P0302 Mercedes Code: Diagnosis, Causes, and Solutions
The P0302 Mercedes code signals “Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected,” pinpointing a combustion problem in your engine’s second cylinder. This means the engine control module (ECM) has detected that cylinder 2 isn’t firing correctly, which can impact your Mercedes’ performance. Dealing with a P0302 code promptly is important, and at CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer the tools and expertise to help you diagnose and resolve this issue efficiently. This comprehensive guide will walk you through understanding, diagnosing, and fixing the P0302 code, ensuring your Mercedes runs smoothly again. We’ll cover everything from misfire causes to troubleshooting techniques, including utilizing tools like OBD-II scanners and multimeters, along with discussing the role of proper maintenance to prevent future issues.
1. Decoding the P0302 Mercedes Code: A Deep Dive
The P0302 code on your Mercedes indicates a misfire in cylinder 2. A misfire happens when the combustion process in that cylinder is incomplete or doesn’t occur at all. This can stem from several underlying problems that need to be addressed for optimal engine performance.
1.1. What Does Cylinder 2 Misfire Mean?
A cylinder misfire occurs when one or more cylinders in your engine fail to produce the necessary power due to incomplete or absent combustion. This can lead to decreased engine efficiency and performance. For the P0302 code specifically, the issue is isolated to cylinder 2.
1.2. Common Causes of P0302 in Mercedes Vehicles
Understanding the root causes of a P0302 error is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here’s a list of common culprits:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn or damaged spark plugs can fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
- Defective Ignition Coils: Ignition coils provide the spark needed for combustion; a failing coil can cause a misfire.
- Fuel Injector Problems: A clogged or malfunctioning fuel injector can disrupt the fuel supply to cylinder 2.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the vacuum system can alter the air-fuel mixture, leading to misfires.
- Low Compression: Compression issues within the cylinder can prevent proper combustion.
- Wiring and Connector Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring and connectors can disrupt the electrical signals needed for ignition and fuel delivery.
- Engine Control Module (ECM) Problems: Although rare, a faulty ECM can incorrectly trigger a P0302 code.
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: Incorrect readings from the oxygen sensor can cause the engine to misfire.
- Catalytic Converter Problems: Although usually a result of a misfire, a failing catalytic converter can cause a misfire.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Issues: Inaccurate MAF sensor readings can cause misfires.
1.3. Identifying Symptoms Associated with P0302
Recognizing the symptoms of a P0302 error can help you address the issue quickly and prevent further damage:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Rough Idle: The engine may run roughly, especially when idling.
- Engine Stalling: The engine may stall unexpectedly, particularly at low speeds.
- Reduced Power: You may notice a decrease in overall engine power and acceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A misfiring cylinder can lead to a noticeable drop in fuel efficiency.
- Engine Hesitation: The engine may hesitate or stumble during acceleration.
- Unusual Noises: Misfires can sometimes cause unusual noises, such as popping or knocking sounds.
- Smell of Fuel: Unburnt fuel can sometimes be smelled from the exhaust.
1.4. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Diagnosing P0302
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the urgency of diagnosing and resolving engine issues. We provide advanced diagnostic tools, such as OBD-II scanners and multimeters, to help you accurately identify the cause of the P0302 code. Our tools are designed for both experienced mechanics and DIY enthusiasts. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for expert advice and support.
Alt: Mercedes-Benz engine with visible components, highlighting the area where cylinder misfires can occur, suitable for diagnosing P0302 error.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing the P0302 Code
Diagnosing the P0302 code requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the exact cause of the misfire. Here’s a detailed guide to help you through the process.
2.1. Initial Inspection and Preparation
Before diving into advanced diagnostics, start with a thorough visual inspection and gather the necessary tools.
- Gather Tools:
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- Spark plug socket
- Compression tester
- Fuel pressure tester
- Safety First: Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface and the engine is cool to avoid burns. Wear safety glasses and gloves.
- Visual Inspection:
- Check for any obvious signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked hoses, or loose connections.
- Inspect the spark plugs and ignition coils for visible wear or damage.
- Look for any fuel leaks around the fuel injectors.
- Documentation: Keep a detailed record of your findings as you go. This will help you track the potential causes and solutions.
