**How to Fix Car Engine Knocking: A Comprehensive Guide**
Is your car engine knocking? CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through the common causes of engine knocking, from worn components to fuel issues, and provide effective solutions to restore your vehicle’s smooth performance and prevent costly damage. Discover proven methods to diagnose and fix engine knocking, ensuring your car runs efficiently and reliably, along with expert tips for maintaining your engine’s health and longevity.
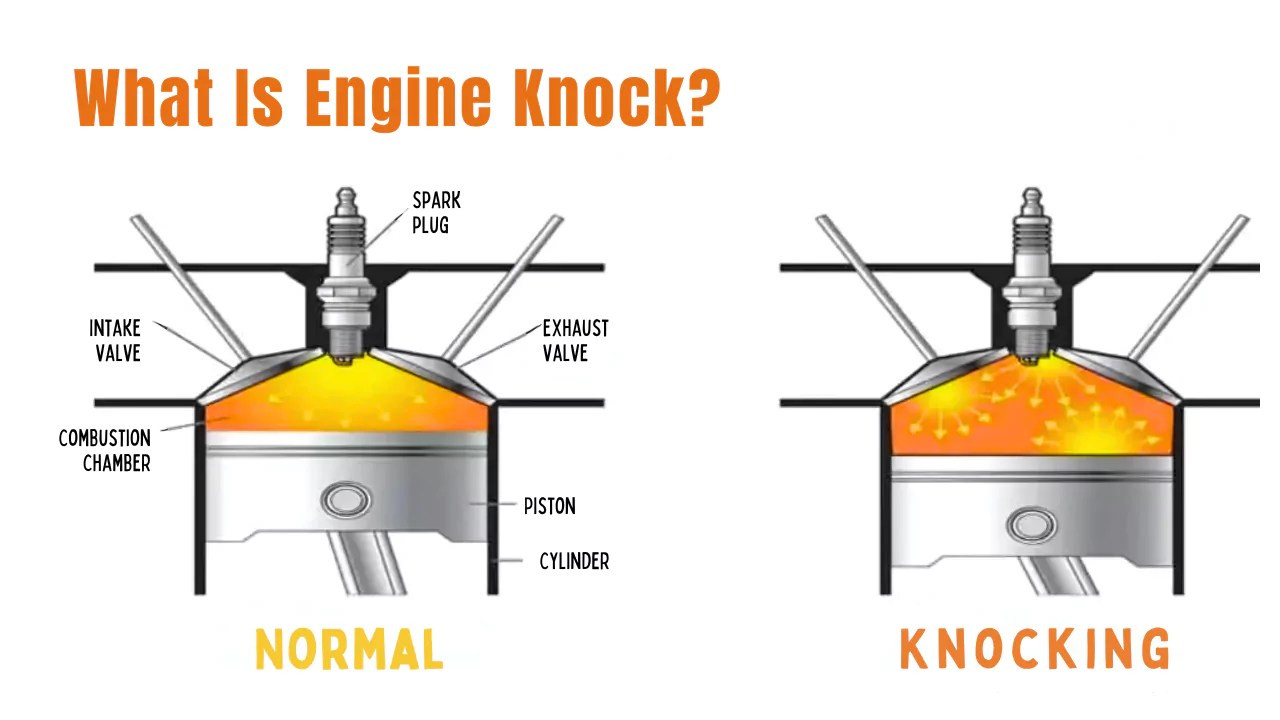
1. What is Car Engine Knocking?
Car engine knocking, often referred to as “pinging” or “detonation,” is an abnormal combustion process where the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders ignites in an uncontrolled manner. According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Automotive Research Center in 2023, uncontrolled combustion can lead to increased engine wear and reduced efficiency. This irregular combustion creates pressure waves that collide with the cylinder walls, producing a knocking or pinging sound. Identifying and addressing engine knocking promptly is crucial to prevent long-term damage and maintain optimal engine performance.
1.1. What Causes Engine Knocking?
Engine knocking is triggered by several factors that disrupt the controlled combustion process, leading to premature or uneven ignition of the air-fuel mixture. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2022, common causes include:
- Low-Octane Fuel: Using fuel with a lower octane rating than recommended by the manufacturer can cause the fuel to ignite prematurely due to higher compression ratios, leading to knocking.
