How to Diagnose Sensor and Radar Systems Using Xentry?

Navigating the complexities of modern vehicle systems demands precision. This guide explores how to effectively diagnose sensor and radar systems using Xentry, empowering you to ensure accurate and reliable vehicle performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic tools tailored to meet these challenges. Unlock the power of accurate diagnostics with Xentry and elevate your repair capabilities.
Table of Contents
- What is Xentry and Why is it Important?
- Understanding Sensor and Radar Systems in Modern Vehicles
- Key Components of Sensor and Radar Systems
- Common Issues with Sensor and Radar Systems
- Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Sensor and Radar Systems Using Xentry
- Using Xentry for Initial System Scan
- Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Live Data Analysis with Xentry
- Component Testing with Xentry
- Calibration and Adjustment Procedures
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- Software Updates and Module Programming
- Ensuring Accurate Sensor Alignment
- Best Practices for Maintaining Sensor and Radar Systems
- The Role of OEM Information
- Tools and Equipment Recommended for Sensor and Radar Diagnostics
- Troubleshooting Common Diagnostic Challenges
- Case Studies: Real-World Diagnostic Scenarios
- The Future of Sensor and Radar Technology
- Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Xentry and Why is it Important?
Xentry is the official diagnostic software used by Mercedes-Benz to diagnose, troubleshoot, and program electronic control units (ECUs) in their vehicles, and it’s crucial for maintaining modern car systems. It allows technicians to perform in-depth diagnostics, read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view live data, perform component testing, and calibrate sensors and radar systems, making it an indispensable tool for any automotive professional working on Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Xentry ensures that repairs are performed accurately and efficiently, maintaining the vehicle’s safety and performance.
Why is Xentry Important?
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Xentry provides access to all vehicle systems, allowing for a thorough diagnosis.
- Accurate Troubleshooting: It helps identify the root cause of issues quickly, reducing downtime.
- Module Programming: Xentry enables software updates and module programming, ensuring systems are up-to-date.
- Calibration: Necessary for ADAS and other advanced systems, ensuring they function correctly after repairs.
- OEM-Level Access: Provides access to the same diagnostic capabilities as Mercedes-Benz dealerships.
2. Understanding Sensor and Radar Systems in Modern Vehicles
Modern vehicles rely heavily on sensor and radar systems to provide advanced safety features such as Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM), Lane Keeping Assist (LKA), and Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB). These systems use a combination of sensors and radar units to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, detect potential hazards, and assist the driver in avoiding accidents. Understanding these systems is essential for effective diagnosis and repair.
The Growing Importance of ADAS
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ADAS technologies have the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents and fatalities. For example, AEB systems can reduce rear-end collisions by up to 50%. As these systems become more prevalent, the need for skilled technicians who can diagnose and repair them will continue to grow.
Integration with Vehicle Systems
Sensor and radar systems are integrated with various vehicle systems, including:
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): Manages engine performance based on sensor inputs.
- Brake Control System (ABS/ESP): Enhances braking performance and stability.
- Steering System: Assists with lane keeping and steering corrections.
- Driver Information System: Provides alerts and warnings to the driver.
