9040 Mercedes Fault Code: Diagnosis and Solutions
CARDIAGTECH.NET presents expert guidance on troubleshooting the 9040 Mercedes fault code, focusing on identifying the root cause and providing effective repair strategies. This article equips you with the knowledge to address this issue confidently and efficiently, potentially saving time and money on repairs. Explore effective diagnostic techniques, component testing, and CAN bus communication analysis to resolve Mercedes-Benz electrical system problems, and learn about SAM module defects and their impacts on vehicle operation.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz 9040 Fault Code
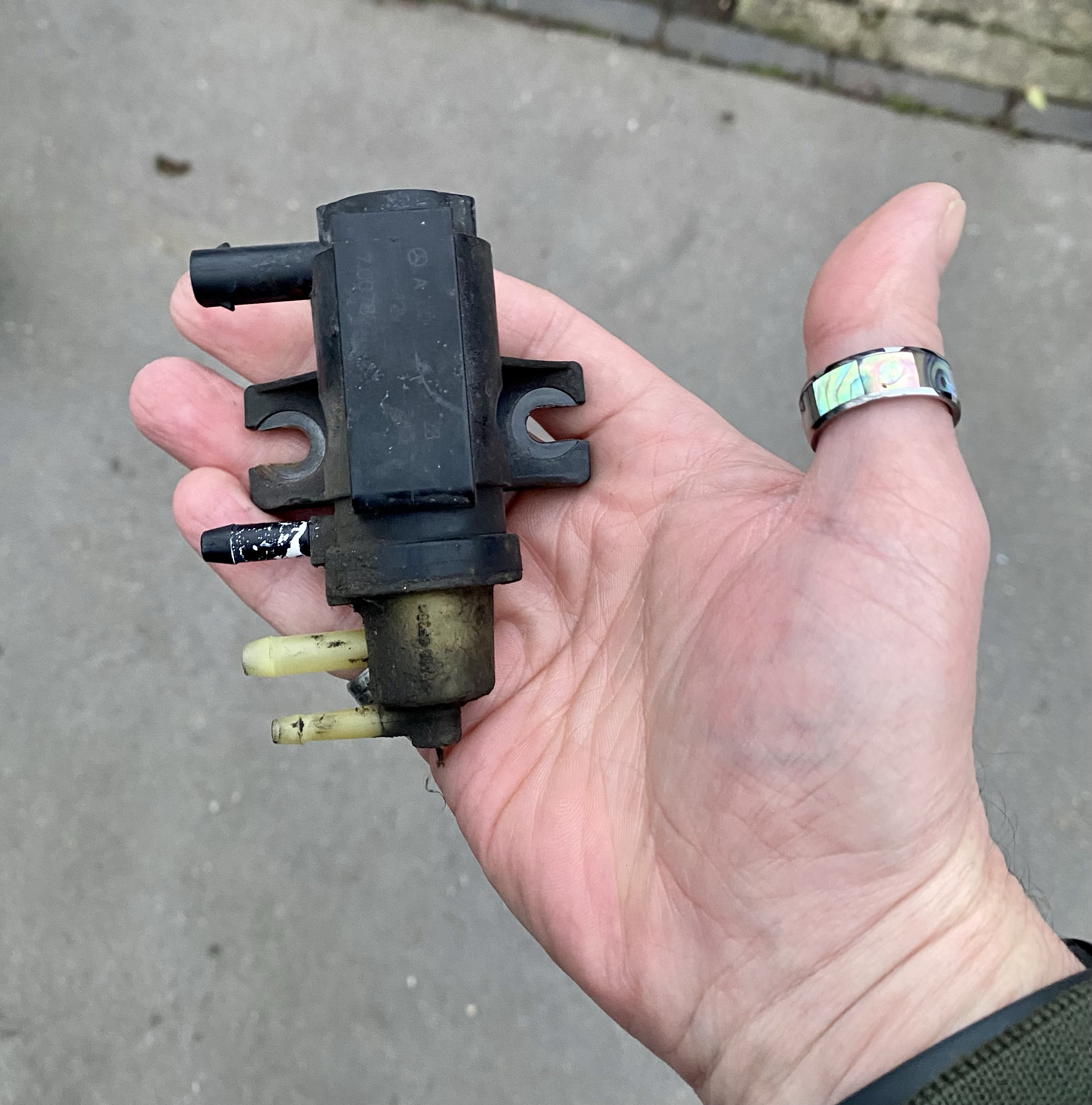
The Mercedes-Benz 9040 fault code, specifically related to the Driver’s SAM (Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module), indicates a defect or absence of the component N10/1kO, which is the fan relay module. This SAM module plays a crucial role in controlling various electrical functions in the vehicle, making its proper operation essential for overall system functionality. Understanding the specific role and potential issues with the SAM module can greatly aid in diagnosing the root cause of the problem.
