Mercedes Fault Code P200B: Diagnosis, Causes, and Solutions
Mercedes fault code P200B indicates an issue with the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) system, specifically on bank 2. This comprehensive guide from CARDIAGTECH.NET will explore the causes, symptoms, and troubleshooting steps for P200B, empowering you to resolve the issue efficiently and restore your Mercedes’ performance. We’ll explore the intricacies of the IMRC system and how to address issues promptly and effectively.
1. Understanding the Mercedes P200B Fault Code
The P200B code, in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, signifies a problem within the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) system on engine bank 2. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects the system’s performance is not within the designed parameters. This system optimizes engine performance and emissions. This section delves into the function, symptoms, and diagnostic approach for the P200B fault code to help you understand the code’s meaning.
1.1. What the P200B Code Means for Your Mercedes
The P200B code means the PCM has identified a discrepancy in the expected operation of the IMRC system on bank 2. Bank 2 refers to the side of the engine opposite cylinder #1. The IMRC system utilizes flaps inside the intake manifold to adjust airflow, improving fuel efficiency and power output.
1.2. Function of the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) System
The IMRC system is designed to optimize engine airflow. At low RPMs, it restricts airflow for better fuel economy and reduced emissions. At higher RPMs, it opens up to maximize power. This is achieved through the use of flaps or valves within the intake manifold that are controlled by the PCM. Proper IMRC operation ensures the engine receives the correct amount of air for optimal combustion under varying conditions.
1.3. Common Symptoms Associated with P200B
When the P200B code is triggered, you might observe these symptoms in your Mercedes:
- Reduced Engine Performance: A noticeable decrease in acceleration and overall power.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Lower miles per gallon due to inefficient combustion.
- Rough Idle: Unstable or erratic engine behavior when idling.
- Hesitation During Acceleration: A delay or stumble when pressing the accelerator pedal.
- Check Engine Light: The malfunction indicator lamp on the dashboard will illuminate.
1.4. How the PCM Detects the P200B Fault
The PCM monitors the IMRC system using sensors that track the position of the intake manifold runner flaps. The PCM compares the actual position of the flaps with the desired position based on engine speed, load, and other factors. If the PCM detects a significant difference, indicating the IMRC system is not functioning correctly, it will store the P200B code. This discrepancy alerts you to a potential problem.
2. Diagnosing the Mercedes P200B Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effectively resolving the P200B fault code. This section outlines a systematic approach to diagnosing the issue, using tools like OBD-II scanners and digital multimeters. It also covers visual inspections and interpreting freeze frame data.
2.1. Essential Tools for Diagnosing P200B
To accurately diagnose the P200B code, you’ll need the following tools:
- OBD-II Scanner: To read the stored fault codes and view live data.
- Digital Multimeter (DMM): To test the electrical components of the IMRC system.
- Vacuum Gauge: To check vacuum lines and actuators.
- Inspection Light: To visually inspect hard-to-reach areas.
- Vehicle-Specific Repair Manual: To understand the IMRC system layout and specifications for your Mercedes model.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of professional-grade diagnostic tools to assist you in accurately diagnosing and resolving the P200B code. Consider the Autel MaxiSYS MS906BT or the Launch X431 V+ PRO for comprehensive diagnostics. Contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
2.2. Performing a Visual Inspection of the IMRC System
Begin the diagnostic process with a thorough visual inspection of the IMRC system components:
- Inspect Vacuum Lines: Check for cracks, leaks, or disconnections.
- Examine Electrical Connectors: Look for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Check Linkages and Actuators: Ensure they move freely without binding.
- Inspect the Intake Manifold: Look for any signs of damage or leaks.
Any visible damage should be addressed before moving on to further testing.
Alt: Visual inspection of the intake manifold runner control system on a Mercedes-Benz engine, highlighting vacuum lines and electrical connections.
