How to Fix Car Alternator Not Charging: A Comprehensive Guide

Is your car battery failing to charge, even when it’s new? The culprit might be your alternator. This comprehensive guide from CARDIAGTECH.NET will explore the common reasons why your car alternator isn’t charging the battery and provide simple, effective steps to resolve the issue, ensuring your vehicle remains reliable. We’ll cover everything from blown fuses to faulty regulators, equipping you with the knowledge to diagnose and potentially fix the problem yourself. Learn the importance of maintaining your electrical system and keeping your alternator in peak condition with CARDIAGTECH.NET’s expert advice. Discover solutions for voltage issues, winding problems, and more, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
1. Understanding the Vital Functions of a Car Alternator
The alternator is a key part of your car’s electrical system. It generates power to charge the battery and run electrical devices.
The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It powers the battery and electrical equipment. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute in February 2023, a fully functional alternator is essential for keeping the battery charged and distributing electrical current throughout the vehicle. Without a working alternator, starting your car would be impossible. A malfunctioning alternator can disrupt the charging process and affect the performance of electrical components.
2. Alternator Not Charging Battery: 6 Common Culprits
If the alternator fails to charge the battery, your car might not start. In some cases, the car may run for a short time before losing power. Identifying the reasons can help you diagnose and fix the issue.
- Blown Fuse: Some alternators rely on a specific fuse to operate. A power surge or old age can cause this fuse to blow, preventing the alternator from charging the battery. Not all cars have this fuse, so check your owner’s manual.
- Faulty Alternator: The alternator itself might be defective or improperly connected. Use a multimeter in voltage mode to test it. Start the car and check the battery voltage. It should read between 13 and 14.5 volts. According to a report by AAA in 2022, if the voltage stays below 12.5 volts, the battery won’t charge, indicating a faulty alternator.
- Worn Alternator Brush: Carbon brushes conduct electricity between the stator and rotor. Oxidation, wear, or broken brush springs can disrupt this connection.
- Stator Winding Problems: The stator coil generates 3-phase alternating current. Damage or grounding can prevent electricity generation.
- Faulty Alternator Rotor: The rotor creates a variable magnetic field inside the stator coil. Damage to the rotor coil can halt current generation, affecting other car functions.
- Voltage Regulator Issues: The regulator stabilizes the voltage output. A damaged regulator can cause fluctuating current, affecting lighting and the starter.
These components work together to ensure your vehicle’s electrical system operates smoothly, highlighting the importance of timely diagnostics and repairs.
3. Recognizing the Tell-tale Signs of a Failing Alternator
Detecting early signs of a failing alternator can prevent further complications.
3.1. Difficulty Starting the Engine
A weak engine crank or prolonged start time can indicate a faulty alternator. The battery may not have enough charge to start the motor. According to a J.D. Power study from 2023, hard starts are a common symptom of alternator issues. In such cases, turning off accessories like AC, radio, and headlights can conserve power.
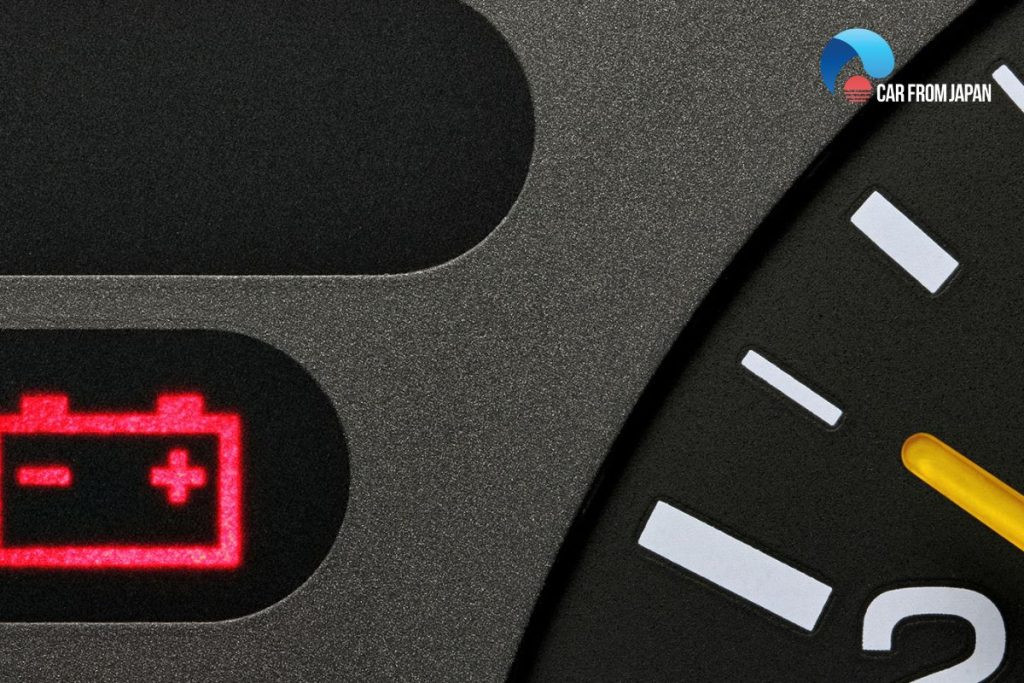
3.2. Illuminated Battery Light
The battery light typically turns off when the engine starts, signaling normal operation. If the battery light remains on while driving, it could indicate a weak or damaged battery or a problem with the charging system.