1.1. What is the Driver’s SAM and its Role?
The Driver’s SAM (Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module) is an essential electronic control unit in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, responsible for managing and distributing electrical signals and power to various components. Think of it as a central hub connecting different parts of your car’s electrical system.
- Location: Usually found in the driver’s side footwell or under the dashboard.
- Functions:
- Controls lighting: headlights, taillights, turn signals
- Manages windshield wipers and washers
- Operates power windows and door locks
- Monitors sensor inputs for various systems
- Communicates with other control units via the CAN bus
1.2. Symptoms of a Defective Driver’s SAM
When the Driver’s SAM malfunctions, several issues may arise, impacting various electrical systems within the vehicle. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in diagnosing the problem quickly.
- Lighting Problems: Headlights, taillights, or turn signals not working correctly
- Wiper Issues: Windshield wipers failing to operate or functioning erratically
- Power Window/Lock Malfunctions: Inability to control power windows or door locks
- Cooling Fan Problems: Continuous operation of the engine cooling fan at maximum speed
- Communication Errors: Fault codes related to CAN bus communication with other control units
1.3. Potential Causes of the 9040 Fault Code
Several factors can trigger the 9040 fault code, including issues directly related to the fan relay module or broader problems within the SAM itself. Identifying the root cause is essential for an effective repair.
- Defective Fan Relay Module: The relay module (N10/1kO) itself may be faulty, preventing proper operation of the cooling fan.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring connections to the fan relay module or the SAM can disrupt communication and power supply.
- SAM Failure: The Driver’s SAM module may be failing internally due to electrical overload, water damage, or age.
- Software Glitches: Software issues within the SAM module can cause it to misinterpret signals or fail to operate correctly.
- CAN Bus Communication Problems: Disruptions in the CAN bus communication can prevent the SAM from receiving or sending necessary signals.
2. Detailed Diagnostic Steps for the 9040 Fault Code
Diagnosing the 9040 fault code requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the exact cause. This includes checking the fan relay module, inspecting wiring, and assessing the SAM module’s overall functionality.
2.1. Initial Inspection and Preliminary Checks
Before diving into complex diagnostics, start with a visual inspection and basic checks to rule out obvious issues.
- Visual Inspection: Check the Driver’s SAM module and the fan relay module for any visible signs of damage, such as burnt components, corrosion, or water damage.
- Wiring Inspection: Examine the wiring harness connected to the SAM and the fan relay module for any signs of damage, fraying, or loose connections.
- Fuse Check: Verify that the fuses related to the cooling fan and the SAM module are intact and not blown. Consult the vehicle’s fuse diagram for the correct fuse locations.
- Battery Voltage: Ensure the vehicle’s battery is fully charged and providing the correct voltage. Low voltage can cause erratic behavior in electronic modules.
2.2. Testing the Fan Relay Module (N10/1kO)
The fan relay module is a common culprit for the 9040 fault code. Testing its functionality can quickly determine if it is the source of the problem.
- Locate the Relay: Find the fan relay module (N10/1kO) in the Driver’s SAM. Refer to the vehicle’s wiring diagram for its exact location.
- Visual Inspection: Check the relay for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or burnt marks.
- Relay Testing with Multimeter:
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity between the relay’s terminals.
- Resistance Test: Measure the resistance of the relay coil to ensure it falls within the specified range (typically 70-120 ohms).
- Voltage Test: Apply voltage to the relay coil and listen for a click, indicating the relay is switching properly.