2.2. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading and interpreting error codes.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Read the Codes: Turn on the ignition (but don’t start the engine) and use the scanner to read the stored codes. Note all codes, including any pending or historical codes.
- Understand the Codes: The scanner will display the P0302 code along with any other related codes. This information can help you narrow down the potential causes.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After noting the codes, you can clear them to see if the P0302 code returns after testing and repairs.
2.3. Testing the Ignition System
The ignition system is a common source of misfires. Testing the spark plugs, ignition coils, and wiring is critical.
2.3.1. Spark Plug Inspection and Testing
- Visual Inspection:
- Remove the spark plug from cylinder 2.
- Check for signs of wear, such as a worn electrode, cracks, or carbon buildup.
- Compare the condition of the spark plug to others in the engine. Unusual wear can indicate a problem in that cylinder.
- Spark Plug Testing:
- Use a spark plug tester to check if the spark plug is producing a strong, consistent spark.
- If the spark plug is damaged or not producing a spark, replace it.
2.3.2. Ignition Coil Testing
- Swap Test:
- Swap the ignition coil from cylinder 2 with another cylinder (e.g., cylinder 1).
- Clear the codes and restart the engine.
- If the misfire moves to cylinder 1 (P0301), the ignition coil is likely the problem.
- Multimeter Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check the primary and secondary resistance of the ignition coil.
- Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the resistance is out of range, replace the ignition coil.
2.3.3. Wiring and Connector Inspection
- Visual Inspection:
- Check the wiring and connectors leading to the ignition coil and spark plug for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
- Continuity Test:
- Use a multimeter to perform a continuity test on the wiring.
- Ensure there is a good connection between the ECM and the ignition coil.
2.4. Fuel System Checks
Problems with the fuel system can also cause misfires. Testing the fuel injector and fuel pressure is essential.
2.4.1. Fuel Injector Testing
- Listening Test:
- Use a stethoscope or a long screwdriver to listen to the fuel injector while the engine is running.
- You should hear a clicking sound, indicating that the injector is firing.
- If the injector is silent, it may be clogged or malfunctioning.
- Resistance Test:
- Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the fuel injector.
- Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the resistance is out of range, replace the fuel injector.
- Injector Cleaning:
- Consider having the fuel injectors professionally cleaned to remove any clogs or deposits.
- You can also use fuel injector cleaner additives in the fuel tank.
2.4.2. Fuel Pressure Testing
- Connect the Tester:
- Connect a fuel pressure tester to the fuel rail.
- Check the Pressure:
- Turn on the ignition (but don’t start the engine) to activate the fuel pump.
- Check the fuel pressure reading.
- Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If the fuel pressure is too low, there may be a problem with the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel pressure regulator.
- Leak-Down Test:
- After turning off the ignition, observe the fuel pressure for any drop.
- A rapid drop in fuel pressure can indicate a leak in the fuel system.
2.5. Compression Testing
Low compression in cylinder 2 can prevent proper combustion, leading to a misfire.
- Preparation:
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature.
- Disable the ignition system and fuel injection to prevent the engine from starting.
- Remove all spark plugs.
- Compression Test:
- Insert the compression tester into the spark plug hole of cylinder 2.
- Crank the engine for several seconds and record the compression reading.
- Repeat the test for all cylinders and compare the readings.
- Interpreting Results:
- Low compression in cylinder 2 compared to the other cylinders indicates a problem.
- Possible causes include worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket.
- Wet Compression Test:
- If the compression is low, add a small amount of oil to the cylinder and repeat the test.
- If the compression increases, the problem is likely with the piston rings.
- If the compression remains low, the problem is likely with the valves.
2.6. Vacuum Leak Detection
Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and cause misfires.
- Visual Inspection:
- Check all vacuum hoses for cracks, breaks, or loose connections.
- Smoke Test:
- Use a smoke machine to introduce smoke into the vacuum system.
- Look for smoke escaping from any leaks.
- Carburetor Cleaner Test:
- Spray carburetor cleaner around vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets.
- Listen for a change in engine idle. If the idle changes, there is likely a vacuum leak in that area.
2.7. Advanced Diagnostic Steps
If the basic tests do not reveal the cause of the P0302 code, further diagnostics may be necessary.