2.3. Using an OBD-II Scanner to Retrieve Freeze Frame Data
Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve the freeze frame data associated with the P200B code. This data provides a snapshot of the engine conditions when the code was set, including:
- Engine Speed (RPM): The engine speed at the time of the fault.
- Engine Load: The percentage of maximum engine load.
- Coolant Temperature: The engine coolant temperature.
- Intake Air Temperature: The temperature of the air entering the engine.
Analyzing this data can help identify the specific conditions that triggered the P200B code.
2.4. Testing the IMRC Actuator and Sensor
- Actuator Test: Use the OBD-II scanner to activate the IMRC actuator and observe its movement. If the actuator does not move or moves erratically, it may be faulty.
- Sensor Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the IMRC sensor’s voltage or resistance. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. A sensor that does not meet the specifications should be replaced.
2.5. Checking the Wiring and Connectors
- Continuity Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the continuity of the wires in the IMRC system. A break in the wire can cause a P200B code.
- Voltage Test: Check the voltage at the IMRC actuator and sensor connectors. Ensure they are receiving the correct voltage.
3. Common Causes of the Mercedes P200B Code
The P200B code can stem from various issues within the IMRC system. This section identifies common causes, such as faulty actuators, vacuum leaks, and electrical problems, and provides troubleshooting guidance for each.
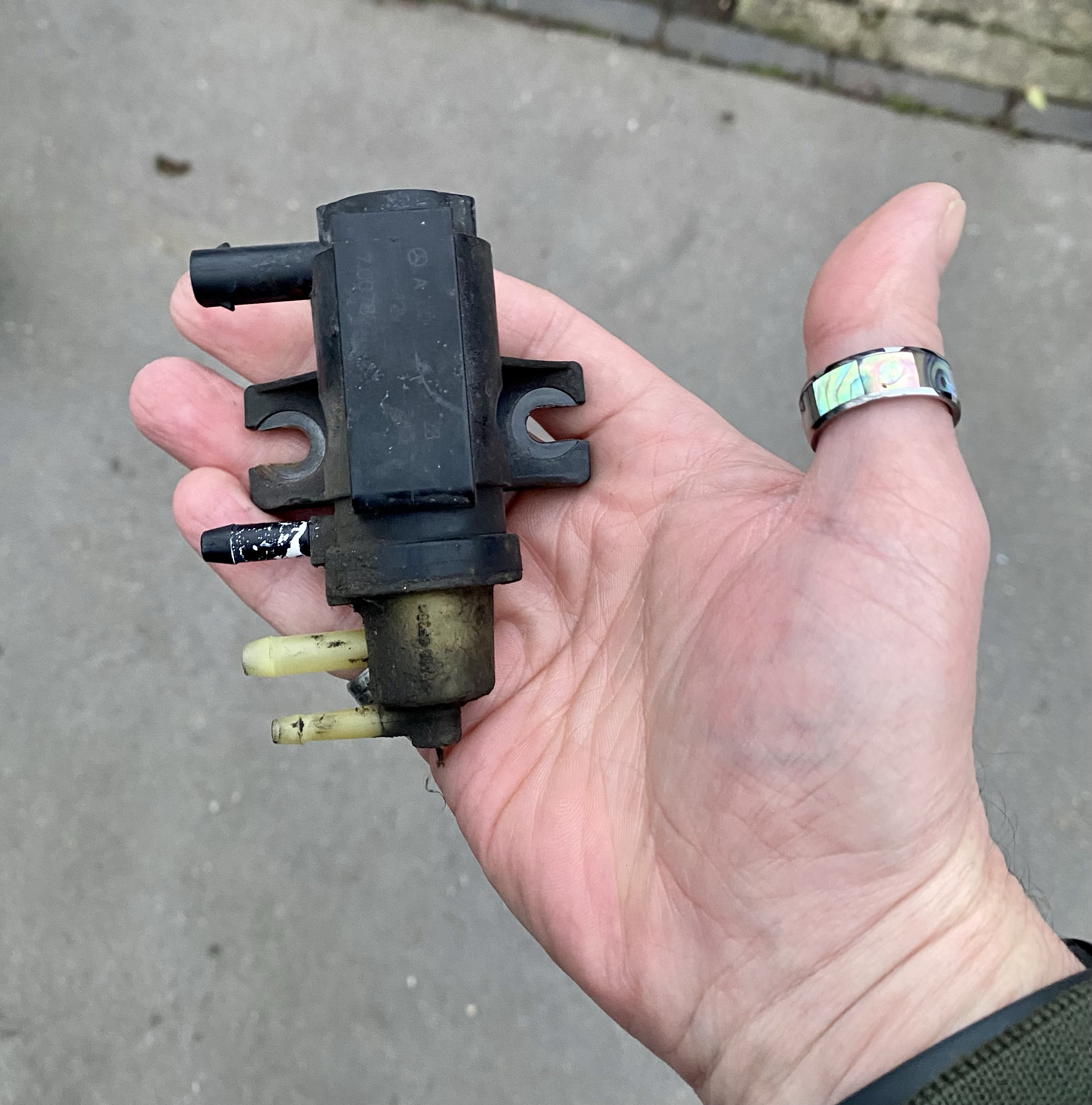
3.1. Faulty IMRC Actuator
The IMRC actuator controls the movement of the intake manifold runner flaps. If the actuator fails, the flaps may not open or close properly, leading to the P200B code.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the actuator for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Actuation Test: Use an OBD-II scanner to activate the actuator and observe its movement.
- Voltage Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the voltage at the actuator connector.
