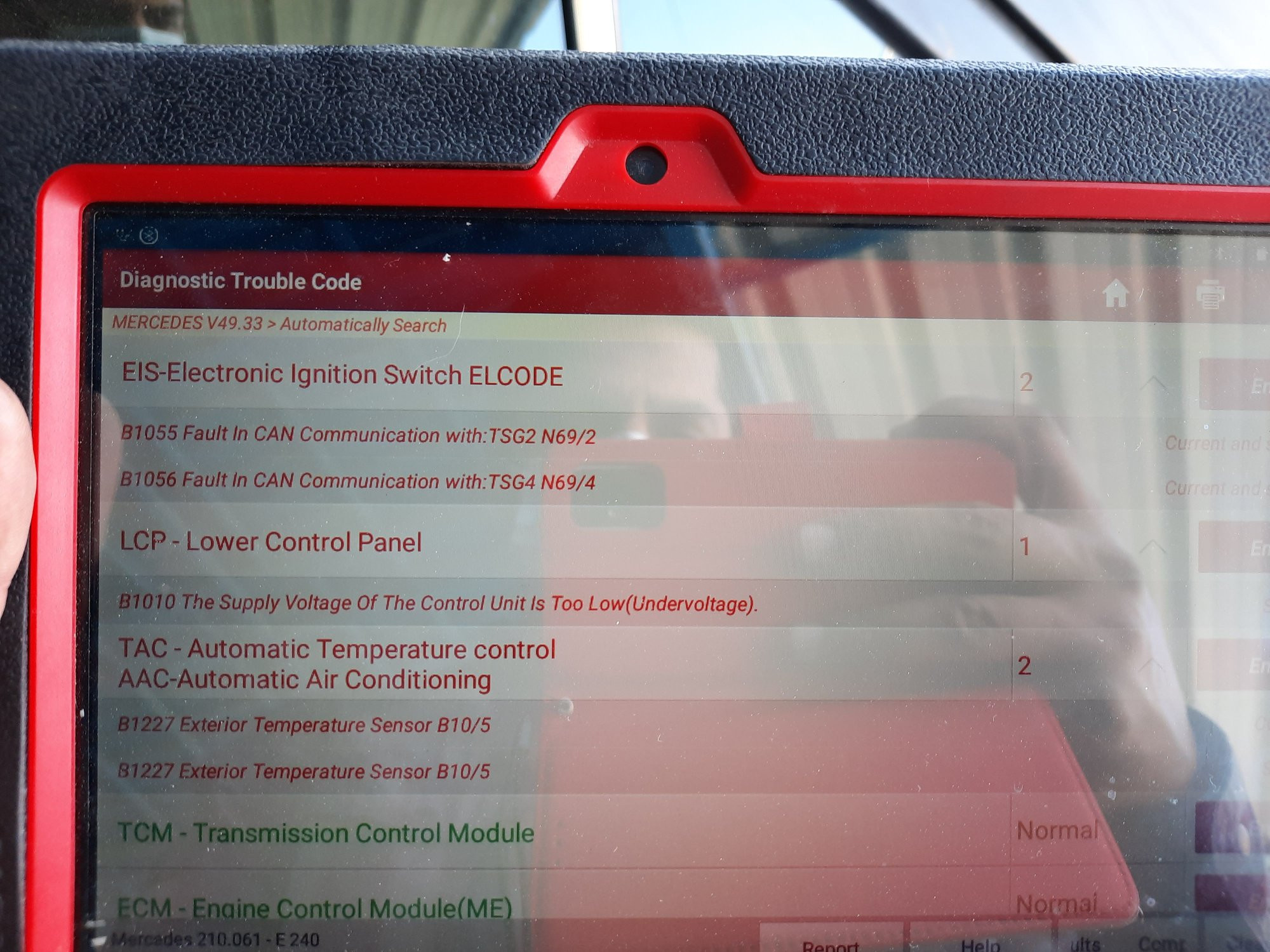
Mercedes Climate Control Codes: Your Guide to Understanding and Repair
Mercedes climate control codes are diagnostic trouble codes that your Mercedes-Benz uses to communicate problems within its climate control system, including the refrigerant system. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you understand and resolve these codes efficiently, ensuring your comfort and enhancing your vehicle’s performance by providing top-notch tools. With the correct climate control system tools, you can efficiently identify and fix issues, saving time and ensuring customer satisfaction, utilizing resources and equipment that can keep your garage competitive.