- Check Engine Mounts: Damaged or worn engine mounts can cause excessive vibration, leading to misfires.
- Inspect Crankshaft and Camshaft Sensors: Faulty sensors can cause timing issues and misfires.
- Evaluate the ECM: Although rare, a faulty ECM can cause misfires. Consult a professional for ECM testing.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks can affect the engine’s backpressure and cause misfires.
2.8. Utilizing CARDIAGTECH.NET for Advanced Diagnostics
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic tools and resources to help you tackle even the most challenging P0302 cases. Our team of experts can provide guidance and support to ensure you find the right solution. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: OBD-II scanner tool connected to a car’s diagnostic port, illustrating the initial step in diagnosing the P0302 error code.
3. Repairing the P0302 Code: Practical Solutions
Once you’ve identified the cause of the P0302 code, it’s time to implement the necessary repairs. Here are practical solutions to address common issues.
3.1. Replacing Faulty Spark Plugs
Replacing worn or damaged spark plugs is a straightforward but effective solution.
- Tools Needed:
- Spark plug socket
- Socket wrench
- Torque wrench
- New spark plugs
- Gap tool
- Procedure:
- Remove the Old Spark Plug: Disconnect the ignition coil and remove the spark plug from cylinder 2.
- Inspect the Spark Plug: Check the old spark plug for signs of wear, carbon buildup, or damage.
- Gap the New Spark Plug: Use a gap tool to ensure the new spark plug has the correct gap setting as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Install the New Spark Plug: Carefully thread the new spark plug into the cylinder head by hand to avoid cross-threading.
- Tighten the Spark Plug: Use a torque wrench to tighten the spark plug to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reconnect the Ignition Coil: Reconnect the ignition coil to the spark plug.
3.2. Replacing Defective Ignition Coils
Replacing a faulty ignition coil can restore proper spark delivery to the cylinder.
- Tools Needed:
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- New ignition coil
- Procedure:
- Disconnect the Old Ignition Coil: Disconnect the wiring harness from the ignition coil.
- Remove the Old Ignition Coil: Remove the bolts or screws holding the ignition coil in place.
- Install the New Ignition Coil: Install the new ignition coil in the same location.
- Secure the Ignition Coil: Tighten the bolts or screws to secure the ignition coil.
- Reconnect the Wiring Harness: Reconnect the wiring harness to the ignition coil.
3.3. Repairing or Replacing Fuel Injectors
A malfunctioning fuel injector can disrupt the fuel supply to the cylinder.
- Tools Needed:
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- New or refurbished fuel injector
- Fuel injector cleaner (optional)
- Procedure:
- Disconnect the Fuel Injector: Disconnect the wiring harness from the fuel injector.
- Remove the Fuel Injector: Carefully remove the fuel injector from the fuel rail.
- Inspect the Fuel Injector: Check the fuel injector for signs of damage or clogging.
- Clean the Fuel Injector (Optional): If the injector is not severely damaged, you can try cleaning it with fuel injector cleaner.
- Install the New Fuel Injector: Install the new or refurbished fuel injector into the fuel rail.
- Reconnect the Wiring Harness: Reconnect the wiring harness to the fuel injector.
3.4. Addressing Vacuum Leaks
Repairing vacuum leaks can restore the proper air-fuel mixture.
- Tools Needed:
- Screwdrivers
- Wrench set
- New vacuum hoses
- Hose clamps
- Procedure:
- Locate the Vacuum Leak: Use a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner to locate the vacuum leak.
- Replace the Vacuum Hose: If the leak is in a vacuum hose, replace the hose with a new one.
- Tighten Connections: Ensure all vacuum hose connections are tight and secure.
- Replace Gaskets: If the leak is in an intake manifold gasket, replace the gasket.
3.5. Resolving Compression Issues
Addressing compression issues often requires more extensive repairs.
- Tools Needed:
- Engine repair tools
- New piston rings
- New valves
- Head gasket
- Procedure:
- Diagnose the Compression Issue: Determine the cause of the low compression (e.g., worn piston rings, damaged valves, blown head gasket).
- Repair or Replace Components: Depending on the cause, you may need to replace the piston rings, valves, or head gasket.