If the actuator fails any of these tests, it should be replaced.
3.2. Vacuum Leaks in the IMRC System
Vacuum leaks can disrupt the IMRC system’s operation. Leaks can cause the actuator to malfunction and trigger the P200B code.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check all vacuum lines and connections for cracks, leaks, or disconnections.
- Vacuum Gauge Test: Use a vacuum gauge to check the vacuum pressure at the IMRC actuator.
Repair or replace any damaged or leaking vacuum lines or components.
3.3. Electrical Issues: Wiring and Connectors
Electrical problems, such as damaged wiring or corroded connectors, can interfere with the IMRC system’s operation.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Continuity Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the continuity of the wires in the IMRC system.
- Voltage Test: Check the voltage at the IMRC actuator and sensor connectors.
Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors. Clean any corroded connections.
3.4. Defective IMRC Sensor
The IMRC sensor provides feedback to the PCM about the position of the intake manifold runner flaps. If the sensor is faulty, it may send incorrect information to the PCM, leading to the P200B code.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Resistance Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the resistance of the sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Replace the sensor if it does not meet the specifications.
3.5. Carbon Buildup in the Intake Manifold
Carbon buildup in the intake manifold can restrict the movement of the intake manifold runner flaps, causing the P200B code.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the intake manifold for carbon buildup.
- Cleaning: Clean the intake manifold to remove carbon deposits.
4. Step-by-Step Solutions for Resolving Mercedes P200B
This section provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for addressing the common causes of the P200B code. It includes replacing a faulty actuator, repairing vacuum leaks, and addressing electrical issues to resolve P200B effectively.
