Diagnose and Fix: Mercedes 2716 Code and Shifting Issues
Is your Mercedes-Benz experiencing frustrating shifting problems and displaying the dreaded 2716 code? At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the complexities of modern automotive diagnostics and repair. We provide the tools and knowledge you need to get your Mercedes back on the road, shifting smoothly and reliably. Discover the causes, solutions, and preventative measures to address the 2716 error code effectively. Let’s explore this common Mercedes issue and how to resolve it.
1. Decoding the Mercedes-Benz 2716 Code: Understanding the Root Cause
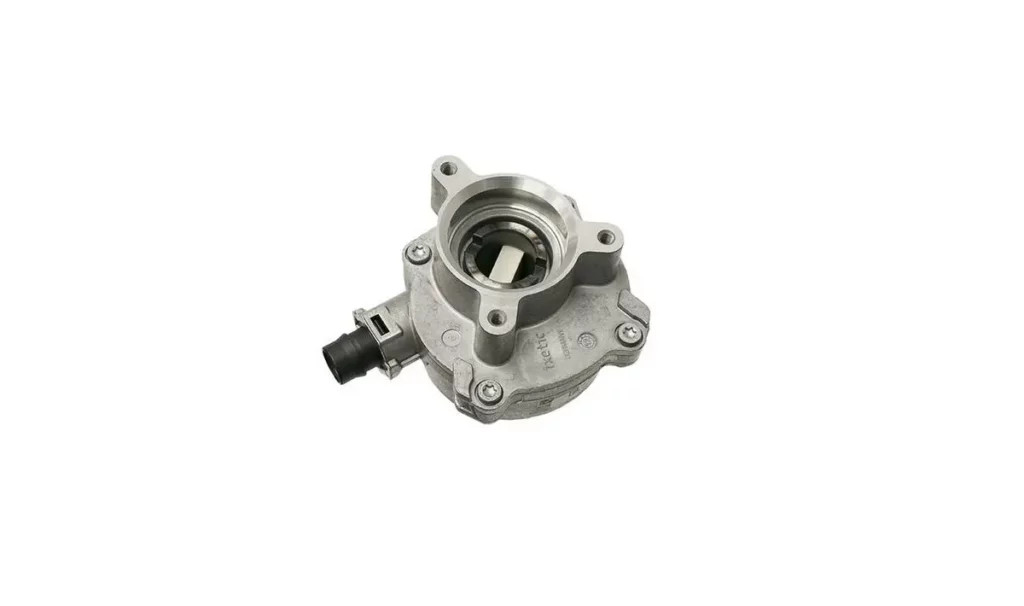
The P2716 code in a Mercedes-Benz indicates a malfunction within the transmission system, specifically related to the “K3 clutch control solenoid valve” (Y3/8y4). This solenoid plays a crucial role in regulating hydraulic pressure to the K3 clutch, which is vital for smooth and accurate gear changes. When this solenoid malfunctions, it can lead to various transmission-related symptoms. According to Mercedes-Benz WIS (Workshop Information System), addressing this issue promptly can prevent further damage.
1.1 Common Symptoms Associated with the 2716 Code
Several noticeable symptoms can indicate a P2716 error in your Mercedes. These include:
- Harsh or Jerky Shifting: The most common symptom is rough gear changes, especially during acceleration or deceleration.
- Delayed Engagement: A noticeable delay when shifting between gears, such as from Park to Drive or Reverse.
- Gear Slippage: The transmission may unexpectedly slip out of gear while driving, leading to a loss of power.
- Limp Mode: In severe cases, the car may enter limp mode, limiting speed and gear selection to protect the transmission.
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The malfunction will trigger the check engine light on your dashboard, signaling the need for diagnostic attention.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: Inefficient gear shifting can result in a decrease in your car’s fuel efficiency.
 Mercedes Transmission Problems
Mercedes Transmission Problems
1.2 Potential Causes Behind the 2716 Error Code
Understanding the potential causes of the P2716 code is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective repair. Key causes include:
- Faulty Solenoid Valve: The most direct cause is a malfunctioning K3 clutch control solenoid valve (Y3/8y4). This could be due to electrical failure, mechanical wear, or internal blockage.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connecting the solenoid to the transmission control unit (TCU) can disrupt the signal and trigger the error code.
- Valve Body Problems: The valve body houses the solenoids and regulates hydraulic fluid flow. Contamination or damage within the valve body can affect solenoid performance.
- Transmission Fluid Issues: Low, contaminated, or incorrect transmission fluid can impede the proper functioning of the solenoids and the overall transmission system.
- TCU Malfunction: Though less common, a faulty TCU can send incorrect signals to the solenoid, leading to the P2716 code.