- Reassemble the Engine: Carefully reassemble the engine, following the manufacturer’s specifications.
3.6. Checking and Repairing Wiring
Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt electrical signals, leading to misfires.
- Tools Needed:
- Multimeter
- Wiring connectors
- Electrical tape
- Wire stripper
- Procedure:
- Inspect the Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors leading to the ignition and fuel systems for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Repair or Replace Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring using wiring connectors and electrical tape.
- Ensure Proper Connections: Ensure all connections are clean and secure.
3.7. Clearing the P0302 Code
After completing the necessary repairs, clear the P0302 code using an OBD-II scanner.
- Procedure:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port.
- Clear the Codes: Turn on the ignition (but don’t start the engine) and use the scanner to clear the stored codes.
- Test Drive the Vehicle: Perform a test drive to ensure the P0302 code does not return.
3.8. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Repairing P0302
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality replacement parts and tools to help you repair the P0302 code effectively. Our expert team can offer advice and support to ensure you complete the repairs successfully. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: Mechanic replacing spark plugs in a car engine, showing the process of ensuring proper ignition for cylinder combustion to fix P0302.
4. Preventing Future Misfires: Maintenance Tips
Preventing future misfires involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Here are essential tips to keep your Mercedes running smoothly and avoid the P0302 code.
4.1. Regular Spark Plug Maintenance
- Scheduled Replacements: Replace spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect spark plugs for wear, damage, and carbon buildup.
- Proper Gapping: Ensure spark plugs are properly gapped to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.2. Ignition System Care
- Ignition Coil Testing: Periodically test ignition coils for proper resistance and spark output.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect wiring and connectors for damage, corrosion, and loose connections.
- Clean Connections: Keep electrical connections clean and secure to ensure proper signal transmission.
4.3. Fuel System Maintenance
- Fuel Injector Cleaning: Use fuel injector cleaner additives in the fuel tank to prevent clogs and deposits.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
- Fuel Pressure Monitoring: Monitor fuel pressure to ensure it is within the specified range.
4.4. Engine Maintenance
- Oil Changes: Perform regular oil changes to keep the engine lubricated and prevent wear.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter to ensure a clean air supply to the engine.
- Coolant Flush: Perform coolant flushes to prevent corrosion and maintain proper engine temperature.
4.5. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
- Monitor Engine Performance: Pay attention to any changes in engine performance, such as rough idling, reduced power, or poor fuel economy.
- Address Issues Early: Address minor issues promptly to prevent them from escalating into major problems.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify and address potential problems before they cause misfires.
4.6. Keeping Your Mercedes in Top Condition with CARDIAGTECH.NET
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your Mercedes running smoothly and prevent issues like the P0302 code. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality parts and tools to help you maintain your vehicle. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for expert advice and support.
Alt: Mechanic performing routine engine maintenance on a Mercedes-Benz, emphasizing the importance of regular care to prevent issues like the P0302 error.
5. Understanding Mercedes-Specific Issues Related to P0302
Mercedes vehicles, while renowned for their performance and reliability, have specific characteristics that can influence the causes and solutions for the P0302 code.
5.1. Common Mercedes Engine Configurations
Mercedes vehicles employ various engine configurations, each with unique characteristics.
- Inline Engines: Some older Mercedes models use inline engines, which may have specific ignition coil or fuel injector layouts.
- V-Engines: Many modern Mercedes models use V6 or V8 engines, which require careful attention to cylinder-specific components.
- Turbocharged Engines: Turbocharged engines, common in many Mercedes models, can experience misfires due to issues with the turbocharger system or related sensors.
5.2. Specific Components and Systems in Mercedes Vehicles
Mercedes vehicles have unique components and systems that may contribute to the P0302 code.
- ME (Motor Electronics) Control Unit: The ME control unit manages the engine’s functions, including ignition, fuel injection, and emissions control.
- Direct Injection Systems: Many Mercedes engines use direct fuel injection, which can be sensitive to fuel quality and injector clogs.
- Variable Valve Timing: Variable valve timing systems can affect cylinder compression and combustion efficiency, leading to misfires if not functioning correctly.
5.3. Diagnostic Tips for Mercedes-Specific Issues
When diagnosing the P0302 code in a Mercedes, consider the following tips.
