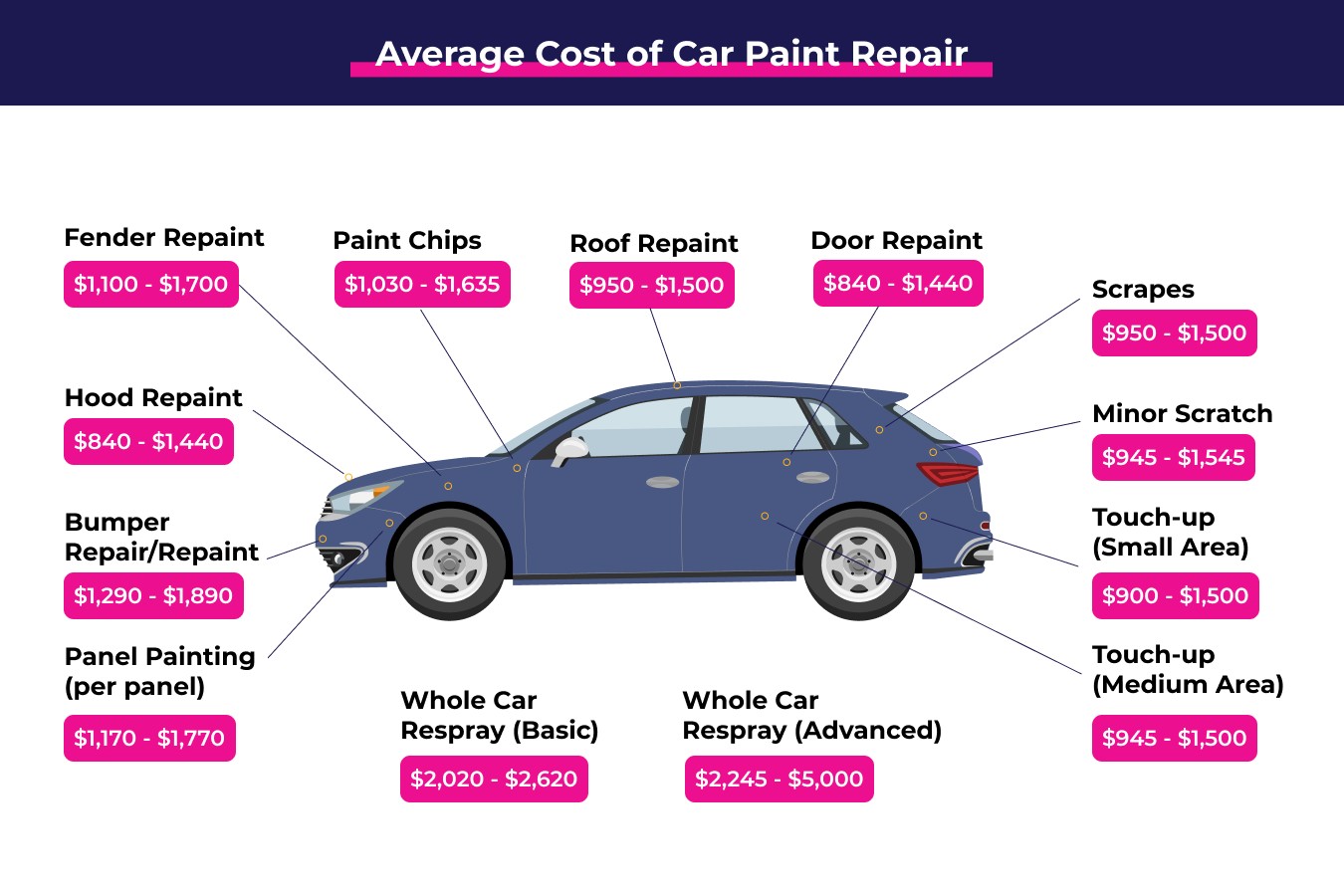
How Much Is It To Fix Heat In A Car?