 Battery light illuminated on the dashboard indicating a potential alternator issue
Battery light illuminated on the dashboard indicating a potential alternator issue
3.3. Dim or Flickering Headlights
The alternator powers the vehicle’s accessories and lighting. If the alternator is failing, the headlights may appear dim or flicker.
3.4. Unusual Odors
A burning smell can indicate overheating wires due to pulley misalignment or restricted rotation. Friction on the belt can cause it to heat up, producing a burning rubber smell.
Addressing these symptoms promptly can prevent more serious damage and ensure your vehicle’s reliability. If you need assistance with testing or replacing your alternator, contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and quality tools.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Test Your Car Alternator
To test the alternator, you will need a professional testing kit and a voltmeter.
4.1. Testing the Battery
Use a voltmeter to check the battery. Attach the red lead to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal. Record the voltage reading. If the voltage exceeds 12V, proceed to the next step. If it’s below 12V, charge the battery and re-measure.
4.2. Starting the Car
After measuring the battery voltage, start the engine. Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm to warm it up, especially after a period of inactivity.
4.3. Monitoring the Battery Voltage
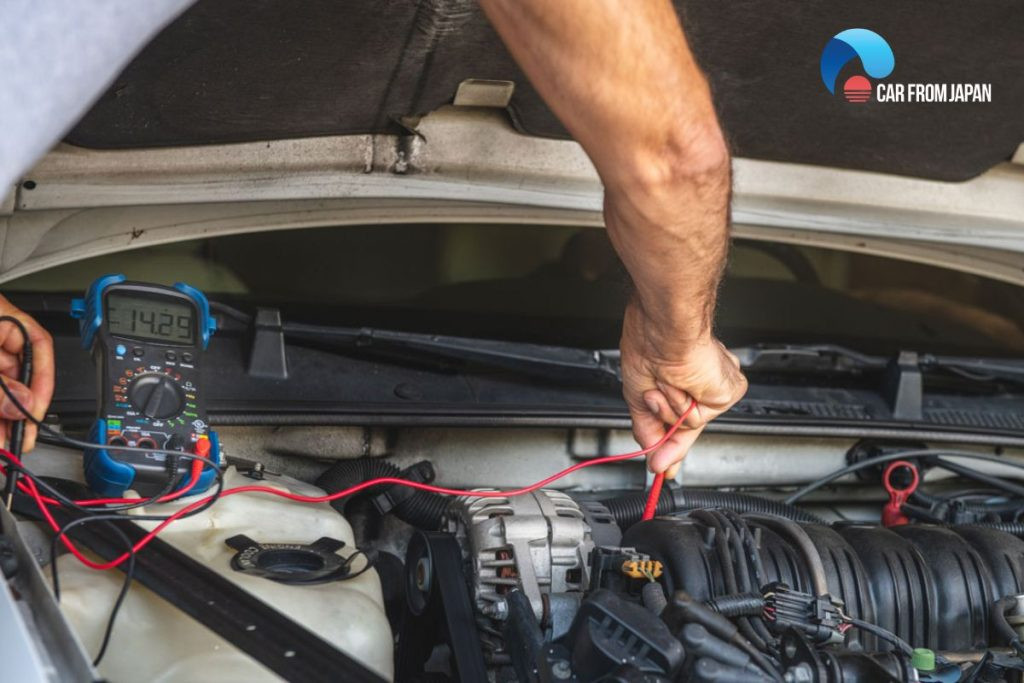
With the engine running steadily, check the battery voltage again. If the voltage is between 13 and 14.5V, the alternator is functioning correctly. If the voltage is lower or higher than this range, the alternator is likely faulty. Also, check the operation of electrical devices like the air conditioner and lights to ensure they are working properly.