- Use Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Tools: Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools can provide more detailed information about the engine’s performance and fault codes.
- Check for Software Updates: Ensure the ME control unit has the latest software updates, as these can address known issues and improve engine performance.
- Consult Mercedes Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Check for TSBs related to the P0302 code, as these can provide valuable insights and repair procedures.
5.4. Expert Advice for Mercedes Owners
For Mercedes owners, seeking expert advice can be invaluable in resolving complex issues like the P0302 code.
- Consult a Mercedes Specialist: A Mercedes specialist has in-depth knowledge of the vehicle’s systems and can provide accurate diagnoses and effective repairs.
- Use Genuine Mercedes Parts: When replacing parts, use genuine Mercedes parts to ensure proper fit and performance.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about Mercedes-specific maintenance requirements and potential issues to proactively address problems.
5.5. Leveraging CARDIAGTECH.NET for Mercedes-Specific Solutions
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a wide range of Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools, parts, and expertise to help you resolve the P0302 code effectively. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: Technician using a Mercedes-specific diagnostic tool to check engine parameters, highlighting the specialized approach required for diagnosing P0302 in Mercedes.
6. Advanced Tools and Techniques for P0302 Diagnostics
For complex P0302 cases, advanced diagnostic tools and techniques can provide deeper insights into the engine’s condition.
6.1. Using Advanced OBD-II Scanners
Advanced OBD-II scanners offer features beyond basic code reading.
- Live Data Streaming: Monitor live engine data, such as spark advance, fuel trim, and oxygen sensor readings, to identify anomalies.
- Actuator Testing: Perform actuator tests to activate specific components, such as ignition coils and fuel injectors, to verify their functionality.
- Graphing Capabilities: Use graphing capabilities to visualize engine data and identify trends or patterns.
6.2. Performing a Cylinder Leakage Test
A cylinder leakage test can identify the source of compression loss.
- Procedure:
- Pressurize the Cylinder: Introduce compressed air into the cylinder through the spark plug hole.
- Listen for Leaks: Listen for air escaping from the exhaust, intake, or coolant system to identify the source of the leak.
- Interpreting Results:
- Air escaping from the exhaust indicates a leaking exhaust valve.
- Air escaping from the intake indicates a leaking intake valve.
- Air escaping from the coolant system indicates a blown head gasket.
6.3. Using an Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope can provide detailed information about electrical signals in the ignition and fuel systems.
- Ignition System Analysis: Analyze the ignition waveform to identify issues with the ignition coil, spark plug, or wiring.
- Fuel Injector Analysis: Analyze the fuel injector waveform to verify proper injector operation and identify any electrical problems.
6.4. Analyzing Fuel Trim Data
Fuel trim data provides insights into the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
- Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT): Indicates immediate adjustments to the air-fuel mixture.
- Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): Indicates long-term adjustments to the air-fuel mixture.
- Interpreting Results:
- High positive fuel trim values indicate a lean condition.
- High negative fuel trim values indicate a rich condition.
6.5. Smoke Testing for Vacuum Leaks
A smoke test is an effective way to locate vacuum leaks.
- Procedure:
- Introduce Smoke: Introduce smoke into the intake system using a smoke machine.
- Observe for Leaks: Look for smoke escaping from any leaks in the vacuum system.
- Identify the Source: Identify the source of the leak and repair or replace the affected components.
6.6. Advanced Techniques with CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic tools and resources to help you tackle even the most challenging P0302 cases. Our team of experts can provide guidance and support to ensure you find the right solution. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: Technician using advanced diagnostic equipment on a car, showcasing the comprehensive approach required for complex P0302 diagnoses.
7. The Impact of Ignoring P0302: Potential Consequences
Ignoring the P0302 code can lead to various engine performance problems and potential damage. Understanding these consequences can motivate prompt action and prevent costly repairs.
7.1. Reduced Fuel Efficiency
A misfiring cylinder results in incomplete combustion, leading to wasted fuel and reduced fuel efficiency. This can translate to higher fuel costs and decreased driving range.
7.2. Increased Emissions
Misfires increase harmful emissions, such as hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). This can contribute to air pollution and potentially lead to failed emissions tests.