Is your car’s heater blowing cold air? “How much is it to fix heat in a car?” is a common question for drivers facing chilly commutes. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the discomfort and potential safety concerns of a malfunctioning car heater, and we’re here to guide you through the potential costs and troubleshooting steps. We’ll explore various factors affecting repair expenses and offer insights into keeping your heating system running efficiently, ensuring a warm and comfortable driving experience. Discover budget-friendly options, preventative maintenance tips, and the best diagnostic tools for your car with our expert advice.
1. Understanding Your Car’s Heating System
Before diving into the costs, let’s understand how your car’s heating system works. The heating system relies on the engine’s heat. Coolant absorbs heat from the engine and circulates to the heater core, a small radiator-like component located inside the dashboard. The blower fan then forces air through the heater core, warming it and sending it into the cabin.
1.1. Key Components of the Heating System
Here’s a breakdown of the main parts:
- Thermostat: Regulates engine temperature by controlling coolant flow.
- Heater Core: Transfers heat from the coolant to the air.
- Blower Motor: Forces air through the heater core and into the cabin.
- Coolant: Transfers heat from the engine to the heater core.
- Hoses: Connect the various components and allow coolant to flow.
- Control Panel: Allows you to adjust the temperature and fan speed.
Alt text: Diagram showcasing essential components of a car heating system, including the heater core, blower motor, coolant hoses, and thermostat, emphasizing their roles in maintaining a comfortable cabin temperature.
1.2. Common Causes of Heating Problems
Several factors can cause your car’s heater to stop working. Here are some common culprits:
- Low Coolant: Insufficient coolant levels prevent proper heat transfer.
- Faulty Thermostat: A malfunctioning thermostat can prevent the engine from reaching operating temperature.
- Clogged Heater Core: Debris and sediment buildup can restrict coolant flow.
- Blower Motor Failure: A broken blower motor won’t circulate warm air.
- Leaking Coolant: Leaks can cause low coolant levels and system inefficiency.
- Blend Door Actuator Issues: These control the mix of hot and cold air, and can fail.
2. Factors Affecting the Cost of Repair
The cost to fix the heat in your car can vary significantly depending on several factors. It’s essential to consider these elements when budgeting for repairs.
2.1. Type of Problem
The complexity of the issue is the primary cost driver. A simple coolant top-off will be far cheaper than replacing a heater core. Diagnostic services at CARDIAGTECH.NET can pinpoint the problem quickly and accurately.
2.2. Make and Model of Your Car
Luxury and high-performance vehicles often have more complex heating systems, and parts can be more expensive. Parts availability and labor costs can also differ based on the make and model.
2.3. Cost of Parts
The price of replacement parts will influence the overall cost. Aftermarket parts may be cheaper, but OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are generally recommended for reliability and fit.
2.4. Labor Costs
Labor rates vary by location and shop. Dealerships tend to have higher labor rates than independent shops. Experience and specialization can also affect labor costs. CARDIAGTECH.NET’s network includes skilled technicians offering competitive rates.
2.5. Diagnostic Fees
Many shops charge a diagnostic fee to determine the cause of the heating problem. This fee may be waived if you proceed with the repair at the same shop.
2.6 Location
The cost of living and the demand for auto repair services can vary by location, impacting both labor rates and parts costs. Urban areas may have higher rates compared to rural areas.
3. Estimated Repair Costs for Common Heating Issues
Here’s a breakdown of estimated repair costs for common heating problems. These are average ranges, and actual costs can vary.
| Problem | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Coolant Leak Repair | Identifying and fixing leaks in hoses, radiator, or other cooling system components. | $100 – $400 |
| Thermostat Replacement | Replacing a faulty thermostat to regulate engine temperature correctly. | $150 – $350 |
| Heater Core Replacement | Replacing the heater core, which is responsible for providing heat to the cabin. | $500 – $1,200 |
| Blower Motor Replacement | Replacing the blower motor, which circulates air through the heating system. | $200 – $500 |
| Blend Door Actuator Repair/Replace | Repairing or replacing the blend door actuator, which controls the mix of hot and cold air. | $200 – $400 |
| Radiator Flush | Cleaning the radiator to remove debris and improve cooling system efficiency. | $100 – $200 |
| Coolant Top-Off | Adding coolant to the system to maintain proper levels. | $20 – $50 |
| Hose Replacement | Replacing damaged or deteriorating hoses in the cooling system. | $80 – $200 |
Note: These are just estimates. Always get a quote from a trusted mechanic.