3. Key Components of Sensor and Radar Systems
To effectively diagnose and repair sensor and radar systems, it’s essential to understand the function of each component. These systems typically include:
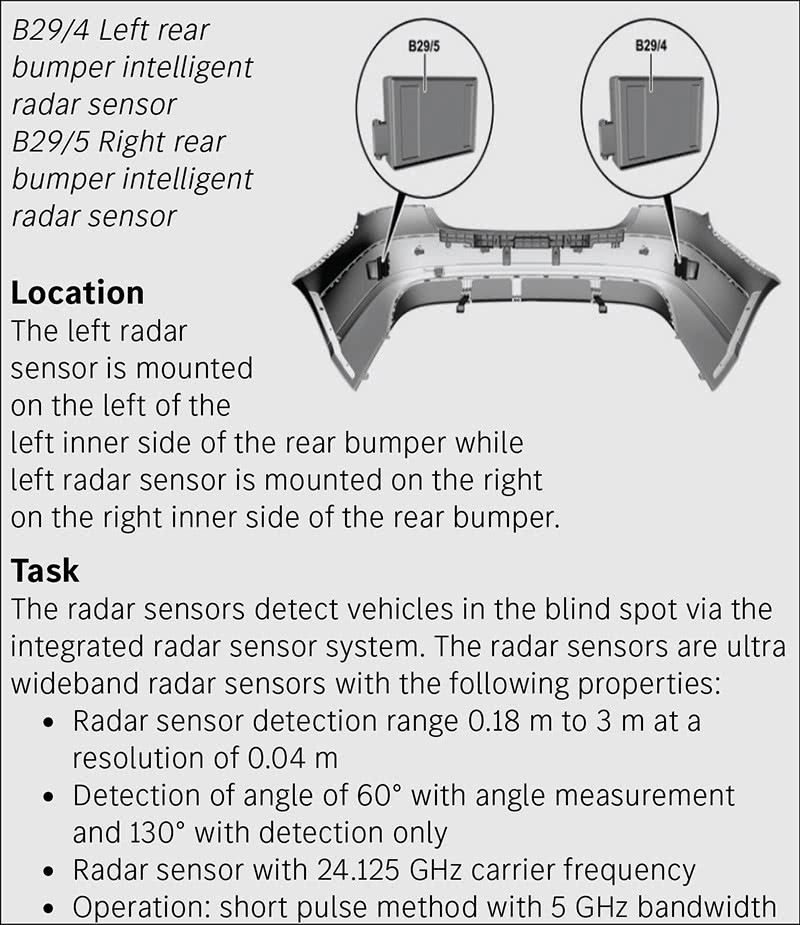
- Radar Sensors: Used for long-range detection of objects, such as vehicles and pedestrians.
- Camera Sensors: Provide visual information for lane keeping, traffic sign recognition, and object detection.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Used for short-range detection, such as parking assistance.
- Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Provides high-resolution 3D mapping of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Control Units: Process data from the sensors and control the vehicle’s response.
Radar Technology
Radar sensors emit radio waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back from objects. This information is used to determine the distance, speed, and direction of the objects. Radar sensors are typically mounted in the front and rear bumpers of the vehicle.
Camera Technology
Camera sensors capture images of the vehicle’s surroundings, which are then processed by image recognition software to identify objects, lane markings, and traffic signs. Camera sensors are typically mounted behind the windshield or in the rearview mirror.
Ultrasonic Technology
Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back from objects. This information is used to detect objects in close proximity to the vehicle, such as when parking.
Lidar Technology
Lidar sensors emit laser beams and measure the time it takes for the beams to bounce back from objects. This information is used to create a high-resolution 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings. Lidar sensors are typically mounted on the roof of the vehicle.
4. Common Issues with Sensor and Radar Systems
Several issues can affect the performance of sensor and radar systems. Common problems include:
- Sensor Damage: Physical damage to sensors due to collisions or environmental factors.
- Sensor Misalignment: Misalignment of sensors due to impacts or improper installation.
- Software Glitches: Software bugs or errors that can cause system malfunctions.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring that can disrupt sensor signals.
- Environmental Factors: Dirt, snow, or ice accumulation on sensors.
Impact of Environmental Factors
According to a study by AAA, environmental factors such as dirt and snow can significantly reduce the performance of ADAS systems. For example, AEB systems may not function correctly if the sensors are blocked by debris. Regular cleaning and maintenance of sensors are essential to ensure optimal performance.
The Role of Calibration
Calibration is essential for ensuring that sensor and radar systems function correctly after repairs or component replacement. Misaligned or uncalibrated sensors can lead to false alarms, system malfunctions, and reduced safety performance.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Sensor and Radar Systems Using Xentry
Diagnosing sensor and radar systems requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process using Xentry:
- Connect Xentry to the Vehicle: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Perform an Initial System Scan: Use Xentry to perform a comprehensive scan of all vehicle systems.