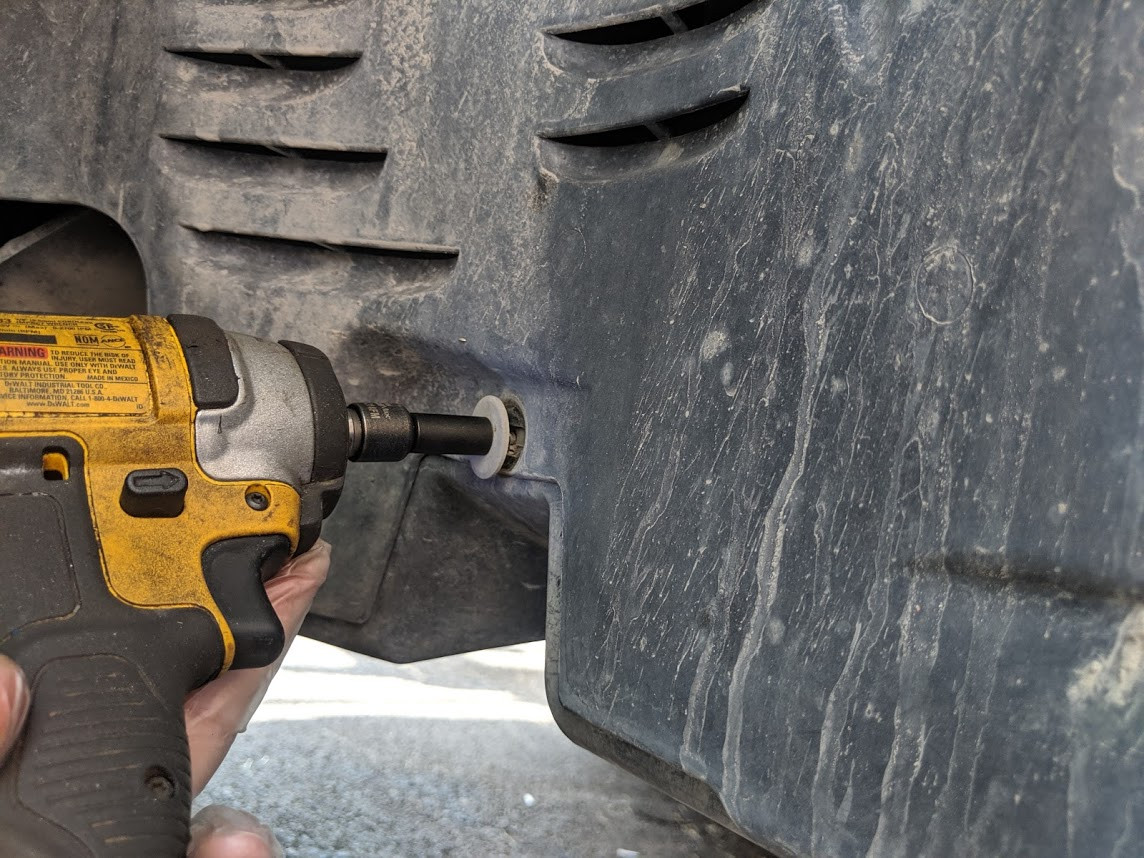
4.1. Replacing a Faulty IMRC Actuator
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: To ensure safety, disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the IMRC system.
- Locate the IMRC Actuator: Refer to your vehicle-specific repair manual to find the location of the IMRC actuator on bank 2.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the IMRC actuator.
- Remove the Actuator: Remove the bolts or screws securing the actuator to the intake manifold.
- Install the New Actuator: Install the new IMRC actuator, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Connect the Electrical Connector: Connect the electrical connector to the new actuator.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P200B code.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the IMRC system is functioning properly.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality IMRC actuators for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Visit our website or contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the right actuator for your vehicle.
4.2. Repairing Vacuum Leaks in the IMRC System
- Locate the Vacuum Leak: Use a vacuum gauge or a smoke machine to locate the vacuum leak in the IMRC system.
- Repair or Replace the Damaged Component: Repair or replace the damaged vacuum line, connector, or component.
- Test the System: Use a vacuum gauge to ensure the vacuum pressure in the IMRC system is within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P200B code.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the IMRC system is functioning properly.
4.3. Addressing Electrical Issues: Wiring and Connectors
- Locate the Damaged Wiring or Connector: Use a visual inspection and a digital multimeter to locate the damaged wiring or connector in the IMRC system.
- Repair or Replace the Damaged Component: Repair or replace the damaged wiring or connector.
- Test the System: Use a digital multimeter to ensure the wiring and connectors in the IMRC system are functioning properly.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P200B code.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the IMRC system is functioning properly.