- Relay Swapping: If possible, swap the fan relay with another identical relay from a different system (e.g., horn relay). If the fault code disappears or the cooling fan starts working, the original relay is defective.
- Testing with a Relay Tester: Use a dedicated relay tester to perform comprehensive tests on the relay, including coil resistance, contact voltage drop, and insulation resistance.
2.3. Checking Wiring and Connections
Wiring issues can often lead to the 9040 fault code. Thoroughly inspecting the wiring and connections associated with the SAM and fan relay module is essential.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any signs of damaged, frayed, or corroded wires and connectors.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring between the SAM and the fan relay module.
- Voltage Drop Test: Measure the voltage drop across the wiring to identify any areas of high resistance. A voltage drop of more than 0.5 volts indicates a problem.
- Connector Inspection: Ensure that all connectors are properly seated and free from corrosion. Clean the connectors with electrical contact cleaner if necessary.
- Harness Inspection: Check the wiring harness for any signs of damage caused by rodents or heat. Repair or replace damaged sections of the harness as needed.
2.4. Evaluating the Driver’s SAM Module
If the fan relay and wiring check out, the issue might lie within the Driver’s SAM module itself.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the SAM module for any signs of physical damage, such as burnt components or water damage.
- CAN Bus Communication Test: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for communication errors between the SAM and other control units. Fault codes related to CAN bus communication can indicate a problem with the SAM.
- Voltage and Ground Checks: Verify that the SAM module is receiving the correct voltage and ground signals. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the SAM’s power and ground terminals.
- Software Update: Check for any available software updates for the SAM module. Outdated software can sometimes cause malfunctions.
- Module Replacement: If all other tests fail, the SAM module may need to be replaced. This often requires programming the new module to match the vehicle’s specifications.
2.5. Using a Diagnostic Scanner
A diagnostic scanner is an indispensable tool for diagnosing the 9040 fault code. It can provide valuable information about the system’s status and help pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the diagnostic scanner into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Read Fault Codes: Retrieve all stored fault codes from the SAM module and other related control units.
- Clear Fault Codes: After noting the fault codes, clear them to see if they reappear during testing.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor live data from the SAM module, such as relay status, voltage readings, and communication signals.
- Actuation Tests: Use the scanner to perform actuation tests on the fan relay module and other components controlled by the SAM.
- Freeze Frame Data: Examine freeze frame data associated with the 9040 fault code to gain insight into the conditions under which the fault occurred.
3. Repairing the 9040 Mercedes-Benz Fault Code
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the 9040 fault code, the next step is to implement the appropriate repair. This could involve replacing the fan relay module, repairing wiring, or replacing/reprogramming the Driver’s SAM.
3.1. Replacing the Fan Relay Module
If the fan relay module is found to be defective, replacing it is a straightforward process.
- Locate the Relay: Identify the fan relay module (N10/1kO) in the Driver’s SAM.
- Disconnect Power: Turn off the ignition and disconnect the vehicle’s battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Remove the Old Relay: Carefully remove the old relay from its socket.
- Install the New Relay: Insert the new relay into the socket, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Reconnect Power: Reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Test the System: Start the engine and verify that the cooling fan is operating correctly.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any stored fault codes.
3.2. Repairing Wiring Issues
Damaged wiring can cause various electrical problems, including the 9040 fault code. Repairing wiring issues requires careful attention to detail.
- Identify the Damage: Locate the damaged section of wiring.
- Disconnect Power: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Repair the Wiring:
- Splicing: Use a proper wire splicing technique to connect the damaged wires.
- Soldering: Solder the wires together for a more secure connection.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Cover the spliced or soldered connection with heat shrink tubing to protect it from moisture and corrosion.
- Replace Connectors: If the connector is damaged, replace it with a new one.
- Secure the Wiring: Secure the repaired wiring harness with zip ties or electrical tape to prevent it from rubbing against other components.
- Reconnect Power: Reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Test the System: Start the engine and verify that the cooling fan is operating correctly.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any stored fault codes.
3.3. Replacing or Reprogramming the Driver’s SAM
If the Driver’s SAM module is found to be faulty, it may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
- Module Replacement:
- Disconnect Power: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Remove the Old SAM: Carefully remove the old SAM module from its location.