7.3. Catalytic Converter Damage
Persistent misfires can cause unburnt fuel to enter the catalytic converter, leading to overheating and damage. Replacing a catalytic converter can be expensive, so addressing misfires promptly is crucial.
7.4. Engine Damage
Continuous misfires can cause excessive vibration and stress on engine components, leading to premature wear and potential damage. This can result in costly engine repairs or even the need for a complete engine replacement.
7.5. Poor Engine Performance
Misfires can cause rough idling, reduced power, and hesitation during acceleration, leading to a poor driving experience. Addressing the P0302 code can restore smooth and responsive engine performance.
7.6. Potential Safety Issues
In severe cases, misfires can cause the engine to stall unexpectedly, which can be dangerous, especially in traffic. Addressing the P0302 code can help prevent such safety issues.
7.7. Long-Term Reliability Concerns
Ignoring the P0302 code can lead to long-term reliability concerns, as the underlying issues can worsen over time. Addressing the problem promptly can help maintain the vehicle’s reliability and prevent future breakdowns.
7.8. Protecting Your Investment with CARDIAGTECH.NET
Addressing the P0302 code promptly is essential to protect your investment in your Mercedes. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers the tools, parts, and expertise to help you resolve the issue and prevent further damage. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: Image of a damaged engine due to misfires, emphasizing the potential consequences of ignoring the P0302 error code in Mercedes.
8. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of P0302 Resolution
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving the P0302 code in Mercedes vehicles.
8.1. Case Study 1: Spark Plug Failure
- Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes C300
- Symptoms: Check engine light, rough idle, reduced power
- Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed P0302 code. Visual inspection showed a worn spark plug in cylinder 2.
- Solution: Replaced all spark plugs with new ones.
- Outcome: Engine performance restored, check engine light cleared.
8.2. Case Study 2: Ignition Coil Malfunction
- Vehicle: 2017 Mercedes E350
- Symptoms: Check engine light, engine hesitation, poor fuel economy
- Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed P0302 code. Swapped ignition coils between cylinders 2 and 1. Misfire moved to cylinder 1 (P0301).
- Solution: Replaced the faulty ignition coil.
- Outcome: Engine performance restored, fuel economy improved.
8.3. Case Study 3: Fuel Injector Clog
- Vehicle: 2013 Mercedes CLS550
- Symptoms: Check engine light, rough idle, engine stalling
- Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed P0302 code. Fuel injector resistance test showed abnormal reading for cylinder 2 injector.
- Solution: Replaced the clogged fuel injector.
- Outcome: Engine performance restored, idling stabilized.
8.4. Case Study 4: Vacuum Leak
- Vehicle: 2016 Mercedes GLC300
- Symptoms: Check engine light, rough idle, poor acceleration
- Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed P0302 code. Smoke test revealed a vacuum leak in the intake manifold gasket.
- Solution: Replaced the intake manifold gasket.
- Outcome: Engine performance restored, acceleration improved.
8.5. Case Study 5: Low Compression
- Vehicle: 2014 Mercedes S550
- Symptoms: Check engine light, rough idle, reduced power
- Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed P0302 code. Compression test showed low compression in cylinder 2.
- Solution: Engine teardown revealed worn piston rings. Replaced piston rings and reassembled the engine.
- Outcome: Engine performance restored, compression normalized.
8.6. Learn From Success Stories with CARDIAGTECH.NET
These case studies demonstrate the importance of accurate diagnosis and effective repair techniques. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the tools and expertise to help you resolve the P0302 code successfully. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, for assistance.
Alt: Image of a car repair shop with a Mercedes-Benz being serviced, symbolizing the real-world scenarios where P0302 is diagnosed and resolved.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About P0302 Mercedes Code
Here are some frequently asked questions about the P0302 Mercedes code to help you better understand the issue and its resolution.