- Identify Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Review the DTCs to identify any faults in the sensor and radar systems.
- Research DTCs: Consult the Mercedes-Benz service manual or online resources to understand the meaning and possible causes of each DTC.
- Inspect Sensors and Wiring: Physically inspect the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Perform Live Data Analysis: Use Xentry to view live data from the sensors and radar units.
- Perform Component Testing: Use Xentry to perform component-specific tests to verify the functionality of individual sensors and radar units.
- Perform Calibration: If necessary, perform calibration procedures to ensure proper sensor alignment and functionality.
- Clear DTCs and Retest: Clear the DTCs and perform another system scan to verify that the faults have been resolved.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to verify that the sensor and radar systems are functioning correctly under real-world conditions.
Importance of Accurate Documentation
Keep detailed records of all diagnostic steps, test results, and repairs performed. This documentation can be helpful for future troubleshooting and warranty claims.
6. Using Xentry for Initial System Scan
The first step in diagnosing sensor and radar systems is to perform an initial system scan using Xentry. This scan will identify any DTCs that are stored in the vehicle’s ECUs, providing a starting point for further investigation.
Steps to Perform a System Scan
- Connect Xentry: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and turn on the ignition.
- Select Vehicle Model: Select the correct vehicle model and year in the Xentry software.
- Initiate Quick Test: Navigate to the “Quick Test” or “Full System Scan” option and initiate the scan.
- Review Results: Review the scan results to identify any DTCs related to the sensor and radar systems.
Interpreting Scan Results
The scan results will display a list of ECUs and any associated DTCs. Pay close attention to ECUs related to ADAS, such as:
- Radar Control Unit
- Camera Control Unit
- Ultrasonic Control Unit
- Driver Assistance System Control Unit
7. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs provide valuable information about the nature and location of faults within the sensor and radar systems. Understanding how to interpret these codes is essential for effective diagnosis.
Common DTCs for Sensor and Radar Systems
| DTC Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C151700 | Radar sensor signal fault | Damaged sensor, wiring issues, misalignment |
| C151A00 | Camera sensor signal fault | Damaged sensor, dirty lens, wiring issues |
| C155500 | Ultrasonic sensor signal fault | Damaged sensor, wiring issues, obstruction |
| C110100 | Lidar sensor signal fault | Damaged sensor, wiring issues, misalignment |
| U010000 | Lost communication with ECU | Wiring issues, faulty ECU, power supply problems |
| C150000 | Calibration required | Sensor replacement, misalignment, software update |
| B221A15 | The supply voltage of the sensor is too low | Wiring issue, faulty sensor, low battery voltage |
| C102000 | The vehicle speed signal is not available or implausible | Faulty wheel speed sensor, ABS module issue, wiring problem |
| C103000 | Yaw rate sensor: General fault | Sensor failure, wiring issue, incorrect installation |
| B201000 | Steering angle sensor: General fault | Sensor failure, wiring issue, mechanical issue with the steering system |
| C151900 | Radar sensor: No signal | Complete sensor failure, disconnected wiring, power supply issue to the sensor |
| C155600 | Ultrasonic sensor: Short circuit to ground | Wiring insulation damage causing a short, sensor malfunction |
| C155700 | Ultrasonic sensor: Short circuit to positive | Wiring insulation damage causing a short, sensor malfunction |
| C150100 | Lateral acceleration sensor: General fault | Sensor failure, incorrect installation, wiring problem |
| C101000 | Longitudinal acceleration sensor: General fault | Sensor failure, wiring issue, incorrect mounting |
| C152000 | Camera sensor: Signal erratic | Environmental obstruction (rain, snow), sensor damage, poor calibration |
| B220000 | LIN bus communication fault | Wiring issue with the LIN bus, ECU issue, connector problem |
| C151800 | Radar sensor: Limited visibility | Obstruction in front of the sensor, sensor needs cleaning, environmental conditions (heavy rain, snow) |
| U015500 | Lost communication with instrument panel cluster control module | Wiring issue, CAN bus problem, instrument cluster malfunction |
| B210000 | Component ‘Check component ID’ has a malfunction | Internal sensor fault, software issue, compatibility problem |
| C150300 | Distance sensor: No adaptation | Calibration issue, sensor replacement without calibration, software mismatch |