- Install the New SAM: Install the new SAM module, ensuring it is properly connected.
- Reconnect Power: Reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Programming: The new SAM module will likely need to be programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications. This may require a specialized diagnostic tool and access to the manufacturer’s software.
- Module Reprogramming:
- Connect Diagnostic Tool: Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access SAM Module: Access the SAM module’s programming menu.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to reprogram the SAM module with the latest software.
- Test the System: Start the engine and verify that the cooling fan is operating correctly.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any stored fault codes.
3.4. Software Updates and Recoding
Keeping the software up-to-date is crucial for optimal performance.
- Check for Updates: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for any available software updates for the SAM module and other related control units.
- Install Updates: Follow the scanner’s instructions to install the updates.
- Recoding: After installing software updates, the SAM module may need to be recoded to ensure it is properly configured for the vehicle.
- Test the System: Start the engine and verify that all systems are functioning correctly.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any stored fault codes.
4. Preventing Future Occurrences of the 9040 Fault Code
Preventing the recurrence of the 9040 fault code involves regular maintenance and proactive measures to protect the vehicle’s electrical system.
4.1. Regular Maintenance Tips
- Keep Battery in Good Condition: Ensure the vehicle’s battery is regularly tested and maintained. A weak battery can cause erratic behavior in electronic modules.
- Check Wiring Regularly: Periodically inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Protect Against Moisture: Keep the SAM module and other electrical components protected from moisture and water damage.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing components, use high-quality parts that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Regular Diagnostic Scans: Perform regular diagnostic scans to check for any stored fault codes or potential problems.
4.2. Protecting Electrical Components from Damage
- Avoid Water Exposure: Avoid exposing the SAM module and other electrical components to water. If the vehicle is exposed to flooding, have the electrical system inspected by a qualified technician.
- Rodent Protection: Take measures to protect the wiring harness from rodent damage. Use rodent repellent sprays or install protective covers on the wiring.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that all electrical components are properly installed and secured. Loose components can vibrate and cause damage to wiring and connections.
- Fuse Protection: Use the correct size fuses for each circuit. Over-sized fuses can allow excessive current to flow, causing damage to electrical components.
4.3. Staying Updated with Software Updates
- Check Regularly: Regularly check for software updates for the SAM module and other control units.
- Professional Installation: Have software updates installed by a qualified technician to ensure they are properly installed and configured.
- Read Release Notes: Before installing software updates, read the release notes to understand the changes and potential benefits of the update.
5. Understanding CAN Bus Communication
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a critical communication system in modern vehicles, allowing various electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other. Understanding how the CAN bus works is essential for diagnosing and repairing many electrical issues, including those related to the 9040 fault code.
5.1. What is CAN Bus and How Does It Work?
The CAN bus is a serial communication protocol that allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in a vehicle without a host computer.
- Components:
- ECUs (Electronic Control Units): These are the various control modules in the vehicle, such as the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), and SAM modules.
- CAN Transceiver: This is the physical interface that connects the ECU to the CAN bus. It transmits and receives data signals.
- CAN Bus Wires: These are the physical wires that carry the data signals between the ECUs. The CAN bus typically consists of two wires: CAN High and CAN Low.
- How it Works:
- Data Transmission: When an ECU needs to send data to another ECU, it transmits the data in the form of a CAN message.
- Message Structure: A CAN message consists of an identifier, data, and error-checking information.
- Message Arbitration: If multiple ECUs attempt to transmit data at the same time, the CAN bus uses a priority-based arbitration scheme to determine which message is transmitted first.
- Data Reception: All ECUs on the CAN bus receive the transmitted message, but only the ECU with the matching identifier processes the data.
5.2. Common CAN Bus Communication Problems
Several issues can disrupt CAN bus communication, leading to various electrical problems in the vehicle.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or shorted CAN bus wires can disrupt communication.
- ECU Failure: A malfunctioning ECU can disrupt CAN bus communication.
- Termination Resistor Problems: The CAN bus requires termination resistors at each end of the network to prevent signal reflections. If these resistors are faulty, it can disrupt communication.
- Software Glitches: Software issues within the ECUs can cause communication errors.