4.4. Cleaning Carbon Buildup in the Intake Manifold
- Remove the Intake Manifold: Refer to your vehicle-specific repair manual for instructions on removing the intake manifold.
- Clean the Intake Manifold: Use a carbon cleaner and a brush to remove carbon deposits from the intake manifold.
- Reinstall the Intake Manifold: Reinstall the intake manifold, ensuring it is properly aligned and sealed.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P200B code.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the IMRC system is functioning properly.
4.5. Replacing a Defective IMRC Sensor
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the IMRC sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the bolts or screws securing the sensor to the intake manifold.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new IMRC sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Connect the Electrical Connector: Connect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the P200B code.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the IMRC system is functioning properly.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for P200B
For complex P200B cases, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary. This section covers using an oscilloscope to analyze sensor signals and performing a PCM reset to clear stored adaptations and optimize the IMRC system.
5.1. Using an Oscilloscope to Analyze Sensor Signals
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the signals from the IMRC sensor and actuator. This can help identify intermittent problems or subtle issues that may not be apparent with a digital multimeter.
Steps for Using an Oscilloscope:
- Connect the Oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope to the IMRC sensor and actuator circuits.
- Monitor the Signals: Monitor the signals while the engine is running and the IMRC system is active.
- Analyze the Waveforms: Analyze the waveforms for any abnormalities, such as signal dropouts, excessive noise, or incorrect signal levels.
5.2. Performing a PCM Reset and Relearn Procedure
A PCM reset can clear stored adaptations and force the PCM to relearn the IMRC system parameters. This can sometimes resolve P200B codes caused by minor discrepancies or adaptations.
Steps for Performing a PCM Reset:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Disconnect the negative battery terminal for at least 15 minutes.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Perform a Relearn Procedure: Follow the vehicle-specific relearn procedure for the IMRC system. This may involve driving the vehicle under specific conditions to allow the PCM to relearn the system parameters.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes IMRC System
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding future P200B codes. This section offers advice on cleaning the intake manifold, inspecting vacuum lines regularly, and ensuring proper electrical connections to keep your IMRC system in top condition.
6.1. Regular Intake Manifold Cleaning
Regularly cleaning the intake manifold can prevent carbon buildup and ensure the intake manifold runner flaps move freely.
Cleaning Frequency:
- Every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
Cleaning Procedure:
- Remove the Intake Manifold: Refer to your vehicle-specific repair manual for instructions on removing the intake manifold.
- Clean the Intake Manifold: Use a carbon cleaner and a brush to remove carbon deposits from the intake manifold.
- Reinstall the Intake Manifold: Reinstall the intake manifold, ensuring it is properly aligned and sealed.
6.2. Inspecting Vacuum Lines and Connections
Regularly inspecting vacuum lines and connections can help identify and address potential leaks before they cause problems.
Inspection Frequency:
- Every 12 months, or during regular maintenance intervals.
Inspection Procedure:
- Visual Inspection: Check all vacuum lines and connections for cracks, leaks, or disconnections.
- Vacuum Gauge Test: Use a vacuum gauge to check the vacuum pressure at the IMRC actuator.
Repair or replace any damaged or leaking vacuum lines or components.
6.3. Ensuring Proper Electrical Connections
Ensuring proper electrical connections can prevent electrical issues that can interfere with the IMRC system’s operation.
Inspection Frequency:
- Every 12 months, or during regular maintenance intervals.
Inspection Procedure:
- Visual Inspection: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Continuity Test: Use a digital multimeter to check the continuity of the wires in the IMRC system.
- Voltage Test: Check the voltage at the IMRC actuator and sensor connectors.
Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors. Clean any corroded connections.
7. The Importance of Using Quality Parts
Using quality replacement parts is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your Mercedes’ IMRC system. This section emphasizes why choosing reputable brands and OEM parts can prevent future issues and maintain optimal performance.
