How To Fix Car Belt: A Comprehensive Guide
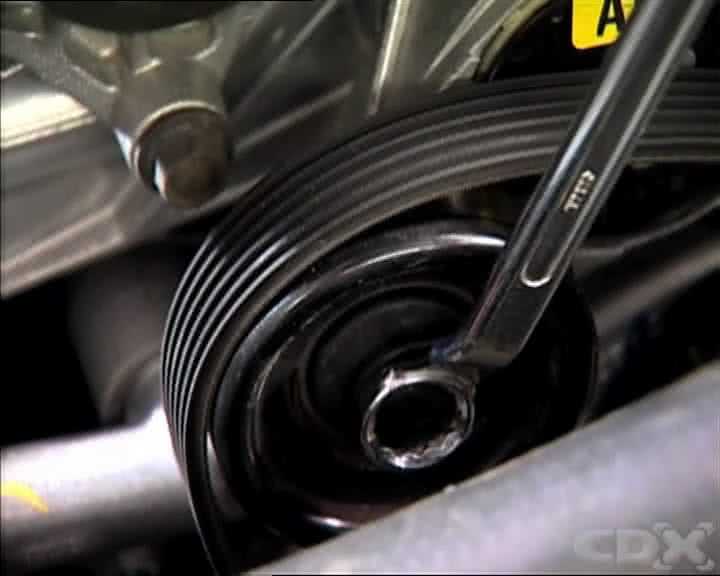
Fixing your car belt can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s a manageable task. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through every step of the process, ensuring a smooth and successful repair. Discover how to identify issues, select the correct replacement, and properly install a new belt, all while saving money and gaining valuable skills. Get ready to enhance your automotive expertise and keep your vehicle running smoothly with our expert advice on belt replacement and tensioning tools. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
1. Understanding Car Belts: Types, Functions, and Importance
Car belts, often overlooked, are crucial for your vehicle’s operation. They transfer power from the engine to various components, ensuring everything runs smoothly. Let’s explore the different types of car belts and their vital functions.
1.1. Types of Car Belts
There are several types of car belts, each designed for specific tasks:
- Serpentine Belts: These are single, long belts that drive multiple accessories, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. They are known for their efficiency and long lifespan.
- V-Belts: Older vehicles often use V-belts, which are trapezoidal in shape and fit into V-shaped grooves on the pulleys. They are typically used for individual accessories.
- Timing Belts: This belt is critical for synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring the engine valves open and close at the correct times. A broken timing belt can cause severe engine damage.
1.2. Functions of Car Belts
Each belt plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s operation:
- Serpentine Belt Functions: Powers the alternator (charging the battery), power steering pump (assisting steering), air conditioning compressor (cooling the cabin), and water pump (cooling the engine).
- V-Belt Functions: Typically powers individual accessories, such as the alternator or power steering pump in older vehicles.
- Timing Belt Functions: Synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft, controlling the timing of the engine’s valves.
1.3. Importance of Maintaining Car Belts
Regularly inspecting and maintaining your car belts is essential for preventing breakdowns and costly repairs. A worn or broken belt can lead to:
- Loss of Power Steering: Making the car difficult to steer, especially at low speeds.
- Overheating Engine: As the water pump may stop functioning, leading to engine damage.
- Electrical Issues: If the alternator stops working, the battery won’t charge, leading to electrical problems and potential stalling.
- Air Conditioning Failure: A broken belt can stop the AC compressor, resulting in a hot and uncomfortable ride.
- Engine Damage: A broken timing belt can cause significant internal engine damage, requiring extensive and expensive repairs.
Table 1: Common Car Belt Types and Functions
| Belt Type | Function | Potential Issues if Broken |
|---|---|---|
| Serpentine Belt | Powers alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, and water pump | Loss of power steering, engine overheating, electrical issues, AC failure |
| V-Belt | Powers individual accessories like alternator or power steering pump (older vehicles) | Loss of specific accessory function (e.g., no power steering or alternator not charging) |
| Timing Belt | Synchronizes crankshaft and camshaft, controlling engine valve timing | Severe engine damage due to valves and pistons colliding |
2. Identifying Symptoms of a Failing Car Belt
Recognizing the signs of a failing car belt early can save you from unexpected breakdowns. Here are the common symptoms to watch out for.