- Overload: Excessive traffic on the CAN bus can cause communication problems.
5.3. Diagnosing CAN Bus Issues
Diagnosing CAN bus issues requires specialized tools and techniques.
- Visual Inspection: Check the CAN bus wires and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the CAN bus wires.
- Resistance Test: Measure the resistance of the termination resistors to ensure they are within the specified range (typically 120 ohms).
- Oscilloscope: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the CAN bus signals and identify any distortions or abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Scanner: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for CAN bus communication errors and monitor live data from the ECUs.
6. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For complex cases, advanced troubleshooting techniques may be necessary to diagnose the 9040 fault code accurately.
7.1. Using Oscilloscopes for Signal Analysis
An oscilloscope is a powerful tool for analyzing electrical signals in detail.
- Signal Waveforms: Use an oscilloscope to examine the waveforms of the signals being sent to and from the SAM module and the fan relay module.
- Voltage Levels: Measure the voltage levels of the signals to ensure they are within the specified range.
- Signal Timing: Analyze the timing of the signals to identify any delays or disruptions.
- Noise and Interference: Detect any noise or interference on the signals that could be causing communication problems.
7.2. Analyzing Wiring Diagrams
Wiring diagrams are essential for understanding the electrical connections in the vehicle.
- Trace Circuits: Use wiring diagrams to trace the circuits related to the SAM module and the fan relay module.
- Identify Components: Identify the locations of the components in the circuits.
- Check Connections: Verify that all connections are properly made and that there are no breaks in the wiring.
7.3. Component Testing In-Depth
Sometimes, individual components need thorough testing to uncover hidden issues.
- Sensors: Test the sensors that provide input to the SAM module to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Actuators: Test the actuators controlled by the SAM module to ensure they are responding properly to commands.
- Ground Connections: Check the ground connections to the SAM module and other electrical components to ensure they are clean and secure.
7. When to Seek Professional Help
While many diagnostic and repair steps can be performed by knowledgeable DIYers, some situations require professional expertise.
7.1. Recognizing Complex Issues
- Unresolved Fault Codes: If you have followed all the diagnostic steps and are still unable to resolve the 9040 fault code, it may be time to seek professional help.
- Intermittent Problems: Intermittent electrical problems can be difficult to diagnose and may require specialized equipment and expertise.
- Multiple Fault Codes: If you are experiencing multiple fault codes related to different systems, it could indicate a more complex underlying issue.
7.2. Benefits of Professional Diagnosis
- Expertise: Professional technicians have the knowledge and experience to diagnose complex electrical problems quickly and accurately.
- Specialized Tools: Professional technicians have access to specialized diagnostic tools and equipment that are not available to the average DIYer.
- Access to Information: Professional technicians have access to manufacturer’s service manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical bulletins.
7.3. Finding a Qualified Technician
- Certifications: Look for technicians who are certified by organizations such as the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
- Experience: Choose a technician who has experience working on Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Reputation: Check online reviews and ask for recommendations from friends and family.
8. Cost Considerations for Repairing the 9040 Fault Code
The cost of repairing the 9040 fault code can vary depending on the cause of the problem and the extent of the repairs required.
8.1. Estimated Costs for Different Repairs
| Repair | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Fan Relay Module Replacement | $50 – $150 |
| Wiring Repair | $100 – $300 |
| SAM Module Replacement | $500 – $1500 |
| SAM Module Reprogramming | $100 – $300 |
| Diagnostic Scan | $75 – $150 |
8.2. Factors Affecting Repair Costs
- Location: Labor rates can vary depending on your geographic location.
- Shop Type: Dealerships tend to charge higher labor rates than independent repair shops.
- Parts Quality: Using high-quality parts can increase the cost of repairs.
- Complexity: More complex repairs will generally cost more than simple repairs.
8.3. DIY vs. Professional Repair Costs
- DIY: DIY repairs can save money on labor costs, but you will need to purchase the necessary tools and parts.
- Professional Repair: Professional repairs will cost more in labor, but you can be confident that the repairs will be done correctly.