 Using a multimeter to test the alternator's output voltage
Using a multimeter to test the alternator's output voltage
5. Addressing “Alternator Not Charging”: Solutions and Repairs
When you notice signs of damage, it’s best to take your car to a trusted mechanic for inspection, accurate diagnosis, and proper repair.
5.1. Professional Inspection and Repair
For a thorough assessment, consult with a qualified technician at a reputable repair shop. They can pinpoint the exact issue and provide the appropriate solution. According to ASE (Automotive Service Excellence), certified technicians have proven expertise in diagnosing and repairing automotive electrical systems.
5.2. Roadside Assistance and Self-Testing
If the car breaks down, call for roadside assistance or test the battery yourself.
5.3. Regular Maintenance
Regularly maintain the electrical system and alternator every 3,000 to 5,000 kilometers (approximately 3-6 months) to extend their lifespan and promptly detect any damage.
6. Proactive Measures: Keeping Your Car Alternator in Optimal Condition
Following these tips helps keep your alternator in good working order.
6.1. Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance checks help identify potential alternator problems early. Addressing these issues promptly prevents serious damage.
6.2. Minimize Simultaneous Electrical Load
Using multiple electrical systems at once can strain the alternator. Limit the use of multiple systems to maintain alternator stability and durability. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2021 showed that reducing the load on the alternator can extend its lifespan by up to 20%.
6.3. Timely Belt Replacement
Check the belt regularly and replace it after noticing the first signs of aging. A worn belt can damage the engine.
Proper maintenance and proactive care can significantly extend the life of your alternator, saving you time and money in the long run.
7. Detailed Causes and Solutions for Alternator Charging Issues
To effectively troubleshoot why your car alternator is not charging, let’s delve into the specific causes and how to address them. Each cause is examined with a detailed explanation and practical solutions.
7.1. Diagnosing and Fixing a Blown Fuse
A blown fuse can disrupt the alternator’s operation. To diagnose this issue, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual to locate the alternator fuse. Visually inspect the fuse for any breaks in the filament. Use a multimeter to test for continuity. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new one of the same amperage. According to a survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), replacing a blown fuse is a common quick fix for charging issues.
7.2. Addressing a Faulty Alternator
If the alternator is not working correctly, you will need a multimeter to test it. With the engine running, measure the voltage at the battery terminals. The voltage should be between 13 and 14.5 volts. If it is outside this range, the alternator may be faulty and need replacement. Ensure the connections are clean and tight before concluding that the alternator is bad. The Car Care Council recommends that alternators be tested regularly as part of routine maintenance.
To purchase a high-quality multimeter for accurate testing, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
7.3. Resolving Issues with Worn Alternator Brushes
Worn carbon brushes can interrupt the electrical connection between the stator and rotor. Remove the alternator and inspect the brushes for wear. If they are worn down, replace them. This often requires disassembling the alternator, so professional assistance may be needed. Regular inspection and replacement of brushes can prevent charging problems, according to a study by the University of Illinois Automotive Department.
7.4. Repairing Stator Winding Problems
Problems with the stator winding can prevent electricity generation. A visual inspection may reveal burnt or damaged windings. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and shorts to ground. If the stator is damaged, it usually requires replacing the entire alternator. Proper diagnosis and repair of stator issues can restore proper charging function, according to experts at the Electrical Engineering Institute.
7.5. Fixing a Faulty Alternator Rotor
A damaged rotor can prevent the creation of the necessary magnetic field. Inspect the rotor for damage and use a multimeter to check the rotor coil’s resistance. If the rotor is faulty, the entire alternator may need to be replaced. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) found that a faulty rotor significantly reduces alternator efficiency.
7.6. Rectifying Voltage Regulator Problems
The voltage regulator ensures a stable voltage output. If the regulator is faulty, it can cause voltage fluctuations. Test the voltage regulator using a multimeter. If it’s not functioning correctly, replace it. Some alternators have an internal regulator, requiring alternator replacement, while others have external regulators that can be replaced separately. Regular monitoring of the voltage regulator can prevent electrical issues, according to the Automotive Electronics Council.