2. Diagnosing the 2716 Code: Step-by-Step Guide
Proper diagnosis is crucial to accurately identify the root cause of the P2716 code and implement the correct repair. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
2.1 Initial Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the transmission system:
- Check Transmission Fluid Level and Condition: Use the dipstick to check the fluid level. The fluid should be bright red and free of debris. Dark or burnt fluid indicates contamination or overheating.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Examine the wiring and connectors leading to the transmission and solenoid valves for any signs of damage, corrosion, or looseness.
- Look for Leaks: Inspect the transmission housing and surrounding area for any signs of fluid leaks.
2.2 Diagnostic Scan
Use a professional-grade diagnostic scanner to read the fault codes stored in the TCU:
- Confirm the P2716 Code: Verify that the P2716 code is present along with any other related transmission codes.
- Read Freeze Frame Data: Examine the freeze frame data associated with the P2716 code. This data provides valuable information about the conditions when the error occurred, such as engine speed, load, and temperature.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that are perfect for accurately reading and interpreting these codes.
2.3 Testing the Solenoid Valve
To determine if the solenoid valve is functioning correctly, perform the following tests:
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the solenoid valve. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications. An open circuit or short circuit indicates a faulty solenoid.
- Activation Test: Use the diagnostic scanner to activate the solenoid valve and listen for a clicking sound. The absence of a click suggests the solenoid is not functioning.
- Voltage Test: Check the voltage supply to the solenoid valve using a multimeter. Ensure the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage.
 Mercedes Diagnostic Scan
Mercedes Diagnostic Scan
2.4 Valve Body Inspection
If the solenoid tests appear normal, the issue may lie within the valve body:
- Remove the Valve Body: Carefully remove the valve body from the transmission, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect for Contamination: Check the valve body passages for any signs of debris, sludge, or metal particles.
- Test Valve Movement: Ensure all valves move freely within the valve body.
3. Repairing the 2716 Code: Practical Solutions
Once you’ve accurately diagnosed the cause of the P2716 code, you can proceed with the appropriate repair.
3.1 Replacing the Solenoid Valve
If the solenoid valve is found to be faulty, replacement is necessary:
- Purchase a New Solenoid: Obtain a high-quality replacement solenoid valve from a reputable supplier like CARDIAGTECH.NET to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Install the New Solenoid: Carefully install the new solenoid valve, ensuring it is properly seated and connected.
- Test the Transmission: After installation, test the transmission to verify the issue is resolved and the shifting is smooth.
3.2 Addressing Wiring Issues
Repairing wiring issues involves careful inspection and repair or replacement:
- Repair Damaged Wires: Repair any damaged or corroded wires by splicing in new sections of wire and using heat-shrink tubing to protect the connections.
- Replace Faulty Connectors: Replace any faulty connectors to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
- Check for Shorts or Opens: Use a multimeter to check for shorts or opens in the wiring harness.
3.3 Cleaning or Replacing the Valve Body
If the valve body is contaminated or damaged, cleaning or replacement may be required:
- Clean the Valve Body: Thoroughly clean the valve body using a specialized solvent to remove any debris or sludge.
- Replace the Valve Body: If the valve body is severely damaged or cleaning is not effective, replace it with a new or remanufactured unit.
- Ensure Proper Installation: Properly install the valve body, ensuring all valves and solenoids are correctly positioned.
3.4 Changing the Transmission Fluid
Changing the transmission fluid is a crucial step in maintaining the health of the transmission:
- Drain the Old Fluid: Drain the old transmission fluid from the transmission pan.
- Replace the Filter: Replace the transmission filter to remove any contaminants.
- Refill with New Fluid: Refill the transmission with the correct type and amount of transmission fluid, as specified by the manufacturer.
- Check Fluid Level: Verify the fluid level using the dipstick and adjust as needed.
 Mercedes Diagnostic Scan
Mercedes Diagnostic Scan
3.5 TCU Replacement or Reprogramming
If the TCU is suspected to be faulty, it may need to be replaced or reprogrammed:
- Replace the TCU: Replace the TCU with a new or remanufactured unit.
- Reprogram the TCU: Reprogram the TCU using a diagnostic scanner to ensure it is properly configured for your vehicle.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers high-quality TCU units and programming tools to ensure your vehicle operates smoothly.
4. Preventative Measures: Keeping Your Mercedes Transmission Healthy
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some preventative measures to help keep your Mercedes transmission healthy and avoid future issues with the P2716 code:
4.1 Regular Transmission Fluid Changes
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for transmission fluid changes. Regular fluid changes help to maintain the fluid’s lubricating properties and prevent the buildup of contaminants.
4.2 Inspect for Leaks
Regularly inspect the transmission for any signs of fluid leaks. Address any leaks promptly to prevent low fluid levels and potential damage to the transmission.