9.1. What does the P0302 code mean for my Mercedes?
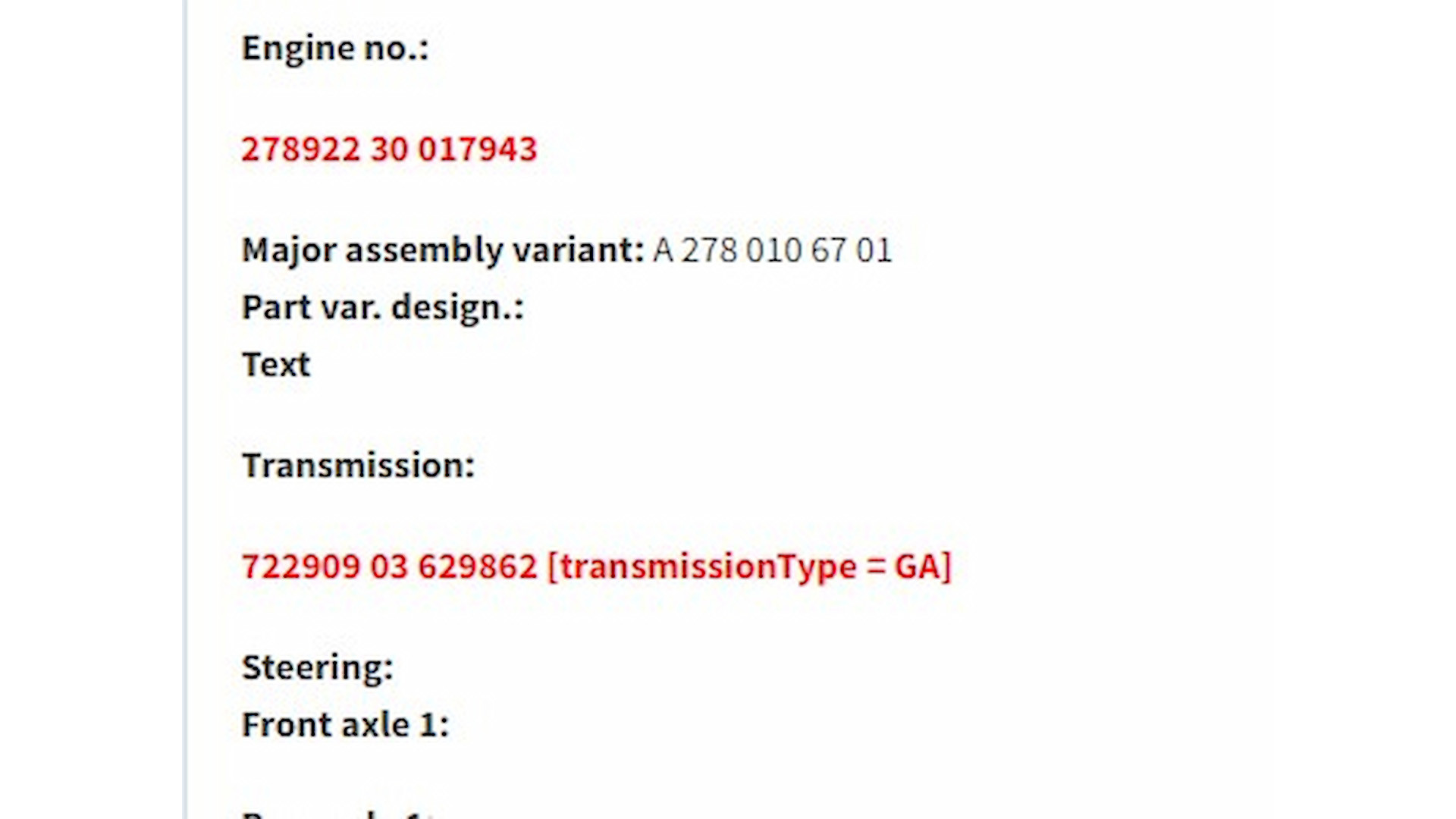
The P0302 code indicates that the engine control module (ECM) has detected a misfire in cylinder 2 of your Mercedes. This means that the combustion process in that cylinder is not occurring correctly.
9.2. Can I drive my Mercedes with a P0302 code?
While it is possible to drive with a P0302 code, it is not recommended. Driving with a misfire can cause further engine damage, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. It is best to diagnose and repair the issue promptly.
9.3. What are the common causes of the P0302 code in Mercedes vehicles?
Common causes include faulty spark plugs, defective ignition coils, fuel injector problems, vacuum leaks, low compression, and wiring issues.