1. Understanding Mercedes Climate Control Codes
Do you know what Mercedes climate control codes signify? These codes are essentially diagnostic messages from your car’s climate control system, indicating potential issues that need attention.
Mercedes-Benz climate control codes are used to diagnose problems within the automatic climate control (ACC) system. These codes can help identify issues related to sensors, actuators, and other components that regulate the temperature and airflow inside the vehicle. The climate control system aims to maintain a comfortable environment inside the vehicle by regulating temperature, humidity, and air distribution. When the system detects a malfunction, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be accessed using diagnostic tools. By understanding these codes, technicians can efficiently diagnose and repair climate control problems, ensuring optimal comfort for drivers and passengers. Common issues include sensor failures, refrigerant leaks, and problems with the control module or actuators. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to these codes can prevent more significant problems and maintain the system’s performance.
1.1. What are Mercedes Climate Control Codes?
Mercedes climate control codes are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) generated by your car’s climate control system to indicate malfunctions or issues. These codes help technicians diagnose problems with the ACC system, which regulates temperature, humidity, and airflow, ensuring a comfortable environment inside the vehicle. When the system detects a malfunction, it stores a DTC that can be accessed using diagnostic tools. Understanding these codes allows for efficient diagnosis and repair of climate control problems, ensuring optimal comfort for drivers and passengers. Common issues include sensor failures, refrigerant leaks, and problems with the control module or actuators. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to these codes can prevent more significant problems and maintain the system’s performance.
1.2. Why are Mercedes Climate Control Codes Important?
Mercedes climate control codes are crucial because they facilitate accurate and efficient diagnosis of climate control system issues. Instead of guessing, technicians can use these codes to pinpoint the exact problem area, saving time and resources. These codes help in identifying malfunctions related to sensors, actuators, and other components that regulate temperature and airflow. This precision ensures that repairs are targeted and effective, reducing the likelihood of recurring problems. Regular monitoring and addressing these codes can prevent minor issues from escalating into major, costly repairs. Moreover, a properly functioning climate control system enhances the comfort and safety of the vehicle’s occupants by maintaining optimal environmental conditions inside the car.
1.3. Where Can You Find Mercedes Climate Control Codes?
Mercedes climate control codes can be accessed through the climate control unit display or by using an OBD-II scanner.
- Climate Control Unit Display: Some Mercedes models allow you to retrieve climate control codes directly from the climate control unit display. The exact procedure varies depending on the model year and series but generally involves pressing a specific sequence of buttons on the climate control panel.
- OBD-II Scanner: The most common method is using an OBD-II scanner, which plugs into the vehicle’s diagnostic port. Modern diagnostic tools like those available at CARDIAGTECH.NET can read these codes, providing detailed information about the problem.
- Professional Diagnostic Services: If you’re not comfortable performing the diagnostics yourself, a professional mechanic or Mercedes-Benz service center can retrieve and interpret these codes for you.
1.4. When Should You Check Mercedes Climate Control Codes?
You should check your Mercedes climate control codes when you notice any irregularities in your car’s climate control system’s performance. Here are some common scenarios:
- Reduced Cooling or Heating: If the air conditioning isn’t cooling as effectively as it used to or the heater isn’t providing sufficient warmth, it’s time to check the codes.
- Unusual Noises: Strange sounds coming from the climate control system, such as clicking, hissing, or buzzing, can indicate a problem.
- Inconsistent Airflow: If the airflow from the vents is weak or uneven, this could be a sign of a malfunctioning component.
- Error Messages on Display: Some Mercedes models display error messages related to the climate control system directly on the dashboard.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly checking the codes as part of your vehicle’s maintenance routine can help catch minor issues before they become major problems.
2. Common Mercedes Climate Control Codes
What are the common Mercedes climate control codes you might encounter? Several codes frequently appear, each indicating specific issues within the system.