7.1. Benefits of OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts
- OEM Parts: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are made by the same manufacturer that made the original parts for your vehicle. They are designed to fit and function perfectly, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
- Aftermarket Parts: Aftermarket parts are made by third-party manufacturers. While they may be less expensive, they may not meet the same quality standards as OEM parts. This can lead to premature failure and other problems.
7.2. Recommended Brands for IMRC System Components
When replacing IMRC system components, consider using reputable brands such as:
- Bosch: A well-known manufacturer of high-quality automotive parts, including IMRC actuators and sensors.
- Pierburg: A leading supplier of automotive components, including vacuum pumps and actuators.
- Genuine Mercedes-Benz Parts: OEM parts that are designed specifically for your Mercedes vehicle.
7.3. Where to Purchase Reliable Parts
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality OEM and aftermarket parts for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Visit our website or contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the right parts for your vehicle. You can also find reliable parts at reputable auto parts stores and online retailers.
8. How CARDIAGTECH.NET Can Help You Resolve P200B
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools, replacement parts, and expert advice to help you resolve the P200B fault code efficiently and effectively. This section details the specific products and services available to assist you.
8.1. Recommended Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Autel MaxiSYS MS906BT: A comprehensive diagnostic scanner that can read and clear fault codes, view live data, and perform actuation tests.
- Launch X431 V+ PRO: A versatile diagnostic tool that offers advanced diagnostic capabilities and wide vehicle coverage.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A user-friendly diagnostic scanner that is perfect for DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians alike.
8.2. Available IMRC System Components
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of IMRC system components, including:
- IMRC Actuators: High-quality actuators that are designed to fit and function perfectly in your Mercedes vehicle.
- IMRC Sensors: Reliable sensors that provide accurate feedback to the PCM.
- Vacuum Lines and Connectors: Durable vacuum lines and connectors that are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of the engine compartment.
8.3. Expert Support and Consultation
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides expert support and consultation to help you diagnose and resolve the P200B fault code. Our team of experienced technicians can provide guidance on troubleshooting, repair procedures, and parts selection. Contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
9. Understanding the Costs Associated with P200B Repair
Being aware of the costs related to diagnosing and repairing the P200B code can help you plan your budget and make informed decisions. This section provides an overview of potential expenses, from diagnostic fees to the cost of replacement parts and labor.
9.1. Average Diagnostic Costs
The cost of diagnosing the P200B code can vary depending on the diagnostic tools and expertise required.
Estimated Diagnostic Costs:
- DIY Diagnosis: Using your own OBD-II scanner can cost anywhere from $50 to $500, depending on the features and capabilities of the scanner.
- Professional Diagnosis: Hiring a professional technician to diagnose the P200B code can cost anywhere from $75 to $150 per hour.
9.2. Replacement Part Costs
The cost of replacement parts for the IMRC system can vary depending on the brand, quality, and source of the parts.
Estimated Replacement Part Costs:
| Part | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| IMRC Actuator | $150 – $400 |
| IMRC Sensor | $50 – $150 |
| Vacuum Lines/Connectors | $20 – $50 |
9.3. Labor Costs for Repair
The labor costs for repairing the P200B code can vary depending on the complexity of the repair and the hourly rate of the technician.
Estimated Labor Costs:
- Simple Repairs: Replacing a vacuum line or connector may take 1-2 hours of labor.
- Complex Repairs: Replacing the IMRC actuator or cleaning the intake manifold may take 3-5 hours of labor.
- Average Hourly Rate: The average hourly rate for a professional technician is $75 to $150 per hour.
10. Real-World Case Studies of P200B Resolution
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how the P200B code is diagnosed and resolved in practice. This section presents several case studies, detailing the symptoms, diagnostic steps, solutions, and outcomes.
10.1. Case Study 1: Faulty IMRC Actuator
Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz C250
Symptoms: Reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and a stored P200B code.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Visual inspection revealed no obvious damage to the IMRC system.
- OBD-II scanner retrieved the P200B code and freeze frame data.
- Actuator test revealed that the IMRC actuator was not moving properly.