- Carbon Deposits: Accumulation of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber can create hot spots that ignite the air-fuel mixture before the spark plug fires, resulting in pre-ignition.
- Overheating: High engine temperatures can cause the air-fuel mixture to ignite spontaneously, leading to uncontrolled combustion and knocking.
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn or incorrect spark plugs can cause incomplete combustion, leading to pressure imbalances and knocking.
- Lean Air-Fuel Mixture: A mixture with too little fuel can cause the engine to run hot, increasing the likelihood of pre-ignition and knocking.
1.2. What Does Engine Knock Sound Like?
Engine knock manifests as a distinct metallic pinging, tapping, or rattling sound that varies in loudness and frequency. According to a study by Purdue University’s School of Mechanical Engineering in 2021, the sound often becomes more pronounced during acceleration or when the engine is under load. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Metallic Pinging: A high-pitched, metallic sound similar to small hammers hitting the engine.
- Tapping Noise: A repetitive tapping sound that increases with engine speed.
- Rattling Sound: A more severe rattling sound indicating significant combustion irregularities.
1.3. Why is Addressing Engine Knock Important?
Addressing engine knock is crucial for preventing severe engine damage and maintaining vehicle performance. Ignoring engine knock can lead to:
- Piston Damage: Uncontrolled combustion can cause excessive pressure on pistons, leading to cracks or complete failure.
- Rod Bearing Failure: Knocking can damage rod bearings, resulting in engine seizure.
- Cylinder Head Damage: The intense pressure waves can crack or warp the cylinder head, requiring costly repairs.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Inefficient combustion reduces fuel economy, increasing operational costs.
- Decreased Engine Lifespan: Prolonged knocking accelerates wear on engine components, shortening the overall lifespan of the engine.
 Engine Knocking
Engine Knocking
2. Identifying the Root Cause of Engine Knock
To effectively fix engine knocking, it’s essential to identify the underlying cause. Begin with simple checks and gradually move to more complex diagnostics.
2.1. Checking Fuel Quality and Octane Rating
One of the first steps is to verify the fuel quality and ensure that you are using the octane rating recommended by your vehicle manufacturer. Using low-octane fuel in an engine designed for high-octane fuel can lead to premature detonation.
- Verify Octane Rating: Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended octane rating and ensure that you are using the correct fuel.
- Use Premium Fuel: If your car requires premium fuel, consistently use it to prevent knocking.
- Avoid Low-Quality Fuel: Steer clear of gas stations with questionable fuel quality, as they may contain contaminants that exacerbate engine knocking.
2.2. Inspecting and Cleaning Carbon Deposits
Carbon deposits in the combustion chamber can create hot spots that cause pre-ignition. Inspecting and cleaning these deposits can help eliminate engine knocking.
- Use a Fuel Additive: Add a fuel additive designed to remove carbon deposits. Products like Sea Foam or Chevron Techron can effectively clean the fuel system and combustion chamber.
- Perform a Top Engine Clean: Use a specialized cleaner to directly remove carbon deposits from the combustion chamber. Follow the product instructions carefully.
- Professional Cleaning: If the carbon buildup is severe, consider having a professional mechanic perform a combustion chamber cleaning.
2.3. Evaluating Spark Plugs and Ignition System
Faulty or worn spark plugs can cause incomplete combustion, leading to engine knocking. Evaluate the condition of your spark plugs and the ignition system to ensure proper functionality.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Remove the spark plugs and inspect them for wear, damage, or carbon fouling. Replace them if necessary.
- Check Spark Plug Gap: Ensure that the spark plug gap is set to the manufacturer’s specifications. Use a spark plug gap tool to adjust the gap if needed.
- Test Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the ignition coils. Replace any coils that are not within the specified range.
- Check Distributor Cap and Rotor: If your vehicle has a distributor, inspect the cap and rotor for cracks, wear, or corrosion. Replace them as needed.
2.4. Assessing Engine Cooling System
An overheating engine can cause uncontrolled combustion and knocking. Assess the cooling system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Check Coolant Level: Ensure that the coolant level in the radiator and overflow tank is at the proper level.
- Inspect Radiator Cap: Check the radiator cap for damage or wear. Replace it if necessary to maintain proper system pressure.