Common Mercedes climate control codes include those related to refrigerant pressure, temperature sensors, and circuit malfunctions. For example, codes indicating low refrigerant pressure can point to leaks or a failing compressor, while codes related to temperature sensors might suggest a faulty sensor or wiring issue. Circuit malfunctions can stem from wiring problems, module failures, or issues with individual components like blower motors or actuators. Identifying these common codes and their potential causes enables technicians to streamline the diagnostic process, leading to faster and more accurate repairs. Proper tools and diagnostic equipment, such as those offered by CARDIAGTECH.NET, are essential for effectively interpreting these codes and performing the necessary repairs.
2.1. B1078 – Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Malfunction
The B1078 code indicates a malfunction in the refrigerant pressure sensor. This sensor monitors the pressure of the refrigerant in the AC system, and a malfunction can lead to incorrect readings, affecting the system’s performance. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), faulty sensors can cause the climate control system to operate inefficiently, leading to poor cooling or heating performance.
- Symptoms: The AC may not cool properly, the compressor might not engage, or the system may cycle on and off frequently.
- Possible Causes: Defective refrigerant pressure sensor, wiring issues, or a problem with the climate control module.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the wiring and connections to the sensor.
- Test the sensor’s voltage and resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the sensor if it’s faulty.
- Inspect the climate control module for any issues.
2.2. B1079 – Refrigerant Temperature Sensor Malfunction
The B1079 code signifies a problem with the refrigerant temperature sensor. This sensor measures the temperature of the refrigerant, providing critical data to the climate control module for optimal system operation. A malfunctioning sensor can cause the system to make incorrect adjustments.
- Symptoms: Inconsistent cooling or heating, the AC system not functioning correctly, or error messages on the display.
- Possible Causes: Faulty refrigerant temperature sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem within the climate control module.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Examine the wiring and connections to the sensor.
- Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage and resistance.
- Replace the sensor if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Check the climate control module for any faults.
2.3. B1081 – Evaporator Temperature Sensor Malfunction
The B1081 code indicates a malfunction in the evaporator temperature sensor. This sensor monitors the temperature of the evaporator core, preventing it from freezing. A faulty sensor can lead to the evaporator freezing up, reducing airflow and cooling efficiency.
- Symptoms: Reduced airflow from the vents, the AC not cooling properly, or the system cycling on and off.
- Possible Causes: Defective evaporator temperature sensor, wiring problems, or issues with the climate control module.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections to the sensor.
- Test the sensor’s voltage and resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the sensor if it is defective.
- Examine the climate control module for any issues.
2.4. B1231 – ECT Sensor (B11/4)
The B1231 code refers to the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor. This sensor measures the engine coolant temperature and provides this information to the climate control system and the engine control unit (ECU). Incorrect readings from this sensor can affect both the engine’s performance and the climate control system.
- Symptoms: Poor engine performance, incorrect temperature readings, or the climate control system not working correctly.
- Possible Causes: Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the ECU.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the wiring and connections to the ECT sensor.
- Test the sensor’s voltage and resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the sensor if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Check the ECU for any faults.
2.5. B1234 – Sun Sensor Malfunction
The B1234 code indicates a problem with the sun sensor. This sensor measures the intensity of sunlight entering the cabin, allowing the climate control system to adjust the temperature accordingly. A malfunctioning sun sensor can cause the system to overcompensate or undercompensate for the sun’s effect.
- Symptoms: The climate control system not adjusting correctly to sunlight, inconsistent cabin temperature, or the AC blowing too cold or too hot.
- Possible Causes: Defective sun sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the climate control module.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections to the sun sensor.
- Test the sensor’s voltage using a multimeter.
- Replace the sensor if it is faulty.
- Examine the climate control module for any issues.
2.6. B1416 – Coolant Circulation Pump
The B1416 code indicates a problem with the coolant circulation pump. This pump circulates coolant through the heater core, providing heat to the cabin. A malfunctioning pump can result in a lack of heat or inconsistent heating performance.
- Symptoms: No heat from the vents, the engine overheating, or inconsistent heating performance.
