C1200 Mercedes Fault Code: Expert Troubleshooting Guide
Decoding the C1200 Mercedes fault code can be challenging, but CARDIAGTECH.NET offers insights to diagnose and resolve ABS issues efficiently. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of the C1200 code, its symptoms, potential causes, and effective solutions, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz performs optimally with the correct diagnostic tools.
1. Understanding the C1200 Mercedes Fault Code
The C1200 fault code in a Mercedes-Benz typically refers to a malfunction within the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). It generally indicates an issue with one of the wheel speed sensors, which are critical for the ABS, Electronic Stability Program (ESP), and Traction Control System (TCS) to function correctly. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) relies on these sensors to monitor wheel speed and detect any discrepancies that might lead to skidding or loss of control.
1.1. Common Symptoms of a C1200 Fault
When the C1200 code is triggered, several symptoms may become apparent:
- ABS warning light illuminates on the dashboard
- ESP/TCS warning lights activate
- Reduced braking performance
- Erratic behavior of the speedometer
- Potential locking of wheels during braking
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) stored in the vehicle’s computer
1.2. Potential Causes of the C1200 Code
Several factors can trigger the C1200 fault code:
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor: The most common cause is a malfunctioning wheel speed sensor.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or disconnected wiring to the wheel speed sensor can disrupt the signal.
- Sensor Ring Damage: The sensor ring (also known as the tone wheel or reluctor ring) can become damaged or corroded, affecting the sensor’s ability to read wheel speed accurately.
- ABS Control Module Failure: In rare cases, the ABS control module itself may be faulty.
- Contamination: Debris or contaminants on the sensor or sensor ring.
- Incorrect Installation: Improper installation or replacement of a wheel speed sensor.
2. Diagnosing the C1200 Mercedes Fault Code
Diagnosing the C1200 fault code accurately requires a systematic approach and the right diagnostic tools. Here’s a detailed process:
2.1. Initial Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection:
- Check Wheel Speed Sensors: Examine each wheel speed sensor for visible damage, loose connections, or corrosion.
- Inspect Wiring: Trace the wiring from the sensors to the ABS control module, looking for cuts, breaks, or frayed wires.
- Examine Sensor Rings: Inspect the sensor rings (tone wheels) for cracks, damage, or excessive rust.
2.2. Using Diagnostic Tools
Employ diagnostic tools for a more precise assessment:
- Scan Tool: Use an OBD-II scanner to confirm the presence of the C1200 code and retrieve any additional fault codes.
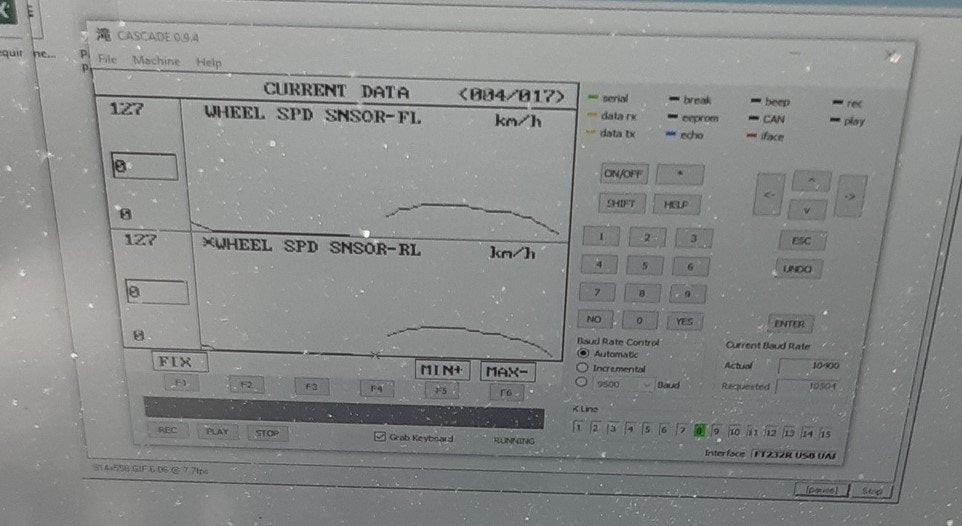
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor the wheel speed sensors’ readings in real-time using the scan tool. Compare the readings from each sensor while driving at a slow, steady speed (e.g., 20-30 mph). Any significant discrepancies can indicate a faulty sensor or related wiring issue.