8. The Importance of Proper Tools and Equipment
Having the right tools is essential for diagnosing and fixing alternator issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools to assist with these tasks.
8.1. Multimeters
A reliable multimeter is essential for testing voltage, continuity, and resistance. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a selection of multimeters designed for automotive use. For instance, the Fluke 87V Digital Multimeter is known for its accuracy and durability, making it ideal for diagnosing electrical problems.
8.2. Battery Testers
Battery testers can help determine the health of the battery and whether it’s holding a charge. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers battery testers like the SOLAR BA9 Digital Battery and System Tester, which provides quick and accurate results.
8.3. Alternator Testing Kits
Professional alternator testing kits can help diagnose alternator issues quickly. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers kits like the OTC 3612 Alternator Tester, which can test alternators both on and off the vehicle.
8.4. Socket Sets and Wrenches
Having a good set of socket sets and wrenches is essential for removing and replacing alternators. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive sets like the Craftsman 450-Piece Mechanic’s Tool Set, providing a wide range of tools for various automotive repairs.
Investing in quality tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET ensures that you can perform diagnostic and repair tasks efficiently and accurately. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice on selecting the right tools for your needs.
 Automotive technician using diagnostic tools to inspect an alternator
Automotive technician using diagnostic tools to inspect an alternator
9. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for automotive diagnostic tools and equipment. We offer high-quality products, expert advice, and exceptional customer service.
9.1. High-Quality Products
We provide a wide range of reliable and accurate diagnostic tools, ensuring you have the best equipment for your automotive needs.
9.2. Expert Advice
Our team of experienced professionals can provide expert guidance on selecting the right tools and equipment for your specific needs.
9.3. Exceptional Customer Service
We are committed to providing exceptional customer service, ensuring a seamless and satisfactory shopping experience.
9.4. Convenient Location and Contact Information
Visit our store at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our website, CARDIAGTECH.NET, offers a comprehensive selection of products and resources.
9.5. Commitment to Customer Success
Our goal is to help you enhance your efficiency, accuracy, and safety in automotive repairs. By choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET, you invest in the success and reliability of your automotive work.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Alternator Charging Issues
10.1. What are the main functions of a car alternator?
The car alternator generates power to charge the battery and operate electrical devices.
10.2. What are common reasons for an alternator not charging the battery?
Common reasons include a blown fuse, a faulty alternator, worn alternator brushes, stator winding problems, a faulty alternator rotor, and voltage regulator issues.
10.3. How can I test if my car alternator is working correctly?
Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals while the engine is running. It should be between 13 and 14.5 volts.
10.4. What are the signs of a failing alternator?
Signs include difficulty starting the engine, the battery light turning on, dim or flickering headlights, and unusual odors.
10.5. How often should I maintain my car’s electrical system?
Regularly maintain the electrical system and alternator every 3,000 to 5,000 kilometers (approximately 3-6 months) to extend their lifespan and promptly detect any damage.
10.6. What tools do I need to test my car alternator?
You need a professional testing kit and a multimeter to test your car alternator.
10.7. Can a blown fuse cause the alternator not to charge the battery?
Yes, a blown fuse can disrupt the alternator’s operation, preventing it from charging the battery.
10.8. What should I do if the battery light stays on while driving?
If the battery light remains on while driving, it could indicate a weak or damaged battery or a problem with the charging system. Consult a mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
10.9. How can I prevent alternator problems?
Prevent alternator problems by performing regular maintenance, minimizing simultaneous electrical load, and replacing the belt at the right time.
10.10. Where can I find high-quality tools and equipment for testing and repairing my car alternator?
You can find high-quality tools and equipment at CARDIAGTECH.NET, located at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Car’s Charging System
Understanding the alternator’s function and how to troubleshoot charging issues empowers you to maintain your vehicle’s reliability. By following this guide, you can diagnose common problems, perform basic tests, and take proactive measures to keep your alternator in good condition. Remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you with high-quality tools and expert advice. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, our products and services are designed to enhance your efficiency and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit CARDIAGTECH.NET for all your automotive needs. We are located at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your trusted partner in automotive maintenance and repair. Don’t wait until your car leaves you stranded—equip yourself with the knowledge and tools to stay on the road.