- Possible Causes: Faulty coolant circulation pump, wiring issues, or a blockage in the coolant system.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the wiring and connections to the pump.
- Test the pump’s operation by applying voltage directly.
- Replace the pump if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Check the coolant system for any blockages.
2.7. B1417 – Series Interface (K1) Connection to Instrument Cluster (A1)
The B1417 code indicates a communication problem between the climate control system and the instrument cluster. This interface is used to share data between the two systems, and a malfunction can cause incorrect information to be displayed or affect the operation of both systems.
- Symptoms: Error messages on the instrument cluster, the climate control system not working correctly, or communication errors.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, a faulty climate control module, or a problem with the instrument cluster.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections between the climate control system and the instrument cluster.
- Check the climate control module for any faults.
- Examine the instrument cluster for any issues.
2.8. B1418 – Series Interface (K2) Connection to Instrument Cluster (A1)
The B1418 code is similar to B1417 and also indicates a communication problem between the climate control system and the instrument cluster, but it refers to a different communication line (K2). The same issues and troubleshooting steps apply.
- Symptoms: Error messages on the instrument cluster, the climate control system not working correctly, or communication errors.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, a faulty climate control module, or a problem with the instrument cluster.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections between the climate control system and the instrument cluster.
- Check the climate control module for any faults.
- Examine the instrument cluster for any issues.
2.9. B1422 – Series Interface (K1) Connection to Instrument Cluster (A1)
The B1422 code also indicates a series interface issue but might be more specific to certain data transmissions or components within the communication line.
- Symptoms: The climate control system not working correctly, error messages on the instrument cluster, or intermittent communication issues.
- Possible Causes: Wiring problems, a faulty climate control module, or issues with the instrument cluster.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections between the climate control system and the instrument cluster.
- Check the climate control module for any faults.
- Examine the instrument cluster for any issues.
2.10. B1459 – Series Interface (K2) Connection to Instrument Cluster (A1)
The B1459 code is yet another variation of the series interface communication problem, potentially pointing to specific data errors or component failures within the K2 communication line.
- Symptoms: The climate control system not working correctly, error messages on the instrument cluster, or sporadic communication failures.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, a faulty climate control module, or problems with the instrument cluster.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the wiring and connections between the climate control system and the instrument cluster.
- Check the climate control module for any faults.
- Examine the instrument cluster for any issues.
3. Decoding Mercedes Climate Control Codes
How do you decode Mercedes climate control codes to understand their meaning? Decoding involves using diagnostic tools and resources to translate the codes into actionable information.
Decoding Mercedes climate control codes involves using diagnostic tools to read the codes and consulting repair manuals or online databases to understand their meaning. Resources like ALLDATA and Mitchell OnDemand provide detailed information on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic codes, including possible causes and troubleshooting steps. Professional diagnostic tools, such as those available from CARDIAGTECH.NET, often include built-in code readers and diagnostic assistance to help technicians quickly identify and resolve issues. This process ensures accurate diagnosis and efficient repair of climate control system problems. In addition, online forums and communities dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles can offer valuable insights and shared experiences related to specific codes.
3.1. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is a tool used to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer system. It connects to the car’s OBD-II port, usually located under the dashboard, and reads the stored codes. These codes provide information about potential issues with various systems in the vehicle, including the engine, transmission, and climate control.
- Steps to Use:
- Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port.
- Turn on the ignition but do not start the engine.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the codes.
- Record the codes and research their meaning.
3.2. Consulting a Repair Manual
A repair manual provides detailed information on vehicle systems, components, and troubleshooting procedures. It includes diagrams, specifications, and step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing various issues. Repair manuals are essential resources for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
- Benefits:
- Detailed diagrams and component locations
- Step-by-step troubleshooting guides
- Technical specifications and torque settings
3.3. Online Resources and Databases
Several online resources and databases offer information on diagnostic trouble codes and repair procedures. These resources can be valuable for understanding the meaning of codes and finding potential solutions.
- Examples:
- ALLDATA: A comprehensive database with OEM repair information.
- Mitchell OnDemand: Another extensive database for repair procedures and diagnostic information.
- Mercedes-Benz Forums: Online communities where owners and technicians share information and experiences.
