator? Jump-starting a car can potentially damage the alternator if not done correctly. Follow these precautions to minimize the risk:
- Proper Cables: Use high-quality jumper cables with clean, secure connections.
- Correct Polarity: Ensure the cables are connected to the correct terminals (positive to positive, negative to negative).
- Gradual Charge: Let the charging car run for a few minutes before attempting to start the disabled car.
Repeated jump starts can put stress on the alternator, so it’s essential to address the underlying issue that caused the battery to die.
18. Understanding Alternator Overcharging and Its Effects
What does it mean when an alternator is overcharging, and how can it harm your car? Alternator overcharging can damage your car’s electrical system. Here’s what you need to know:
- Normal Voltage: A healthy alternator should maintain a voltage between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Overcharging: Overcharging occurs when the alternator produces voltage above this range.
- Damage: Overcharging can damage the battery, ECU, and other electrical components.
Symptoms of overcharging include a hot battery, boiling battery acid, and electrical problems.
19. How Does a Car Alternator Work?
Could you explain the basic mechanics of how a car alternator functions? A car alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy to power the vehicle’s electrical system and charge the battery. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Mechanical Energy: The engine turns a pulley connected to the alternator.
- Electromagnetic Induction: The alternator uses electromagnetic induction to generate electricity.
- AC to DC Conversion: The alternator converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) for use by the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Voltage Regulation: The alternator regulates the voltage output to prevent overcharging or undercharging the battery.
Understanding how the alternator works can help you troubleshoot problems and maintain your vehicle.
20. Choosing the Right Alternator for Your Vehicle
How do you select the correct replacement alternator for your specific car model? Choosing the right alternator for your vehicle is essential for proper performance and reliability. Consider the following factors:
- Vehicle Specifications: Match the alternator to your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Amperage Rating: Choose an alternator with the correct amperage rating for your vehicle’s electrical system.
- Mounting Style: Ensure the alternator has the correct mounting style for your vehicle.
- Electrical Connections: Verify that the alternator has the correct electrical connections for your vehicle.
Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or a trusted mechanic for guidance.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Car Alternator Repair
1. How long does it take to replace an alternator?
The labor time to replace an alternator typically ranges from 1 to 3 hours, depending on the vehicle and the complexity of the job.
2. Can I drive with a bad alternator?
It is not recommended to drive with a bad alternator, as it can lead to a dead battery and other electrical problems.
3. How do I know if my alternator is bad?
Common symptoms of a bad alternator include dim or flickering lights, a battery light on, and difficulty starting the engine.
4. What is the difference between an alternator and a generator?
An alternator and a generator both produce electrical energy, but they use different methods. Alternators are more efficient and reliable than generators.
5. Can a bad battery cause the alternator to fail?
Yes, a bad battery can put extra strain on the alternator, leading to premature failure.
6. How often should I replace my alternator?
The lifespan of an alternator can vary, but it typically lasts between 5 and 10 years or 80,000 to 150,000 miles.
7. What is the warranty on a remanufactured alternator?
The warranty on a remanufactured alternator typically ranges from 3 months to 1 year.
8. Can I replace the alternator myself?
If you have experience with car repairs and own the necessary tools, you can replace the alternator yourself. However, it is recommended to have a professional do the job.
9. How much does a new alternator cost?
A new alternator can range from $150 to $500, depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
10. What is a serpentine belt?
The serpentine belt is a long, winding belt that drives various engine components, including the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
Conclusion
Understanding the costs associated with fixing a car alternator, the factors that influence those costs, and how to maintain your alternator can save you time and money. Whether you choose to DIY the repair or hire a professional, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide you with the tools and expertise you need.
For high-quality tools and expert advice, contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET today to explore our wide range of auto repair solutions. Don’t let alternator problems keep you off the road – we’re here to help you get back on track.