2.1. Squealing or Chirping Noises
One of the most common signs of a worn or loose belt is a squealing or chirping noise coming from the engine, especially when starting the car or accelerating. This noise is often caused by the belt slipping on the pulleys.
2.2. Visible Cracks and Wear
Inspect your car belts regularly for visible signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or missing chunks. These are clear indicators that the belt is deteriorating and needs replacement. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), belts with visible cracks are at a higher risk of failure.
2.3. Glazed or Shiny Appearance
A glazed or shiny appearance on the belt’s surface indicates that it has hardened and lost its flexibility. This can cause the belt to slip and not grip the pulleys properly.
2.4. Loss of Power Steering or Air Conditioning
If your power steering becomes difficult or your air conditioning stops working, it could be due to a failing serpentine or V-belt. These belts power these accessories, and a worn belt may not provide enough grip to operate them effectively.
2.5. Overheating Engine
A failing serpentine belt can cause the water pump to stop working, leading to engine overheating. If you notice your temperature gauge rising, check the condition of your belts.
2.6. Battery Warning Light
If the serpentine belt that drives the alternator is failing, it can cause the battery not to charge properly, triggering the battery warning light on your dashboard.
Table 2: Symptoms of a Failing Car Belt
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Urgency |
|---|---|---|
| Squealing or Chirping Noises | Worn or loose belt slipping on pulleys | Medium |
| Visible Cracks and Wear | Deteriorating belt material | High |
| Glazed or Shiny Appearance | Hardened belt losing flexibility | Medium |
| Loss of Power Steering/AC | Failing belt not powering accessories effectively | High |
| Overheating Engine | Water pump not functioning due to failing belt | Critical |
| Battery Warning Light | Alternator not charging due to failing belt | High |
3. Tools and Materials Needed to Fix Car Belt
Having the right tools and materials on hand is crucial for a successful car belt replacement. Here’s a comprehensive list to ensure you’re well-prepared.
3.1. Essential Tools
- Socket Set: A variety of socket sizes will be needed to loosen and tighten bolts on the belt tensioner and other components.
- Wrench Set: Wrenches are necessary for accessing hard-to-reach bolts and nuts.
- Belt Tensioner Tool: This specialized tool is designed to release the tension on the belt, making it easier to remove and install.
- Pry Bar: A pry bar can be helpful for maneuvering the belt into place.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips screwdrivers may be needed for removing covers or clips.
3.2. Necessary Materials
- Replacement Belt: Ensure you have the correct size and type of belt for your vehicle. Check your vehicle’s manual or use an online parts finder like the one available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt and grease.
- Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris.
- Shop Rags: Keep your work area clean and wipe off any spills.
- Belt Dressing (Optional): While not always necessary, belt dressing can help improve grip and reduce noise.
- Pen and Paper/Camera: To help you remember the belt routing
3.3. Safety Equipment
- Jack and Jack Stands: If you need to access the belt from underneath the vehicle, use a jack and jack stands to safely lift and support the car.
- Wheel Chocks: Prevent the car from rolling while you are working on it.
- Work Light: Provides adequate lighting to see what you are doing.
Table 3: Tools and Materials for Car Belt Replacement
| Tool/Material | Purpose | Importance | Where to Get It |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socket Set | Loosening and tightening bolts | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Wrench Set | Accessing hard-to-reach bolts and nuts | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Belt Tensioner Tool | Releasing tension on the belt for removal and installation | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Pry Bar | Maneuvering the belt into place | Helpful | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Screwdrivers | Removing covers or clips | Helpful | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Replacement Belt | Replacing the old, worn belt | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Gloves | Protecting hands from dirt and grease | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store, Hardware Store |
| Safety Glasses | Protecting eyes from debris | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store, Hardware Store |
| Shop Rags | Cleaning work area and wiping spills | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store, Hardware Store |
| Belt Dressing | Improving belt grip and reducing noise (optional) | Optional | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Jack and Jack Stands | Safely lifting and supporting the vehicle (if needed) | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Wheel Chocks | Preventing the car from rolling | Essential | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store |
| Work Light | Providing adequate lighting | Helpful | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store, Hardware Store |
| Pen and Paper/Camera | To help you remember the belt routing | Helpful | CARDIAGTECH.NET, Auto Parts Store, Hardware Store |
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Car Belt
Replacing a car belt is a straightforward process if you follow these steps carefully. Safety is paramount, so ensure the engine is off and cool before starting.