3.4. Professional Diagnostic Tools
Professional diagnostic tools, such as those offered by CARDIAGTECH.NET, provide advanced features for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues. These tools often include code readers, live data streaming, and bi-directional control capabilities.
- Features:
- Code reading and clearing
- Live data monitoring
- Component testing and activation
- Advanced diagnostic functions
4. Troubleshooting Mercedes Climate Control Issues
How do you troubleshoot Mercedes climate control issues effectively? Troubleshooting involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem and implement the appropriate solution.
Troubleshooting Mercedes climate control issues involves a systematic approach beginning with code retrieval, followed by a component inspection, and ending with testing. First, retrieve the climate control codes using an OBD-II scanner to pinpoint the area of the issue. Next, inspect the relevant components, such as sensors, actuators, and wiring, for visible damage or corrosion. Then, use diagnostic tools to test the functionality of these components, comparing their performance to the manufacturer’s specifications. If a component is faulty, replace it and clear the codes. Finally, retest the system to ensure the problem is resolved. Resources like repair manuals and online databases can provide valuable guidance during the troubleshooting process.
4.1. Checking Refrigerant Levels
Low refrigerant levels are a common cause of climate control problems. Check the refrigerant level using a manifold gauge set to ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Steps:
- Connect the manifold gauge set to the AC system’s service ports.
- Read the pressure on both the high and low sides.
- Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the refrigerant level is low, add refrigerant according to the vehicle’s specifications.
4.2. Inspecting Sensors and Wiring
Faulty sensors or damaged wiring can cause incorrect readings and malfunctions in the climate control system. Inspect all relevant sensors and wiring for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Steps:
- Locate the sensors related to the climate control system, such as the refrigerant pressure sensor, temperature sensors, and sun sensor.
- Visually inspect the sensors and their wiring for damage.
- Use a multimeter to check the wiring for continuity and proper voltage.
- Replace any faulty sensors or repair damaged wiring.
4.3. Testing Actuators and Motors
Actuators and motors control the airflow and temperature in the climate control system. Test these components to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Steps:
- Locate the actuators and motors related to the climate control system, such as the blend door actuator and the blower motor.
- Use a diagnostic tool to activate the actuators and motors and observe their movement.
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage and current to the actuators and motors.
- Replace any faulty actuators or motors.
4.4. Clearing Codes and Retesting
After performing repairs, clear the diagnostic trouble codes and retest the climate control system to ensure the problem has been resolved.
- Steps:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the diagnostic trouble codes.
- Start the engine and turn on the climate control system.
- Monitor the system’s performance to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Scan for any new diagnostic trouble codes.
5. Preventing Mercedes Climate Control Problems
How can you prevent Mercedes climate control problems? Regular maintenance and proactive care can help prevent many common issues.
Preventing Mercedes climate control problems involves regular maintenance, such as checking refrigerant levels, inspecting components, and replacing filters. Routine inspections can identify potential issues before they escalate, saving time and money on repairs. Regularly replacing the cabin air filter ensures proper airflow and prevents contaminants from entering the system, improving air quality inside the vehicle. Additionally, using the climate control system regularly, even during colder months, helps keep the components lubricated and functioning properly. Addressing minor issues promptly prevents them from causing more significant damage over time.
5.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing climate control problems. This includes checking refrigerant levels, inspecting components, and replacing filters.
- Tips:
- Check refrigerant levels annually.
- Inspect sensors and wiring for damage.
- Replace the cabin air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles.
- Have the system professionally serviced every two to three years.
5.2. Cabin Air Filter Replacement
A clean cabin air filter ensures proper airflow and prevents contaminants from entering the climate control system. Replace the cabin air filter regularly to maintain optimal performance.
- Steps:
- Locate the cabin air filter, usually behind the glove box or under the dashboard.
- Remove the old filter.
- Install the new filter, ensuring it is properly oriented.
- Replace the access panel.
5.3. Using the Climate Control System Regularly
Using the climate control system regularly, even during colder months, helps keep the components lubricated and functioning properly.
- Benefits:
- Prevents refrigerant from settling and causing corrosion.