- Voltage test confirmed that the actuator was receiving power, but not functioning correctly.
Solution: Replaced the faulty IMRC actuator.
Outcome: The vehicle’s performance was restored, fuel economy improved, and the P200B code was cleared.
10.2. Case Study 2: Vacuum Leak in the IMRC System
Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz E350
Symptoms: Rough idle, hesitation during acceleration, and a stored P200B code.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Visual inspection revealed a cracked vacuum line in the IMRC system.
- Vacuum gauge test confirmed a vacuum leak at the IMRC actuator.
Solution: Replaced the cracked vacuum line.
Outcome: The vehicle’s idle was smoothed out, acceleration improved, and the P200B code was cleared.
10.3. Case Study 3: Electrical Issues: Wiring and Connectors
Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz GLC300
Symptoms: Intermittent loss of power, occasional stalling, and a stored P200B code.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Visual inspection revealed a corroded connector at the IMRC sensor.
- Continuity test confirmed a break in the wiring to the IMRC sensor.
Solution: Repaired the corroded connector and replaced the damaged wiring.
Outcome: The vehicle’s performance was stabilized, stalling issues were resolved, and the P200B code was cleared.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Mercedes P200B
This FAQ section addresses common questions related to the Mercedes P200B fault code, providing concise answers to help you better understand the issue and its resolution.
11.1. What Does the P200B Code Mean?
The P200B code indicates a problem with the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) system on bank 2 of your Mercedes-Benz engine. This system regulates airflow to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
11.2. Can I Drive My Mercedes with a P200B Code?
While it is technically possible to drive with a P200B code, it is not recommended. The issue can cause reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and potential damage to other engine components.
11.3. How Do I Fix the P200B Code?
To fix the P200B code, you will need to diagnose the underlying issue and address it. This may involve replacing a faulty IMRC actuator, repairing vacuum leaks, addressing electrical issues, or cleaning carbon buildup in the intake manifold.
11.4. How Much Does It Cost to Fix the P200B Code?
The cost of fixing the P200B code can vary depending on the diagnostic tools and expertise required. Contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
11.5. Is the P200B Code Serious?
The P200B code should not be classified as severe but should be addressed at the earliest convenient opportunity.
11.6. What Tools Do I Need to Diagnose the P200B Code?
To accurately diagnose the P200B code, you’ll need the following tools:
- OBD-II Scanner
- Digital Multimeter (DMM)
- Vacuum Gauge
- Inspection Light
- Vehicle-Specific Repair Manual
11.7. Where Can I Find High-Quality Replacement Parts for My Mercedes?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality OEM and aftermarket parts for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Visit our website or contact our support team at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the right parts for your vehicle.
11.8. Can Carbon Buildup Cause the P200B Code?
Yes, carbon buildup in the intake manifold can restrict the movement of the intake manifold runner flaps, causing the P200B code.
11.9. How Often Should I Clean My Intake Manifold?
You should clean your intake manifold every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
11.10. What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty IMRC Actuator?
Symptoms of a faulty IMRC actuator may include reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, rough idle, and hesitation during acceleration.
12. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
If you’re struggling with the Mercedes P200B fault code or need assistance with diagnostic tools and replacement parts, don’t hesitate to contact CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our team of experts is ready to help you resolve the issue efficiently and restore your vehicle’s performance.
12.1. How to Reach Our Support Team
You can reach our support team via:
- Phone: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Email: [email protected]
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
12.2. Schedule a Consultation
Schedule a consultation with one of our experienced technicians to discuss your specific concerns and receive personalized advice.
12.3. Visit Our Website
Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our wide range of diagnostic tools, replacement parts, and resources for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
Take Action Now
Is the P200B code causing you headaches? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today. Our expert team is ready to provide the tools, parts, and support you need to resolve the issue and get your Mercedes running smoothly again. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit CARDIAGTECH.NET for immediate assistance. Don’t let the P200B code hold you back – reach out to CARDIAGTECH.NET and drive with confidence!