4.1. Preparation
- Gather Your Tools and Materials: Ensure you have all the necessary tools and a new belt that matches your vehicle’s specifications.
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent electrical accidents. Engage the parking brake and use wheel chocks for added safety.
- Locate the Belt: Identify the belt you need to replace. Refer to your vehicle’s manual if needed.
- Diagram the Belt Routing: Before removing the old belt, make a diagram or take a photo of its routing. This will be extremely helpful when installing the new belt.
4.2. Removing the Old Belt
- Locate the Belt Tensioner: Find the belt tensioner pulley. It’s usually spring-loaded and designed to maintain tension on the belt.
- Release the Tension: Use a belt tensioner tool or a wrench to rotate the tensioner pulley, releasing the tension on the belt. Some tensioners have a square hole for a socket wrench.
- Remove the Belt: With the tension released, carefully slide the old belt off the pulleys.
- Inspect the Pulleys: Check all the pulleys for wear, cracks, or damage. Make sure they spin freely. Replace any damaged pulleys before installing the new belt.
4.3. Installing the New Belt
- Follow Your Diagram: Refer to the diagram or photo you made earlier to ensure correct belt routing.
- Route the Belt: Carefully route the new belt around all the pulleys, except for the tensioner pulley.
- Release Tensioner and Secure Belt: Use the belt tensioner tool or wrench to release the tensioner again. Slide the new belt over the tensioner pulley.
- Check Belt Alignment: Ensure the belt is properly seated in all the pulley grooves.
- Release Tensioner Slowly: Slowly release the tensioner, allowing it to apply tension to the new belt.
4.4. Final Checks and Adjustments
- Inspect Belt Routing: Double-check the belt routing to make sure it’s correct.
- Start the Engine: Reconnect the negative battery terminal and start the engine.
- Observe Belt Operation: Watch the belt to ensure it runs smoothly and doesn’t slip off the pulleys.
- Check Tension: After a few minutes of operation, stop the engine and recheck the belt tension. Adjust if necessary.
Table 4: Step-by-Step Car Belt Replacement Guide
| Step | Action | Tools/Materials Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Gather tools, disconnect battery, locate belt, diagram routing | Socket Set, Wrench Set, Replacement Belt, Pen/Paper | Safety First! Ensure engine is off and cool. |
| 2. Removing Old Belt | Locate tensioner, release tension, remove belt, inspect pulleys | Belt Tensioner Tool, Pry Bar, Socket Set | Check pulleys for wear and damage. Replace if necessary. |
| 3. Installing New Belt | Follow diagram, route belt around pulleys, release tensioner, secure belt | Belt Tensioner Tool, Replacement Belt | Ensure correct belt routing. |
| 4. Final Checks and Adjustments | Inspect routing, start engine, observe belt operation, check tension | Socket Set, Wrench Set | Double-check belt alignment and tension. |
 Diagram of a serpentine belt routing
Diagram of a serpentine belt routing
4.5. Seeking Professional Assistance
If you’re unsure about any step or encounter difficulties, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance from a certified mechanic. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and quality tools.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Fixing a Car Belt
Replacing a car belt can be a straightforward task, but it’s easy to make mistakes if you’re not careful. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid.
5.1. Incorrect Belt Size
Using the wrong size belt is a common mistake. A belt that’s too long will slip, while one that’s too short may be impossible to install or put excessive strain on the pulleys. Always check your vehicle’s manual or use an online parts finder to ensure you get the correct belt size. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a convenient tool to find the right belt for your specific vehicle.
5.2. Incorrect Belt Routing
Routing the belt incorrectly is another frequent error. If the belt isn’t routed properly, it won’t drive the accessories effectively, leading to issues like loss of power steering or overheating. Always refer to your diagram or photo taken before removing the old belt.
5.3. Over or Under-Tensioning the Belt
Proper belt tension is crucial. Over-tensioning can damage the belt and the bearings in the accessories it drives, while under-tensioning can cause the belt to slip. Use a belt tension gauge to ensure the correct tension.
5.4. Neglecting Pulley Inspection
Failing to inspect the pulleys for wear or damage can lead to premature belt failure. Rough or damaged pulleys can quickly wear down a new belt. Always check the pulleys and replace any that are damaged.