| U014000 | Lost communication with body control module | Wiring issue, CAN bus problem, BCM malfunction |
| C151600 | Radar sensor: Overheated | Sensor is overheating due to internal failure, software issue, external heat source |
| B200500 | Crash signal stored | Previous accident, crash sensor issue, software problem |
| U100100 | Communication with the engine control unit has a malfunction | CAN bus issue, wiring problem, ECU failure |
| C150400 | Rain/light sensor: General fault | Sensor failure, wiring issue, dirty or damaged sensor lens |
| B221000 | Operating voltage outside of tolerance | Voltage supply issue, battery problem, alternator problem |
| C150500 | Steering column module: General fault | Steering column module failure, wiring issue, mechanical issue with the steering column |
| C150600 | Tire pressure monitoring system: General fault | TPMS sensor failure, wiring issue, incorrect tire pressure |
| C150700 | Automatic high beam control: General fault | Camera or sensor failure, wiring issue, windshield obstruction |
| B221500 | Component is defective or the signal is outside permissible range | Sensor failure, incorrect installation, wiring issue, software incompatibility |
| U015100 | Lost communication with restraint control module | Wiring issue, CAN bus problem, RCM malfunction |
Using OEM Resources
Always consult the Mercedes-Benz service manual or online resources for detailed information about specific DTCs. These resources will provide valuable troubleshooting tips and repair procedures.
8. Live Data Analysis with Xentry
Live data analysis involves monitoring the real-time data output from sensors and radar units. This can help identify intermittent faults, signal inconsistencies, and other issues that may not be apparent from DTCs alone.
Accessing Live Data
- Connect Xentry: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and turn on the ignition.
- Select ECU: Select the ECU related to the sensor or radar system you want to analyze.
- Navigate to Live Data: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Actual Values” section.
- Select Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as sensor voltage, signal frequency, and object distance.
Interpreting Live Data
Monitor the live data for any unusual readings or inconsistencies. Compare the readings to the specifications in the Mercedes-Benz service manual to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
Example of Live Data Analysis
If you suspect a faulty radar sensor, you can monitor the sensor’s object detection range and accuracy. If the sensor is not detecting objects within the specified range, or if the detected distance is inaccurate, this could indicate a problem with the sensor.
9. Component Testing with Xentry
Component testing involves using Xentry to perform specific tests on individual sensors and radar units. This can help verify the functionality of the components and isolate faults.
Performing Component Tests
- Connect Xentry: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and turn on the ignition.
- Select ECU: Select the ECU related to the sensor or radar system you want to test.
- Navigate to Component Tests: Navigate to the “Component Tests” or “Actuations” section.
- Select Test: Select the specific test you want to perform, such as a sensor signal test or a radar unit activation test.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test and interpret the results.
Example of Component Testing
For a radar sensor, you might perform a test to verify that the sensor is emitting and receiving signals correctly. The test results will indicate whether the sensor is functioning within the specified parameters.
10. Calibration and Adjustment Procedures
Calibration is essential for ensuring that sensor and radar systems function correctly after repairs or component replacement. Misaligned or uncalibrated sensors can lead to false alarms, system malfunctions, and reduced safety performance.
When is Calibration Required?
Calibration is typically required in the following situations:
- Sensor Replacement: After replacing a sensor or radar unit.
- Windshield Replacement: After replacing the windshield, which can affect camera alignment.
- Suspension Work: After performing suspension repairs that can affect vehicle ride height and sensor angles.
- Collision Repair: After any collision that may have affected sensor alignment.
Calibration Procedures with Xentry
- Connect Xentry: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and turn on the ignition.
- Select ECU: Select the ECU related to the sensor or radar system you want to calibrate.
- Navigate to Calibration: Navigate to the “Calibration” or “Adaptation” section.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the calibration procedure. This may involve using specialized targets or alignment tools.