- Keeps seals and O-rings lubricated to prevent leaks.
- Ensures actuators and motors remain functional.
5.4. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from causing more significant damage over time. If you notice any irregularities in the climate control system’s performance, have it checked by a professional.
- Examples:
- Reduced cooling or heating performance
- Unusual noises from the system
- Inconsistent airflow
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
What are some advanced diagnostic techniques for Mercedes climate control systems? These techniques involve using specialized tools and procedures to diagnose complex problems.
Advanced diagnostic techniques for Mercedes climate control systems include using specialized tools for testing refrigerant leaks, performing component-level diagnostics, and utilizing advanced scan tools for real-time data analysis. Electronic leak detectors can identify even the smallest refrigerant leaks that traditional methods may miss. Component-level diagnostics involve testing individual parts of the system, such as sensors and actuators, to ensure they meet the manufacturer’s specifications. Advanced scan tools provide real-time data on system performance, allowing technicians to monitor parameters such as refrigerant pressure, temperature, and airflow. By integrating these advanced techniques, professionals can ensure accurate diagnoses and effective repairs of complex climate control issues.
6.1. Refrigerant Leak Detection
Refrigerant leaks can cause a variety of climate control problems. Use specialized tools to detect and repair leaks in the system.
-
Tools:
- Electronic leak detectors
- UV dye and black light
- Bubble leak detectors
-
Steps:
- Add UV dye to the AC system.
- Use a black light to inspect the system for leaks.
- Use an electronic leak detector to pinpoint the exact location of the leak.
- Repair the leak and recharge the system.
6.2. Component-Level Diagnostics
Component-level diagnostics involve testing individual components to ensure they are functioning correctly. This can help identify faulty parts that may not be obvious through basic troubleshooting.
-
Tools:
- Multimeter
- Oscilloscope
- Diagnostic scan tool
-
Steps:
- Identify the component you want to test.
- Use a multimeter to check the component’s voltage, resistance, and continuity.
- Use an oscilloscope to analyze the component’s waveform.
- Compare the results to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replace the component if it’s faulty.
6.3. Using Advanced Scan Tools
Advanced scan tools provide real-time data and diagnostic functions that can help pinpoint complex climate control problems.
-
Features:
- Live data streaming
- Component testing and activation
- Bi-directional control
- Advanced diagnostic functions
-
Steps:
- Connect the scan tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Select the climate control system from the scan tool’s menu.
- Monitor live data to identify any abnormalities.
- Use the scan tool to perform component testing and activation.
- Analyze the results and perform necessary repairs.
6.4. Analyzing System Performance Data
Analyzing system performance data involves monitoring various parameters to identify any deviations from the norm. This can help pinpoint the root cause of complex climate control problems.
-
Parameters to Monitor:
- Refrigerant pressure
- Refrigerant temperature
- Evaporator temperature
- Airflow
- Sensor readings
-
Steps:
- Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle.
- Access the live data stream for the climate control system.
- Monitor the key parameters mentioned above.
- Compare the data to the manufacturer’s specifications or baseline measurements.
- Identify any deviations and investigate their cause.
7. Tools and Equipment for Mercedes Climate Control Repair
What tools and equipment are essential for Mercedes climate control repair? Having the right tools ensures efficient and accurate repairs.
Essential tools and equipment for Mercedes climate control repair include an OBD-II scanner, a manifold gauge set, a vacuum pump, and refrigerant recovery machine. An OBD-II scanner is necessary for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes, while a manifold gauge set is used for measuring refrigerant pressure. A vacuum pump is essential for evacuating the AC system before recharging, and a refrigerant recovery machine safely recovers and recycles refrigerant. Additionally, specialized tools such as electronic leak detectors and component testers aid in diagnosing complex issues. Having these tools on hand enables technicians to perform comprehensive and efficient repairs, ensuring customer satisfaction.
7.1. OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes. It connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and provides access to the climate control system’s data.
- Features to Look For:
- Code reading and clearing
- Live data streaming
- Bi-directional control
- Coverage for Mercedes-Benz vehicles
7.2. Manifold Gauge Set
A manifold gauge set is used to measure the pressure in the AC system. It is essential for diagnosing refrigerant-related problems and ensuring the system is properly charged.