4.3 Avoid Aggressive Driving
Avoid aggressive driving habits such as hard acceleration and abrupt braking, which can put excessive strain on the transmission.
4.4 Professional Maintenance
Schedule regular maintenance checks with a qualified mechanic to ensure the transmission is functioning properly and to identify any potential issues early on.
4.5 Use High-Quality Parts and Fluids
Always use high-quality parts and fluids that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications. This helps to ensure the reliability and longevity of the transmission.
5. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Mercedes Repair Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing our customers with the highest quality diagnostic tools, replacement parts, and technical support to ensure successful Mercedes repairs. Here’s why you should choose us:
5.1 Extensive Product Range
We offer a wide range of diagnostic scanners, solenoid valves, valve bodies, transmission fluids, and other essential components for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
5.2 Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance to help you diagnose and repair your Mercedes.
5.3 High-Quality Products
We source our products from reputable manufacturers to ensure they meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
5.4 Competitive Pricing
We offer competitive pricing on all our products to make Mercedes repairs more affordable.
5.5 Customer Satisfaction
We are committed to providing excellent customer service and ensuring your satisfaction with our products and services.
6. Understanding Transmission Solenoids: Key to Smooth Shifting
Transmission solenoids are vital components in modern automatic transmissions, playing a critical role in managing gear shifts and overall transmission performance.
6.1 Role of Solenoids in Transmission
Solenoids are essentially electro-hydraulic valves that control the flow of transmission fluid within the valve body. These solenoids receive signals from the Transmission Control Unit (TCU), which dictates when and how gear shifts should occur. When a solenoid receives a signal, it opens or closes, directing fluid to specific clutches or bands, which then engage or disengage to change gears.
6.2 Types of Transmission Solenoids
There are several types of transmission solenoids, each serving a specific function:
- Shift Solenoids: These solenoids control the actual gear shifts by directing fluid to the appropriate clutches or bands.
- Pressure Control Solenoids: These solenoids regulate the hydraulic pressure within the transmission, ensuring smooth and precise shifts.
- Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoids: These solenoids control the engagement and disengagement of the torque converter clutch, improving fuel efficiency and reducing slippage.
6.3 Symptoms of Solenoid Failure
When a transmission solenoid fails, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
- Harsh or Erratic Shifting
- Delayed Shifting
- Gear Slippage
- Stuck in Gear
- Reduced Fuel Economy
- Check Engine Light
6.4 Diagnosing Solenoid Issues
Diagnosing solenoid issues typically involves using a diagnostic scanner to read fault codes, testing the solenoid’s resistance and voltage, and performing activation tests to ensure it is functioning properly.
6.5 Replacing a Solenoid
Replacing a faulty solenoid involves removing the transmission pan, accessing the valve body, and carefully removing and replacing the solenoid. It’s important to use high-quality replacement solenoids to ensure reliable performance.
7. Valve Body: The Hydraulic Heart of Your Transmission
The valve body is a critical component of the automatic transmission system, serving as the central control unit for hydraulic fluid flow.
7.1 Function of the Valve Body
The valve body is a complex assembly of channels, valves, and solenoids that work together to regulate the flow of transmission fluid. It receives signals from the TCU and directs fluid to the appropriate clutches and bands, enabling smooth and precise gear shifts.
7.2 Components of the Valve Body
The valve body consists of several key components:
- Channels and Passages: These channels direct the flow of transmission fluid throughout the valve body.
- Valves: These valves control the flow of fluid, opening and closing to direct fluid to the appropriate clutches and bands.
- Solenoids: These electro-hydraulic valves receive signals from the TCU and control the movement of the valves.
- Accumulators: These components help to cushion shifts, reducing harshness and improving overall transmission performance.
7.3 Common Valve Body Problems
Common valve body problems include:
- Contamination: Debris, sludge, and metal particles can accumulate in the valve body, clogging channels and preventing valves from moving freely.
- Worn Valves: Over time, the valves can wear out, leading to leaks and reduced hydraulic pressure.
- Sticking Valves: Valves can become stuck due to contamination or wear, preventing proper fluid flow.
- Solenoid Failure: As mentioned earlier, solenoid failure can also affect valve body performance.
7.4 Cleaning and Maintaining the Valve Body
Regular cleaning and maintenance can help to prevent valve body problems. This includes:
- Regular Transmission Fluid Changes: Changing the transmission fluid regularly helps to prevent the buildup of contaminants in the valve body.
- Cleaning the Valve Body: If the valve body is contaminated, it can be cleaned using a specialized solvent to remove any debris or sludge.
- Replacing Worn Components: Replacing worn valves and solenoids can help to restore proper valve body performance.