9. Keeping Your Mercedes-Benz Running Smoothly with CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing you with the highest quality diagnostic tools and equipment to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
9.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools Available at CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Diagnostic Scanners: We offer a wide range of diagnostic scanners that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Multimeters: Our multimeters are designed for accurate and reliable testing of electrical circuits.
- Oscilloscopes: Our oscilloscopes provide detailed signal analysis for advanced troubleshooting.
- Relay Testers: Our relay testers allow you to quickly and easily test the functionality of relays.
- Wiring Repair Kits: Our wiring repair kits include everything you need to repair damaged wiring.
9.2. Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools
- Accuracy: Our tools are designed for accurate and reliable testing.
- Durability: Our tools are built to last.
- Ease of Use: Our tools are easy to use, even for beginners.
- Compatibility: Our tools are compatible with a wide range of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Support: We offer excellent customer support to help you with any questions or issues.
9.3. Contact Us for Your Diagnostic Tool Needs
If you are experiencing the 9040 Mercedes fault code or any other electrical issues, contact us at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our team of experts can help you diagnose the problem and recommend the right tools and equipment for the job.
Contact Information:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Don’t let electrical problems keep you off the road. Trust CARDIAGTECH.NET for all your diagnostic tool needs.
9. Expert Insights and Additional Resources
10.1. Insights from Mercedes-Benz Technicians
According to experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians, the 9040 fault code often stems from a combination of factors. One technician noted, “The SAM module is sensitive to voltage fluctuations. Always ensure the battery is in top condition before diagnosing further.” Another added, “Check the ground connections thoroughly. A poor ground can mimic a faulty module.” These insights emphasize the importance of basic checks before diving into complex diagnostics.
10.2. Recommended Reading and Further Learning
To deepen your understanding of Mercedes-Benz electrical systems, consider the following resources:
- Mercedes-Benz Service Manuals: Provide detailed procedures and specifications for troubleshooting and repair.
- Online Forums: Engage with other Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians to share experiences and solutions.
- Technical Training Courses: Enroll in automotive electrical courses to enhance your diagnostic skills.
10.3. Staying Updated on Mercedes-Benz Technology
Mercedes-Benz continuously introduces new technologies and systems. Staying updated is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Subscribe to industry newsletters, attend training seminars, and regularly consult Mercedes-Benz technical bulletins to stay informed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What does the 9040 fault code mean on a Mercedes-Benz?
The 9040 fault code indicates a defect or absence of the fan relay module (N10/1kO) within the Driver’s SAM (Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module). - Can I fix the 9040 fault code myself?
Depending on your technical skills and experience, you may be able to fix it yourself. Start with basic checks like inspecting the fan relay module and wiring. If the problem persists, professional help may be needed. - How much does it cost to repair the 9040 fault code?
The cost can range from $50 for a relay replacement to $1500 for a SAM module replacement. The exact cost depends on the cause and the repair shop’s labor rates. - What are the symptoms of a faulty Driver’s SAM?
Symptoms include lighting problems, wiper issues, power window/lock malfunctions, cooling fan problems, and CAN bus communication errors. - Is it safe to drive with the 9040 fault code?
Driving is generally safe, but the cooling fan issue could lead to overheating. Address the problem as soon as possible. - How do I test the fan relay module?
Use a multimeter to check continuity, resistance, and voltage. You can also swap it with a known good relay to see if the problem resolves. - What is the CAN bus, and why is it important?
The CAN bus is a communication system that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate in a vehicle. It’s essential for diagnosing electrical issues, including the 9040 fault code. - Where is the Driver’s SAM module located?
It’s typically located in the driver’s side footwell or under the dashboard. - Do I need to reprogram the SAM module after replacement?
Yes, a new SAM module usually needs to be programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications. - How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help me with the 9040 fault code?
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment to help you diagnose and repair the 9040 fault code. Contact us for expert advice and support.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to diagnose and resolve the 9040 Mercedes fault code, ensuring your vehicle remains in top condition. And remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you with the best tools and expertise in the industry. If you’re facing challenges diagnosing the 9040 Mercedes fault code or need assistance selecting the right diagnostic tools, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our team at CARDIAGTECH.NET is ready to provide expert guidance and support to ensure you get the job done right. Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. We’re here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.