- Features to Look For:
- High-quality gauges with accurate readings
- Color-coded hoses for easy identification
- Compatibility with different refrigerants
- Durable construction
7.3. Vacuum Pump
A vacuum pump is used to evacuate the AC system before recharging. This removes moisture and air from the system, ensuring optimal performance.
- Features to Look For:
- High vacuum rating (typically 3-5 CFM)
- Durable construction
- Oil-less design for easy maintenance
- Quiet operation
7.4. Refrigerant Recovery Machine
A refrigerant recovery machine is used to safely recover and recycle refrigerant from the AC system. This is essential for environmental protection and compliance with regulations.
- Features to Look For:
- Compliance with SAE standards
- Automatic operation
- Built-in filter and dryer
- Efficient recovery rate
7.5. Specialized Tools
Specialized tools, such as electronic leak detectors and component testers, can aid in diagnosing complex climate control problems.
- Examples:
- Electronic leak detectors for pinpointing refrigerant leaks
- Component testers for testing sensors and actuators
- Infrared thermometers for measuring temperature
8. The Future of Mercedes Climate Control Technology
What does the future hold for Mercedes climate control technology? Expect advancements in efficiency, integration, and personalization.
The future of Mercedes climate control technology includes advancements in energy efficiency, enhanced integration with vehicle systems, and increased personalization. Innovations such as smart climate control systems that use AI to learn driver preferences and automatically adjust settings are becoming more prevalent. Advanced sensor technology will provide more accurate and real-time data, allowing for more precise temperature and airflow control. Sustainable refrigerants and energy-efficient components will reduce the environmental impact of climate control systems. Integration with connected car technologies will enable remote control and monitoring of the climate control system via smartphone apps.
8.1. Smart Climate Control Systems
Smart climate control systems use sensors and artificial intelligence to learn driver preferences and automatically adjust settings.
- Features:
- Automatic temperature and airflow adjustment
- Personalized climate profiles
- Integration with navigation systems to anticipate changes in weather
- Voice control
8.2. Advanced Sensor Technology
Advanced sensor technology provides more accurate and real-time data, allowing for more precise temperature and airflow control.
- Examples:
- Infrared sensors for measuring occupant temperature
- Humidity sensors for controlling cabin humidity
- Air quality sensors for detecting pollutants
8.3. Sustainable Refrigerants
Sustainable refrigerants reduce the environmental impact of climate control systems.
-
Examples:
- R-1234yf
- CO2 (R-744)
-
Benefits:
- Lower global warming potential
- Reduced ozone depletion
- Improved energy efficiency
8.4. Integration with Connected Car Technologies
Integration with connected car technologies enables remote control and monitoring of the climate control system via smartphone apps.
- Features:
- Remote start and climate control activation
- Real-time monitoring of system performance
- Over-the-air software updates
- Predictive maintenance alerts
9. Case Studies: Solving Real-World Mercedes Climate Control Problems
How can case studies help you understand Mercedes climate control troubleshooting? Real-world examples provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving common issues.
Case studies provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving real-world Mercedes climate control problems by showcasing step-by-step troubleshooting processes, diagnostic techniques, and repair solutions. By examining specific cases, such as a B1078 refrigerant pressure sensor malfunction or a B1081 evaporator temperature sensor issue, technicians can learn how to apply their knowledge and skills effectively. These case studies often include detailed descriptions of the symptoms, diagnostic steps, tools used, and the final resolution. This practical approach enhances problem-solving abilities and provides a deeper understanding of the complexities involved in climate control system repairs. Furthermore, case studies help in recognizing patterns and common pitfalls, leading to more efficient and accurate diagnoses in the future.
9.1. Case Study 1: B1078 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Malfunction
- Symptoms: The AC was not cooling properly, and the compressor would not engage.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieved the B1078 code using an OBD-II scanner.
- Inspected the wiring and connections to the refrigerant pressure sensor.
- Tested the sensor’s voltage and resistance using a multimeter.
- Resolution: Replaced the faulty refrigerant pressure sensor, cleared the code, and retested the system. The AC now cools properly, and the compressor engages as expected.