Importance of Proper Alignment
Proper sensor alignment is critical for accurate system performance. Use the correct alignment tools and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure that the sensors are properly aligned.
11. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
In some cases, diagnosing sensor and radar systems may require advanced diagnostic techniques. These techniques can help identify complex issues that may not be apparent from standard diagnostic procedures.
Using Oscilloscopes
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of sensor signals. This can help identify signal distortions, noise, and other issues that may be affecting sensor performance.
Performing Wiring Diagnostics
Thoroughly inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to check for continuity, voltage, and resistance in the wiring circuits.
Analyzing Network Communication
Use Xentry to monitor the communication between different ECUs on the vehicle’s network. This can help identify communication errors or conflicts that may be affecting sensor and radar system performance.
12. Software Updates and Module Programming
Software updates and module programming are essential for ensuring that sensor and radar systems are functioning correctly and have the latest features and improvements.
Performing Software Updates
- Connect Xentry: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and turn on the ignition.
- Check for Updates: Use Xentry to check for available software updates for the sensor and radar system ECUs.
- Install Updates: Follow the on-screen instructions to download and install the software updates.
Module Programming
Module programming involves replacing or reprogramming an ECU with new software. This may be necessary if an ECU is faulty or if you are installing a new component that requires specific software.
Importance of Correct Software
Ensure that you are using the correct software version for the vehicle and the specific sensor or radar system. Using the wrong software can lead to system malfunctions and other issues.
13. Ensuring Accurate Sensor Alignment
Accurate sensor alignment is critical for the proper functioning of ADAS features such as lane keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. Proper alignment ensures that the sensors can accurately detect the vehicle’s surroundings, enabling these systems to function effectively.
Tools for Sensor Alignment
Several tools are available to assist with sensor alignment, including:
- Laser Alignment Tools: These tools use laser beams to precisely align sensors.
- Target Boards: These boards are used as reference points for aligning camera and radar sensors.
- Calibration Software: Specialized software is used to guide the alignment process and verify the accuracy of the alignment.
Step-by-Step Alignment Process
- Prepare the Vehicle: Ensure that the vehicle is on a level surface and that the tires are properly inflated.
- Connect Diagnostic Tool: Connect the Xentry diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access Alignment Procedure: Navigate to the alignment procedure for the specific sensor you are aligning.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to position the alignment tools and adjust the sensor.
- Verify Alignment: Use the diagnostic tool to verify that the sensor is properly aligned.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failing to Level the Vehicle: Ensure that the vehicle is on a level surface before starting the alignment process.
- Using Incorrect Targets: Use the correct targets for the specific sensor you are aligning.
- Skipping Verification Steps: Always verify the alignment using the diagnostic tool to ensure accuracy.
14. Best Practices for Maintaining Sensor and Radar Systems
Maintaining sensor and radar systems is essential for ensuring their continued performance and reliability. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean sensors regularly to remove dirt, snow, and ice that can obstruct their view.
- Inspect Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Perform Calibrations: Perform calibrations after any repairs or component replacements that may affect sensor alignment.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Keep the software for the sensor and radar systems up-to-date with the latest updates and improvements.
- Follow OEM Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance and repair procedures.
The Importance of Proactive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance can help prevent many common issues with sensor and radar systems. By following these best practices, you can ensure that the systems continue to function correctly and provide the intended safety benefits.
15. The Role of OEM Information
Accessing and utilizing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) information is crucial for accurate and effective diagnostics and repairs of sensor and radar systems. OEM information includes service manuals, technical bulletins, wiring diagrams, and calibration procedures, which are essential for understanding the specific requirements of each vehicle and system.
Accessing OEM Information
- Mercedes-Benz Service Information: Subscribe to the Mercedes-Benz service information portal to access the latest technical documentation.
- I-CAR: Utilize I-CAR resources for training and technical information on ADAS and sensor systems.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to share knowledge and learn from other technicians.
Using OEM Information Effectively
- Follow Procedures: Follow the OEM procedures for diagnostics, repairs, and calibrations to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Use Correct Parts: Use OEM parts or approved aftermarket parts to ensure compatibility and performance.
- Stay Updated: Stay updated with the latest technical bulletins and service information to address any known issues or updates.
16. Tools and Equipment Recommended for Sensor and Radar Diagnostics
Having the right tools and equipment is essential for diagnosing and repairing sensor and radar systems effectively. Here are some recommended tools:
- Xentry Diagnostic Tool: The official diagnostic tool for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Multimeter: Used to check for continuity, voltage, and resistance in wiring circuits.
- Oscilloscope: Used to analyze the waveforms of sensor signals.
- Laser Alignment Tools: Used to precisely align sensors.
- Target Boards: Used as reference points for aligning camera and radar sensors.
- Wiring Repair Kit: Includes tools and materials for repairing damaged wiring.
Investing in Quality Tools
Investing in high-quality tools and equipment is essential for accurate and reliable diagnostics and repairs. While cheaper tools may be tempting, they may not provide the same level of accuracy or durability, leading to incorrect diagnoses and potential safety issues.
17. Troubleshooting Common Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing sensor and radar systems can be challenging, even with the right tools and information. Here are some common diagnostic challenges and how to troubleshoot them:
- Intermittent Faults: Intermittent faults can be difficult to diagnose because they only occur sporadically. Use live data analysis and record data over time to try to capture the fault when it occurs.
- Ghost Codes: Ghost codes are DTCs that appear without any apparent cause. Clear the codes and retest the system to see if the codes reappear.
- Communication Errors: Communication errors can occur when there is a problem with the vehicle’s network. Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Calibration Issues: Calibration issues can occur if the sensors are not properly aligned or if the calibration procedure is not performed correctly. Double-check the alignment and calibration procedures to ensure accuracy.
Seeking Expert Assistance
If you are struggling to diagnose a sensor or radar system issue, don’t hesitate to seek expert assistance from experienced technicians or online forums. Collaboration and knowledge sharing can be valuable resources for troubleshooting complex problems.
18. Case Studies: Real-World Diagnostic Scenarios
Analyzing real-world diagnostic scenarios can provide valuable insights into the practical application of diagnostic techniques. Here are a few case studies:
Case Study 1: Radar Sensor Fault
A Mercedes-Benz vehicle has a DTC indicating a fault with the front radar sensor. The technician performs an initial system scan using Xentry and identifies the DTC C151700, indicating a radar sensor signal fault.
- Inspection: The technician inspects the radar sensor and wiring for any signs of damage.
- Live Data Analysis: The technician uses Xentry to view live data from the radar sensor and notices that the sensor is not detecting objects within the specified range.
- Component Testing: The technician performs a component test on the radar sensor and confirms that the sensor is not functioning correctly.
- Solution: The technician replaces the faulty radar sensor and performs a calibration procedure using Xentry. After clearing the DTCs and performing a road test, the system is functioning correctly.
Case Study 2: Camera Sensor Misalignment
A Mercedes-Benz vehicle has issues with its lane keeping assist system. The technician performs an initial system scan using Xentry and identifies a DTC indicating a camera sensor misalignment.
- Inspection: The technician inspects the camera sensor and windshield for any signs of damage.
- Calibration: The technician uses Xentry to perform a calibration procedure for the camera sensor, using specialized targets and alignment tools.
- Verification: After completing the calibration procedure, the technician verifies that the sensor is properly aligned using Xentry.
- Solution: After performing the calibration, the lane keeping assist system is functioning correctly.
19. The Future of Sensor and Radar Technology
Sensor and radar technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements being introduced regularly. Some of the future trends in this technology include:
- Higher Resolution Sensors: Future sensors will offer higher resolution and greater accuracy, enabling more precise object detection and tracking.
- Sensor Fusion: Sensor fusion involves combining data from multiple sensors to create a more comprehensive view of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will play an increasing role in sensor and radar systems, enabling more advanced features such as predictive maintenance and autonomous driving.
- Improved Cybersecurity: As sensor and radar systems become more connected, cybersecurity will become increasingly important to protect against hacking and data breaches.
Preparing for the Future
To stay ahead of the curve, technicians need to continuously update their knowledge and skills in sensor and radar technology. This includes:
- Attending Training Courses: Attend training courses and workshops to learn about the latest advancements in sensor and radar technology.
- Reading Technical Publications: Stay informed by reading technical publications and industry news.
- Participating in Online Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to share knowledge and learn from other technicians.
20. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the complexities of diagnosing and repairing modern vehicle systems. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you tackle even the most challenging issues.
Our Offerings
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: We provide access to the latest diagnostic tools, including Xentry and other OEM-level diagnostic solutions.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance.
- Training Resources: We offer a variety of training resources to help you stay up-to-date with the latest technology.
- Competitive Pricing: We offer competitive pricing on all of our products and services.
Benefits of Choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET
- Improved Efficiency: Our diagnostic tools can help you diagnose and repair issues quickly and efficiently.
- Increased Accuracy: Our tools provide accurate and reliable results, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By providing high-quality diagnostic and repair services, you can enhance customer satisfaction and build a loyal customer base.
Ready to take your diagnostic capabilities to the next level? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and support on selecting the right tools and equipment for your needs. Visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. You can also explore our offerings online at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Let us help you equip your shop with the best in diagnostic technology.
21. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is Xentry and why is it used for diagnosing sensor and radar systems?
Xentry is the official diagnostic software used by Mercedes-Benz. It’s essential for diagnosing sensor and radar systems because it provides comprehensive access to vehicle systems, accurate troubleshooting, module programming, and calibration capabilities necessary for maintaining ADAS and other advanced systems.
Q2: What are the common issues that can affect sensor and radar systems in modern vehicles?
Common issues include sensor damage, misalignment, software glitches, wiring problems, and environmental factors such as dirt or snow accumulation.
Q3: How often should sensor and radar systems be calibrated?
Calibration is typically required after sensor replacement, windshield replacement, suspension work, or any collision that may have affected sensor alignment.
Q4: What tools are essential for diagnosing sensor and radar systems?
Essential tools include the Xentry diagnostic tool, multimeter, oscilloscope, laser alignment tools, target boards, and a wiring repair kit.
Q5: Can environmental factors really affect the performance of sensor and radar systems?
Yes, environmental factors such as dirt, snow, and ice can significantly reduce the performance of ADAS systems by obstructing the sensors.
Q6: What should I do if I encounter an intermittent fault while diagnosing a sensor or radar system?
Use live data analysis and record data over time to try to capture the fault when it occurs. This can help identify patterns or specific conditions that trigger the fault.
Q7: How important is it to use OEM information when diagnosing and repairing sensor and radar systems?
Accessing and utilizing OEM information is crucial for accurate and effective diagnostics and repairs. OEM information includes service manuals, technical bulletins, wiring diagrams, and calibration procedures, which are essential for understanding the specific requirements of each vehicle and system.
Q8: What are some future trends in sensor and radar technology?
Future trends include higher resolution sensors, sensor fusion, artificial intelligence, and improved cybersecurity.
Q9: Why is proper sensor alignment so important for ADAS?
Proper sensor alignment is critical because it ensures that the sensors can accurately detect the vehicle’s surroundings, enabling ADAS features like lane keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking to function effectively.
Q10: How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with diagnosing and repairing sensor and radar systems?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers advanced diagnostic tools, expert support, training resources, and competitive pricing to help you tackle even the most challenging issues in diagnosing and repairing modern vehicle systems. Contact us for expert advice and support to select the right tools and equipment for your needs.
 Mercedes-Benz Logo
Mercedes-Benz Logo
Accurate diagnostics are vital for ensuring vehicle safety and performance. By leveraging Xentry and adhering to best practices, automotive professionals can confidently tackle sensor and radar system challenges. Remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is your partner in providing the tools and knowledge needed to excel in this evolving field.