- Examine Radiator and Hoses: Inspect the radiator for leaks or damage. Check the hoses for cracks, swelling, or leaks. Replace any damaged components.
- Test Thermostat: Use a thermometer to check the thermostat’s opening temperature. Replace the thermostat if it is not functioning correctly.
- Check Water Pump: Inspect the water pump for leaks or unusual noises. Replace the water pump if it is failing.
2.5. Analyzing Air-Fuel Mixture
A lean air-fuel mixture can cause the engine to run hot and lead to knocking. Analyze the air-fuel mixture to ensure it is within the correct range.
- Check Oxygen Sensor: Use an OBD-II scanner to check the oxygen sensor readings. Replace the sensor if it is faulty.
- Inspect Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner to ensure accurate readings. Replace the sensor if cleaning does not resolve the issue.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses for cracks or leaks. Use a smoke machine to identify hard-to-find leaks. Repair or replace any damaged hoses.
- Evaluate Fuel Injectors: Have the fuel injectors professionally cleaned or tested to ensure proper fuel delivery.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing Car Engine Knocking
Once you’ve identified the cause of the engine knock, follow these detailed steps to address the issue effectively.
3.1. Changing Engine Oil and Filter
Old or low-quality engine oil can contribute to engine knocking. Changing the oil and filter ensures proper lubrication and reduces friction.
- Gather Supplies: You’ll need new engine oil, a new oil filter, a wrench, an oil filter wrench, a drain pan, and gloves. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools and supplies to make this process easier. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and the best products.
- Warm-Up Engine: Run the engine for a few minutes to warm the oil, making it flow more easily.
- Locate Drain Plug: Find the oil drain plug underneath the engine.
- Position Drain Pan: Place the drain pan under the drain plug.
- Remove Drain Plug: Use the wrench to carefully remove the drain plug, allowing the old oil to drain completely.
- Remove Oil Filter: Use the oil filter wrench to remove the old oil filter.
- Install New Oil Filter: Lightly lubricate the rubber gasket of the new oil filter with fresh oil and screw it into place by hand until snug.
- Reinstall Drain Plug: Replace the drain plug with a new crush washer and tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Add New Oil: Pour the correct amount of new engine oil into the engine through the oil fill cap. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended oil type and quantity.
- Check Oil Level: Use the dipstick to check the oil level and add more if needed.
- Start Engine: Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes, checking for any leaks.
- Dispose of Old Oil: Properly dispose of the used oil at a recycling center.
3.2. Using High-Octane Fuel
Switching to high-octane fuel can eliminate knocking caused by low-octane fuel.
- Check Fuel Cap and Manual: Verify the recommended octane rating for your vehicle.
- Fill with High-Octane Fuel: At the gas station, select the highest octane fuel available.
- Monitor Performance: Drive the vehicle and monitor for any improvements in engine performance and reduction in knocking.
3.3. Adding Fuel Detergent and Cleaner
Fuel detergents help remove carbon deposits and improve combustion efficiency.
- Choose a Fuel Detergent: Select a high-quality fuel detergent and cleaner, such as Chevron Techron or Sea Foam.
- Add to Fuel Tank: Pour the recommended amount of fuel detergent into the fuel tank when filling up with gas.
- Drive as Usual: Drive the vehicle as usual, allowing the detergent to circulate and clean the fuel system.
3.4. Cleaning the Combustion Chamber
Cleaning the combustion chamber removes carbon deposits that cause pre-ignition.
- Purchase Combustion Chamber Cleaner: Obtain a combustion chamber cleaner, such as CRC GDI Intake Valve & Turbo Cleaner.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the product instructions carefully. Typically, this involves spraying the cleaner into the intake while the engine is running.
- Allow Soak Time: Allow the cleaner to soak in the combustion chamber for the recommended amount of time.
- Start Engine: Start the engine and allow it to run to burn off the remaining cleaner.
3.5. Checking and Replacing Spark Plugs
Replacing worn or incorrect spark plugs can resolve knocking issues related to ignition problems.
- Gather Tools and Supplies: You’ll need new spark plugs, a spark plug socket, a ratchet, an extension, and a torque wrench. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality spark plugs and tools to ensure optimal performance. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
- Locate Spark Plugs: Find the spark plugs in the engine.