9.2. Case Study 2: B1081 Evaporator Temperature Sensor Malfunction
- Symptoms: Reduced airflow from the vents and the AC not cooling properly.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieved the B1081 code using an OBD-II scanner.
- Inspected the wiring and connections to the evaporator temperature sensor.
- Tested the sensor’s voltage and resistance using a multimeter.
- Resolution: Replaced the defective evaporator temperature sensor, cleared the code, and retested the system. The airflow is now normal, and the AC cools properly.
9.3. Case Study 3: B1234 Sun Sensor Malfunction
- Symptoms: The climate control system was not adjusting correctly to sunlight, causing inconsistent cabin temperature.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieved the B1234 code using an OBD-II scanner.
- Inspected the wiring and connections to the sun sensor.
- Tested the sensor’s voltage using a multimeter.
- Resolution: Replaced the faulty sun sensor, cleared the code, and retested the system. The climate control system now adjusts correctly to sunlight, maintaining a consistent cabin temperature.
9.4. Case Study 4: B1416 Coolant Circulation Pump Failure
- Symptoms: No heat from the vents and the engine overheating.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieved the B1416 code using an OBD-II scanner.
- Checked the wiring and connections to the coolant circulation pump.
- Tested the pump’s operation by applying voltage directly.
- Resolution: Replaced the faulty coolant circulation pump, cleared the code, and retested the system. Heat now flows from the vents, and the engine no longer overheats.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Mercedes Climate Control Codes
Do you have questions about Mercedes climate control codes? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand these codes and how to address them.
10.1. What Does a Mercedes Climate Control Code Mean?
A Mercedes climate control code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) generated by the vehicle’s climate control system. It indicates a specific problem or malfunction within the system, such as issues with sensors, actuators, or other components. These codes help technicians diagnose and repair the system efficiently.
10.2. How Do I Retrieve Mercedes Climate Control Codes?
You can retrieve Mercedes climate control codes using an OBD-II scanner, which connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and reads the stored codes. Some Mercedes models also allow you to access the codes directly through the climate control unit display.
10.3. Can I Fix Climate Control Problems Myself?
Depending on the problem, you might be able to fix some climate control issues yourself, especially if it involves simple tasks like replacing a cabin air filter. However, more complex issues, such as refrigerant leaks or sensor malfunctions, may require professional diagnostic tools and expertise.
10.4. How Often Should I Check My Climate Control System?
You should check your climate control system regularly, ideally as part of your vehicle’s annual maintenance. Also, check it whenever you notice any irregularities in the system’s performance, such as reduced cooling or heating, unusual noises, or inconsistent airflow.
10.5. What Are the Most Common Climate Control Problems in Mercedes Vehicles?
The most common climate control problems in Mercedes vehicles include low refrigerant levels, faulty sensors, malfunctioning actuators, and issues with the blower motor. Diagnostic trouble codes can help pinpoint these problems accurately.
10.6. How Do I Know if My Refrigerant Level Is Low?
Signs of low refrigerant levels include reduced cooling performance, the AC blowing warm air, and the compressor cycling on and off frequently. You can check the refrigerant level using a manifold gauge set.
10.7. What Tools Do I Need to Repair My Climate Control System?
Essential tools for repairing a climate control system include an OBD-II scanner, a manifold gauge set, a vacuum pump, and refrigerant recovery machine. Specialized tools like electronic leak detectors and component testers can also be helpful.
10.8. How Much Does It Cost to Repair a Climate Control System?
The cost to repair a climate control system can vary widely depending on the nature of the problem, the parts required, and the labor costs. Simple repairs, such as replacing a sensor, might cost a few hundred dollars, while more complex repairs, such as replacing the compressor, could cost over a thousand dollars.
10.9. Can a Faulty Climate Control System Affect Fuel Efficiency?
Yes, a faulty climate control system can affect fuel efficiency. If the AC compressor is constantly running due to a malfunction, it can increase the load on the engine and reduce fuel economy.
10.10. Where Can I Find Reliable Information on Mercedes Climate Control Codes?
You can find reliable information on Mercedes climate