5.5. Not Disconnecting the Battery
Working on your car’s electrical system without disconnecting the battery is dangerous. Disconnecting the negative battery terminal prevents accidental shorts and potential injuries.
5.6. Using the Wrong Tools
Using the wrong tools can damage components and make the job more difficult. Always use the correct tools, such as a belt tensioner tool, to avoid damaging the tensioner or other parts.
Table 5: Common Mistakes to Avoid When Replacing a Car Belt
| Mistake | Consequence | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Belt Size | Belt slippage or excessive strain on pulleys | Check vehicle manual or use an online parts finder |
| Incorrect Belt Routing | Ineffective accessory operation (e.g., loss of power steering) | Refer to diagram or photo of old belt routing |
| Over/Under-Tensioning | Damage to belt and accessory bearings or belt slippage | Use a belt tension gauge |
| Neglecting Pulley Inspection | Premature belt failure | Inspect pulleys for wear and damage; replace if necessary |
| Not Disconnecting Battery | Risk of electrical shorts and injuries | Disconnect negative battery terminal before starting work |
| Using Wrong Tools | Damage to components and increased difficulty | Use correct tools, such as a belt tensioner tool |
6. Troubleshooting Car Belt Problems
Even after replacing a car belt, you might encounter some issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot common problems.
6.1. Belt Squealing After Replacement
If the new belt is squealing, it could be due to:
- Incorrect Tension: The belt may be too loose. Adjust the tension to the correct specification.
- Misalignment: The belt may not be properly aligned on the pulleys. Check the alignment and adjust as needed.
- Contamination: Oil or other contaminants on the belt can cause it to slip and squeal. Clean the belt and pulleys with a degreaser.
- Pulley Issues: A worn or damaged pulley can cause the belt to squeal. Inspect the pulleys and replace if necessary.
6.2. Belt Slipping
Belt slipping can occur if:
- The Belt is Too Loose: Adjust the tension to the correct specification.
- The Pulley is Worn: Replace the worn pulley.
- There is Contamination: Clean the belt and pulleys with a degreaser.
6.3. Belt Breaking Prematurely
If the belt breaks shortly after replacement, consider these causes:
- Incorrect Installation: Ensure the belt was installed correctly and routed properly.
- Pulley Misalignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to wear unevenly and break.
- Over-Tensioning: Too much tension can cause the belt to break prematurely.
- Defective Belt: Although rare, the belt itself could be defective. Replace it with a new one from a reputable brand like those available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
Table 6: Troubleshooting Car Belt Problems
| Problem | Possible Cause(s) | Solution(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Squealing After Replacement | Incorrect tension, misalignment, contamination, pulley issues | Adjust tension, check alignment, clean belt and pulleys, inspect/replace pulleys |
| Belt Slipping | Belt too loose, worn pulley, contamination | Adjust tension, replace pulley, clean belt and pulleys |
| Belt Breaking Prematurely | Incorrect installation, pulley misalignment, over-tensioning, defective belt | Ensure correct installation, check pulley alignment, adjust tension, replace belt with a reputable brand (e.g., from CARDIAGTECH.NET) |
7. Choosing the Right Car Belt: A Buyer’s Guide
Selecting the correct replacement belt is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here’s what to consider when buying a car belt.
7.1. Belt Type
Ensure you choose the correct type of belt for your vehicle. Serpentine belts, V-belts, and timing belts each have specific applications. Refer to your vehicle’s manual or use an online parts finder to identify the right type.
7.2. Belt Size
Getting the right size is essential. A belt that’s too long will slip, while one that’s too short may be impossible to install. Use the parts finder tool on CARDIAGTECH.NET to find the exact size for your vehicle.
7.3. Material and Construction
Car belts are typically made from rubber or synthetic materials. High-quality belts use reinforced materials for added durability and resistance to wear. Look for belts made from EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber, which offers excellent heat and ozone resistance.
7.4. Brand Reputation
Choose belts from reputable brands known for their quality and reliability. Well-known brands often offer warranties, providing added peace of mind. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a selection of trusted brands to ensure you get a high-quality product.