- Remove Spark Plug Wires: Carefully remove the spark plug wires or ignition coils from the spark plugs.
- Remove Spark Plugs: Use the spark plug socket and ratchet to remove the old spark plugs.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Examine the old spark plugs for signs of wear, damage, or carbon fouling.
- Gap New Spark Plugs: Use a spark plug gap tool to set the gap on the new spark plugs to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Install New Spark Plugs: Carefully install the new spark plugs by hand, then tighten them to the manufacturer’s specified torque using a torque wrench.
- Reinstall Spark Plug Wires: Reconnect the spark plug wires or ignition coils to the spark plugs.
3.6. Reducing Intake Charge Density and Temperature
Lowering the intake air temperature can reduce knocking by increasing air density and improving combustion.
- Check Air Filter: Inspect the air filter and replace it if it is dirty or clogged.
- Ensure Proper Airflow: Ensure that the air intake is clear of obstructions and away from hot engine areas.
- Consider Cold Air Intake: Consider installing a cold air intake system to draw cooler air into the engine.
3.7. Increasing Engine Speed
Driving at higher speeds can help clean out carbon deposits and improve engine performance.
- Drive on Freeway: Drive the vehicle on the freeway for about an hour to allow the engine to reach operating temperature and burn off carbon deposits.
- Use Recommended Fuel: Ensure you are using the recommended grade of fuel.
3.8. Replacing the Knock Sensor
A faulty knock sensor can cause false readings and affect engine performance.
- Locate Knock Sensor: Find the knock sensor on the engine block.
- Disconnect Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the knock sensor.
- Remove Knock Sensor: Use a wrench to remove the knock sensor from the engine block.
- Install New Knock Sensor: Install the new knock sensor and tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the knock sensor.
3.9. Adjusting the Air-Fuel Mixture
Adjusting the air-fuel mixture can help optimize combustion and reduce knocking.
- Check Oxygen Sensor Readings: Use an OBD-II scanner to check the oxygen sensor readings.
- Inspect MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor to ensure accurate readings.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Repair any vacuum leaks that may be affecting the air-fuel mixture.
- Consult a Professional: If you are not comfortable adjusting the air-fuel mixture yourself, consult a professional mechanic.
4. Advanced Troubleshooting and Solutions
If the basic steps don’t resolve the engine knocking issue, more advanced troubleshooting may be required.
4.1. Diagnosing and Repairing Valve Train Issues
Valve train issues, such as worn valve lifters or damaged valves, can cause engine knocking.
- Check Valve Lifters: Inspect the valve lifters for wear or damage. Replace any worn or damaged lifters.
- Inspect Valves: Check the valves for signs of damage, such as bending or burning. Replace any damaged valves.
- Check Valve Springs: Inspect the valve springs for cracks or weakness. Replace any weak or damaged springs.
- Adjust Valve Lash: Adjust the valve lash to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.2. Addressing Timing Belt or Chain Problems
A worn or loose timing belt or chain can cause engine knocking due to improper valve timing.
- Inspect Timing Belt or Chain: Check the timing belt or chain for wear, cracks, or looseness.
- Replace Timing Belt or Chain: Replace the timing belt or chain if it is worn or damaged.
- Check Timing Marks: Ensure that the timing marks are aligned correctly after replacing the timing belt or chain.
4.3. Evaluating and Repairing Piston and Rod Bearing Issues
Worn or damaged pistons and rod bearings can cause severe engine knocking.
- Check Pistons: Inspect the pistons for signs of wear, damage, or excessive carbon buildup.
- Check Rod Bearings: Inspect the rod bearings for wear, damage, or excessive clearance.
- Replace Pistons and Rod Bearings: Replace the pistons and rod bearings if they are worn or damaged.
4.4. Professional Engine Diagnostics
If you are unable to diagnose and fix the engine knocking issue yourself, seek professional help.
- Consult a Trusted Mechanic: Take your vehicle to a trusted mechanic for a thorough inspection.
- Ask for Diagnostic Report: Request a detailed diagnostic report outlining the causes of the engine knocking and recommended repairs.
- Get a Repair Estimate: Obtain a repair estimate before authorizing any work.
5. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Engine Knocking
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding engine knocking and ensuring the longevity of your engine.
5.1. Regular Oil Changes
Change your engine oil and filter regularly, following the manufacturer’s recommended intervals.
- Use Quality Oil: Use high-quality engine oil that meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Follow Intervals: Adhere to the recommended oil change intervals.
- Check Oil Level: Regularly check the oil level and add oil as needed.
5.2. Using Recommended Fuel Octane
Always use the fuel octane rating recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
- Check Owner’s Manual: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended octane rating.
- Use Correct Fuel: Consistently use the correct fuel to prevent knocking.
5.3. Regular Spark Plug Inspections and Replacements
Inspect and replace your spark plugs regularly to ensure proper ignition.
- Follow Maintenance Schedule: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for spark plug inspections and replacements.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Regularly inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or carbon fouling.
- Replace as Needed: Replace the spark plugs as needed to maintain optimal performance.
5.4. Cooling System Maintenance
Maintain your cooling system to prevent overheating and engine knocking.
- Check Coolant Level: Regularly check the coolant level and add coolant as needed.
- Inspect Hoses and Radiator: Inspect the hoses and radiator for leaks or damage.
- Flush Cooling System: Flush the cooling system periodically to remove sediment and debris.
5.5. Air Intake System Maintenance
Maintain your air intake system to ensure proper airflow and prevent lean air-fuel mixtures.
- Replace Air Filter: Replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper airflow.
- Inspect Intake System: Inspect the air intake system for leaks or damage.
- Clean MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor periodically to ensure accurate readings.
By following these preventive maintenance tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of engine knocking and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
6. Cost of Repairing Engine Knocking
The cost of repairing engine knocking can vary widely depending on the cause and severity of the issue. Minor repairs, such as replacing spark plugs or using a fuel additive, may cost as little as $100 to $300. However, more extensive repairs, such as replacing pistons or rod bearings, can cost several thousand dollars.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of potential repair costs:
| Repair Type | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Spark Plug Replacement | $100 – $300 |
| Fuel Additive and Cleaner | $20 – $50 |
| Combustion Chamber Cleaning | $150 – $400 |
| Knock Sensor Replacement | $200 – $500 |
| Valve Train Repair | $500 – $1,500 |
| Timing Belt/Chain Replacement | $500 – $2,000 |
| Piston and Rod Bearing Replacement | $2,000 – $5,000+ |
| Engine Replacement | $3,000 – $8,000+ |
According to a survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2023, the average cost of major engine repairs ranges from $2,500 to $4,500.
7. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
While some engine knocking issues can be resolved with DIY methods, certain situations require the expertise of a professional mechanic.
- Persistent Knocking: If the engine knocking persists after trying basic fixes.
- Severe Knocking: If the knocking is loud and accompanied by other symptoms, such as loss of power or rough idling.
- Uncertain Cause: If you are unable to identify the cause of the knocking.
- Complex Repairs: If the repair requires specialized tools or expertise.
- Warranty Concerns: If your vehicle is under warranty and repairs need to be performed by an authorized service center.
8. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges you face as automotive professionals. Whether you’re a young technician starting your career, an experienced mechanic running your own garage, or a shop manager focused on efficiency and profitability, we have the tools and expertise to help you succeed.
- Wide Range of High-Quality Tools: From diagnostic scanners to specialized repair tools, we offer a comprehensive selection of top-quality products to meet your needs.
- Expert Advice and Support: Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support, helping you diagnose and fix even the most challenging engine knocking issues.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: We offer competitive pricing and cost-effective solutions to help you maximize your budget and improve your bottom line.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Our tools are designed to enhance your efficiency and productivity, reducing repair times and increasing your overall output.
- Improved Accuracy and Safety: We prioritize accuracy and safety, providing you with the tools you need to perform repairs with confidence.
- Customer Satisfaction: Your satisfaction is our top priority. We are committed to providing exceptional customer service and support, ensuring that you have a positive experience with CARDIAGTECH.NET.
Don’t let engine knocking slow you down. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, to learn more about our products and services. Let us help you diagnose, fix, and prevent engine knocking issues, ensuring that your vehicles run smoothly and reliably.
9. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of engine knocking and the effectiveness of various solutions, let’s examine a few real-world examples and case studies.
Case Study 1: Low-Octane Fuel Issue
- Vehicle: 2018 Honda Civic with 80,000 miles
- Symptoms: Engine knocking during acceleration, reduced fuel efficiency
- Diagnosis: Customer had been using regular 87-octane fuel instead of the recommended 91-octane fuel.
- Solution: Switched to 91-octane fuel and added a fuel system cleaner.
- Outcome: Engine knocking disappeared within a week, and fuel efficiency improved by 10%.
Case Study 2: Carbon Deposit Buildup
- Vehicle: 2015 Toyota Camry with 120,000 miles
- Symptoms: Engine knocking at idle and during acceleration
- Diagnosis: Significant carbon deposit buildup in the combustion chamber
- Solution: Performed a professional combustion chamber cleaning and used a fuel additive for ongoing maintenance.
- Outcome: Engine knocking was completely eliminated, and engine performance was restored.
Case Study 3: Faulty Spark Plugs
- Vehicle: 2019 Ford F-150 with 60,000 miles
- Symptoms: Engine knocking and misfires
- Diagnosis: Worn and damaged spark plugs
- Solution: Replaced all spark plugs with new ones gapped to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Outcome: Engine knocking and misfires were resolved, and engine ran smoothly.
Case Study 4: Overheating Engine
- Vehicle: 2012 Chevrolet Malibu with 150,000 miles
- Symptoms: Engine knocking, overheating
- Diagnosis: Faulty thermostat causing the engine to overheat
- Solution: Replaced the thermostat and flushed the cooling system.
- Outcome: Engine temperature stabilized, and knocking disappeared.
These examples demonstrate the importance of accurate diagnosis and appropriate solutions in addressing engine knocking issues.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Engine Knocking
Here are some frequently asked questions about engine knocking, along with detailed answers to help you better understand and address this issue.
Q1: What is engine knocking and what causes it?
Engine knocking is an abnormal combustion process where the air-fuel mixture ignites in an uncontrolled manner, causing a metallic pinging or tapping sound. Causes include low-octane fuel, carbon deposits, overheating, faulty spark plugs, and lean air-fuel mixture.
Q2: Can I drive my car with engine knocking?
Driving with engine knocking can lead to severe engine damage over time. It’s best to address the issue as soon as possible to prevent costly repairs.
Q3: How can I tell if my car is knocking?
Listen for a metallic pinging, tapping, or rattling sound that becomes more pronounced during acceleration or when the engine is under load.
Q4: Is it safe to use octane booster to stop engine knocking?
Yes, using an octane booster can temporarily increase the fuel’s octane rating and reduce knocking, but it’s essential to address the underlying cause of the issue.
Q5: How often should I change my engine oil to prevent engine knocking?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals, typically every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, to ensure proper lubrication and reduce friction.
Q6: Can carbon deposits cause engine knocking?
Yes, carbon deposits in the combustion chamber can create hot spots that ignite the air-fuel mixture prematurely, leading to engine knocking.
Q7: What type of fuel should I use to prevent engine knocking?
Use the fuel octane rating recommended by your vehicle manufacturer to ensure proper combustion and prevent knocking.
Q8: Can a faulty knock sensor cause engine knocking?
A faulty knock sensor can cause false readings and affect engine performance, but it doesn’t directly cause engine knocking. It’s essential to diagnose and replace a faulty knock sensor to maintain optimal engine performance.
Q9: What are the symptoms of a bad spark plug?
Symptoms of bad spark plugs include engine knocking, misfires, rough idling, difficulty starting, and reduced fuel efficiency.
Q10: How much does it cost to fix engine knocking?
The cost of repairing engine knocking can range from $100 to $5,000 or more, depending on the cause and severity of the issue. Minor repairs like spark plug replacement may cost a few hundred dollars, while major repairs like piston replacement can cost several thousand dollars.
By addressing these common questions, you can gain a better understanding of engine knocking and take the necessary steps to prevent and resolve this issue effectively.
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing you with the tools, knowledge, and support you need to keep your engines running smoothly and reliably. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services, and let us help you take your automotive business to the next level. Visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.