7.5 When to Replace the Valve Body
In some cases, the valve body may be too damaged or worn to be repaired, and replacement may be necessary. Signs that the valve body needs to be replaced include:
- Severe Contamination
- Extensive Valve Wear
- Cracked or Damaged Housing
8. Choosing the Right Transmission Fluid: A Critical Decision
Selecting the correct transmission fluid is vital for maintaining the health and performance of your Mercedes transmission.
8.1 Importance of Using the Correct Fluid
Using the wrong transmission fluid can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Poor Shifting Performance
- Increased Wear and Tear
- Transmission Damage
- Reduced Fuel Economy
8.2 Types of Transmission Fluid
There are several types of transmission fluid, each designed for specific types of transmissions:
- ATF (Automatic Transmission Fluid): This is the most common type of transmission fluid, used in most automatic transmissions.
- CVT Fluid (Continuously Variable Transmission Fluid): This fluid is specifically designed for CVT transmissions, which use a belt or chain instead of gears.
- DCT Fluid (Dual-Clutch Transmission Fluid): This fluid is designed for dual-clutch transmissions, which use two clutches to provide faster and smoother shifts.
8.3 How to Choose the Right Fluid
To choose the right transmission fluid for your Mercedes, follow these steps:
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual will specify the correct type of transmission fluid for your vehicle.
- Check the Fluid Specifications: Look for fluid specifications such as Dexron, Mercon, or ATF+4.
- Use a Reputable Brand: Choose a reputable brand of transmission fluid to ensure quality and reliability.
8.4 Changing the Transmission Fluid
When changing the transmission fluid, follow these steps:
- Drain the Old Fluid: Drain the old transmission fluid from the transmission pan.
- Replace the Filter: Replace the transmission filter to remove any contaminants.
- Refill with New Fluid: Refill the transmission with the correct type and amount of transmission fluid, as specified by the manufacturer.
- Check Fluid Level: Verify the fluid level using the dipstick and adjust as needed.
9. Essential Tools for Diagnosing and Repairing the 2716 Code
Having the right tools is essential for accurately diagnosing and effectively repairing the P2716 code. Here are some essential tools you’ll need:
9.1 Diagnostic Scanner
A professional-grade diagnostic scanner is crucial for reading fault codes, accessing freeze frame data, and performing activation tests.
9.2 Multimeter
A multimeter is needed for testing the resistance and voltage of the solenoid valves and wiring.
9.3 Torque Wrench
A torque wrench is essential for properly tightening bolts and fasteners to the manufacturer’s specifications.
9.4 Socket Set
A socket set with a variety of sizes is needed for removing and installing components such as the transmission pan and valve body.
9.5 Jack and Jack Stands
A jack and jack stands are needed for safely lifting the vehicle to access the transmission.
9.6 Transmission Fluid Pump
A transmission fluid pump is needed for refilling the transmission with new fluid.
9.7 Cleaning Supplies
Cleaning supplies such as solvent, brushes, and rags are needed for cleaning the valve body and other components.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Mercedes 2716 Code
Q1: What does the Mercedes 2716 code mean?
The P2716 code indicates an electrical fault with the K3 clutch control solenoid valve in the 722.9 transmission.
Q2: What are the common symptoms of the 2716 code?
Common symptoms include harsh shifting, delayed engagement, gear slippage, and limp mode.
Q3: Can I drive my car with the 2716 code?
It is not recommended to drive your car with the P2716 code, as it can cause further damage to the transmission.
Q4: What are the potential causes of the 2716 code?
Potential causes include a faulty solenoid valve, wiring issues, valve body problems, and low transmission fluid.
Q5: How do I diagnose the 2716 code?
Diagnosing the P2716 code involves performing a diagnostic scan, testing the solenoid valve, and inspecting the valve body.
Q6: Can I fix the 2716 code myself?
Fixing the P2716 code may require specialized tools and knowledge. It is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic.
Q7: How much does it cost to fix the 2716 code?
The cost to fix the P2716 code can vary depending on the cause and the extent of the repair. It is recommended to get a quote from a reputable mechanic.
Q8: What is the function of the K3 clutch control solenoid valve?
The K3 clutch control solenoid valve regulates hydraulic pressure to the K3 clutch, which is essential for smooth and accurate gear changes.
Q9: How often should I change my transmission fluid?
It is recommended to change your transmission fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, depending on your driving conditions and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Q10: Where can I find high-quality replacement parts for my Mercedes transmission?
You can find high-quality replacement parts for your Mercedes transmission at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide range of solenoids, valve bodies, and other essential components.
Experiencing the frustration of a Mercedes-Benz transmission issue is never ideal, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can confidently address the P2716 code and restore your vehicle’s performance. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to supporting you with top-quality diagnostic tools and expert advice. Don’t let transmission problems keep you off the road.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz repair? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for personalized assistance and premium diagnostic tools. Reach us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or call our WhatsApp line at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Let us help you get your Mercedes shifting smoothly again.