7.5. Price vs. Quality
While it’s tempting to go for the cheapest option, investing in a higher-quality belt can save you money in the long run. A durable belt will last longer and perform better, reducing the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
Table 7: Factors to Consider When Choosing a Car Belt
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Type | Ensure correct type (Serpentine, V-Belt, Timing Belt) | Essential |
| Belt Size | Must match vehicle specifications to avoid slippage or installation issues | Essential |
| Material and Construction | Look for durable materials like EPDM rubber for heat and ozone resistance | High |
| Brand Reputation | Choose belts from reputable brands known for quality and reliability (available at CARDIAGTECH.NET) | High |
| Price vs. Quality | Invest in a higher-quality belt for long-term durability and performance | Medium |
8. Maintaining Car Belts for Longevity
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the life of your car belts and prevent unexpected failures. Here are some tips to keep your belts in top condition.
8.1. Regular Inspections
Inspect your car belts regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or glazing. Catching these issues early can prevent breakdowns.
8.2. Keep Belts Clean
Keep your belts clean and free from oil, grease, and other contaminants. Use a degreaser to clean the belts and pulleys if necessary.
8.3. Check Belt Tension
Regularly check the belt tension and adjust as needed. Use a belt tension gauge to ensure the correct tension.
8.4. Replace Worn Pulleys
Replace any worn or damaged pulleys promptly. Rough or damaged pulleys can quickly wear down a new belt.
8.5. Follow Maintenance Schedule
Follow your vehicle’s maintenance schedule for belt replacements. Most manufacturers recommend replacing belts every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but this can vary depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
Table 8: Tips for Maintaining Car Belts
| Maintenance Tip | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Inspections | Check for cracks, fraying, glazing, and other signs of wear | Every 3 months |
| Keep Belts Clean | Remove oil, grease, and other contaminants with a degreaser | As needed |
| Check Belt Tension | Ensure correct tension using a belt tension gauge | Every 6 months |
| Replace Worn Pulleys | Replace rough or damaged pulleys to prevent premature belt wear | As needed |
| Follow Maintenance Schedule | Adhere to manufacturer’s recommendations for belt replacement (typically every 60,000 to 100,000 miles) | As recommended |
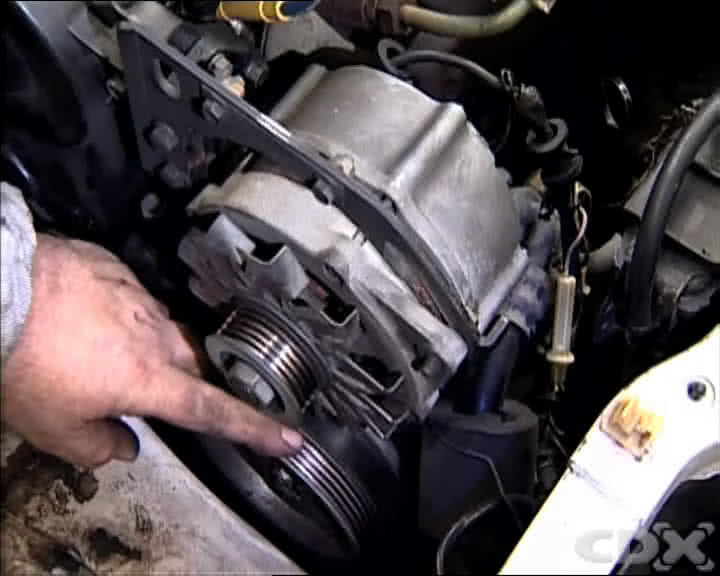 Close-up of a cracked serpentine belt
Close-up of a cracked serpentine belt
9. The Benefits of Using Quality Car Belt Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
Investing in high-quality car belt tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET can make the replacement process easier, safer, and more efficient. Here are some of the benefits.
9.1. Precision and Accuracy
Quality tools provide precision and accuracy, ensuring the job is done right the first time. A good belt tensioner tool, for example, allows you to release the tension on the belt smoothly and safely, preventing damage to the tensioner or other components.
9.2. Durability and Longevity
Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET are made from high-quality materials, ensuring durability and longevity. This means they can withstand the rigors of regular use and won’t break or wear out easily.
9.3. Ease of Use
Ergonomically designed tools are easier to use, reducing fatigue and improving efficiency. A comfortable grip and intuitive design make the job less strenuous.
9.4. Safety
Quality tools enhance safety by reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. A sturdy jack and jack stands, for example, provide a safe and stable platform for working under the vehicle.