4. DIY vs. Professional Repair
Deciding whether to tackle the repair yourself or take it to a professional depends on your skills, tools, and the complexity of the problem.
4.1. DIY Advantages
- Cost Savings: You save on labor costs.
- Learning Experience: You gain knowledge about your car.
- Convenience: You can work on your own schedule.
4.2. DIY Disadvantages
- Time Commitment: Repairs can take longer if you’re inexperienced.
- Risk of Mistakes: Incorrect repairs can cause further damage.
- Tool Investment: You may need to purchase specialized tools.
- Safety Concerns: Working on cars can be dangerous if proper precautions aren’t taken.
4.3. When to Call a Professional
- Complex Issues: Heater core replacement or electrical problems are best left to professionals.
- Lack of Experience: If you’re not comfortable working on cars, seek professional help.
- Specialized Tools Required: Some repairs require tools that are not readily available.
- Warranty Concerns: DIY repairs may void your car’s warranty.
Alt text: A skilled mechanic diligently examines a car engine, ensuring optimal performance and identifying potential issues through careful inspection and expertise.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Common Heating Problems
If you’re inclined to troubleshoot the issue yourself, here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing common heating problems.
5.1. Check Coolant Level
- Locate the Coolant Reservoir: It’s usually a translucent plastic container near the engine.
- Check the Level: Ensure the coolant is between the “Min” and “Max” marks.
- Add Coolant if Needed: Use the correct type of coolant specified in your owner’s manual.
5.2. Inspect the Thermostat
- Start the Engine: Let it run for about 15 minutes.
- Monitor the Temperature Gauge: It should rise to the normal operating range.
- Feel the Upper Radiator Hose: It should gradually get warm as the engine heats up. If it stays cold, the thermostat may be stuck closed.
5.3. Check the Heater Core Hoses
- Locate the Heater Core Hoses: These are usually two hoses going into the firewall on the engine side.
- Feel the Hoses: Both hoses should be hot when the engine is at operating temperature. If one is cold, the heater core may be clogged.
5.4. Inspect the Blower Motor
- Turn on the Blower Fan: Set it to the highest speed.
- Listen for the Fan: If you don’t hear the fan running, check the fuse.
- Check the Fuse: Replace the fuse if it’s blown. If it continues to blow, there may be a problem with the blower motor.
5.5 Blend Door Actuator
- Adjust Temperature: Change the temperature setting from cold to hot.
- Listen for Movement: You should hear a slight whirring or clicking sound as the blend door actuator moves.
- Inspect the Actuator: If you suspect an issue, the actuator can be visually inspected, though this often requires removing parts of the dashboard.
6. Tools and Equipment You Might Need
If you decide to tackle the repair yourself, here’s a list of tools and equipment you might need. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic and repair tools to assist you.
| Tool/Equipment | Description | Approximate Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Socket Set | For removing and installing bolts and nuts. | $30 – $100 |
| Wrench Set | For tightening and loosening bolts and nuts. | $25 – $80 |
| Screwdriver Set | For removing and installing screws. | $20 – $50 |
| Pliers | For gripping and manipulating parts. | $15 – $40 |
| Coolant Flush Kit | For flushing the radiator and heater core. | $20 – $50 |
| Multimeter | For testing electrical circuits. | $25 – $100 |
| OBD-II Scanner | For reading diagnostic trouble codes. | $30 – $200 |
| Safety Glasses | For protecting your eyes. | $10 – $20 |
| Gloves | For protecting your hands. | $5 – $15 |
| Jack and Jack Stands | For safely lifting and supporting the car. | $50 – $150 |
| Drain Pan | For collecting used coolant. | $10 – $25 |
7. Choosing the Right Mechanic
Selecting a reliable mechanic is crucial for ensuring quality repairs and fair pricing. Here are some tips for finding the right mechanic.
7.1. Ask for Recommendations
Ask friends, family, and colleagues for recommendations. Online reviews can also provide valuable insights.
7.2. Check for Certifications
Look for mechanics certified by organizations like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence). Certifications indicate a certain level of knowledge and skill.
7.3. Get Multiple Quotes
Obtain quotes from several shops before making a decision. Compare the estimates and ask about the breakdown of costs.
7.4. Read Online Reviews
Check online review sites like Google, Yelp, and Better Business Bureau. Pay attention to both positive and negative reviews.
7.5. Inquire About Warranty
Ask about the shop’s warranty policy. A reputable shop should stand behind their work.
8. Maintaining Your Car’s Heating System
Preventive maintenance can help avoid costly repairs down the road. Here are some tips for maintaining your car’s heating system.
8.1. Regular Coolant Flushes
Flush the cooling system every 2-3 years to remove debris and sediment.
8.2. Inspect Hoses and Belts
Check hoses and belts for cracks, leaks, and wear. Replace them as needed.
8.3. Check Coolant Level Regularly
Monitor the coolant level and top it off as needed.
8.4. Test the Thermostat
Periodically check the thermostat to ensure it’s functioning properly.
8.5. Professional Inspection
Have your heating system inspected by a professional mechanic during routine maintenance.
Alt text: Close-up view of a car radiator showcasing its intricate design and vital role in regulating engine temperature for optimal vehicle performance.
9. When to Consider Upgrading Your Heating System
In some cases, repairing an old heating system may not be the most cost-effective solution. Consider upgrading if:
- Frequent Repairs: You’re constantly facing heating problems.
- Old Car: Your car is old and has high mileage.
- Improved Efficiency: Newer systems may offer better heating efficiency.
- Enhanced Features: Some aftermarket systems offer advanced features like programmable thermostats.
10. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Modern cars have sophisticated computer systems that monitor various components, including the heating system. When a problem is detected, the system generates a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
10.1. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can read these codes, providing valuable information about the problem. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of OBD-II scanners to suit different needs and budgets.
10.2. Common DTCs Related to Heating Systems
- P0128: Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
- P0116: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
- P0118: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- B1081: Air Conditioning Refrigerant Temperature Sensor Circuit Failure
- B1082: Air Conditioning Refrigerant Temperature Sensor Circuit Short to Ground
- B1083: Air Conditioning Refrigerant Temperature Sensor Circuit Short to Battery
10.3. Interpreting DTCs
DTCs provide a starting point for diagnosing the problem. However, it’s essential to interpret the codes correctly and perform further tests to pinpoint the root cause.
11. The Role of Coolant in Your Car’s Heating System
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, is a vital fluid in your car’s cooling and heating systems. It helps regulate engine temperature and prevent corrosion.
11.1. Types of Coolant
There are several types of coolant, including:
- Conventional (Green): Older formula, typically used in older vehicles.
- OAT (Organic Acid Technology): Longer-lasting formula, often orange or yellow.
- HOAT (Hybrid Organic Acid Technology): Combines OAT with silicates for added protection, often yellow or blue.
- IAT (Inorganic Additive Technology): Commonly used in older vehicles.
11.2. Choosing the Right Coolant
Using the correct type of coolant is crucial. Refer to your owner’s manual for the recommended type. Mixing different types of coolant can cause corrosion and damage.
11.3. Coolant Maintenance
- Check the Level Regularly: Ensure the coolant level is within the recommended range.
- Flush the System: Flush the cooling system every 2-3 years to remove contaminants.
- Inspect for Leaks: Check for leaks around hoses, radiator, and water pump.
12. Addressing Blend Door Actuator Issues
The blend door actuator controls the mixing of hot and cold air in your car’s HVAC system. If it malfunctions, you may experience inconsistent temperatures or no heat at all.
12.1. Symptoms of a Faulty Blend Door Actuator
- Inconsistent Temperatures: One side of the car blows hot air while the other blows cold.
- No Heat or AC: The system blows only hot or cold air, regardless of the setting.
- Clicking or Tapping Noises: The actuator may make noise as it tries to move the blend door.
12.2. Diagnosing Blend Door Actuator Problems
- Listen for the Actuator: Turn the temperature knob and listen for the actuator motor.
- Check for DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for codes related to the blend door actuator.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the actuator for damage or loose connections.
12.3. Repairing or Replacing the Blend Door Actuator
Replacing the blend door actuator can be a challenging task, as it often requires removing parts of the dashboard. It’s best left to a professional mechanic unless you have experience with automotive repairs.
13. Optimizing Your Car’s Heating Performance
Even with a properly functioning heating system, there are steps you can take to optimize its performance.
13.1. Preheating the Car
Allow the engine to warm up for a few minutes before driving. This will allow the coolant to heat up and provide warm air more quickly.
13.2. Using Recirculation Mode
In cold weather, using the recirculation mode can help warm the cabin more quickly by recirculating the warm air inside the car.
13.3. Closing Vents
Close vents that are not needed to direct warm air where it’s needed most.
13.4. Checking Cabin Air Filter
A clogged cabin air filter can restrict airflow and reduce heating efficiency. Replace the filter regularly.
14. Saving Money on Car Heating Repairs
Car repairs can be expensive, but there are ways to save money without sacrificing quality.
14.1. Get Multiple Estimates
Obtain quotes from several shops to compare prices.
14.2. Consider Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts can be cheaper than OEM parts. However, ensure the parts are of good quality.
14.3. Perform Routine Maintenance
Preventive maintenance can help avoid costly repairs.
14.4. Shop Around for Parts
Compare prices at different auto parts stores.
14.5. Ask About Discounts
Ask about discounts for seniors, students, or military personnel.
15. Ensuring Safety During Winter Driving
A properly functioning heating system is essential for safe winter driving.
15.1. Defrosting Windows
Ensure your windshield and windows are fully defrosted before driving.
15.2. Maintaining Visibility
Clean your headlights and taillights to ensure good visibility.
15.3. Checking Tire Pressure
Check your tire pressure regularly, as cold weather can cause it to drop.
15.4. Keeping an Emergency Kit
Keep an emergency kit in your car with items like a blanket, flashlight, jumper cables, and first-aid supplies.
16. The Future of Car Heating Systems
Automotive technology is constantly evolving, and car heating systems are no exception.
16.1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EVs use electric heaters instead of relying on engine heat. These heaters can provide instant warmth but can also reduce the vehicle’s range.
16.2. Heat Pumps
Some EVs use heat pumps to improve heating efficiency. Heat pumps can extract heat from the environment, even in cold weather.
16.3. Zoned Heating
Advanced systems offer zoned heating, allowing you to control the temperature in different areas of the car.
16.4 Remote Start
Remote start features allow you to start and preheat your car from a distance, ensuring a warm cabin before you even step inside.
17. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Car Heating
There are several common misconceptions about car heating systems. Let’s debunk some of them.
17.1. Myth: Running the Heater Will Drain the Battery
The heater itself doesn’t draw much power from the battery. However, the blower motor can draw a significant amount of power, especially at high speeds.
17.2. Myth: You Can Use Tap Water Instead of Coolant
Using tap water can cause corrosion and damage to the cooling system. Always use the correct type of coolant.
17.3. Myth: Adding More Coolant Will Improve Heating Performance
Overfilling the coolant reservoir can cause problems. Always maintain the coolant level within the recommended range.
17.4. Myth: Heater Core Leaks Are Always Obvious
Heater core leaks can be subtle and difficult to detect. Look for signs like a sweet smell inside the car or fogging on the windshield.
18. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective car repairs. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic tools to help you pinpoint the problem quickly and accurately.
18.1. OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II scanners can read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and provide valuable information about the problem.
18.2. Multimeters
Multimeters can be used to test electrical circuits and components.
18.3. Pressure Testers
Pressure testers can be used to check for leaks in the cooling system.
18.4. Thermometers
Thermometers can be used to measure the temperature of various components.
19. Understanding the Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups can help identify potential problems before they become major issues.
19.1. Schedule Routine Maintenance
Follow the maintenance schedule recommended in your owner’s manual.
19.2. Inspect the Cooling System
Have the cooling system inspected by a professional mechanic during routine maintenance.
19.3. Check for Leaks
Inspect for leaks around hoses, radiator, and water pump.
19.4. Test the Thermostat
Periodically check the thermostat to ensure it’s functioning properly.
20. Addressing Climate Control Issues
Modern cars often have sophisticated climate control systems that regulate temperature, humidity, and airflow.
20.1. Symptoms of Climate Control Problems
- Inconsistent Temperatures: One side of the car blows hot air while the other blows cold.
- No Heat or AC: The system blows only hot or cold air, regardless of the setting.
- Weak Airflow: The system blows air weakly, even at high fan speeds.
- Unusual Noises: The system makes unusual noises, such as clicking or hissing.
20.2. Diagnosing Climate Control Problems
- Check for DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for codes related to the climate control system.
- Inspect the Blower Motor: Check the blower motor for proper operation.
- Check the Blend Door Actuator: Inspect the blend door actuator for damage or loose connections.
- Check the Refrigerant Level: Low refrigerant levels can cause cooling problems.
20.3. Repairing Climate Control Problems
Climate control problems can be complex and may require specialized tools and knowledge. It’s often best to seek professional help.
Fixing the heat in your car can range from a simple coolant top-off to a more complex heater core replacement. Understanding the factors that influence the cost can help you budget for repairs and make informed decisions. Whether you choose to tackle the repair yourself or seek professional help, remember that a properly functioning heating system is essential for a comfortable and safe driving experience.
Don’t let a faulty heater leave you in the cold! Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or WhatsApp us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and the best tools to diagnose and fix your car’s heating problems. Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET today and ensure a warm and comfortable ride all winter long. Let us help you find the right tools to get the job done efficiently and effectively, saving you time and money.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
How much does it cost to diagnose a heating problem in my car?
Diagnostic fees typically range from $75 to $150, but some shops may waive the fee if you proceed with the repair.
-
Can I replace a heater core myself?
Replacing a heater core is a complex job that requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s best left to a professional mechanic.
-
How often should I flush my car’s cooling system?
It’s generally recommended to flush the cooling system every 2-3 years or 30,000 to 50,000 miles.
-
What type of coolant should I use in my car?
Refer to your owner’s manual for the recommended type of coolant. Using the wrong type can cause corrosion and damage.
-
What are the symptoms of a faulty thermostat?
Symptoms include the engine overheating or not reaching operating temperature, poor heating performance, and erratic temperature gauge readings.
-
How can I save money on car heating repairs?
Get multiple estimates, consider aftermarket parts, perform routine maintenance, and shop around for parts.
-
Is it safe to drive with a malfunctioning heater?
While it may not be unsafe from a mechanical standpoint, a malfunctioning heater can affect visibility and comfort, especially in cold weather.
-
What is a blend door actuator, and what does it do?
The blend door actuator controls the mixing of hot and cold air in your car’s HVAC system. A faulty actuator can cause inconsistent temperatures.
-
How can I tell if my car has a coolant leak?
Look for signs like a sweet smell inside the car, fogging on the windshield, or puddles of coolant under the car.
-
What are some common diagnostic trouble codes related to heating systems?
Common codes include P0128 (Coolant Thermostat) and P0116 (Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/Performance).