- Multimeter Testing:
- Resistance Test: Disconnect the wheel speed sensor and use a multimeter to measure its resistance. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications. An open circuit or a reading outside the specified range indicates a faulty sensor.
- Voltage Test: With the sensor connected, measure the voltage signal while rotating the wheel. Look for a consistent and smooth voltage output. Erratic or absent voltage suggests a sensor or wiring problem.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope can provide a visual representation of the sensor’s signal, allowing you to identify any irregularities or dropouts.
- ABS Scan Tool: A specialized ABS scan tool can perform more in-depth diagnostics, including reading ABS-specific codes and performing actuation tests.
2.3. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedure
- Read and Record Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to read all stored fault codes. Record these codes for future reference.
- Clear Fault Codes: Clear the fault codes and take the vehicle for a short test drive to see if the C1200 code reappears.
- Live Data Analysis: If the code returns, use the scan tool to monitor live data from the wheel speed sensors while driving. Focus on identifying any inconsistencies or abnormal readings.
- Sensor Testing: Conduct resistance and voltage tests on each wheel speed sensor using a multimeter. Compare the results to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Wiring Inspection and Testing: Thoroughly inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the wheel speed sensors. Check for continuity and shorts using a multimeter.
- Sensor Ring Inspection: Examine the sensor rings for damage, corrosion, or debris. Clean or replace as necessary.
- ABS Module Check: If all other components check out, consider the possibility of a faulty ABS control module. This typically requires specialized diagnostic equipment and expertise.
2.4. Resources and References
- Mercedes-Benz Service Manuals: Consult the official Mercedes-Benz service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and specifications.
- Online Forums: Engage with online communities and forums dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Experienced technicians and enthusiasts can provide valuable insights.
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Check for any relevant TSBs issued by Mercedes-Benz that may address common issues related to the C1200 code.
 ABS Sensor Issues
ABS Sensor Issues
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid During Diagnosis
- Ignoring Basic Checks: Don’t skip the initial visual inspection. Simple issues like loose connections or damaged wiring can often be the cause.
- Relying Solely on Fault Codes: Fault codes provide a starting point but don’t always pinpoint the exact problem. Always perform thorough testing and analysis.
- Neglecting Wiring Issues: Wiring problems are a common cause of ABS faults. Don’t overlook the importance of inspecting and testing the wiring and connectors.
- Using Low-Quality Parts: When replacing components, use high-quality parts from reputable suppliers to ensure proper function and longevity.
- Skipping Calibration: After replacing a wheel speed sensor or ABS control module, ensure that the system is properly calibrated according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Overlooking Sensor Ring Damage: Damage to the sensor ring can cause intermittent or inaccurate readings. Always inspect the sensor ring for cracks, corrosion, or debris.
- Ignoring Power and Ground Issues: Power and ground supply issues can lead to ABS problems. Check the voltage and ground connections to the ABS control module and wheel speed sensors.
- Assuming the ABS Module is Always the Problem: The ABS control module is often the last thing to suspect. Test all other components before considering a module replacement.
- Forgetting to Clear Codes: After completing repairs, clear the fault codes and perform a test drive to ensure that the issue is resolved.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing the C1200 Fault Code
Once you’ve accurately diagnosed the cause of the C1200 fault code, follow these steps to carry out the repair:
4.1. Replacing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Gather Tools and Parts:
- New wheel speed sensor
- Wrench or socket set
- Screwdriver
- Torque wrench
- Wheel chocks
- Jack and jack stands
- Prepare the Vehicle:
- Park the vehicle on a level surface.
- Engage the parking brake.
- Chock the rear wheels.
- Loosen the lug nuts on the affected wheel.
- Jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the wheel.
- Remove the Old Sensor:
- Locate the wheel speed sensor on the wheel hub or knuckle.
- Disconnect the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Remove any retaining bolts or clips securing the sensor.
- Carefully remove the old sensor from the hub.
- Install the New Sensor:
- Clean the sensor mounting surface.
- Install the new sensor into the hub.
- Secure the sensor with the retaining bolts or clips.
- Connect the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Reassemble and Test:
- Reinstall the wheel.
- Tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque.
- Remove the jack stands and lower the vehicle.
- Clear the fault codes using a scan tool.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the C1200 code is resolved and the ABS system is functioning correctly.
4.2. Repairing Wiring Issues
- Gather Tools and Materials:
- Wire stripper
- Crimping tool
- Electrical tape or heat shrink tubing
- New wiring (if needed)
- Electrical connector cleaner
- Inspect the Wiring:
- Carefully inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the affected wheel speed sensor.
- Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Repair or Replace Damaged Wiring:
- If you find any damaged or corroded wires, repair them by stripping the ends and splicing in new sections of wire. Use crimp connectors or solder to ensure a secure connection.
- Protect the repaired wires with electrical tape or heat shrink tubing.
- Clean and Secure Connectors:
- Clean the electrical connectors with electrical connector cleaner.
- Ensure that the connectors are properly seated and secured.
- Test the Repair:
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring and ensure that there are no shorts to ground.
- Clear the fault codes using a scan tool.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the C1200 code is resolved and the ABS system is functioning correctly.
4.3. Replacing a Damaged Sensor Ring
- Gather Tools and Parts:
- New sensor ring (tone wheel)
- Hammer
- Punch or chisel
- Bearing press (optional)
- Wheel bearing grease
- Prepare the Vehicle:
- Follow the same steps as outlined in the “Replacing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor” section to prepare the vehicle.
- Remove the Old Sensor Ring:
- Carefully remove the old sensor ring from the wheel hub using a hammer and punch or chisel. Be careful not to damage the hub or bearing.
- Install the New Sensor Ring:
- Clean the hub surface where the new sensor ring will be installed.
- Apply a thin layer of wheel bearing grease to the hub surface.
- Position the new sensor ring on the hub.
- Use a bearing press or a hammer and punch to carefully press the new sensor ring into place. Ensure that it is fully seated and aligned correctly.
- Reassemble and Test:
- Reinstall the wheel.
- Tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque.
- Remove the jack stands and lower the vehicle.
- Clear the fault codes using a scan tool.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the C1200 code is resolved and the ABS system is functioning correctly.
4.4. Replacing the ABS Control Module
- Gather Tools and Parts:
- New ABS control module
- Wrench or socket set
- Screwdriver
- Scan tool with ABS programming capabilities
- Prepare the Vehicle:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the ABS control module (typically located in the engine compartment).
- Remove the Old Module:
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the ABS control module.
- Remove any retaining bolts or screws securing the module.
- Carefully remove the old module from its mounting location.
- Install the New Module:
- Install the new ABS control module in its mounting location.
- Secure the module with the retaining bolts or screws.
- Connect the electrical connectors to the module.
- Programming and Calibration:
- Use a scan tool with ABS programming capabilities to program the new module to the vehicle.
- Perform any necessary calibration procedures as outlined in the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reassemble and Test:
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the fault codes using a scan tool.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the C1200 code is resolved and the ABS system is functioning correctly.
5. Tools and Equipment Recommended by CARDIAGTECH.NET
Having the right tools and equipment can significantly enhance your diagnostic and repair capabilities. CARDIAGTECH.NET recommends the following tools for dealing with the C1200 Mercedes fault code:
- OBD-II Scanner: A high-quality OBD-II scanner with live data capabilities is essential for reading and clearing fault codes, as well as monitoring sensor data in real-time.
- Multimeter: A digital multimeter is necessary for testing the resistance, voltage, and continuity of electrical components.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope can provide a visual representation of sensor signals, allowing you to identify any irregularities or dropouts.
- ABS Scan Tool: A specialized ABS scan tool can perform more in-depth diagnostics and actuation tests on the ABS system.
- Wiring Repair Kit: A comprehensive wiring repair kit with wire strippers, crimping tools, and connectors is essential for repairing damaged wiring.
- Wheel Bearing Press: A wheel bearing press can be used to safely and efficiently install and remove sensor rings.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is necessary for tightening fasteners to the specified torque values.
- Mercedes-Benz Service Manual: The official Mercedes-Benz service manual provides detailed diagnostic and repair procedures for your vehicle.
5.1. Tool Comparison Table
| Tool | Description | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanner | Reads and clears fault codes, monitors live data | Live data streaming, code definitions, freeze frame data | $100 – $500 |
| Digital Multimeter | Measures resistance, voltage, and continuity | Auto-ranging, data hold, backlight | $50 – $200 |
| Oscilloscope | Visualizes sensor signals | High sampling rate, multiple channels, waveform analysis | $200 – $1000+ |
| ABS Scan Tool | Performs in-depth ABS diagnostics and actuation tests | ABS-specific codes, actuation tests, module programming | $300 – $1500+ |
| Wiring Repair Kit | Contains wire strippers, crimping tools, and connectors | Assorted connectors, heat shrink tubing, wire terminals | $50 – $150 |
| Wheel Bearing Press | Safely installs and removes wheel bearings and sensor rings | Hydraulic or manual operation, assorted adapters | $200 – $1000+ |
| Torque Wrench | Tightens fasteners to specified torque values | Adjustable torque settings, digital display, audible alert | $80 – $300 |
| Mercedes-Benz Service Manual | Provides detailed diagnostic and repair procedures for Mercedes-Benz vehicles | Step-by-step instructions, wiring diagrams, component locations | $100 – $300 (per manual) |
5.2. Precision Measurement and Calibration
- Alignment Tools: To ensure proper wheel alignment after suspension or steering repairs.
- Torque Wrenches: Essential for tightening bolts and nuts to precise specifications, preventing over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Pressure Gauges: For accurately measuring tire pressure and system pressures (e.g., fuel, oil, coolant).
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ABS System
Preventive maintenance is crucial for keeping your Mercedes-Benz ABS system in optimal condition and preventing the recurrence of the C1200 fault code. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the wheel speed sensors, wiring, and sensor rings for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Cleanliness: Keep the wheel speed sensors and sensor rings clean and free of debris.
- Proper Wiring Maintenance: Ensure that the wiring and connectors associated with the ABS system are in good condition. Repair any damaged or corroded wiring promptly.
- Brake Fluid Maintenance: Replace the brake fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Contaminated brake fluid can affect the performance of the ABS system.
- Wheel Alignment: Maintain proper wheel alignment to prevent uneven wear on the tires and stress on the ABS system.
- Professional Service: Have the ABS system professionally serviced at regular intervals to ensure that all components are functioning correctly.
6.1. Tips for Longevity
- Gentle Driving: Avoid harsh braking and aggressive driving, which can put unnecessary stress on the ABS system.
- Proper Storage: Store your Mercedes-Benz in a dry, covered location to protect it from the elements.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any ABS-related issues promptly to prevent them from escalating into more significant problems.
- Quality Parts: When replacing components, use high-quality parts from reputable suppliers to ensure proper function and longevity.
7. Real-World Case Studies
To illustrate the diagnostic and repair process, let’s examine a few real-world case studies involving the C1200 Mercedes fault code:
7.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz C300
- Complaint: ABS warning light illuminated on the dashboard.
- Diagnostic Findings:
- OBD-II scan revealed the C1200 fault code, indicating an issue with the front left wheel speed sensor.
- Live data monitoring showed that the front left wheel speed sensor was providing erratic readings.
- Resistance testing of the sensor confirmed that it was faulty.
- Repair: The front left wheel speed sensor was replaced with a new OEM sensor.
- Outcome: The C1200 fault code was resolved, and the ABS system functioned correctly after the repair.
7.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Issue
- Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz E350
- Complaint: ABS and ESP warning lights illuminated on the dashboard.
- Diagnostic Findings:
- OBD-II scan revealed the C1200 fault code, indicating an issue with the rear right wheel speed sensor.
- Visual inspection revealed damaged wiring to the rear right wheel speed sensor.
- Continuity testing confirmed that there was a break in the wiring.
- Repair: The damaged wiring was repaired by splicing in a new section of wire and securing the connection with heat shrink tubing.
- Outcome: The C1200 fault code was resolved, and the ABS and ESP systems functioned correctly after the repair.
7.3. Case Study 3: Damaged Sensor Ring
- Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz GLC300
- Complaint: ABS warning light illuminated on the dashboard, and the ABS system was not functioning correctly.
- Diagnostic Findings:
- OBD-II scan revealed the C1200 fault code, indicating an issue with the front right wheel speed sensor.
- Visual inspection revealed that the sensor ring on the front right wheel hub was damaged.
- Repair: The damaged sensor ring was replaced with a new OEM sensor ring.
- Outcome: The C1200 fault code was resolved, and the ABS system functioned correctly after the repair.
8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For complex cases, consider these advanced techniques:
- CAN Bus Diagnostics: Use a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus analyzer to monitor communication between the ABS module and other vehicle systems.
- Signal Tracing: Use a signal tracer to follow the electrical signals from the wheel speed sensors to the ABS module to identify any breaks or shorts in the wiring.
- Module Testing: Send the ABS module to a specialized repair facility for testing and repair.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the ABS module has the latest software updates installed.
8.1. Ensuring Accuracy
- Double-Check Connections: Always double-check all electrical connections and wiring to ensure they are secure and properly connected.
- Verify Sensor Placement: Ensure that the wheel speed sensors are properly installed and correctly positioned in relation to the sensor rings.
- Use Quality Components: Use only high-quality replacement parts from reputable suppliers to ensure reliable performance.
9. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
CARDIAGTECH.NET plays a pivotal role in supporting Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians in diagnosing and resolving complex issues like the C1200 fault code. Here’s how:
- Expert Advice: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides expert advice and guidance on diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- High-Quality Tools and Equipment: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Technical Resources: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides access to a wealth of technical resources, including service manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical service bulletins.
- Community Support: CARDIAGTECH.NET fosters a community of Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and technicians who can share their knowledge and experience.
9.1. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET?
- Expertise: CARDIAGTECH.NET has a team of experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians and diagnostic specialists.
- Quality: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers only the highest quality tools and equipment from reputable manufacturers.
- Support: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides excellent customer support and technical assistance.
- Value: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers competitive pricing and a wide range of products to meet your needs.
10. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
If you’re struggling to diagnose or repair the C1200 Mercedes fault code, don’t hesitate to contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert assistance. Our team of experienced technicians and diagnostic specialists can provide the guidance and support you need to get your Mercedes-Benz back on the road.
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
We understand the challenges you face as a Mercedes-Benz technician or owner. Dealing with complex diagnostic issues like the C1200 fault code can be time-consuming and frustrating. That’s why we’re here to offer our expertise and support.
Are you tired of struggling with complex Mercedes-Benz diagnostic issues?
Do you want to improve your efficiency and accuracy when diagnosing and repairing vehicles?
Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today!
Let us help you overcome your challenges and achieve your goals. With our high-quality tools, expert advice, and dedicated support, you’ll be able to diagnose and repair Mercedes-Benz vehicles with confidence. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more.
Don’t let the C1200 fault code keep you off the road. With CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can diagnose and repair your Mercedes-Benz quickly and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does the C1200 fault code mean on a Mercedes-Benz?
The C1200 fault code typically indicates an issue with a wheel speed sensor in the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). It often means that the ECU is not receiving a consistent or accurate signal from one or more of the wheel speed sensors.
2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the C1200 fault code?
While it may be possible to drive with the C1200 fault code, it is not recommended. The ABS, ESP, and TCS systems may not function correctly, which can compromise safety. It’s best to diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible.
3. How do I reset the C1200 fault code?
You can reset the C1200 fault code using an OBD-II scanner. However, simply clearing the code without addressing the underlying issue will likely result in the code reappearing.
4. How much does it cost to repair the C1200 fault code?
The cost of repairing the C1200 fault code can vary depending on the cause of the problem and the repair shop’s labor rates. Replacing a wheel speed sensor can cost between $200 and $500, while more complex repairs, such as ABS module replacement, can cost upwards of $1000.
5. Can a bad wheel bearing cause the C1200 fault code?
Yes, a bad wheel bearing can indirectly cause the C1200 fault code. A worn or damaged wheel bearing can affect the alignment of the sensor ring, leading to inaccurate readings from the wheel speed sensor.
6. Are there any Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related to the C1200 fault code?
Yes, there may be TSBs related to the C1200 fault code for specific Mercedes-Benz models. Check with your local Mercedes-Benz dealer or online resources to see if any relevant TSBs apply to your vehicle.
7. What is the role of the ABS control module in the C1200 fault code?
The ABS control module is responsible for receiving and processing the signals from the wheel speed sensors. If the module is faulty, it may not be able to interpret the signals correctly, leading to the C1200 fault code.
8. How do I test a wheel speed sensor?
You can test a wheel speed sensor using a multimeter to measure its resistance and voltage output. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
9. What is the difference between an ABS sensor and a wheel speed sensor?
The terms “ABS sensor” and “wheel speed sensor” are often used interchangeably. They both refer to the same component, which is responsible for measuring the speed of the wheel and sending that information to the ABS control module.
10. Where can I find a reliable Mercedes-Benz technician?
You can find a reliable Mercedes-Benz technician by searching online directories, asking for referrals from friends and family, or contacting your local Mercedes-Benz dealer.
By addressing these common questions and providing detailed answers, this FAQ section aims to further assist Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians in understanding and resolving the C1200 fault code.