9.5. Time Savings
With the right tools, you can complete the job more quickly and efficiently, saving valuable time. A belt tensioner tool, for example, makes belt replacement much faster and easier than using makeshift methods.
Table 9: Benefits of Using Quality Car Belt Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Precision/Accuracy | Ensures job is done correctly the first time; prevents damage to components | Reduces the risk of errors and rework; ensures optimal performance |
| Durability/Longevity | Made from high-quality materials; withstands regular use without breaking or wearing out | Saves money on replacements; provides long-term value |
| Ease of Use | Ergonomically designed tools reduce fatigue and improve efficiency | Makes the job less strenuous; increases productivity |
| Safety | Reduces the risk of accidents or injuries; provides a stable and secure working environment | Protects the user from harm; ensures a safe working environment |
| Time Savings | Completes the job more quickly and efficiently | Frees up time for other tasks; increases overall efficiency |
10. Car Belt Replacement Cost: DIY vs. Professional
Deciding whether to replace a car belt yourself or hire a professional involves weighing the costs and benefits. Here’s a breakdown to help you make an informed decision.
10.1. DIY Replacement Costs
- Replacement Belt: $20 – $50 (depending on the vehicle and belt type)
- Tools (if needed): $50 – $200 (for a basic socket set, wrench set, and belt tensioner tool)
- Optional Materials: $10 – $20 (for gloves, safety glasses, and shop rags)
Total DIY Cost: $80 – $270
10.2. Professional Replacement Costs
- Labor: $75 – $150 per hour (most belt replacements take 1-2 hours)
- Replacement Belt: $30 – $70 (parts markup)
- Shop Supplies: $10 – $30
Total Professional Cost: $115 – $350
10.3. Pros and Cons
DIY Replacement:
- Pros: Lower cost, gain valuable skills, convenience
- Cons: Requires time and effort, potential for mistakes, need for tools
Professional Replacement:
- Pros: Expertise, convenience, warranty
- Cons: Higher cost, scheduling required
Table 10: DIY vs. Professional Car Belt Replacement Costs
| Cost Category | DIY Replacement Cost | Professional Replacement Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Replacement Belt | $20 – $50 | $30 – $70 |
| Tools (if needed) | $50 – $200 | N/A |
| Labor | N/A | $75 – $150 per hour |
| Shop Supplies | $10 – $20 | $10 – $30 |
| Total Cost | $80 – $270 | $115 – $350 |
CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you with high-quality tools and expert advice, whether you choose to DIY or seek professional help. Contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for all your automotive needs.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Car Belts
1. How often should I replace my car belts?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing belts every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but it’s best to consult your vehicle’s manual for specific recommendations.
2. Can I drive with a squealing belt?
While you can drive with a squealing belt, it’s not recommended. The squealing indicates that the belt is slipping, which can lead to accessory failure and potential breakdowns.
3. What causes car belts to fail?
Car belts can fail due to wear and tear, exposure to heat and chemicals, misalignment, and over-tensioning.
4. Can I use belt dressing to fix a squealing belt?
Belt dressing can temporarily stop a squealing belt, but it’s not a long-term solution. It’s best to address the underlying cause of the squealing, such as replacing the belt or adjusting the tension.
5. How do I know if my timing belt needs to be replaced?
Check your vehicle’s manual for the recommended replacement interval. Some vehicles also have a timing belt inspection cover that allows you to visually inspect the belt for wear.
6. What happens if my timing belt breaks?
If your timing belt breaks, it can cause severe engine damage, including bent valves and damaged pistons. It’s crucial to replace the timing belt according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
7. Can I replace a car belt myself?
Yes, you can replace a car belt yourself with the right tools and knowledge. However, if you’re not comfortable working on your car, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
8. What tools do I need to replace a car belt?
You’ll need a socket set, wrench set, belt tensioner tool, pry bar, screwdrivers, and a replacement belt. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality tools for car belt replacement.
9. How do I find the right size belt for my car?
You can find the right size belt by checking your vehicle’s manual or using an online parts finder, such as the one available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
10. Is it better to replace all car belts at the same time?
Replacing all car belts at the same time can save you time and hassle in the long run. If one belt is worn, the others are likely nearing the end of their lifespan as well.
Ready to tackle your car belt replacement? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 for the best tools and expert advice. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly



